Sail Types: A Comprehensive Guide to 8 Types of Sails
Sailboats come in all shapes and sizes. And that means there are many types of sails on the market! For those who might not know, sails are made of canvas and use wind power to propel sailboats through the water.
Understandably, different sails are required for different types of sailboats . And sailboats are categorized by the number of hulls they have. Monohulls have a single-hull design, catamarans have two hulls, and trimarans have three. Generally, sailors use catamarans for upwind sailing (but they can be used to sail downwind in certain conditions).
The type of sail you'll need for your sailboat depends on the kind of sailboat you have. Additionally, sails are highly dependent on the wind and weather conditions. Therefore, it's always a good idea to have different types of sails on board to navigate the ever-changing weather conditions.


8 Types of Sails for Sailboats
As mentioned, you should carry multiple sails when sailing to prepare for various weather conditions. Here's a brief overview of the types of sails for sailboats:
1. Mainsails
The mainsail is the largest and most important sail. Therefore, it's probably the first sail to come to mind when you think of camping. Typically, it's situated directly behind the mast — connected to the boom — and uses wind energy to move the vessel. The mainsail plays a significant role in tacking and gybing, making it essential for any voyage.
Since the mainsail is a larger sail, it doesn't require wind to propel it forward. And the fact that it can be moved by moving the boom makes it uber-easy to operate.
Learn More About Sailing
2. Headsail
The headsail often accompanies the mainsail, though it is smaller in size. Regardless of your sailboat type, the headsail is positioned at the front of the mast – over the sailboat's bow.
Because headsails are small, they are helpful when navigating through windy conditions. Smaller sails catch less wind, preventing them from propelling your boat as strongly as larger sails. Additionally, headsails help lift, balance, and protect the vessel from inclement weather conditions.
While the term 'headsail' refers to any sail in front of the mast, the jib is the most common type of headsail. (And when a jib is so large that it overlaps the mast, it's called a genoa.)
Learn More About Sailboats
3. Genoa
The genoa is a large sail that attaches to the front of the forestay. (In this instance, it's similar to a headsail.) However, the genoa is larger than the headsail and overlaps the mainsail partially or completely to help the boat go faster.
Genoa sails are useful when sailing through light or medium wind. You can also use it when the wind comes directly from the rear. If you use a Genoa sail during high winds, you'll probably start sailing too quickly and put yourself and your boat at risk.
4. Spinnaker
The spinnaker is a large and whimsical (often colorful) sail. Spinnaker sails are usually symmetrical, allowing them to reach different points of sail. Generally, these are lighter sails and don't cover the mast like the genoa.
Because spinnaker sails are on the larger side, you have to be incredibly careful with them. Don't use them in rough conditions. Instead, save them for sailing in low winds and calm seas.
5. Gennaker
As the name suggests, the Gennaker sail combines a spinnaker and a Genoa sail. They are as large as the spinnaker, although they're not symmetrical.
They come in handy whenever the wind changes from a pure dead run to a reaching point of sail, as sailors can navigate various wind types with the same sail. It's still only meant for lighter and milder winds, but it's more versatile than the spinnaker and genoa.
6. Light Air Sails
Light air sails are useful in calmer conditions when the headsail and mainsail alone aren't cutting it. They include:
- Code Zero : A code zero sail is a gennaker sail ideal for sailing in light to mild winds. It's designed to create lift and boost boat speed whenever regular sails don't generate enough power. For that reason, many racers and cruisers use code zero sails to improve performance and gain control in various situations.
- Windseeker : This small, special sail is reserved for no wind or light wind. Essentially, it helps boats remain maneuverable in extremely calm conditions. And for that reason, it's valuable to long-distance sailors.
7. Storm Jib
Storm jibs can be used as a headsail whenever the weather is particularly rough and windy. Because it functions as a safety seal, it prevents boats from capsizing by reducing the sail area exposed to the wind. Therefore, it's a necessary sail for every sailor.
Read Next: Boating in Inclement Weather
During strong winds and storms, sailors can raise a trysail — a small, triangular sail near the boat's stern — for better control and stability. Generally, sailors do this whenever the mainsail becomes too large and challenging to maneuver.

Join Our Newsletter!
Get community news, buying bargains, and how-to guides at your fingertips.

The Different Types Of Sails And When To Use Them – Complete Guide

Sail forms an integral part of a sailboat. When you sail on the open water and observe other boats (in various sizes), you’d have noticed how each boat type has a specific model of sail. If you’re a beginner in boating, you must know that there are a ton of different sails and they each have their own purpose.
As a general setup, sailboats will use three common sails, including headsail, mainsail, and specialty sail. Due to the varying wind conditions and the model of the sailboat, there are many types of sails including jib, genoa, trysail, storm jib, code zero, gennaker, and spinnaker.
While that sounds like too many models of sails, you can easily differentiate between them and choose the ideal model based on your purpose. This article guides you on this aspect. Let’s begin!
Different Types of Sails & When To Use Them
1. mainsail.
Mainsail is by far the most widely spotted sail model, and it’s usually fixed to the boom and fitted behind the mast. This offers the highest mileage to your sailboat, thereby maximizing speed and performance.
You can use a mainsail if:
- You’re concerned about the performance
- You need to go faster and utilize all wind power
- You need to steer your boat irrespective of the wind’s status
- You’ve a large boat and can offer adequate space to this sail.
This mainsail displays a wide surface area to make the most out of the available wind condition. As a result, you can steer your boat quite easily. However, the downside is its size. It is very large and hard to store if you need to take it down for some reason.
Check out my other article all about maintaing sails!
2. Headsail
Similar to a mainsail, it’s very easy to spot a head sail. Just look at the bow of the boat and see if there is a sail. If you see one then yes that’s a headsail. Also called a jib or genoa, a headsail is smaller in size compared to a mainsail and attaches in front of the mast to the forestay. The Foresail will not have a boom for the clew of the sail to attach to. The clew will be attached to the foresails sheet. It can be used without the mainsail in certain conditions but for the most part the two sails are used together. The foresail is always forward of the main.
The headsail comes in many different forms such as a jib, genoa, spinnaker or storm jib. The most common headsail is a jib or genoa.
You can use a headsail if:
- Your sailboat is set up for it.
- You don’t want to use the mainsail at this time.
- Your mainsail is not usable.
The biggest advantage of a headsail is the option to protect yourself even if the wind turns unpredictable or wild. This all depends on the type of headsail you are using.
So, what are the different types of headsails? Let’s take a look!
As more boaters chose to use a headsail for their boats, the jib was introduced as one of its forms. The Jib is a form of headsail that is attached to a shackle present on the deck’s front region.
The Jib is a sail that does not go past the mast when it is raised and in use. If it goes past the mast then you probably have a genoa.
You can use a jib if:
- You are out for a normal day of sailing in moderate wind speeds
- You have a roller furling. Which is a sail that wraps up around itself.
Some weather conditions can make maneuvering harder or tighter than usual. As a result, it’s essential to use a jib in such cases. It functions well with boats containing a roller furling as the jib handles different positions and tackles the movement of the boat at ease.
2.2 Genoa
Just when you’ve got acquainted with the jib, genoa comes into the picture as a larger version of the jib. If you’re boating along a coastal region, the genoa sail is the one widely used and is attached to the front area of the deck as well.
Here’s a quick trick to find out if a boat has a genoa sail. This genoa is usually larger than a Jib. This means that the genoa effortlessly overlaps and extends itself beyond the mast, thereby covering the mainsail as well.
You should use a genoa sail if:
- You’re planning to sail in minimum wind conditions. Less wind means you need more sail.
- You find the wind to originate from the rear area.
- You own a large boat. Remember that genoa can partially or completely cover the mainsail too. Larger sails for larger boats!
While it’s great for sailing in regular conditions, there are downsides associated with it. A genoa can put you in a dangerous situation if you are sailing in high wind conditions and don’t have the ability to furl in the sail. Furling in the sail will reduce the area of the sail and catch less wind.
Genoas do come in many sizes as well such as 110% or 120%.
The next section of the sail list are ones that aren’t necessary but can be helpful in certain situations. Let’s look at specialty sails!
3. Specialty Sail
While headsails and mainsails are quite commonly used, there are also specialty sails in the market to address specific requirements. Some of the widely seen specialty sails are spinnakers, storm jibs, and code zeros.
3.1 Spinnakers
Spinnaker is a sail dedicated to downwind and is quite large. Think of a beautifully covered parachute.
It’s easy to spot spinnakers as they resemble kites or parachutes. However, it crosses the bow of the boat and isn’t attached to the forestay.
Unlike the genoa sail that covers the mast, a spinnaker fails to do so. The advantage of a spinnaker is the surface area. When the wind is light, the spinnaker can catch a lot more wind giving you more speed. The Spinnaker is usually fixed to three points – pole, halyard, and sheet.
You should use a spinnaker if:
- You have minimal wind on a run.
- You are trying to harness as much wind power as you can.
While it has a wide surface area, the downside is its inability to steer the boat during strong wind conditions. It can even put the passengers at risk when the wind is at high speeds.
Make sure you have experience before trying out the spinnaker.
3.2 Storm Jibs
Storm jib is another type of specialty sail meant exclusively for rough weather. It’s a tiny, triangular structure that helps during offshore racing or cruising. Just think of it as a smaller jib.
You should use a storm jib if:
- You’re going to sail in heavy weather conditions.
- You anticipate high wind speeds.
- You’re going to be in an offshore race and they are an approved sail type.
Note: In the case of an offshore racing requirement, it’s critical to take prior permission from the regulatory authority for using a storm jib.
3.3 Code Zeros
Code zero is another updated version of a spinnaker that’s meant to be a combination of genoa and gennaker sails. It resembles the look of a genoa but is a lot bigger.
You should use a code zero if:
- You’re looking for an overlapping flying headsail.
- You’re sailing only in light air conditions.
- You’re looking for an alternative to a Genoa.
Having said that, a code zero or a screecher does the job of a genoa with better efficiencies.
3.4 Trysail
Trysail is another type of specialty sail that’s tiny, triangular, and can be fixed right above a gooseneck on the sailboat.
The Trysail is less known in the market as most boaters go ahead with common mainsails and headsails. It’s essential to acknowledge trysail as a front-and-aft mainsail model. It offers excellent performance and contains a permanent pennant in it.
You should use a trysail if:
- You’re sailing in heavy weather conditions.
- You’re looking for a storm replacement.
- You are experienced with using them.
The quadrilateral sail in a trysail is usually turned and bent to a mast, and this helps in heading the vessel during windy conditions.
3.5 Gennakers
If you’ve been able to spot genoa and spinnaker in the past, identifying a gennaker is incredibly easy. A gennaker is a hybrid sail form that is small, slow, and requires no pole attached to the mast.
You should use a gennaker if:
- You’re looking for a smaller version of a spinnaker.
- You’ve no space to fix a pole to the mast.
- You require the sail to be easily manageable.
- You’re sailing in a region requiring minimum downwind levels.
Choosing a hybrid sail has a lot of benefits as it combines the usefulness of 2 sail models. However, being aware of their cons is critical to planning a safe sail.
As you begin using these sails, you can also look for better customizations. There are drifters, wind seekers, and other jib types that are meant to handle different wind conditions.
How Many Sails On A Sailboat ?
In general, a sailboat contains two sails. Two sails is the typical setup for the best performance of the boat during different wind conditions. It’s essential to pick your two sails based on your sailing plan.
Why Are There Two Sails On A Sailboat?
A sailboat uses two sails because the wind left over by the first sail is easily caught by the second sail. This helps in steering the sailboat to a better extent and gives the sailboat more power.
Final Thoughts
Sails are one of the major assets of a sailboat. From managing wind to maximizing the performance and longevity of a sailboat, the type of sails you use, plays a huge role. From the various sail types listed in this article, you can choose the best model that fits your sailing routine. Just make sure to remember to check and make sure they are the correct size for your vessel.
Make sure to plan ahead and have the right sails for your sailing weekend. Cheers!
Boatlifehq owner and author/editor of this article.
Recent Posts
Sailboat Racing - Rules & Regulations Explained
Sailboat racing, a blend of skill, strategy, and adherence to intricate rules and regulations, offers a thrilling and intellectually stimulating experience on the water. Navigating through the...
What is the best sailboat to live on? Complete Guide
Embarking on the journey of living aboard a sailboat requires careful consideration of your budget, desired amenities, and storage options. This guide offers a concise, step-by-step approach to...

Type Of Sails: A Complete Guide

Table of Contents
Last Updated on September 29, 2023 by Boatsetter Team
If you are approaching sailing and sailboats from a very beginner’s perspective , then the concept of different kinds of sails can be a strange one. We often believe we see one kind of sailboat with one kind of sail, and our simple minds lead us to believe you are only meant to move them around, and you will get to where you need to go.
However, you would not have landed on this article if you did not suspect that there was more to sails and sailboats. So here, you can have a kind of in-depth, kind of summarized review of the different kinds of sails and the most popular sail and mast configurations out there.
It is also important to understand why there are so many different kinds of sails. When you are out on the water, different weather conditions can occur. Your sail acts as a motor of some sort, moving your sailboat forwards, but your sail is also highly dependent on the wind conditions around it. This is why having different kinds of sails can help you navigate your weather conditions and turn them to your own advantage while sailing.
Different sails also come with different danger levels in case of strong wind, so knowing what kinds you might need to watch out for is also extremely important. So, without further ado, let us get into it.
You may have heard of this one before or seen it portrayed in movies and TV shows. As the name suggests, the mainsail is the most popular kind of sail on any sailboat, and they are found behind the mast. They are also attached to the boom. Because they take up so much space on your sailboat, they are also one of the most important sails to take care of and keep an eye on.
Since the mainsail is such a large sail, it does not require too strong a wind to propel it forward , as its large surface area will easily catch a breeze. At the same time, the fact that it can be moved around by moving the boom makes it, so it is easy to steer. This makes it so that the mainsail is the most important sail on your sailboat.
Headsail/Jib
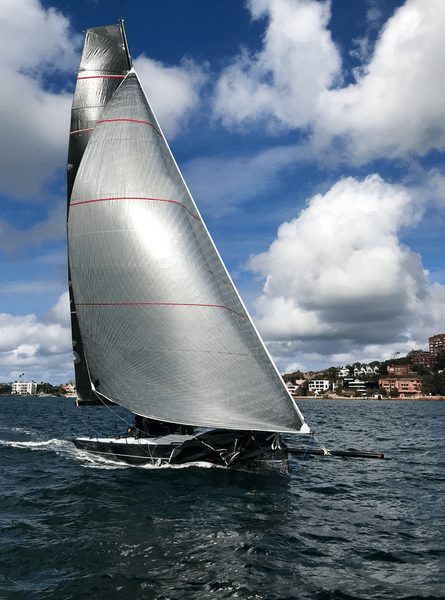

The headsail, or the jib, is likely the second most popular kind of sail found on sailboats. This is because it often accompanies the mainsail, the most popular kind. On all sailboats , the headsail is put at the front of the mast over the sailboat’s bow . It is always a smaller sail than the mainsail.
The fact that the headsail is smaller can be especially useful if you are caught in strong winds. In this situation, you likely do not want to use your mainsail (or trim it as much as possible) to move slower and not be thrown around by the winds. Smaller sails catch less wind, meaning they do not propel your boat as strongly as larger sails.
Having a good headsail can be an incredible safety measure, especially if the seas you are trying to sail are known to be wild and unpredictable.
You may have seen a genoa sail before if you have been around boats or have ever lived in a coastal town. This kind of sail is a large sail that you can attach to the front of the forestay (similarly to the headsail). This is a larger sail than the headsail and can even cover the mainsail either partially or completely. For this reason, the genoa also used to be called an “overlapping jib.”
You should use a genoa if you are sailing through either light or medium winds and if your sailboat is at a dead run point of sail (this means that the wind is coming directly from the rear. If you attempt to use a genoa sail in stronger winds , you might start going too fast and put yourself and your boat at risk since it is such a large sail. So, it is important to be careful .
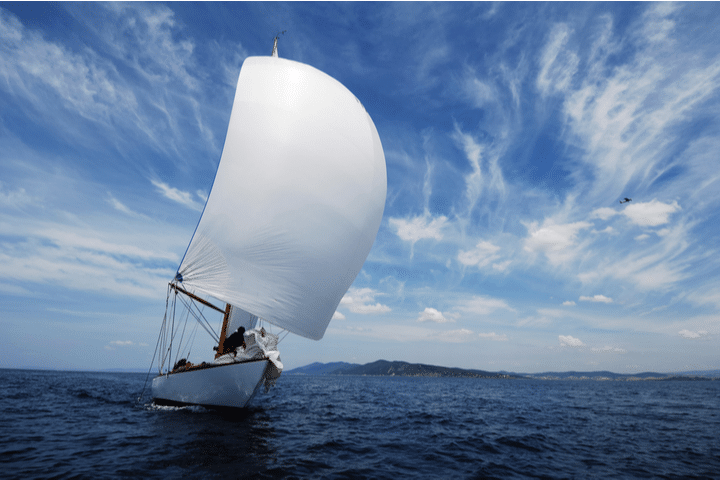

The spinnaker is the most whimsical kind of sail since it is a large and colorful kind. They are also often symmetrical, which means they are more appropriate for reaching different points of sail, such as the running point of sail. They are lighter sails, and they do not cover the mast as the genoa sail does. You do not attach a spinnaker to the forestay and instead let it stretch out past the boat’s bow.
The large surface area of the spinnaker means that you have to be even more careful than with others on the kind of conditions you choose to use this sail in. If the winds are too strong, you could be putting yourself and your passengers at serious risk using this sail, so you should choose to use it only at times when the wind is low or in seas that are known for their low winds and tranquility.
As the name suggests, the gennaker sail mixes the genoa sail and the spinnaker sail. These kinds of sails are more recent inventions. They are as large as the spinnaker sail, but they are not symmetrical. Unlike the genoa or the headsail, they are also not meant to be attached to the forestay, like the spinnaker sail.
The usefulness of this sail is that if the winds change from a pure dead run to a reaching point of sail, then sailors do not have to resort to using a spinnaker from a genoa, instead of being able to take advantage of different winds while still using the same sail as they were before. This kind of sail is still only meant for lighter and milder winds , but there is more flexibility with the gennaker than the genoa and the spinnaker sails.
Popular Sail and Mast Configurations
There are many different ways to place the sails we have learned about in the above section. We have compiled a list of some of the most popular ones so you can understand how these sails can be used to make a sailboat move through the oceans.
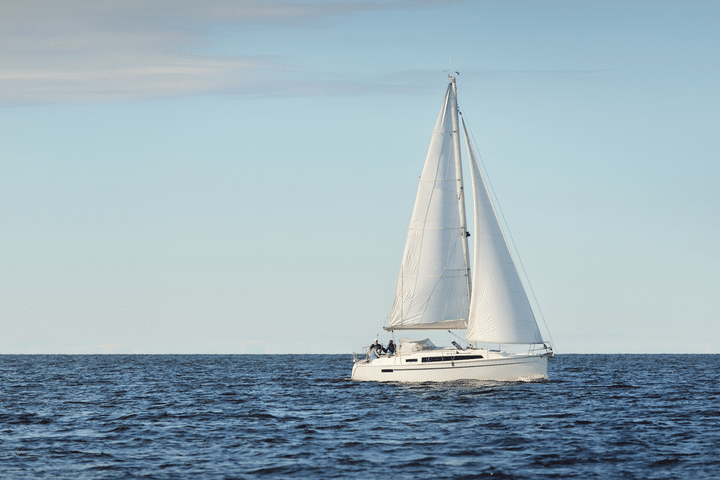

A sloop is by far the most popular configuration. It features a single mast, double sail (the mainsail and the headsail), and mast configuration. The headsail is located from the forestay on the mast to the top of it. The type of headsail used can also vary from a genoa, a spinnaker, or a gennaker sail.
Fractional Rig Sloop
A fractional rig sloop also features a single mast with a double sail setup similar to a sloop. However, what makes the fractional rig sloop different is that the forestay does not reach the top of the mast. This means the headsail is constricted to a smaller amount of surface than on a regular sloop, making it so that your sailboat captures less wind and moves slower .
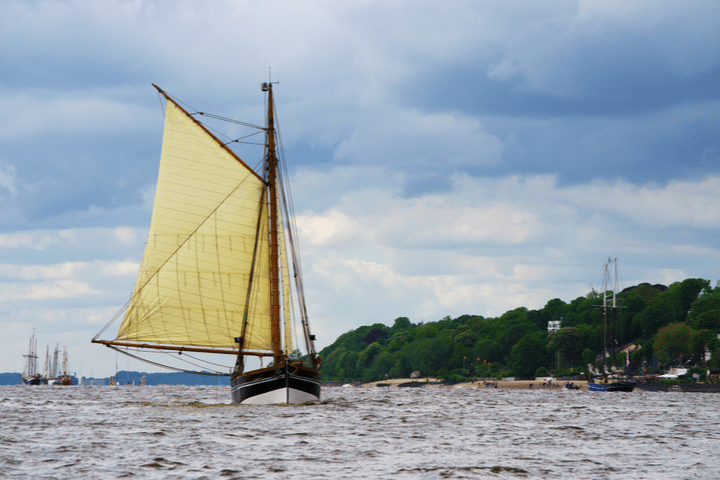

Cutters are interesting because they’re like a sloop but with a second forestay. This can be useful because it allows them to carry two headsails (a mainsail and one of the jibs). Cutters are good for cruising because they offer a range of wind options, giving you more time to get from place to place.
This is a less common mast configuration than previous others on this list. This is because a ketch features two masts. There is a larger mast fit for the mainsail and the headsail and a smaller mast between the mainmast and the stern (the rear) of the boat. This kind of mast configuration is more commonly found among Northern European freighters or fishing boats. This mast configuration is also called the mizzen mast.
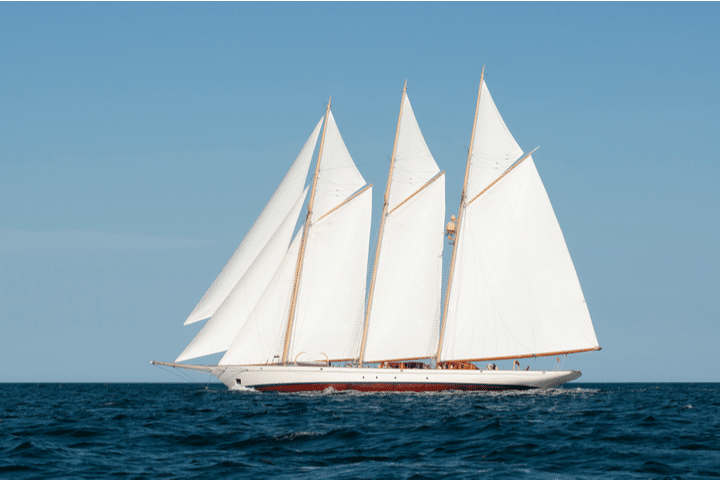

A schooner mast configuration features two or more masts. This is similar to the previous configuration, the ketch. It also features multiple sails. While a ketch’s aft mast (also known as the rear mast) is higher than the forward mast, a schooner’s aft mast is shorter than the forward mast. A schooner can also have up to six masts (although two are the most common). These are the main differences between the two.
This one is quite similar to a ketch mast configuration (mentioned above). The only real difference between them is that the mizzen mast is put directly behind the sailboat’s rudder post in a yawl.
A cat sail will have one mast and one sail. The mast is put at the bow of the sailboat. This kind of mast configuration is often found on smaller boats, more specifically on dingy boats. Boats with the cat mast configuration are also often called catboats.
Final Verdict
Having the appropriate kind of sail on your sailboat is incredibly important. At the same time, being aware of the kinds of sails that there are and the kind of sail and mast configuration can make you into a more well-rounded and informed sailor. With that in mind, we hope that you leave this article feeling more confident in your skills when you are out at sea.

Boatsetter empowers people to explore with confidence by showing them a world of possibility on the water. Rent a boat, list your boat, or become a Boatsetter captain today.
Browse by experience

Explore articles

Why Cape Coral Needs to Be Your Summer Destination

Boat Fuel Consumption: 5 Tips for Measurement, Efficiency, and Savings

Fishing Licenses: Explained and Simplified

App Update: Owner App 2.0

Types of Sails: A Comprehensive Guide
In the enchanting world of sailboat dynamics, where the dance between wind and water takes center stage, the significance of sails cannot be overstated. Like the wings of a bird, these meticulously crafted sails unfurl to catch the slightest whisper of breeze, converting it into a powerful forward thrust that carries us through the vast expanse of the ocean. They are the very essence of a sailboat, the conduits through which dreams and aspirations set sail.
Join us on a captivating voyage as we unfurl the secrets of the myriad types of sails adorning the mastheads of sailboats across the globe. From the grandeur of the mainsail, proudly dominating the skyline, to the nimble headsails that steer with precision, and the enigmatic mizzensails that add an extra touch of finesse, we shall embark on a comprehensive exploration of the diverse array of sail types.
Different Types of Sails on a Sailboat: Why Use Different Sails at All?
Different sail types for different wind conditions.
Triangular sails, such as the mainsail and jib, are commonly used on modern sailboats to optimize performance when sailing upwind. The shape of these sails helps to create lift, which propels the boat forward even against the wind’s direction. The mainsail is attached to the mast at the front edge and a boom at the bottom. Jibs, on the other hand, are headsails that are attached to a stay near the bow of the boat.
Balloon sails, like spinnaker sails, are designed for downwind sailing and catching more wind to increase boat speed when sailing with the wind behind it. These types of sails have a large surface area that allows them to catch more wind than triangular sails. Spinnaker sails can come in different shapes depending on their intended use and can be flown from a spinnaker pole or directly from the bow.
Sail Plans: Different Combinations for Different Boats
Sail plans refer to how different types of sails are arranged and combined on a sailing craft. Sail plans can vary depending on specific design features and intended use of boats. For example, some boats may have multiple masts with several triangular-shaped sails attached while others may only have one mast with one triangular sail (mainsail) and one square sail (spinnaker). The combination of different types of sails can also affect how easy it is to handle a boat under certain conditions.
Understanding Sail Anatomy
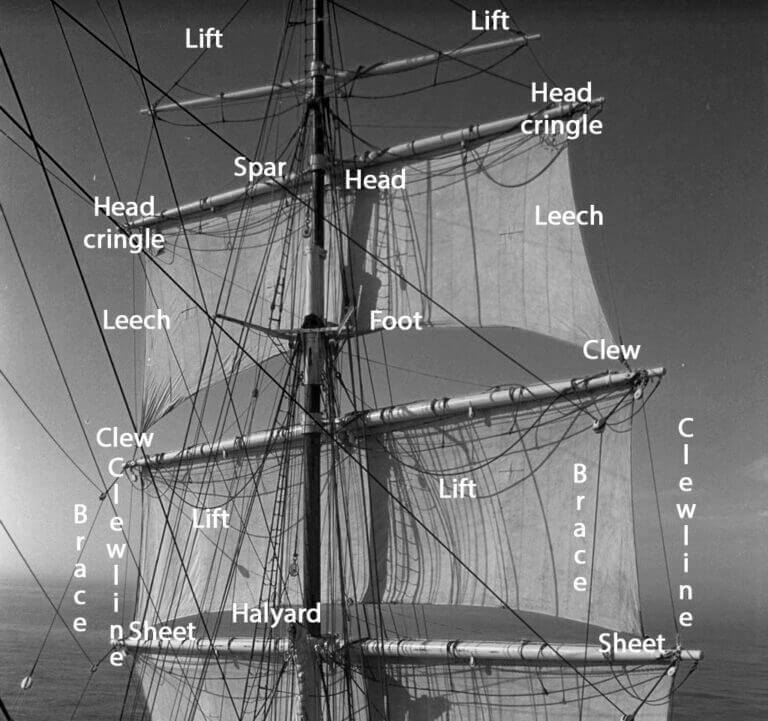
Head, tack, foot, luff, leech, and clew. These are the different parts that make up a sail’s anatomy. But what exactly are they and why are they important? In this section, we’ll take a closer look at each part and how it contributes to the performance of a sailboat.

The Head: The Top of the Sail
Starting from the top, we have the head of the sail. This is where the halyard (the rope or wire used to hoist the sail) is attached. The head determines how high or low the sail sits on its mast. A higher head means more power but less control over the sail’s shape. Conversely, a lower head provides better control but less power.
The Tack: The Lower Front Corner of the Sail
Next is the tack which is found at the lower front corner of most sails. It’s where one end of a line called a “sheet” attaches to control how much wind enters through this corner of your sail. Adjusting your sheet will affect your boat’s speed and direction.
The Foot: The Bottom of the Sail
At the bottom edge of any sail lies its foot which helps determine its overall shape and size. Generally speaking, longer feet result in larger sails that provide more power while shorter feet result in smaller sails with better maneuverability.
The Luff: The Forward Edge of the Sail
The forward edge of any sail is called its luff which runs along its mast track or forestay depending on what type of rigging you have set up on your boat. It helps maintain proper airflow over your sails by keeping them from flapping around too much in high winds.
The Leech: The Back Edge of Your Sail
Opposite from your luff is your leech – or back edge – which helps create lift by allowing air to flow smoothly over your sail. A longer leech will result in a more powerful sail, while a shorter one will provide better control and maneuverability.
The Clew: The Bottom Back Corner of Your Sail
Lastly, we have the clew which is found at the bottom back corner of most sails. It’s where the other end of your sheet attaches to control how much wind enters through this corner of your sail. Adjusting your sheet here can affect how well you’re able to steer your boat.
Primary Sail Types
The main sail is attached to the main mast and boom and can be adjusted to match the wind conditions. Its main purpose is to keep the boat steady and under control by providing stability to the stern (back) of the vessel.
There are several variations of mainsails that sailors can choose from depending on their needs. One popular type of mainsail is an in-mast furling mainsail. This type of sail can be easily furled and unfurled by pulling a line, making it ideal for short-handed sailing or cruising. Another variation is a slab reefing mainsail, which has horizontal strips called battens that help maintain its shape. Finally, there is also a boom furling mainsail, which uses a roller system inside the boom to make it easier to handle.
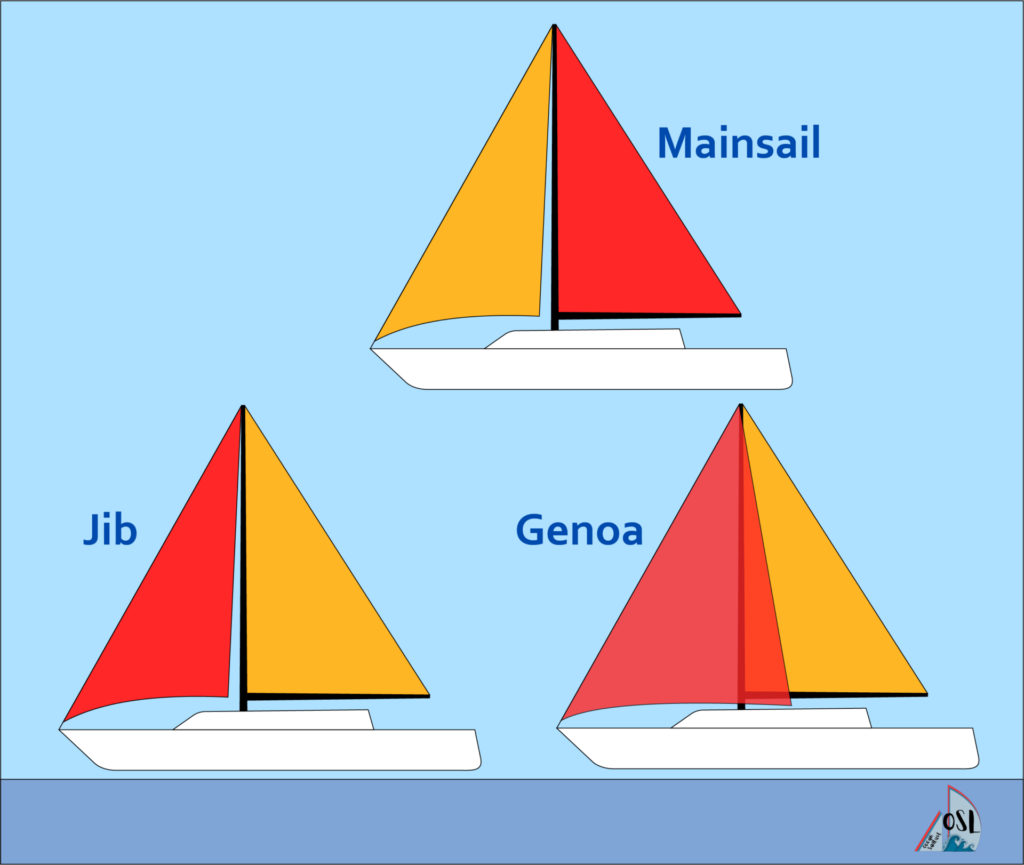
A headsail is any sail located forward of the mast on a sailing vessel. These sails are designed to work in conjunction with the main sail to provide optimal performance under varying wind conditions. There are several types of headsails available, each with its own unique characteristics and purposes.
One popular type of headsail is known as a genoa. This large foresail extends beyond the mast and overlaps with the main sail, providing additional power when sailing upwind or reaching across wind angles. Genoas come in various sizes ranging from 110% up to 150%, depending on how much overlap you want.
Another common type of headsail is called a jib. This smaller foresail does not overlap with the main sail but instead works in conjunction with it. The jib is typically used in higher wind conditions when a smaller sail area is needed to maintain control of the boat.
A staysail is a smaller sail located between the mast and the forestay. This type of headsail is typically used on larger boats to provide additional power when sailing upwind or reaching across wind angles. Staysails are often used in conjunction with other sails, such as a genoa or main sail.
Finally, there is also a mizzensail, which is located aft of the main mast on ketches and yawls. This sail provides additional power when sailing downwind or reaching across wind angles. Mizzensails come in various sizes and can be either fully battened or free-flying.
Lightwind Sails
Spinnaker sails are a type of downwind sail that can be used to increase boat speed when sailing in light winds. They are typically used in wind conditions below 10 knots, which are considered light air sails. Spinnakers come in two types: symmetrical and asymmetrical.

Symmetrical vs Asymmetrical Spinnaker
The symmetrical spinnaker is designed to sail directly downwind or with the wind coming from behind the boat. It is shaped like a balloon, with equal amounts of material on both sides of the sail. The sail is attached to a spinnaker pole, which extends out from the mast and holds the sail away from the boat.
Asymmetrical spinnakers, on the other hand, are designed for sailing at angles off the wind. They have an uneven shape, with more material on one side than the other. This design allows them to be flown without a spinnaker pole, making them easier to handle for smaller crews.
Another type of downwind sail is called a gennaker. Gennakers are similar to asymmetrical spinnakers but have a hybrid characteristic between a spinnaker and a genua. They are designed for reaching or running downwind at higher speeds than traditional cruising chutes or asymmetric spinnakers.
For those who prefer an even more user-friendly option than asymmetrical spinnakers or gennakers, parasailors might be what you’re looking for! A parasailor combines aspects of both a traditional spinnaker and a parachute into one easy-to-use package. The unique design of this sail makes it ideal for use in light winds when other sails may not perform well enough.
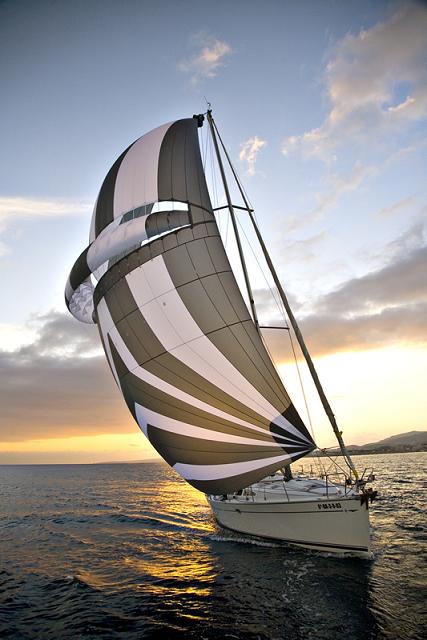

Finally, there’s another type of upwind/downwind sail called the code zero. Code zeros are designed to be used in light winds when sailing upwind, but they can also be used for reaching and running downwind. These sails have a flat shape that allows them to generate lift even in very light wind conditions.
Heavy Weather Sails
Heavy weather sailing is a challenging and potentially dangerous activity. The use of heavy weather sails, such as trysails, is crucial to ensure the safety of sailors and their vessels.
A trysail is a small triangular sail made of heavy-duty material, typically spinnaker cloth or other lightweight fabric. It is designed to be used in stormy weather conditions when winds are high and the seas are rough.
The role of a trysail is to provide an alternative source of propulsion when the main sail or jib cannot be used. In addition, it helps reduce the heeling effect on the vessel caused by strong winds. Trysails are rigged using a separate halyard and can be set up quickly when needed.
A trysail should be used in severe weather conditions when winds exceed 40 knots or more. It is recommended that sailors practice setting up their trysail before they need it so that they can do it quickly and efficiently in an emergency situation.

Another type of heavy weather sail that every sailor should have on board is a storm jib. This sail is typically much smaller than a regular jib and made from heavier materials such as Dacron or nylon. Its purpose is to provide additional stability during high wind speeds and rough seas.
The features of a storm jib include its size, shape, and weight distribution. It has a large luff (the leading edge) which allows it to be hoisted higher up on the rigging than other sails. This helps keep the boat stable during high-speed sailing in strong winds.
A storm jib should be used in extreme weather conditions where wind speeds exceed 50 knots or more. When using this sail, it is important to ensure that the halyard is properly tensioned and that the sail is sheeted in tightly. This will help prevent any unnecessary movement or fluttering of the sail.
Overview Common Sail Types
100% of mainsail
Light – High
100% of foretriangle
Moderate – High
triangular, overlapping
110% – 150% of foretriangle
Light – Moderate
60% – 80% of foretriangle
Close Reach – Broad Reach
Lightwind, Downwind
balloon shape, free flying
200% of mainsail (or even more)
Broad Reach, Running
parachute shape
100% of spinnaker
80% – 85% of spinnaker
Lightwind, Upwind
75% of spinnaker
30% – 60% of mainsail
Mainsail, heavy weather
17.5% of mainsail (or less)
Headsail, heavy weather
max. 65% of the hight of the foretriangle
Unconventional Sails
Wing sails are a type of sail design that is not commonly used in traditional sailboat designs. They are essentially vertical airfoils that generate lift and propulsion by directing the wind over the surface of the sail. Wing sails have become increasingly popular in modern sailing craft, particularly in high-performance racing boats.
One of the main advantages of wing sails is their ability to produce a significant amount of power with very little heeling force. This means that they can be used effectively in high-wind conditions without causing the boat to tip over. Additionally, wing sails are highly efficient at sailing upwind, which allows sailors to point higher into the wind than with other types of sails.
While wing sails may seem like a relatively new concept, they have actually been around for quite some time. The first recorded use of a wing sail was by German engineer Wolfgang Zimmermann in 1959. Since then, many different variations on the design have been developed and tested.

Kite sails are another unconventional type of sail that has gained popularity in recent years. Unlike traditional downwind sails such as spinnaker or parasailors, kite sails are flown from a line attached to the bow of the boat and do not require a mast or boom.
Sail Materials and Technology
Traditional sail materials.
Sails have been used for thousands of years to harness the power of the wind and propel boats across water. Traditional sail materials were flax, hemp, or cotton. These natural fibers were woven together to create a strong, yet flexible material that could withstand the harsh conditions at sea. However, as technology advanced and sailors began to demand more from their sails, new materials were developed.
Modern Sail Materials
Modern sailboats use synthetic materials such as polyester, nylon, or laminated fabrics for their sails. These materials are lightweight and incredibly strong, allowing sailors to achieve greater speeds with less effort. They are also more durable than traditional sail materials and can withstand prolonged exposure to sunlight and saltwater.
Popular Sail and Mast Configurations

The sloop rig is one of the most popular sail plans for modern sailboats. It features a single mast and one headsail, like a jib or genoa. The mainsail is typically triangular in shape and hoisted up the main mast using a backstay to support it. The jib or genoa is attached to the forestay that runs from the top of the mast to the bow of the boat.
Another popular sail plan is the cutter rig, which also features a single mast but has two headsails – an overlapping jib and a smaller staysail. The mainsail is still triangular in shape and hoisted up the main mast with a backstay for support.
Moving onto two-masted rigs, we have ketch rig, which features a main mast and a shorter mizzen mast located in front of the rudder. The mainsail is still triangular in shape and hoisted up the main mast with a backstay for support, while the mizzen sail is generally smaller and triangular or quadrilateral in shape.
Lastly, we have the yawl rig which is similar to the ketch rig but has its shorter mizzenmast located aft of the rudder. The mainsail is still triangular in shape and hoisted up the main mast with a backstay for support, while the mizzen sail is generally smaller and triangular or quadrilateral in shape.
Conclusion: Understanding the Different Types of Sails
Understanding the Different Types of Sails is crucial for any sailor who wants to optimize their performance and safety on the water. Whether you’re racing, cruising or simply enjoying a day out on your sailboat, having the right sails for the conditions can make all the difference.
Ultimately, understanding the different types of sails is essential for any sailor looking to improve their skills on the water. By selecting the right sail for your boat and conditions, you can optimize your performance while staying safe and comfortable during your time at sea.
So whether you’re a seasoned sailor or just starting out, take some time to explore the various types of sails available and find the ones that work best for you. With a little knowledge and experience under your belt, you’ll be well on your way to mastering this exciting sport!
Similar Posts
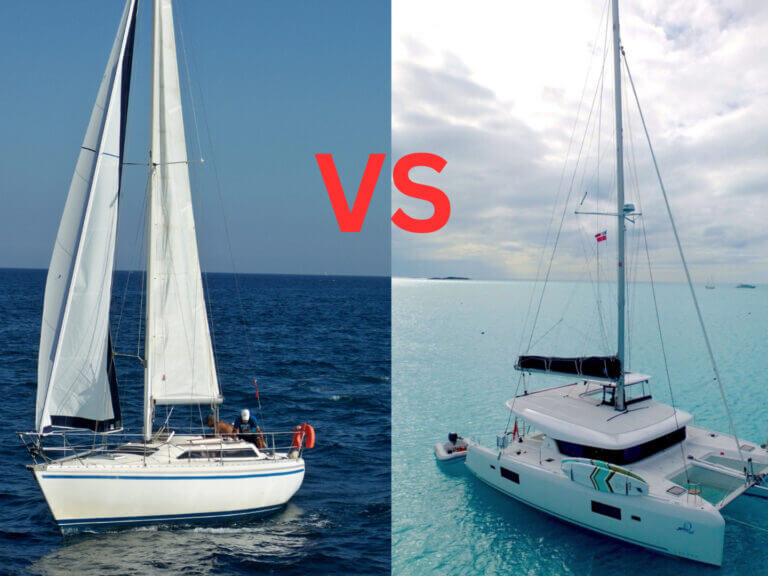

Monohulls vs. Catamarans: Which One is Best for You?
If you’re considering purchasing a sailboat, you might be wondering which type of vessel is best suited for your seafaring adventures. Fear not, for we’re here to help you weigh the differences between monohulls vs. catamarans to make an informed decision. Now, before we dive into the nitty-gritty details of hull design, sail handling, and…

How Does a Marine Toilet Work?
Have you ever wondered how a marine toilet works? If you’re planning to embark on a boating adventure or just curious about the mechanism of a marine toilet, this article is for you. Marine toilets work similarly to the ones on land with a bowl, a seat, and a flushing mechanism that uses water. However,…

Whats the Difference between Standing Rigging and Running Rigging?
Running rigging refers to the movable lines and ropes used to control the position and shape of the sails on a sailboat. Standing rigging, on the other hand, refers to the fixed wires and cables that support the mast and keep it upright. As the sun rises on another day, we find ourselves immersed in…
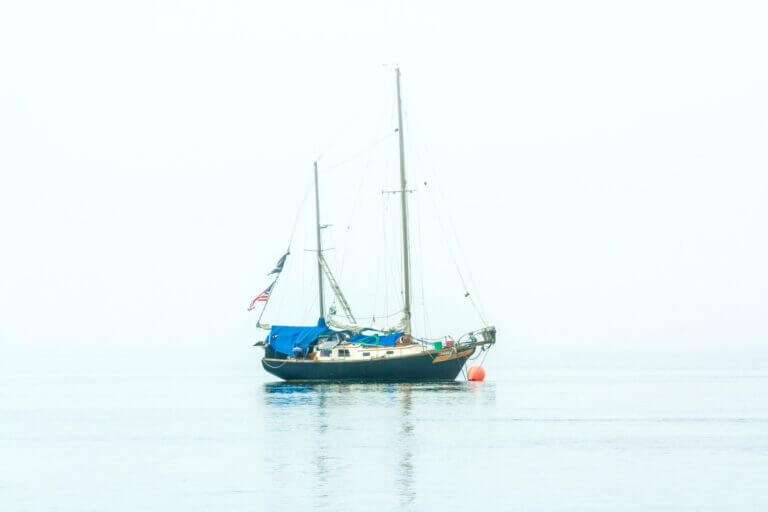

What is a Ketch Sailboat?
Ketch boats are frequently seen in certain regions and offer various advantages in terms of handling. However, what is a ketch and how does it stand out? A ketch is a sailboat with two masts. The mainmast is shorter than the mast on a sloop, and the mizzenmast aft is shorter than the mainmast. Ketches…

Basic Sailing Terminology: Sailboat Parts Explained
Sailing is a timeless activity that has captivated the hearts of adventurous souls for centuries. But, let’s face it, for beginners, sailing can be as intimidating as trying to navigate through a dark, labyrinthine maze with a blindfold on. The vast array of sailing terminology, sailboat parts and jargon can seem like a foreign language…

What is a Keel?: The Backbone of a Ship
As ships sail through tumultuous seas, their stability and maneuverability are tested to the fullest extent. The intricate design and engineering that go into a ship’s construction ensure that it can withstand the forces of nature and navigate through any challenging conditions. One of the most critical components of a ship’s design is the keel,…

Most Popular Types of Sails on a Sailboat

Learning about how there were different types of sails on sailboats for me was a bit strange at first. I thought something along the lines of “Don’t you just need to put some fabric on some polls and grab the wind?” Obviously, there’s far more to it than that.
So what are the most popular types of sails on sailboats? The mainsail, headsail (or jib), genoa, spinnaker, and gennaker are the most popular types of sails on sailboats. There are also a number of different configurations when considering the type of sail and mast in use including a sloop, fractional rig sloop, cutter, ketch, schooner, yawl, and cat.
Simply put, different sailboat sails serve different purposes when out on the water.
The sail is kind of like the “engine” of your sailboat (of course, sailboats can have actual engines) in that it’s the main source of forward propulsion.
So, it’s important to know when best to use either type of sail and why including the many different names of sails on a ship.
Types of Sails
There are a number of reasons why you’d want to use one sail over another, but the most important points to consider have to do with the point of sail you’re sailing in and the wind strength.
Maybe you need downwind sails, square sails, or a triangular sail. Maybe a unique sail shape, sail cloth, or sail area. With that in mind, let’s check out the different sail types!
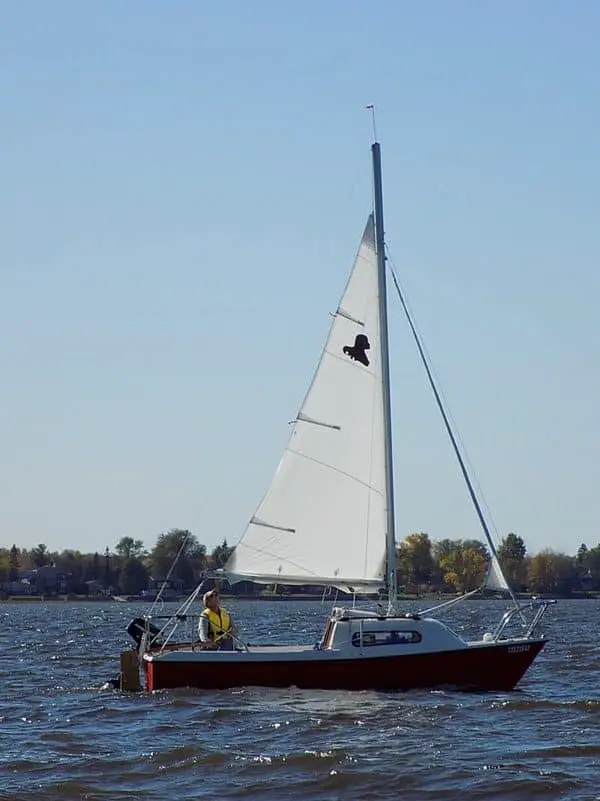

The mainsail is by far the most popular type of sail on sailboats and is often the first image that comes to mind when thinking about a sailboat.
Mainsails are found behind the mast and attached to the boom, which makes it a common part of the sailboat to keep an eye on as it takes up a lot of real estate on a boat with sails especially during a sail tack.
Mainsails are able to cover a lot of surface area with respect to incoming winds, especially since they’re attached to the boom.
The fact that they have a large surface area means they don’t require very strong winds to provide good forward propulsion on a sailboat.
Also, since the position of the mainsail can be easily configured thanks to the boom, all points of sail are achievable.
Headsail/Jib

The headsail (or jib) is probably the second most popular type of sail on sailboats since it usually accompanies the mainsail.
The headsail is always placed at the front of the mast and can cover a good amount of the bow of the sailboat. It’s also smaller than a mainsail, making it more portable and easy to work with.
Headsails aren’t as big as mainsails, therefore they have a smaller surface area which results in the fact that they’re not capable of catching as much wind as a mainsail.
This is an important point though since if the current wind is exceptionally strong and your mainsail has been trimmed as much as possible, being able to put away your mainsail and depend on your headsail alone is an excellent strategy to reduce speed.
When the wind is just too strong to keep your mainsail out, putting it away and using only your headsail is a great option.
You won’t be grabbing as much wind as with the mainsail and you’ll be able to have a much more enjoyable (and safer!) sailing experience.
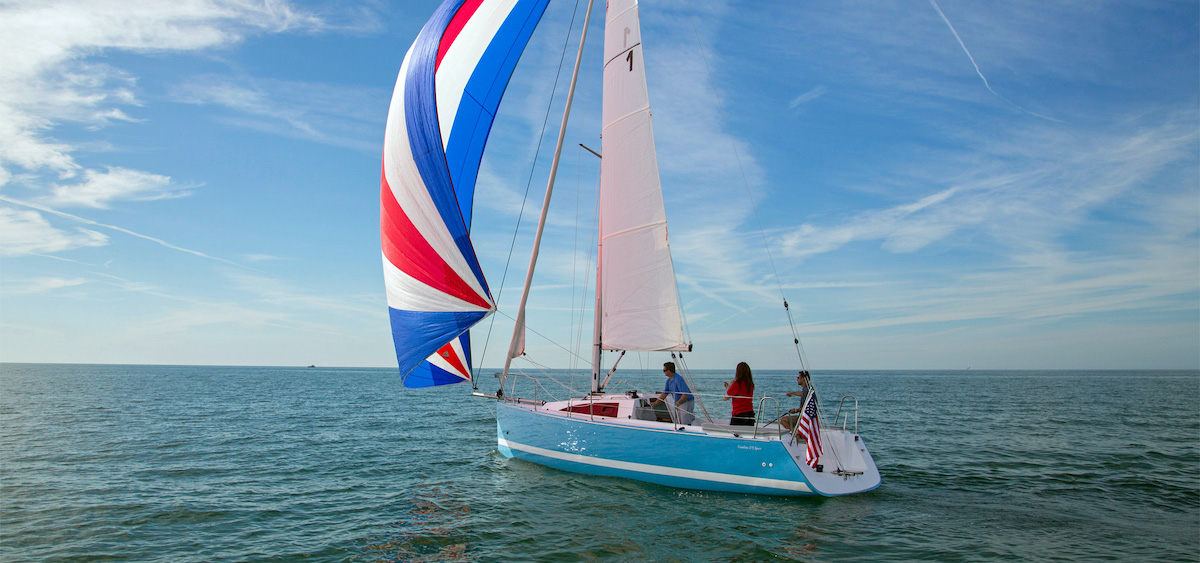
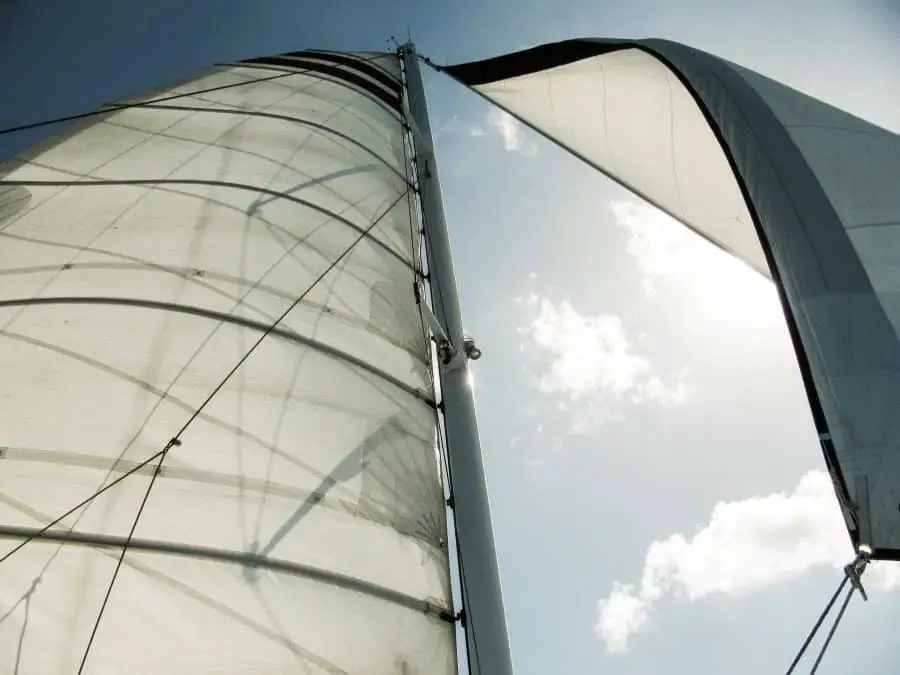
One of the most picturesque sailing images one can conjure up is the one with a sailboat using a genoa sail (see the image above on the right).
A genoa is a type of large jib that’s attached to the front of the forestay just like a headsail.
One of the main differences with the genoa sail is that it’s bigger than the normal headsail and oftentimes extends behind the mast partially or completely covering the mainsail. It actually used to be called an “overlapping jib”.
Using a genoa sail means you have light to medium winds and your sailboat is more or less in a dead run point of sail (wind coming directly from the rear or sailing downwind).
Since the surface area of a genoa sail is so large, it’s important only to use it when winds are relatively low. Otherwise, you’ll be moving exceptionally fast resulting in a potentially risky situation.
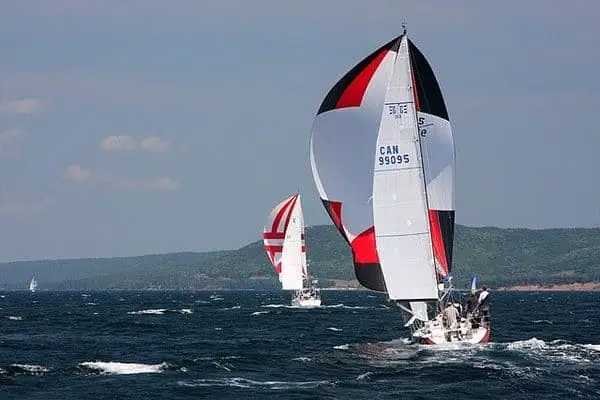

A spinnaker sail is a fun sail to use since it’s quite large, colorful, and can pick up a lot of wind.
Unlike a genoa sail, they’re often symmetrical making them more sensitive to the reaching points of sail and thus more appropriate for the running point of sail. They’re also lighter and have a “kite” kind of feel to them.
The reason they resemble a “kite” is not only that they’re generally lighter and more colorful than other types of jibs, but also they don’t cover the mast like a genoa sail.
Instead, they don’t attach to the forestay and stretch out toward and past the bow of a sailboat. Since they’re bigger than genoa sails, you want to be even more careful to only use them in relatively low and non-volatile wind environments.

A gennaker sail is a more recent type of sail on sailboats since they were developed around 1990.
Gennakers are a cross between genoa and spinnaker sails (as the name might suggest), which are big like a spinnaker, aren’t as symmetric as a spinnaker, and aren’t attached to the forestay like a genoa sail or headsail.
The reason for the invention of the gennaker is that sailors wanted to take advantage of lighter winds without having to resort to using a spinnaker if the winds change from a pure dead run to more of a reaching point of sail.
All in all, the gennaker sail is able to bridge the performance gap between a genoa and spinnaker sail in terms of being able to take on a more flexible point of sail while taking advantage of relatively softer winds.
Popular Sail and Mast Configurations
Now that you’re familiar with the most popular types of sails on a sailboat, it’s good to get an idea of how these sail types relate to the configuration of a sailboat’s mast.
There are a huge number of combinations when it comes to sails and mast configurations, so I thought I’d lay out the most popular ones you’ll likely run into out on the water.

A sloop is the most common type of sail and mast configuration for sailboats. The sloop is the classic single mast, double sail setup.
The sails on a sloop consist of a mainsail and a headsail. The headsail can be different types of jibs, including the genoa, spinnaker, or gennaker sails. The headsail is connected to the forestay on the mast and runs all the way to the top of the mast.
Fractional Rig Sloop
Similar to a sloop, a fractional rig sloop has a single mast, double sail setup. The only difference, however, is that the forestay doesn’t reach the top of the mast, resulting in the headsail being restricted to a fractional amount of space a normal sloop would allow for.
This reduction of surface area for the headsail means that less wind can be captured and, thus, reduced sailboat speed.
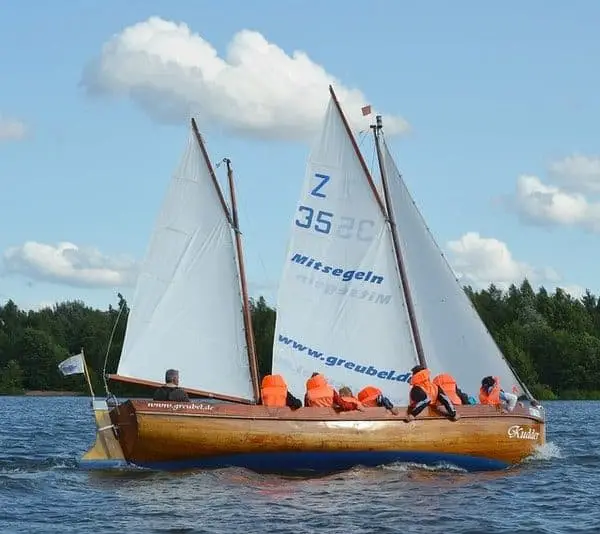

A cutter is an interesting setup since it’s just like the sloop and fractional rig sloop setup, but instead of one forestay it has two. With two forestays on the mast, cutters are able to house two headsails.
This can be a preferred setup because it allows for easy cruising due to it offering a diverse combination of points of sail for different strengths of wind.
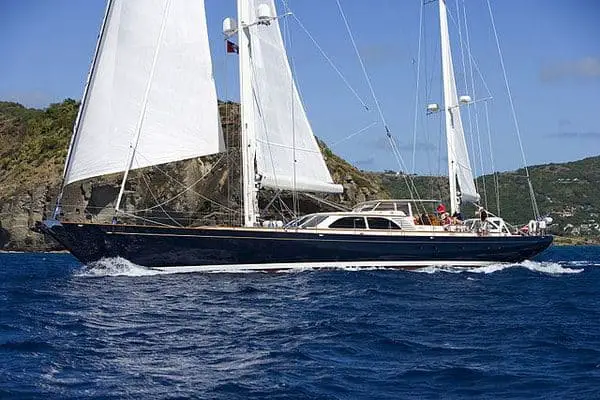

A ketch is a less common setup when compared to the previous setups since it has two masts.
Just like a sloop, it has a mast that allows for a mainsail and headsail with a full range forestay, but it also has a smaller sized mast between the mainmast and the stern of the sailboat.
This mast configuration was commonly used in Northern European freighter and fishing boats and is called the mizzen mast.
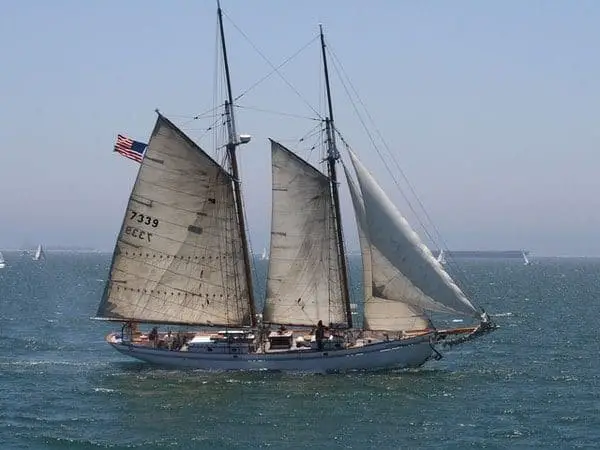

If you’ve ever seen Pirates of the Carribean, you’ll have seen almost nothing but schooners. A schooner is when a sailboat has two or more masts, similar to a ketch, while having a number of sails to manage.
The main differences between a ketch and a schooner are that a schooner’s aft mast (the rear mast) is taller than the forward mast and a schooner can have up to six masts some including a square sail or two. This makes names of sails on a schooner the fore and aft sail (or fore and aft rig).
A yawl is almost identical to a ketch with the only difference being that the mizzen mast is located directly behind the sailboat’s rudder post. In terms of a ketch vs yawl, the mizzen sail is also much smaller than the mizzen sail on a ketch due to its position on the sailboat.
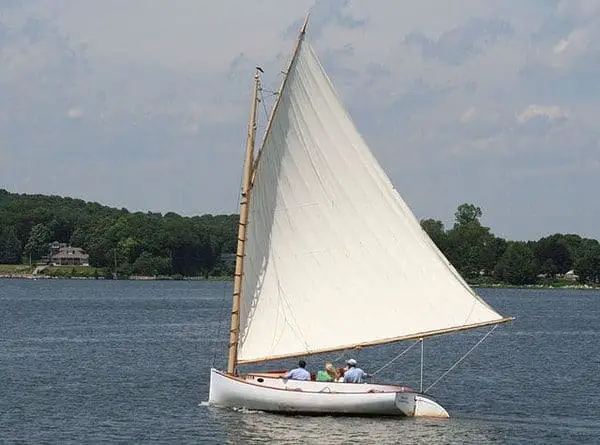

A cat has one mast and one sail with the mast being positioned at the bow of the sailboat. This mast configuration is most commonly found on smaller sailboats, especially dingy sailboats. These types of sailboats are colloquially called “catboats”.
Get the very best sailing stuff straight to your inbox
Nomadic sailing.
At Nomadic Sailing, we're all about helping the community learn all there is to know about sailing. From learning how to sail to popular and lesser-known destinations to essential sailing gear and more.
Quick Links
Business address.
1200 Fourth Street #1141 Key West, FL 33040 United States
Copyright © 2024 Nomadic Sailing. All rights reserved. Nomadic Sailing is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means to earn fees by linking to Amazon.com and affiliated sites.


Types of Sails on Sailboats: A Comprehensive Guide
Sailboats come in many shapes and sizes, but all have one thing in common: sails. The type of sail used on a boat can make a big difference in how it performs on the water. Understanding the different types of sails and their advantages and disadvantages can help sailors choose the right sail for their boat and the conditions they will be sailing in.
One of the most common types of sails is the mainsail. This sail is attached to the mast and boom and is used to catch the wind and propel the boat forward. Mainsails come in many different shapes and sizes, including full-batten, partial-batten, and no-batten designs. Each design has its own advantages and disadvantages, depending on the type of sailing the boat will be doing.

Another important sail on a sailboat is the headsail. This sail is located at the front of the boat and is used to catch the wind from the side. Headsails come in many different shapes and sizes, including genoas, jibs, and spinnakers. Choosing the right headsail can make a big difference in how the boat performs , especially in heavy wind conditions.
Basic Types of Sails
Sails are an essential part of any sailboat. They are used to harness the wind to propel the boat forward. There are several types of sails available for sailboats , and each serves a different purpose. Here are the three basic types of sails:
The mainsail is the most critical sail on a sailboat. It is a large, triangular sail that is hoisted up the mast. The mainsail is the primary source of propulsion for the boat and is used to control the boat’s direction. The mainsail is attached to the boom, which is a horizontal spar that runs along the bottom of the sail. The boom helps to control the mainsail’s shape and angle to the wind.
The mainsail can be adjusted using a variety of controls, including the mainsheet, the traveler, and the boom vang. These controls allow the sailor to adjust the sail’s shape and angle to the wind, which can help to optimize the boat’s speed and performance.
The jib is a smaller sail that is located at the front of the boat. It is a triangular sail that is attached to the forestay, which is a wire that runs from the top of the mast to the bow of the boat. The jib is used to balance the boat and to help control its direction. It is often used in conjunction with the mainsail to provide additional power and control.
The jib can be adjusted using a variety of controls, including the jib sheet and the jib halyard. These controls allow the sailor to adjust the sail’s shape and angle to the wind, which can help to optimize the boat’s speed and performance.
The spinnaker is a large, colorful sail that is used for downwind sailing. It is a symmetrical sail that is attached to the boat’s mast and bow. The spinnaker is used to catch the wind and provide additional power to the boat. It is often used in racing and can help to increase the boat’s speed and performance.
The spinnaker can be adjusted using a variety of controls, including the spinnaker sheet and the spinnaker halyard. These controls allow the sailor to adjust the sail’s shape and angle to the wind, which can help to optimize the boat’s speed and performance.
Specialty Sails
While many sailors may be familiar with the standard mainsail and jib combination, there are a variety of specialty sails that can be used for specific purposes. These sails can be particularly useful for racing, cruising, or for handling difficult weather conditions.
The genoa is a type of jib that is larger than the standard jib and overlaps the mainsail. This sail is particularly useful for upwind sailing as it provides more power and lift than a standard jib. The genoa is also useful for light wind conditions where a larger sail area is needed to catch the breeze.
A storm sail is a heavy-duty sail that is designed for use in strong winds and heavy seas. These sails are typically smaller than the standard mainsail and jib, and are made from heavy-duty materials such as Dacron or Kevlar. The storm sail is used to reduce sail area and provide better control in difficult conditions.
The gennaker is a hybrid between a spinnaker and a genoa. This sail is designed for downwind sailing and is particularly useful in light wind conditions. The gennaker is typically made from a lightweight nylon material and is larger than a spinnaker, but smaller than a genoa. This sail is particularly popular with cruising sailors as it provides a comfortable and stable ride in light wind conditions.
Sail Materials
Sailboats are equipped with sails made from a variety of materials. The type of sail material used depends on the intended use of the sailboat, as well as the budget of the sailor. The following are some of the most common sail materials used on sailboats today:
Dacron is a synthetic material that is commonly used in sails. It is durable, easy to handle, and relatively inexpensive. Dacron sails are ideal for cruising and recreational sailing, as they are not designed for racing or high-performance sailing.
Dacron sails are available in a variety of weights, with heavier sails being more durable and lighter sails providing better performance. Dacron sails are also available in a variety of colors, allowing sailors to customize the look of their sailboat.
Kevlar is a high-performance synthetic material that is commonly used in racing sails . Kevlar sails are lightweight, strong, and have a low stretch rate, making them ideal for high-performance sailing. However, Kevlar sails are more expensive than Dacron sails and require more maintenance.
Kevlar sails are available in a variety of weights and colors, allowing sailors to customize the look and performance of their sailboat.
Carbon Fiber
Carbon fiber is a high-performance material that is commonly used in racing sails. Carbon fiber sails are extremely lightweight and have a low stretch rate, making them ideal for high-performance sailing. However, carbon fiber sails are the most expensive option and require the most maintenance.
Carbon fiber sails are available in a variety of weights and colors, allowing sailors to customize the look and performance of their sailboat.
In conclusion, the type of sail material used on a sailboat depends on the intended use of the sailboat and the budget of the sailor. Dacron is the most common sail material used for cruising and recreational sailing, while Kevlar and carbon fiber are used for racing and high-performance sailing.
Sail Shapes
Sail shape is an important factor in determining the performance of a sailboat. Different sail shapes are designed for different wind conditions, and the choice of sail shape can greatly affect a boat’s speed and maneuverability. Here are three common sail shapes:
Bermuda Rig
The Bermuda rig is the most common sail shape on modern sailboats. It consists of a triangular mainsail and a smaller jib or foresail. The triangular shape of the mainsail allows for efficient wind capture, while the jib helps to balance the boat and control the sail’s shape. The Bermuda rig is versatile and can be used in a wide range of wind conditions, making it a popular choice for cruising and racing sailboats .
The gaff rig is an older sail shape that was commonly used on sailing vessels in the 19th and early 20th centuries. It features a four-sided mainsail with a gaff spar at the top, which provides additional sail area. The gaff rig is less efficient than the Bermuda rig, but it has a distinctive appearance and can be used in light to moderate wind conditions. Gaff-rigged sailboats are often seen in traditional and classic boat regattas.
The lateen rig is a triangular sail shape that is commonly used on small boats and traditional sailing vessels in the Mediterranean and Middle East. It consists of a single, triangular sail that is mounted on a long, diagonal spar called a yard. The lateen rig is efficient in light to moderate winds and is particularly well-suited to sailing downwind. It is often used on small sailing dinghies and traditional wooden boats.
About the author
I worked as an officer in the deck department on various types of vessels, including oil and chemical tankers, LPG carriers, and even reefer and TSHD in the early years. Currently employed as Marine Surveyor carrying cargo, draft, bunker, and warranty survey.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Latest posts

Boat Painting Guide: How to Paint a Boat Efficiently
Interested in learning how to paint a boat? Boat paint has to be tailored for water transportation and extreme weather conditions.
What Is a TEU In Regards to Marine Shipping?
What is a TEU? A twenty-foot equivalent unit (TEU) is a widely accepted standard unit of measurement in marine shipping, representing the capacity of a standard 20-foot-long container.

Sustainable and Luxurious: Discovering Split’s Yachting Paradise
Split, the Adriatic jewel, offers a yachting paradise where history meets pristine maritime beauty. Here, to rent a yacht means unlocking the gateway to exploring secluded bays, experiencing cultural heritage […]

Boat Sailor
Type of sails: a comprehensive guide to sails.

As an avid sailing enthusiast and advisor, I am excited to share a complete guide to different types of sails for sailboats. Choosing the right sail is crucial for optimizing sailing performance and ensuring safety in various weather conditions. In this article, we will explore the main type of sails, their advantages, and when to use them effectively. So let’s set sail and delve into the world of sails!
The Main Types of Sails
Mainsail: The Backbone of Sailing
The mainsail, being the largest and most essential sail on a sailboat, plays a central role in driving the vessel forward. It is a fore-and-aft rigged sail attached to the mast and the boom. Mainsails are incredibly versatile and suitable for various wind conditions, making them the go-to sail for most situations. They are easy to steer, even in light winds, making them ideal for relaxed cruising.
Headsail/Jib: Your Go-To Sail for Safety
The headsail, also known as a jib , is a smaller sail located forward of the mast. Its primary purpose is to maintain stability and balance the boat in strong winds. When the wind picks up, the mainsail can become overpowering, and that’s when the headsail steps in to ensure safe and controlled sailing. It’s like having a safety net during rough weather conditions.
Genoa: Power and Versatility Combined
The genoa is a type of headsail that offers more sail area and power compared to a standard jib. It’s perfect for boosting speed and maneuverability, especially in light winds. Genoas are incredibly versatile, making them an excellent choice for sailors who want to get the most out of their sailboat in various conditions.
Sailing Ship Rigs: A Historical Perspective
In the era of the “golden age of sail,” different sail plans were used on sailing vessels to optimize their performance and accommodate smaller crews.
Fore and Aft Rig
The fore-and-aft rig, consisting of sails aligned along the length of the boat, includes popular designs like schooners and sloops. These rigs required smaller crews and were well-suited for coastal and fishing trades.
Square topsail schooners with athwart sails were also prevalent during that time. They were used for cargo ships and long voyages, but their complex rigging required larger crews to handle the sails effectively.
The Golden Age of Sail
This period marked the peak of sailing ship technology and saw remarkable advancements in shipbuilding and sail design. It’s a fascinating chapter in the history of sailing that continues to inspire sailors to this day.
Type of Sails Names: Decoding the Terminology
Mainsail and Foresail
The mainsail, as mentioned earlier, is the principal sail that catches the wind to move the boat forward. Foresail is a general term that includes various sails positioned near the bow of the sailboat, such as the jib and genoa.
Genoa and Jib
The genoa and jib are both types of foresails. The genoa is larger and overlaps the mainsail, providing additional power and efficiency. The jib, on the other hand, is smaller and is used when the wind is stronger.
Staysail and Spinnaker
Staysails are triangular sails set between masts and stays, used to improve stability and balance. Spinnakers are large, balloon-shaped sails used for downwind sailing, providing an extra boost of speed.
Choosing the Right Sail for Different Conditions
Sailing in Light Winds
In light winds, the mainsail is your best friend. It’s highly efficient and capable of catching even the slightest breeze, propelling the boat forward smoothly.
Sailing in Strong Winds
When the wind picks up, it’s time to rely on the headsail or jib. These sails provide a reduced surface area, preventing the boat from becoming overpowered and ensuring a controlled sail.
Navigating Challenging Weather
Different weather conditions call for different sails. Understanding the intricacies of each sail and when to use them will help you navigate through challenging weather with ease.
Type of Sails Materials: Quality Matters
Traditional Canvas Sails
Traditional canvas sails, made of materials like cotton or linen, were commonly used in the past. While they offer a classic charm, their performance and durability have limitations compared to modern sail materials.
Modern Sail Materials
Today, sail manufacturers utilize advanced materials like Dacron, Mylar, and Kevlar. These materials offer superior strength, low stretch, and better shape retention, contributing to improved sailing performance.
Pros and Cons of Each Material
Understanding the pros and cons of different sail materials will help you make an informed decision when purchasing or maintaining your sails.
Understanding Sail Shapes and Configurations
The Science of Sail Shape
Sail shape is crucial for maximizing performance and efficiency. Properly trimmed sails allow you to sail efficiently, whether you’re sailing upwind or downwind.
Balancing Performance and Stability
Finding the right balance between performance and stability is essential. Adjusting sail shape and trim can significantly impact your sailing experience.
Fine-Tuning Sail Trim
Sail trim is an art form. Mastering the art of fine-tuning sail trim will make you a more skilled sailor and enhance your overall sailing experience.
The Evolution of Sail Designs
From Classic to Cutting-Edge
Sail design has come a long way. From classic traditional sails to modern, innovative designs, sailmaking has witnessed significant evolution.
How Technology Impacted Sail Design
Technological advancements have revolutionized sailmaking, resulting in more efficient, aerodynamic, and performance-oriented sails.
Innovation in Sailmaking
Sailmakers are continually exploring new materials and construction techniques to create sails that are lighter, stronger, and more efficient than ever before.
Sailing Techniques: Getting the Most Out of Your Sails
Tacking and Gybing
Tacking and gybing are essential sailing maneuvers used to change the direction of the boat and optimize the use of wind.
Maximizing Speed
To get the most out of your sails, understanding how to trim them properly and sail at optimal angles is crucial for achieving higher speeds.
Safety Precautions
Sailing is exhilarating, but safety should always be a top priority. Understanding safety procedures and precautions will ensure a safe and enjoyable sailing experience.
Maintaining and Storing Sails
Sail Care and Maintenance
Proper care and maintenance are essential to prolong the life of your sails and keep them in top condition.
Storing Sails Properly
When not in use, storing sails correctly can prevent damage and maintain their performance over time.
Extending the Lifespan of Sails
With proper care and attention, you can extend the lifespan of your sails, making them a worthy investment.
Sustainable Sailing: Eco-Friendly Sail Materials
The Impact of Traditional Sails on the Environment
Traditional sail materials, while charming, may have a more significant environmental impact compared to modern, eco-friendly alternatives.
Eco-Friendly Sail Options
Eco-conscious sailors can explore sustainable sail materials that minimize environmental harm without compromising performance.
Embracing Sustainable Practices
As sailors, we have a responsibility to protect the oceans and environment. Embracing sustainable practices in sailing is essential for the well-being of our planet.
As we conclude this comprehensive guide to different type of sails, I hope you now have a deeper understanding of the critical role sails play in sailing. Choosing the right sail and mastering sail techniques will elevate your sailing experience to new heights. Remember, sailing is an ever-evolving journey of learning and adventure.
Which sail is best for light winds?
The mainsail is the most suitable sail for light winds as it can efficiently catch even the slightest breeze and keep the boat moving smoothly.
What is the purpose of a genoa?
The genoa is a type of sails that provides additional power and versatility, making it an excellent choice for boosting speed and maneuverability in various wind conditions.
What sail material is most durable?
Modern sail materials like Dacron and Kevlar offer superior strength and durability compared to traditional canvas sails made of cotton or linen.
How do I maintain my sails?
Proper care and maintenance, including regular cleaning and inspection, will help prolong the life of your sails and ensure they perform optimally.
Are there eco-friendly sail options?
Yes, eco-conscious sailors can opt for sustainable sail materials that minimize environmental impact, contributing to a greener and more sustainable sailing experience.

Michael Thompson
Embarking on a lifelong love affair with the sea, I found solace and exhilaration in the art of sailing. From navigating treacherous waters to harnessing the wind's untamed power, my passion has evolved into a mission to inspire others. Join me on a voyage of discovery as we explore the vast horizons of sailing's timeless allure.
More to Explore

Sailing Greek Islands

Sailing Apparel: Essential Gear for Smooth Sailing

Sail Boat Trailers: Your Guide to Safe and Convenient Transportation
How to choose the right sails for your sailboat
Choosing the right sails for your sailboat is crucial to ensure optimal performance, safety, and enjoyment while out on the water. This guide will help you navigate the world of sails and make an informed decision based on your sailing style, boat size, budget, and maintenance preferences.
How to Choose the Right Sails for Your Sailboat
Welcome to our unique and adventurous website, dedicated to those who are leaving the rat race behind, purchasing a boat, and setting sail to explore the world with their families. In this article, we will discuss one of the most important aspects of sailing: choosing the right sails for your sailboat. This comprehensive guide will cover everything you need to know about sails, from the different types and materials to the factors you should consider when making your decision.
Table of Contents
Introduction, storm sails, carbon fiber, sailing style, maintenance.
Sails are the heart and soul of any sailboat, providing the power needed to propel the boat through the water. Choosing the right sails for your sailboat is crucial to ensure optimal performance, safety, and enjoyment while out on the water. With so many options available, it can be overwhelming to decide which sails are best suited for your needs. This guide will help you navigate the world of sails and make an informed decision based on your sailing style, boat size, budget, and maintenance preferences.
Types of Sails
There are four main types of sails that you will encounter when outfitting your sailboat: mainsails, headsails, spinnakers, and storm sails. Each type of sail serves a specific purpose and is designed for different sailing conditions.
The mainsail is the primary sail on a sailboat and is attached to the mast and boom. It is responsible for generating the majority of the boat’s forward motion and is used in nearly all sailing conditions. Mainsails come in various shapes and sizes, with the most common being the standard triangular shape. Some other popular mainsail designs include the square-top, roach, and full-batten mainsails.
Headsails, also known as jibs or genoas, are the secondary sails on a sailboat and are attached to the forestay, a cable that runs from the mast to the bow of the boat. Headsails are used in conjunction with the mainsail to increase the boat’s speed and maneuverability. They come in various sizes, with larger headsails (genoas) providing more power in light wind conditions and smaller headsails (jibs) offering better control in stronger winds.
Spinnakers are large, lightweight sails designed for sailing downwind, with the wind coming from behind the boat. They are typically used in racing or when cruising in light wind conditions to maximize speed and performance. Spinnakers come in two main types: symmetrical and asymmetrical. Symmetrical spinnakers are used for sailing directly downwind, while asymmetrical spinnakers are designed for sailing at an angle to the wind, known as reaching.
Storm sails are small, heavy-duty sails designed for use in extreme weather conditions when the wind is too strong for the mainsail and headsail. They are typically made from a durable material like heavy-duty Dacron or Kevlar and are designed to withstand high winds and rough seas. Storm sails include the storm jib, which replaces the headsail, and the trysail, which replaces the mainsail.
Sail Materials
Sails are made from a variety of materials, each with its own unique properties and benefits. The most common sail materials include Dacron, laminate, Mylar, Kevlar, and carbon fiber.
Dacron is a type of polyester fabric that is widely used for sail construction due to its durability, affordability, and ease of maintenance. It is a popular choice for cruising sails, as it can withstand the wear and tear of long-term use and requires minimal maintenance. Dacron sails are typically heavier than other sail materials, which can result in reduced performance in light wind conditions.
Laminate sails are made from multiple layers of material, including a film of Mylar or other plastic, sandwiched between layers of woven fabric. This construction provides a lightweight, strong, and low-stretch sail that is ideal for racing or performance-oriented cruising. Laminate sails are more expensive than Dacron sails and require more maintenance, as the layers can delaminate over time, especially in high UV exposure areas.
Mylar is a type of polyester film that is used in the construction of laminate sails. It provides excellent strength and low stretch properties, making it ideal for high-performance sails. However, Mylar is susceptible to UV damage and can become brittle over time, requiring more frequent replacement than other sail materials.
Kevlar is an aramid fiber that is known for its incredible strength and lightweight properties. It is often used in the construction of high-performance racing sails, as it provides minimal stretch and excellent shape retention. Kevlar sails are more expensive than other sail materials and can be more difficult to maintain, as the fibers are prone to chafe and UV damage.
Carbon fiber is a high-tech material that is used in the construction of some of the most advanced racing sails on the market. It offers exceptional strength, lightweight properties, and minimal stretch, making it ideal for high-performance applications. Carbon fiber sails are the most expensive option and require specialized care and maintenance to ensure their longevity.
Factors to Consider
When choosing the right sails for your sailboat, there are several factors to consider, including your sailing style, boat size, budget, and maintenance preferences.
Your sailing style will play a significant role in determining the type of sails that are best suited for your needs. If you primarily sail for leisure and enjoy cruising with your family, you may prioritize durability and ease of maintenance over performance. In this case, Dacron sails may be the best choice for you. On the other hand, if you are an avid racer or performance-oriented cruiser, you may prefer the lightweight and low-stretch properties of laminate, Kevlar, or carbon fiber sails.
The size of your boat will also influence your sail selection, as larger boats require more powerful sails to propel them through the water. If you have a small to medium-sized boat, you may find that Dacron or laminate sails provide sufficient power and performance for your needs. However, if you have a larger boat, you may need to consider high-performance materials like Kevlar or carbon fiber to achieve the desired performance.
Your budget will undoubtedly play a role in your sail selection, as sail prices can vary significantly depending on the material and construction. Dacron sails are typically the most affordable option, making them a popular choice for budget-conscious sailors. Laminate sails are moderately priced, while Kevlar and carbon fiber sails are the most expensive options. It’s essential to weigh the benefits of each material against the cost to determine the best choice for your needs and budget.
Finally, consider the maintenance requirements of each sail material when making your decision. Dacron sails are known for their durability and low maintenance requirements, making them an excellent choice for sailors who prefer a low-maintenance option. Laminate, Kevlar, and carbon fiber sails require more specialized care and maintenance, including regular inspections for chafe, UV damage, and delamination. If you are willing to invest the time and effort into maintaining these high-performance sails, they can provide exceptional performance and longevity.
Choosing the right sails for your sailboat is a critical decision that will impact your sailing experience, performance, and enjoyment. By understanding the different types of sails, materials, and factors to consider, you can make an informed decision that best suits your needs and preferences. Whether you prioritize durability, performance, or a balance of both, there is a sail option out there that will help you achieve your sailing goals and enjoy your time on the water.
Sailboat Types of Sails: A Comprehensive Guide
by Emma Sullivan | Aug 1, 2023 | Sailboat Lifestyle

Short answer sailboat types of sails:
There are several types of sails used in sailboats, including the mainsail, jib, genoa, spinnaker, and staysail. Each sail type serves a specific purpose and is designed to perform optimally under different wind conditions and points of sail.
Introduction to Sailboat Types of Sails: A Comprehensive Guide
When it comes to sailing, it’s not just about the boat itself – the type of sail you choose is also crucial in determining your overall experience on the water. The sails are not only what enable you to harness the wind’s power and navigate through the vast open seas but also play a vital role in maneuverability and speed. In this comprehensive guide, we will take you on an exciting journey through various sailboat types and their unique sails, providing you with all the information you need to choose the perfect sail for your sailing adventures.
1. Main Sail:
Let’s start with one of the most important sails – the main sail. As its name suggests, this large triangular-shaped sail is positioned at the aft (rear) of most sailboats and is responsible for capturing most of the wind’s power. It plays a substantial role in propelling your vessel forward, especially when sailing upwind or close-hauled. Depending on your skill level and adventurous spirit, variations of main sails are available to suit different conditions and preferences.
2. Jib/Genoa:
Moving forward from our discussion on main sails, let us now explore jibs and genoas – dynamic front sails that enhance maneuverability and ensure optimal performance while tackling changing winds on open waters. Jibs are smaller triangular-shaped fore-sails that work in conjunction with mainsails to provide additional propulsion when sailing close-hauled or beating into the wind. Genoas, on the other hand, are larger headsails that can be raised over jibs to increase surface area for catching wind and boosting speed.
3. Spinnaker:
One cannot discuss sailboats without mentioning spinnakers – those beautifully colorful billowing sails often seen when boats participate in races or glide effortlessly downwind. The spinnaker is designed specifically for reaching or running with a following wind; its impressive size allows sailors to harness the power of the wind fully. These magnificent sails add a touch of elegance and excitement to your sailing adventures, providing an adrenaline rush as you race against competitors or effortlessly cruise downwind on a sunny day.
4. Storm Sails:
As much as we wish for calm weather and smooth sailing, unpredictable conditions are inevitable at sea. In times of gale force winds or stormy weather, having appropriate sails can make all the difference. Hence, we introduce storm sails – ruggedly built and small in size, they are designed to handle extremely strong winds while maintaining control over your sailboat. Often made from heavy-duty fabrics like Dacron or canvas, these sails offer stability during harsh conditions when reducing speed and maneuverability becomes critical.
5. Gennaker:
Lastly, we present to you the versatile gennaker – an amalgamation of both genoas and spinnakers that offers the best of both worlds! This innovative sail provides tremendous power but is easier to handle than a conventional spinnaker due to its more forgiving nature. It is perfect for sailors seeking enhanced performance on deeper angles relative to the wind direction when cruising or racing competitively.
Conclusion:
Understanding the different types of sails is paramount in choosing what suits your sailing style and preferences. Each sail serves its unique purpose and enhances various aspects of your sailing experience, be it speed, maneuverability, or adaptability in challenging conditions. By familiarizing yourself with these sailboat types and their respective sails – main sails, jibs/genoas, spinnakers, storm sails, and gennakers – you will gain not only a comprehensive understanding but also invaluable knowledge that will undoubtedly elevate your time spent on the water.
So weigh anchor with confidence as you embark on an unforgettable journey with your perfectly chosen sailboat type and set sail towards boundless horizons!
How Different Types of Sails Impact Your Sailboat’s Performance
When it comes to sailing, one of the most critical factors that determines your sailboat’s performance is the type of sails you choose. Different types of sails not only affect how your boat handles different wind conditions but also impact its overall speed and maneuverability. In this blog post, we will delve into the intricate details of how various types of sails can significantly impact your sailboat’s performance.
1. Main Sails: The backbone of any sailboat, the main sail plays a crucial role in harnessing the power of the wind. Its design and shape determine how efficiently it converts wind energy into forward motion. Options such as full-batten or partial-batten mainsails provide distinct benefits. Full-batten mainsails offer enhanced control and stability, while partial-batten mainsails are easier to handle and adjust in lighter winds.
2. Genoas/Jibs: These forward- sailing sails are essential for optimizing a sailboat’s upwind performance. Genoas refer to larger headsails that cover a significant portion of the foredeck, providing more area for capturing wind power when sailing close to or across the wind direction. Alternatively, jibs are smaller headsails suitable for higher wind speeds and improved maneuverability. Selecting the appropriate genoa/jib size according to weather conditions ensures optimal performance during tacking (changing direction against the wind).
3. Spinnakers: Primarily used downwind with favorable winds, spinnakers come in various shapes like asymmetrical or symmetrical designs depending on their intended use. Asymmetrical spinnakers excel at reaching fast speeds with fewer crew members needed due to their ease of handling compared to symmetrical ones.
4. Code Zeros: Code Zero sails find their purpose mainly in light-wind conditions where other conventional sails struggle to generate sufficient power for noticeable boat speed. With their unique shape combining characteristics from both genoas/jibs and spinnakers, code zeros allow sailors to maintain forward momentum even in gentle breezes.
Choosing the right combination of sails for your sailboat requires considering various factors such as wind conditions, sailing objectives, and crew size. Understanding how different types of sails impact performance empowers sailors to optimize their experience on the water.
When evaluating sail choices, several key considerations come into play. Sail material and construction affect their durability, weight, and shape retention over time, directly influencing performance capabilities. High-performance materials like carbon fiber or laminated fabrics offer superior strength-to-weight ratio while maintaining excellent shape under varying wind conditions.
Furthermore, attention should be given to rigging options such as roller furling systems or lazy jacks in order to enhance ease of handling and increase efficiency during sail adjustments and maneuvering . The complexity of rigging can significantly impact the overall ease or difficulty experienced in setting up sails . Therefore, choosing appropriate rigging systems that match your sailing proficiency level is crucial for optimal performance .
Lastly, it is worth mentioning that a well-designed sail plan takes into account not only individual sail characteristics but also their coordination as a whole. Achieving proper balance between the main and headsails ensures efficient wind capture while minimizing unnecessary drag caused by misaligned sails.
In conclusion, the type of sails you select will inherently influence your sailboat’s overall performance characteristics on the water. Being aware of these distinctions allows you to optimize your sailing experiences by selecting suitable sails based on weather conditions and desired outcomes. So next time you hit the open waters, make an informed choice regarding your sails and enjoy a more satisfying journey with improved speed, control, and stability!
Exploring the Various Categories of Sailboat Types of Sails
Sailing is not just a recreational sport; it is a lifestyle, an adventure, and a profound connection with nature. As sailing enthusiasts, we are constantly in awe of the beauty and elegance that sailboats possess. And one of the most crucial components that define a sailboat ‘s performance is undoubtedly its sails.
Sailboat sails can be categorized into various types based on their design, purpose, and functionality. Each type of sail serves a specific function and contributes to the overall sailing experience. In this blog post, we will dive deep into the different categories of sailboat types of sails, giving you a comprehensive understanding of how they work and when to use them.
1. Main Sail: The backbone of every sailboat’s rigging system, the main sail harnesses wind power to propel the boat forward. Usually triangular or trapezoidal in shape, it is attached to the mast at its leading edge and controlled by halyards and boom vangs. The main sail provides primary propulsion and contributes to steering control through trimming techniques.
2. Jib: Positioned forward of the mast, jibs are headsails that assist in maneuvering and balance by controlling the airflow around the bow area. Jibs come in different sizes such as genoas or jib tops depending on their area coverage. These sails are excellent for upwind sailing as they provide lateral force while reducing heeling (when the boat tilts sideways).
3. Genoa: larger than jibs but smaller than spinnakers, genoas offer significant power boosts especially when sailing downwind or broad-reaching. Their large surface area enables efficient catching of wind from various angles, propelling sailboats at exhilarating speeds effortlessly .
4. Spinnaker: Hailed as one of the most thrilling sails to use for downwind sailing conditions, spinnakers are like colorful parachutes specifically designed for speed enthusiasts. With their expansive shape, spinnakers capture the maximum amount of wind possible which propels sailboats with incredible momentum. These sails come in a variety of cuts such as asymmetrical and symmetrical, each suited for different wind angles.
5. Storm Sails: When the fury of Mother Nature unleashes its wrath upon sailors, storm sails become their saviors. Built to withstand extreme weather conditions, these smaller sails are meant to be used in heavy winds and erratic seas. The reduced surface area enables sailors to maintain control over their vessel while navigating through nature’s tempestuous onslaught.
6. Stay Sails: Positioned between the mast and forestay or inner stay, stay sails provide extra power for upwind sailing in challenging weather conditions . They act as an additional source of propulsion when the main sail alone is insufficient to counteract strong headwinds.
7. Mainsail Headsail Combination: Ideal for cruising in mild conditions or when partaking in relaxed leisurely sails, this combination consists of both a mainsail and a headsail (jib or genoa). Together, they deliver balanced performance by combining driving force from the main sail with additional lift from the headsail .
Each type of sail offers distinct advantages depending on specific sailing requirements, weather conditions, and desired speed. Skillful sailors understand how to effectively utilize these different categories of sails to harness wind power efficiently and maximize their sailboat’s potential.
So whether you’re an experienced sailor or just embarking on your sailing journey, understanding the various types of sails opens up a world of possibilities. Combine them strategically, practice trimming techniques diligently, and let your sailboat dance beautifully across the water ‘s surface as it embraces the primal power of nature’s gift – the wind!
Step-by-Step Guide: Choosing the Right Sail for your Sailboat
Welcome to our step-by-step guide on choosing the right sail for your sailboat! Whether you are a seasoned sailor or just starting out, finding the perfect sail can greatly enhance your sailing experience . In this blog post, we will walk you through the process of selecting a sail that matches your needs and preferences. So, grab your compass and let’s set sail !
Step 1: Determine Your Sailing Goals Before diving into the world of sails, it is important to first assess your sailing goals. Are you looking for speed and performance? Or perhaps comfort and ease of use? Understanding what you want to achieve with your sail helps narrow down the options available in the market.
Step 2: Consider Your Boat Size and Design The size and design of your sailboat play a crucial role in selecting the right sail. Smaller boats may require smaller sails that are easier to handle, while larger boats may benefit from larger sails for enhanced performance. Additionally, considering factors such as keel type , mast height, and rigging configuration can also impact your choice.
Step 3: Know Your Sail Types Sail types vary in shape, material, and purpose. Let’s explore some common ones:
a) Mainsails: This vital sail provides most of the propulsion and is situated at the aft end of the boat. It comes in various designs like full-batten mainsails for improved shape control or loose-footed mainsails for easier handling.
b) Headsails: Positioned forward of the mast, these sails help with maneuverability and balance. Genoas offer excellent upwind performance while jibs are more suited for lighter wind conditions.
c) Spinnakers: Ideal for downwind sailing, spinnakers provide an extra boost by catching wind from behind. Asymmetric spinnakers are great for cruising sailors while symmetric ones excel in racing scenarios.
d) Specialty Sails: Depending on your needs, various specialty sails like storm jibs, drifter sails, or gennakers can further expand your sailing capabilities.
Step 4: Material Matters Sail materials have come a long way, offering different trade-offs in terms of durability, weight, and performance. Dacron is the most popular choice for cruising sails due to its durability and affordability. On the other hand, high-performance sailors might opt for laminated sails made from exotic materials like Kevlar or carbon fiber.
Step 5: Seek Expert Advice If you’re feeling overwhelmed by the myriad of options available, seeking advice from sailmakers or experienced sailors can be valuable. They can provide insights based on your unique requirements and guide you towards making an informed decision.
Step 6: Consider Your Budget Finally, while it’s essential to find the perfect sail for your needs, budgetary constraints often come into play. It’s worthwhile to aim for a balance between quality and price by exploring different brands and offerings within your budget range.
By following these step-by-step guidelines and considering each aspect carefully, you’ll be on your way to finding the ideal sail for your sailboat . Remember that selecting a sail is not just about practicality—it’s also about infusing your personality into your sailing adventures. So choose wisely and let your dreams set sail !
Frequently Asked Questions about Sailboat Types of Sails, Answered!
Welcome to our blog where we will be answering all your frequently asked questions about sailboat types of sails! Sailing is a fantastic adventure that allows you to harness the power of the wind and explore vast bodies of water . But with so many sailboat types and sails available, it’s easy to feel overwhelmed. Fear not, as we have got you covered with detailed professional insights delivered in a witty and clever manner.
1. What are the different types of sails used on sailboats?
Ahoy there! Sailboats can sport various types of sails depending on their purpose and design. Let’s weigh anchor and set sails on this journey!
– Mainsail: The workhorse of any sailboat, the mainsail is usually situated behind the mast and provides primary propulsion. It catches wind from behind when sailing downwind or gets trimmed closer to the centerline when heading upwind.
– Jib/Genoa: Positioned at the front (fore) part of a sailboat , jibs are smaller triangular sails aiding in maneuverability during tight turns or upwind sailing. If larger in size, they’re often referred to as genoas.
– Spinnaker: Calling all adrenaline seekers! This oversized, colorful parachute-like sail is flown ahead or beside the boat when sailing primarily downwind. It catches wind from both sides, propelling your vessel at remarkable speeds.
– Gennaker: Combining features of both a spinnaker and a jib/genoa, gennakers are versatile crossover sails suitable for reaching (sailing across the wind). They provide additional speed without requiring complex rigging setups.
2. How do I choose which sail to use?
Navigating through these waters requires understanding your intentions aboard your trusty vessel:
– Cruising Sails: If leisurely cruising is your aim, investing in durable and practical mainsails coupled with genoas/jibs would cater well to most conditions encountered. These sails offer good all-around performance without compromising comfort.
– Racing Sails: If you seek to conquer the racecourse, high-performance sails such as asymmetric spinnakers and advanced upwind sails like genoas with sizeable roach profiles are essential. These sails are designed for maximum aerodynamic efficiency, speed, and agility.
3. Which sailboat type is suited for my needs?
Avast there! Sailboats come in various shapes and sizes, each possessing unique characteristics:
– Monohulls: The most traditional sailboat design featuring a single hull. They provide stability through a keel or centerboard, excel upwind due to their ability to point higher into the wind, and offer comfortable cruising experiences.
– Catamarans: A popular choice among seafarers looking for increased deck space, stability, and shallow draft capabilities. Catamarans have two hulls connected by a deck, making them ideal for coastal cruising or chartering adventures.
– Trimarans: For those seeking maximum speed and adventurous sailing thrills, trimarans are your go-to choice. With three hulls connected via crossbeams, they provide incredible speed while maintaining stability even in rough waters .
So there you have it – our witty and clever explanation of frequently asked questions about sailboat types of sails! We hope this article has brought some clarity amidst the sea of confusion. Remember to always match your sail choices with your sailing goals for smooth voyages ahead. Fair winds and following seas!
Enhance Your Sailing Experience: Understanding the Benefits of Different Sailboat Types of Sails
Title: Enhance Your Sailing Experience: Understanding the Benefits of Different Sailboat Types of Sails
Introduction: Sailing is an exhilarating adventure that connects us with nature’s elements, offering a sense of freedom and peace. However, to truly enhance your sailing experience, understanding the benefits of different sailboat types and sails becomes paramount. In this blog post, we delve into the world of sails and unravel their significance in enabling you to conquer new horizons with confidence. So hop aboard as we embark on a journey to explore the various sail options and their exceptional advantages.
1. The Traditional Beauty of Dacron Sails: When it comes to classic sailboat types, Dacron sails remain an undisputed favorite amongst sailors worldwide. These iconic sails showcase exceptional durability while providing excellent shape retention capabilities. Their polyester fabric composition allows for extraordinary resistance against UV rays, ensuring longevity even under harsh weather conditions . Dacron sails possess substantial stretch characteristics, making them ideal for cruising and long-distance voyages where performance takes precedence over speed.
2. Cruising Elegance with Laminate Sails: For those seeking both performance and style during their sailing adventures, laminate sails emerge as a top choice. Composed of carefully layered fabrics such as Mylar or Kevlar matrixes, these sails offer enhanced shape control while also being lightweight – a crucial factor in increasing boat speed. With advanced aerodynamic profiles and exquisite detailing, laminate sails represent the pinnacle of elegance in modern sailboat design .
3. The High-Octane Thrills of Kevlar/Carbon Fiber Sails: For thrill-seekers yearning for fast-paced maneuvers and exhilarating races, Kevlar or Carbon Fiber composite sails are unrivaled contenders. Renowned for their extraordinary strength-to-weight ratio and superior shape retention properties, these high-tech marvels help saltwater enthusiasts fly across waves with unmatched agility. Although highly performative, keep in mind that Kevlar/Carbon Fiber sails require a delicate touch and careful maintenance to ensure longevity.
4. Embracing Cutting-Edge Innovation with Nylon Spinnaker Sails: When it comes to reaching new speeds and sailing downwind like a pro, nylon spinnaker sails reign supreme. Featuring vibrant colors and distinctive geometric patterns, these sails are not only visually striking but also immensely efficient. Their lightweight nylon fabric ensures quick deployment and fast acceleration, enabling sailors to tap into the true adrenaline of competitive sailing. An indispensable tool for experienced racers, nylon spinnakers deliver an ultimate boost to your sailing experience.
Conclusion: As passionate sailors, we understand that choosing the right sailboat type and sail is crucial to elevate your time on the water. From the timeless strength of Dacron sails to the high-performance wonders of Kevlar/Carbon Fiber options, each sail offers unique advantages based on one’s goals and preferences. By comprehending these nuances, you can optimize your sailing adventure while exploring unruly seas or savoring serene moments amidst vast oceans. So go forth confidently, armed with knowledge about different sailboat types and enjoy a truly enhanced sailing experience!
Recent Posts

- Sailboat Gear and Equipment
- Sailboat Lifestyle
- Sailboat Maintenance
- Sailboat Racing
- Sailboat Tips and Tricks
- Sailboat Types
- Sailing Adventures
- Sailing Destinations
- Sailing Safety
- Sailing Techniques

WHAT ARE THE DIFFERENT SAILS ON A SAILBOAT?

If you’re new to sailing, it can be hard to recognise and memorise all the different types of sails that are used on a modern sailboat. In this article, we’ll run through the main categories of sails and introduce you to some less popular ones, too.
MAINSAIL
This is the most common type of sail and the one most people recognise. Mainsails are attached to the boom of a sailboat and slide through the mast to get raised. These sails tend to be quite powerful, as they have a large surface area.
Being right in the middle of the boat, and fully configurable with the boom, a mainsail works well in any wind direction. However, when running downwind, it can block the wind from reaching the headsail, slowing the boat down.
The headsail is located at the bow, on a furler or forestay that is connected to the mast and the deck. It’s usually smaller than the mainsail, so it can’t catch as much wind. This type of sail is good for sailing downwind, on a broad reach, or on a beam reach.
There are two kinds of headsails:
A jib - a triangular sail positioned in front of the mast
A genoa - a large jib that overlaps the mainsail, which can vary in size.
LIGHT AIR SAILS
In lighter winds, you won’t go very fast by using a standard mainsail and jib. You can use lighter, bigger sails in these conditions to improve performance.
Spinnakers are large, light sails, which fly freely and fill up with air, taking a balloon shape. You can usually recognise them from afar, as they are very colourful. Unlike other sails, they are symmetrical - the luff is as long as the leech.
To raise a spinnaker you need a spinnaker pole and a dedicated halyard. Most people also use a sock (a tapered sleeve made of mesh) to store it, which is helpful when raising and dropping the sail.
A gennaker (or asymmetrical spinnaker) is a cross between a genoa and a spinnaker. So it’s a little slower and easier to handle. A gennaker differs from a spinnaker because it’s asymmetrical, but it flies freely.
Reacher / drifter reacher
A reacher is a large genoa made of lightweight laminated spinnaker fabric. Being about 150-170% the size of a genoa, it offers great performance in lighter winds. However, it’s easier to handle than a spinnaker, because it’s shaped like a genoa.
Code zero reacher
A code zero is a hybrid cross between a genoa and a gennaker that is designed for close reaching. It’s roughly twice the size of a non-overlapping jib.
A windseeker is a small, free-flying staysail for very light wind. This sail is designed to push air onto the lee side of the mainsail. To raise it, use the spinnaker halyard.
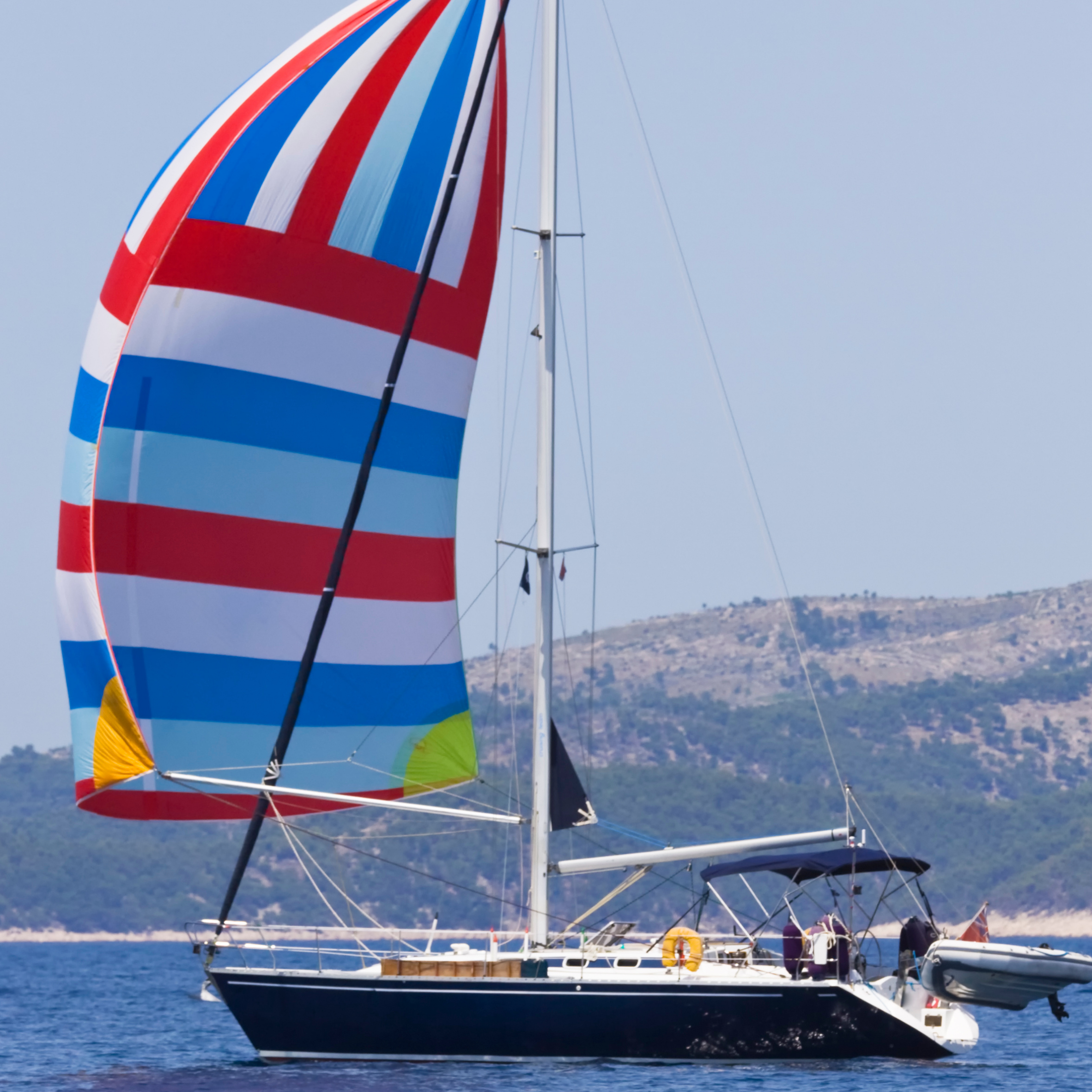

In high winds, you can reef your mainsail and furl your headsail to slow the boat down. However, when the wind is too strong, standard sails can rip. In this instance, you need to raise stormsails - smaller sails that will allow you to keep sailing slowly, so you will have less chance of breaking something onboard.
This is a small triangular staysail that you can use safely in heavy weather. You typically raise it up the headstay, about ⅓ or ½ of the way up.
A trysail can replace the mainsail in the event of a storm. It is rigged above the gooseneck - the part of the boom attached to the mast.

WHY DO SAILORS USE DIFFERENT SAILS?
Sailors tend to use the best sails for the weather conditions they are in. For example, in less than 10-15 knots of wind, using a mainsail and genoa is very inefficient. It’s best to raise a light air sail. In strong winds, on the other hand, a reefed mainsail can increase heeling. A trysail will be safer to use and make the crew more comfortable.
Ease of handling also plays a factor - having two smaller headsails requires less muscle power than using a big genoa, but it pushes the boat at a similar speed.
BOAT RIG TYPES
The type of rig of a sailboat is a deciding factor in the kind and number of sails you can use on your vessel. Let’s quickly look at the main rig types of modern sailboats.
A sloop is the most common type of rig you see out on the water. It features one mast and two sails (a mainsail and a genoa).
A cutter is a one-masted boat that has a mainsail and two headsails; generally a genoa or yankee (a smaller jib) and a staysail (also a smaller jib).
A ketch has two masts, both of which have a mainsail. The shorter mizzen mast is stepped before the rudder head.
A yawl looks almost identical to a ketch. The only difference is that the mizzen mast is stepped aft of the rudder head.
A schooner has two or more masts. The after masts are the same height or taller than the foremast.
Each boat rig requires different kinds of sails and rigging. So choose which rig is right for you before you go boat shopping.
HOW TO SAFELY CHANGE DIRECTION ON A BOAT
How to moor a boat - step by step guide.
Better Sailing

Names of Sails on a Sailboat
Are you a beginner sailor and want to get acquainted with the names of the sails? Are you an experienced sailor and want to learn more details about the sails on a sailboat? Then this article is written for you! Sails form a crucial part of the sailboat because without them, there’s no starting up. For that reason, there are many details about different types of sails concerning their utility, functionality, fabrication materials, and performance. Simply put, each sail serves different purposes when out on the water. Since the sail is the engine of your sailboat, in terms of it being the basic source of propulsion, it’s important to know when best to use either type of sail and why.
Types of Sails on a Sailboat
So, in order to better explain the types of sails, let’s look at their characteristics. The first important distinction between sails is their placement. Generally, the mainsail is placed aft of the mast , which means behind. On the contrary, the headsail is in front of the mast. There are also other sorts of sails that are used for specific conditions. These can be the spinnakers or balloon-shaped sails for downwind use. The second important distinction for the sails is their functionality. The specialized sails have different functionalities and are used in different sailing circumstances and weather conditions. A rule about sails is that large sails are appropriate for downwind use, whereas small sails are good for upwind use. Moreover, large sails perform better on weak winds while small sails are good for strong winds.
The Parts of a Sail and its Shapes
- Head: This is the top of the sail.
- Luff: The forward edge of the sail.
- Leech: Back edge of the sail.
- Tack: The lower front corner of the sail.
- Clew: The bottom back corner of the sail.
- Foot: Bottom of the sail.
There are two sail shapes, the fore-and-aft rigged sails, and square-rigged sails. Nowadays, fore-and-aft sails are more popular, have better performance and maneuverability. To grasp the idea square sails are the ones that Vikings had on their ships and are good at sailing downwind because they run from side to side. But they’re not suitable at all when sailing upwind. On the other hand, a fore-and-aft sail is tied from the front of the mast to the stern and is much better at sailing upwind.
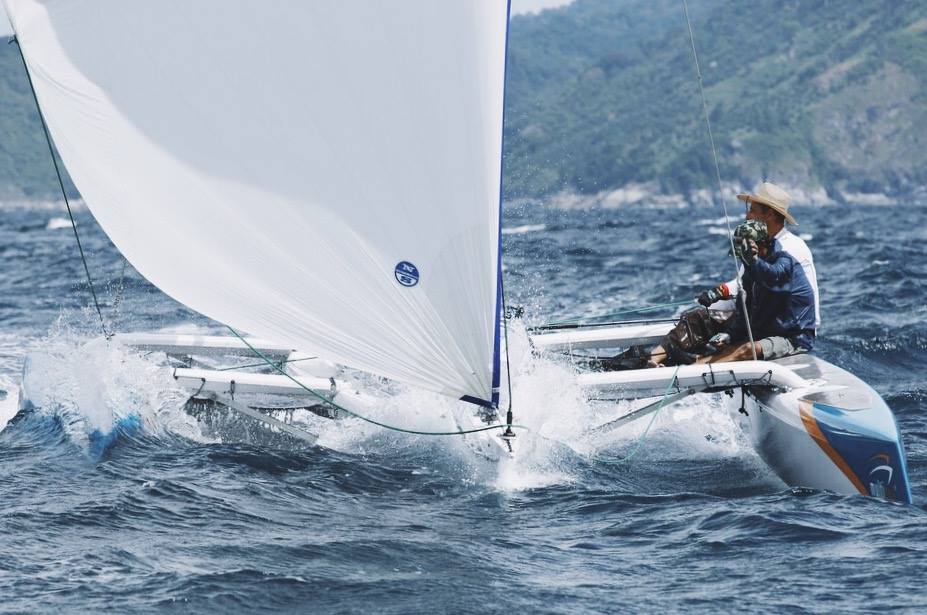

Also Read: What is Sailboat Rigging?

Types and Names of Sails
There are a lot of reasons why you’d want to put one sail over another, but the most important thing to remember has to do with the point of your sail and the wind strength. These points help you understand how your sailboat generates wind power. These points of sail include: into the wind (in irons), beam-reaching, broad-reaching, close-hauled, close-reaching, and running. They all go from windward to leeward and are symmetric from port to starboard . So, let’s get to the point and see the names and explanation of each sail:
- Mainsail : The large sail behind the mast which is attached to the mast and the boom, is called the mainsail. Mainsails cover a lot of surface area concerning incoming winds and by doing that they don’t need very strong winds to provide forward propulsion on a sailboat.
- Headsail or Jib : The small sail placed in front of the mast, attached to the mast and forestay (ie. jib or genoa), is called the headsail. Headsails are smaller than mainsails, thus their surface area is smaller. As a result, they can’t catch the same wind as a mainsail does. However, this is important because in case that the current wind is strong and the mainsail has been enough trimmed, being able to remove the mainsail and depend on the headsail alone, is a good strategy in order to reduce speed.
- Genoa : A genoa is like a large jib and it’s attached to the front of the forestay, like a headsail. When you use a genoa sail then you are expecting light to medium winds. Also, your sailboat would be somehow in a rush point of sail, meaning that the wind comes directly from the rear. Moreover, the surface area of a genoa sail is quite large, so it’s important to use it when winds are relatively low.
- Spinnaker : These downwind sails are symmetrical which makes them more sensitive to the reaching points of the sail and therefore more suitable for the running point of sail. Spinakkers are lighter than other types of jibs, and they don’t cover the mast like a genoa sail. Moreover, they remain unattached to the forestay and stretch out toward and past the bow of a sailboat.
- Gennaker : Gennakers are a mixture of genoa and spinnaker sails. There are small and big gennakers and both are downwind sails. They aren’t as symmetric as a spinnaker and aren’t attached to the forestay like a headsail. Furthermore, the gennaker sail is able to take on a more flexible point of sail while taking advantage of softer winds.
- Drifter Reacher : A drifter is a light air sail, and it’s basically a larger genoa for use in light winds. Its extra sail area offers better downwind performance than a genoa. It’s mostly made from lightweight nylon.
- Code Zero Reacher : This sail is a type of spinnaker, but it looks like a large genoa. However, code zero is designed for better reaching which makes it much flatter than the spinnaker.
- Windseeker : This sail is small, and it’s designed to guide light air onto the lee side of the mainsail. Moreover, it’s tall and thin and ensures a smoother flow of air.
Sail and Mast Configurations
Now that you got an idea of the different types of sails on a sailboat, it would also be an advantage to know how these types of sails are related to the configuration of a sailboat’s mast. There are numerous combinations when it comes to sails and mast configurations, let’s see some of them!
- Cat: A cat is similar to a dinghy and has one mast and one sail. The mast is located at the bow of the sailboat.
- Sloop: The sloop has the classic single mast and a double sail setup. The headsail can be different kinds of jibs, is connected with the forestay on the mast, and runs all the way up to the mast.
- Fractional Rig Sloop: A fractional rig sloop is different from the sloop because its forestay doesn’t reach the top of the mast. Its headsail is restricted to a fractional amount of space and this means that less wind can be captured, therefore the speed of the sailboat is reduced.
- Cutter: Having two forestays on the mast and cutters that are able to house two headsails this setup allows easy cruising because it offers a wide combination of points of sail for different strengths of wind.
- Ketch: Just like a sloop the ketch has a mast that enables the mainsail and headsail to a full range forestay. However, it also has a smaller mast between the mainmast and the stern of the sailboat.
- Schooner: A schooner is when a sailboat has two or more masts but it has a couple of sails to manage. A schooner’s aft mast is taller than the forward mast and sometimes a schooner can have up to six masts.
Names of Sails on a Sailboat – Summary
So, how many types of sails are there? In general, sailboats have one mainsail and one headsail. The rigging also affects the types of sails you can use. As we’ve explained before, the mainsail is a fore-and-aft Bermuda rig. Then, for a headsail, we use a jib or genoa. Most experienced sailors use extra sails to ensure better performance for their sailboat. For example, the spinnaker (a common downwind sail), the gennaker, the code zero (for upwind use), and the storm sail. Keep in mind that every sail has its own use and performance. Want to go downwind fast? Use a spinnaker. Don’t just raise any sail you think suits you best and go for it! It’s of great importance to understand the functionality, use, and performance of each sail.
Peter is the editor of Better Sailing. He has sailed for countless hours and has maintained his own boats and sailboats for years. After years of trial and error, he decided to start this website to share the knowledge.
Related Posts

Lagoon Catamaran Review: Are Lagoon Catamarans Good?

Best Inboard Boat Engine Brands

Are O’Day Sailboats Good? A Closer Look at a Classic Brand

Why Do Sailboats Lean?
- Buyer's Guide
- Destinations
- Maintenance
- Sailing Info
Hit enter to search or ESC to close.

Learn How to Sail a Sailboat: Essential Tips and Techniques
Alex Morgan

Sailing a sailboat is an exhilarating experience that allows you to harness the power of the wind and navigate the open waters. Whether you’re a beginner or have some sailing experience, understanding the fundamentals of sailing and sailboats is essential for a safe and enjoyable journey.
To embark on your sailing adventure, it’s important to have a basic understanding of sailing terminology, as well as the different types of sailboats available. There are two main types:
- Dinghies: These are small, lightweight boats that are typically sailed by one or two people. They are easy to maneuver and are great for learning the basics of sailing.
- Keelboats: These are larger boats with a fixed keel in the center, which provides stability and helps prevent capsizing. Keelboats are suitable for longer journeys and can accommodate more people.
Gaining knowledge of important sailboat terminology is crucial for effective communication and understanding while on the water. This includes familiarizing yourself with terms related to sails and rigging, points of sail (the direction your boat can sail relative to the wind), and maneuvers such as tacking (turning the bow of the boat through the wind) and jibing (turning the stern of the boat through the wind).
Before setting sail, proper preparation is key. This involves checking weather conditions, performing safety checks to ensure the boat is in good working order, and gathering essential equipment such as life jackets, navigation tools, and communication devices.
Once you’re ready to sail, mastering basic sailing techniques is essential. This includes learning how to get underway, steer the boat, change direction, and adjust the sails to optimize performance. Understanding how to maneuver in different wind conditions is also crucial for a successful sailing experience.
As you progress in your sailing journey, you can explore advanced techniques such as sail trimming (adjusting the sails for optimal performance), sailing upwind and downwind, and heaving to (a technique used to pause the boat’s forward momentum).
Safety is of utmost importance while sailing, and knowing emergency procedures is essential. This includes knowing how to perform a man overboard recovery, how to handle capsizing and righting the boat, and how to deal with unexpected weather changes.
By familiarizing yourself with the basics of sailing, gaining practical experience, and adhering to safety practices, you can fully enjoy the thrilling and rewarding experience of sailing a sailboat.
– Sailing a sailboat maximizes the use of wind power: By harnessing the wind, sailors can navigate and move their sailboats without relying on fuel or other energy sources. – Understanding sailboat terminology is crucial: Knowing the different parts of a sailboat and how they function is essential for effectively maneuvering and controlling the boat. – Safety should always come first in sailing: Before setting sail, it is important to check weather conditions, perform safety checks, and gather the necessary equipment to ensure a safe and enjoyable sailing experience.
Types of Sailboats
Ever wondered about the different types of sailboats out there? Let’s set sail and explore the fascinating world of sailboat varieties. From nimble dinghies to sturdy keelboats, each sub-section will take us on a journey through the unique features and uses of these magnificent watercraft. So grab your life jacket and brace yourself for an adventure into the diverse world of sailboats, where the wind becomes our guide and the waves carry us to new horizons.
A table of commonly used dinghies in sailing:
There are many other types of dinghies available, each with its own unique characteristics and purposes. Factors to consider when choosing a dinghy include skill level, intended use, and sailing conditions. It is important to maintain and equip the dinghy with safety gear, and to be familiar with its handling and safety procedures. Dinghies provide an exciting and engaging experience on the water, whether for racing or leisure sailing.
Keelboats are sailboats with a keel attached to the hull. The keel , a fin-like structure, provides stability and allows for sailing upwind . Keelboats are larger and more spacious than dinghies, making them suitable for cruising and overnight trips. They often have cabins , kitchens , and bathrooms . Keelboats can be sailed by a large crew or single-handedly, depending on their size and design . They are used for racing and leisure sailing , offering a comfortable and stable experience. Beginners may prefer keelboats because of their stability and resistance to capsizing . Learning to sail a keelboat involves sail trimming , steering , and maneuvering in different wind conditions.
Understanding Important Sailboat Terminology
Get ready to set sail! In this section, we’ll dive into the essential sailboat terminology that every sailor should know. From understanding the intricate workings of sails and rigging to mastering the different points of sail , we’ll cover it all. Plus, we’ll unravel the mysteries of tacking and jibing , helping you navigate the waters with ease. So, grab your captain’s hat and join us as we explore the fascinating world of sailboat terminology.
Sails and Rigging
The sails and rigging are essential components of a sailboat that enable it to harness the wind and move forward. The durable and lightweight fabric of the sails is attached to a system of ropes and wires called the rigging. The rigging, which includes components such as the mast , boom , and shrouds , supports and controls the sails.
The mast is a tall vertical structure that holds the sails in place and provides stability to the sailboat. The boom , a horizontal spar, connects to the bottom of the mast and supports the foot of the mainsail. The shrouds , diagonal wires or ropes, hold the mast in place and prevent it from swaying or collapsing in the wind.
The sheets , ropes attached to the sails, control their position and shape based on the wind direction. The halyards , ropes used to raise or lower the sails, allow sailors to adjust the amount of sail area exposed to the wind. Sail controls , including the cunningham , outhaul , and vang , fine-tune the sail shape for optimal performance.
The rigging’s ropes and wires are secured and adjusted using knots , cleats , and winches , giving sailors control over the sails.
Points of Sail
The points of sail play a significant role in sailing as they pertain to angles at which a sailboat can navigate in relation to the wind. It is essential for sailors to have a good understanding of these points of sail in order to effectively maneuver their boats. Here is a breakdown of the different points of sail:
– Close-hauled: This is when the sailboat sails as close to the wind direction as possible, usually at an angle of 30 to 45 degrees into the wind.
– Close reach: In this point of sail, the boat sails between close-hauled and a beam reach, at an angle of approximately 45 to 60 degrees to the wind.
– Beam reach: Here, the boat sails perpendicular to the wind, forming a right angle to the wind direction. This point of sail is often considered the fastest and most comfortable.
– Broad reach: The boat sails with the wind coming from behind at an angle of approximately 135 to 150 degrees.
– Running: In this point of sail, the boat sails directly downwind, with the wind coming from directly behind.
– Jibing: This refers to the maneuver of changing from one tack to another by turning the stern of the boat through the wind.
– Tacking: On the other hand, tacking is the maneuver of changing from one tack to another by turning the bow of the boat through the wind.
Sailors must have a mastery of the points of sail to effectively control the speed, stability, and direction of the boat, based on wind conditions and their desired destination.
Tacking and Jibing
When sailing, understanding tacking and jibing is crucial for maneuvering the sailboat effectively. Tacking is the process of changing the sailboat’s direction by turning the bow through the wind. To ensure better handling during the maneuver, it is important to release the jib sheet and loosen the front sail. Turning the boat into the wind involves rotating the helm away from it to turn the bow in the desired direction. As the bow turns, it is necessary to switch the jib sheet by releasing the current one and grabbing the new sheet on the opposite side of the boat. Once the boat has turned, the next step is to trim the sails by pulling in the new jib sheet and adjusting the mainsail for sailing in the new direction.
A true story exemplifies the significance of tacking and jibing in a regatta. During a race, a group of skilled sailors encountered a sudden wind shift as they approached a buoy, requiring a quick tack . Through their expertise in tacking and jibing , the crew efficiently executed the maneuver, maintaining their position in the race and gaining an advantage over their competitors. Their proficiency in these techniques contributed to their success in the regatta.
Preparing to Sail
As you embark on the exhilarating journey of sailing a sailboat , it’s crucial to begin by properly preparing for your adventure. In this section, we will dive into the essential steps of getting ready for a sail . From checking weather conditions for a safe voyage to performing thorough safety checks and gathering the necessary equipment, we’ll equip you with the knowledge and tools you need to set sail with confidence . So, let’s delve into the preparations that will lay the foundation for a successful and enjoyable sailing experience .
Checking Weather Conditions
When embarking on a sailing adventure, it is crucial to prioritize the safety and enjoyment of all those involved. This can be achieved by following a set of essential steps, which include checking weather conditions effectively:
1. Stay up to date: It is important to consistently monitor the latest weather forecasts for your specific sailing location. Trustworthy sources such as the National Weather Service or local marine services should be consulted for accurate information.
2. Wind matters: Pay close attention to both the speed and direction of the wind. Understanding how these factors may change throughout the day, and being aware of any significant gusts or shifts, is vital for a successful sailing experience.
3. Keep an eye on approaching weather systems: Be mindful of any imminent storms or fronts that may be heading your way. These weather events can bring about substantial changes in wind patterns, temperature, and precipitation, which may affect your sailing journey.
4. Evaluate sea conditions: Assessing expected sea conditions, including wave height and swell, is essential for gauging the comfort and safety of your chosen sailing route. Having this information beforehand can help you make informed decisions.
5. Consider local weather phenomena: Familiarize yourself with any weather phenomena specific to your sailing area, such as thermal winds, sea breezes, or tidal currents. These unique factors can significantly impact your overall sailing experience and should be considered in your preparations.
Allow me to recount a true story that emphasizes the significance of checking weather conditions. During the previous summer, a group of sailors failed to adequately assess the weather before setting sail. As they ventured further from the shore, an unexpected storm materialized, bringing with it powerful winds and towering waves. The sailors found themselves struggling to navigate back to safety and ultimately had to seek assistance. Fortunately, everyone was rescued, underscoring the importance of thoroughly examining weather conditions prior to embarking on any sailing expedition. Always bear in mind that your safety and the enjoyment of your sailing venture depend greatly on being well-informed about the prevailing weather conditions.
Performing Safety Checks
Performing safety checks is crucial before sailing. Be sure to follow these steps to ensure the safety of everyone on board:
1. Start by inspecting the hull thoroughly. Look for any cracks, damage, or signs of wear and tear that could compromise the boat’s structural integrity.
2. Pay close attention to the rigging, including the shrouds and stays . Check for any damage or loose connections. It’s also essential to check the rigging tension to maintain stability while sailing.
3. Carefully examine the sails for any tears, fraying, or other damage. Make sure that the battens and reef points are in place and functioning correctly.
4. Test all the safety equipment before setting sail. Check the life jackets, flares, and fire extinguishers to ensure they are up to date and in proper working condition.
5. Take a thorough look at the running rigging, including the lines, halyards, and sheets. Check for any signs of wear, knots, or tangles. It is vital to ensure they can handle the load and stress during sailing.
6. Verify that the navigation equipment, such as the compass, GPS, and depth sounder, is in good working order. Test the navigation lights to ensure they function correctly.
7. If your sailboat has an engine, conduct a comprehensive inspection. Look for any leaks, ensure there are proper fuel levels, and test the ignition and controls.
8. Double-check that all the necessary safety essentials are present on board. Make sure you have a first aid kit, a throwable flotation device, a bilge pump, and an anchor.
9. Before embarking on your voyage, review the weather forecast and any marine advisories for the sailing area. This step will help ensure that you sail in safe conditions.
By performing these safety checks, you can enjoy a worry-free and secure sailing experience.
Gathering Essential Equipment
When sailing , gathering essential equipment is crucial for safety and enjoyment.
– Life Jackets: Everyone on board needs a properly fitted life jacket.
– Navigation Tools: Bring navigation charts, compass, and a GPS device to navigate the waters.
– Sailing Apparel: Wear appropriate clothing, including waterproof jackets, pants, sailing gloves, and non-slip footwear.
– Communication Devices: Carry a marine VHF radio or a waterproof mobile phone for emergencies.
– First Aid Kit: Have a well-stocked kit with medications, bandages, antiseptic, and personal medications.
– Tool Kit: Bring basic tools like a multitool, wrench, duct tape, and spare parts for repairs or adjustments.
– Food and Water: Pack enough food and drinking water to stay hydrated and nourished.
– Safety Equipment: Ensure essential safety equipment including a fire extinguisher, flares, and a bilge pump.
– Anchoring Equipment: Have an anchor, chain, and rope to secure the sailboat.
– Emergency Preparedness: Prepare by having a float plan, informing someone of your sailing plans, and understanding emergency procedures.
In 1960 , Sir Francis Chichester completed the first solo sailing trip around the world, covering 29,630 nautical miles in nine months. His achievement inspired many sailors to embark on their own solo circumnavigations, pushing the boundaries of human endurance and maritime exploration.
Basic Sailing Techniques
Looking to sail a sailboat? In this section, we’ll dive into basic sailing techniques that will have you navigating the waters like a pro. We’ll cover everything from getting underway and steering to adjusting sails and maneuvering in different wind conditions. Get ready to set sail and discover the excitement and freedom of sailing with these essential skills.
Getting Underway
When getting underway on a sailboat journey, it is important to follow these steps for success:
1. Prepare the boat: Make sure that all equipment is securely stowed and that the boat is in proper working condition.
2. Hoist the sails: Use halyards or a winch if necessary to raise the sails. Ensure that the sails are properly unfurled and adjusted.
3. Release the mooring or anchor: Untie the lines or retrieve the anchor and stow it away. Be cautious of other boats or any potential obstacles.
4. Steer the boat: Take control of the tiller or wheel and steer the boat in the desired direction, taking into consideration wind, currents, and navigation.
5. Trim the sails: Optimize the position of the sails in relation to the wind by adjusting the sheets.
6. Monitor the surroundings: Stay alert for other boats, hazards, and any changes in weather conditions. Adjust the course if necessary.
7. Enjoy the journey: Take time to relax and appreciate the sailing experience. Take in the beauty of the water and the freedom of the open sea.
By following these steps, you can safely get underway and embark on your sailboat adventure.
Steering and Changing Direction
– Hold the tiller or wheel firmly to steer the sailboat.
– To turn the sailboat right, push the tiller or wheel left.
– To turn the sailboat left, push the tiller or wheel right.
– Use the sails to assist in changing direction by adjusting them to catch the wind from the desired direction.
– Stay aware of the wind direction and adjust your steering accordingly to maintain control.
– Practice maintaining a proper balance between the sails and the rudder for smooth and efficient steering.
True story:
I remember sailing with friends when we encountered a sudden shift in wind direction. It caught us off guard, and the sailboat veered off course. Our knowledge of steering and changing direction allowed us to quickly react. As a team, we adjusted the tiller and sails, bringing the sailboat back on track. This experience highlighted the importance of understanding effective steering and changing direction while sailing. With improved confidence, we smoothly maneuvered through the changing wind conditions during the rest of our journey.
Adjusting Sails
Adjusted sails are crucial for sailors to optimize their sailboat’s performance in different wind conditions. Adjusting sails is done by considering the following factors:
1. Sail trim: It is important to adjust the angle, tension, and shape of the sails to effectively capture the wind. Maintaining balance between the main sail and the jib or genoa is essential for achieving optimal speed and control.
2. Wind direction: Adjusting the sails according to the wind direction is necessary. Tightening the sails when sailing upwind and loosening them when sailing downwind helps in maximizing speed and efficiency.
3. Sail controls: It is essential to fine-tune the sail’s shape and position using halyards, sheets, and travelers. This allows for optimal sail performance and ensures the sailboat is responsive to changing wind conditions.
4. Crew communication: Effective communication between the helmsman and crew is vital when adjusting sails. Clear and concise instructions ensure that everyone works together to achieve the desired adjustments.
Fact: Did you know that adjusting sails can improve a sailboat’s speed by up to 20%? Mastering the art of sail adjustment is key to sailing efficiently and enjoying a smooth and exhilarating experience on the water.
Maneuvering in Different Wind Conditions
– Adjust sail trim: In different wind conditions, adjust the trim of your sails. Trim the sails in or out to optimize shape and performance based on wind direction and strength.
– Change sail shape: Sail shape plays a significant role in handling different wind conditions. To maneuver effectively, adjust the shape of your sails, such as loosening or tightening the halyard or adjusting the tension on the luff or leech of the sail.
– Use telltales: Telltales are small pieces of ribbon or yarn attached to the sails to indicate airflow. Monitoring telltales helps determine if sails are trimmed properly and if adjustments are needed to maintain maximum efficiency.
– Use different sail combinations: Depending on wind conditions, hoist different sails or use various combinations of sails. For example, in light winds, use a genoa or spinnaker to catch more breeze, while in strong winds, switch to a smaller headsail or reef the mainsail to reduce excessive power.
– Employ steering techniques: Properly steer the boat to maneuver in different wind conditions. Use techniques like weather helm or lee helm, adjust the angle of the rudder, or alter the course to optimize the boat’s performance.
Advanced Sailing Techniques
Get ready to take your sailing skills to the next level with the advanced techniques in sailboat navigation. In this section, we will explore essential practices such as sail trimming , sailing upwind and downwind , and an invaluable technique called heaving to . Discover the key insights and insider tips that will help you navigate the open waters like a true sailing pro. Let’s dive in and unlock the secrets of advanced sailing!
Sail Trimming
Sail Trimming is vital in sailing. It involves adjusting the sails to optimize performance and maintain control of the sailboat. Consider these points for sail trimming:
1. Understanding sail trim: Proper sail trim improves a sailboat’s speed, efficiency, and maneuverability. Adjust the sails’ shape and angle to the wind to maximize power and minimize drag.
2. Maintaining the correct sail shape: Sail shape affects performance. The main sail should be curved , while the jib should be flatter . Adjusting the tension on sail controls, like halyards and sheets, helps achieve the desired shape.
3. Optimizing sail angle: The angle at which the sails are set in relation to the wind is important. Opening the sails slightly away from the centerline of the boat maintains airflow and prevents stalling.
4. Adapting to wind conditions: Sail trim varies with wind strength and direction. Looser sails maximize surface area in lighter winds for better power. Tightening the sails in stronger winds reduces surface area and prevents overpowering.
5. Fine-tuning with sail controls: Use cunningham, boom vang, and outhaul to further refine the sail shape and control tension. These adjustments optimize the sail’s performance in different wind conditions.
6. Observing tell-tales: Tell-tales indicate airflow across the sail’s surface. Monitor their movement and adjust sail trim accordingly to maintain optimal airflow and performance.
7. Regularly reassessing sail trim: Sail trim is an ongoing process. Continuously monitor the sails, observe their performance, and make necessary adjustments during your sail.
By understanding and practicing sail trimming techniques, sailors can improve their skills, enhance boat performance, and have a more enjoyable experience.
Sailing Upwind and Downwind
When participating in the activity of sailing, it is crucial to have a good grasp of the methods used for sailing upwind and downwind. Sailing upwind, which is also referred to as beating or tacking , entails maneuvering the boat away from the wind in order to catch it and propel the boat forward. This involves the constant adjustment of the boat’s direction by turning against the wind.
On the contrary, sailing downwind, also known as running or jibing , involves sailing with the wind at your back, allowing the sails to be let out to capture as much wind as possible, thus propelling the boat forward.
Different sail adjustments and sailing techniques are required for sailing upwind and downwind. When sailing upwind, it is necessary to tighten the sails in order to keep them flat against the wind. This ensures that the boat maintains its course and makes progress against the wind. Conversely, when sailing downwind, it is important to loosen the sails to catch the wind more fully, providing increased speed and stability.
Sailing upwind and downwind are essential skills in the realm of sailing, and mastering these techniques is vital for any sailor. Whether one is engaging in racing or leisurely sailing, having a solid understanding of how to navigate and make sail adjustments based on the wind direction significantly enhances the overall sailing experience.
It is a known fact that sailing upwind is typically slower than sailing downwind, as it presents the added challenge of navigating against the wind.
When sailing, the technique of “ heaving to ” can be very useful in certain situations. It helps a sailor control their boat while remaining stationary. Here are the steps to heaving to :
- Release the mainsail sheet to luff the sail.
- Turn the helm towards the wind to bring the boat head to wind .
- Secure the helm by using a tiller tamer or lashing it in the desired position.
- Backwind the jib slightly by adjusting the headsail or jib sheet.
- Find a balance between the helm and headsail that keeps the boat stable with slow forward motion.
Heaving to has various applications, such as taking a break, waiting for daylight, or in heavy weather conditions. It allows the boat to maintain position without continuous steering, making it easier to attend to other tasks or rest. It’s important to note that heaving to may not be suitable for all boats or circumstances, so practicing and understanding the technique of heaving to is essential.
Safety and Emergency Procedures
When it comes to sailing a sailboat, safety should always be a top priority. In this section, we’ll take a closer look at the essential safety and emergency procedures every sailor should know. From mastering the techniques of man overboard recovery to handling a capsized boat and navigating unexpected weather changes, we’ll equip you with the knowledge and skills to ensure a safe and enjoyable sailing experience. So, let’s dive in and explore the vital procedures that will keep you prepared for any situation on the open water.
Man Overboard Recovery
In 1986, during the Sydney to Hobart Yacht Race, a man overboard recovery took place.
Crew member John Bennetto fell overboard in treacherous conditions.
The crew of the yacht Unicef followed the steps mentioned above and successfully saved Bennetto’s life.
This incident emphasized the importance of preparedness and quick thinking in man overboard situations.
It serves as a reminder for sailors to prioritize safety and regularly practice man overboard drills for everyone’s well-being on board.
Capsizing and Righting the Boat
If a sailboat capsizes, it is important to stay calm and hold onto the boat.
It is crucial to ensure that everyone on board is wearing a life jacket for their safety.
In the event of a capsizing, you can signal for help by either yelling or using a whistle .
It is also essential to assess the situation and determine if it is possible to right the boat yourself.
If it is safe to do so, attempt to climb onto the hull of the capsized boat.
To try and right the boat, grab onto the centerboard or keel and push upwards.
In case the boat does not right itself, you can try rocking it back and forth to gain momentum .
If all attempts fail, it may be necessary to abandon the boat and seek assistance.
On the other hand, if the boat does right itself, climb back on board and carefully bail out any water.
It is always a good idea to check for any damage to the rigging or sails before resuming sailing.
Remember that practicing capsizing and righting a boat in a controlled environment with an experienced instructor can help you feel more confident and prepared for such situations.
Dealing with Unexpected Weather Changes
Dealing with unexpected weather changes is crucial for sailors. Responding effectively to changing conditions ensures a safe and enjoyable sailing experience. Here are key strategies to keep in mind:
1. Stay alert: Always be aware of weather conditions while sailing. Pay attention to signs of changes in wind speed or direction, cloud formations, shifts in temperature, and sudden changes in wave patterns.
2. Monitor weather forecasts: Check the latest weather forecasts before setting sail. This informs you about what to expect and helps in making informed decisions about when to go out and which routes to take.
3. Have a plan: Develop a contingency plan in case the weather becomes unfavorable. Consider alternative routes, safe harbors, or anchorages for seeking shelter if needed.
4. Reef the sails: If winds suddenly pick up or become gusty, reef the sails to maintain control of the boat and prevent overpowering. Practice reefing techniques beforehand to be prepared.
5. Adjust course: Be ready to adjust your course if unexpected weather changes occur. This may involve altering your intended destination or finding a more favorable angle to the wind.
6. Keep communication open: Maintain regular communication with your crew and other boats in the area. Share information about changing weather conditions and potential hazards you encounter.
Remember, sailing in unpredictable weather can be challenging and potentially dangerous. Prioritize safety and be prepared to respond quickly and effectively to any unexpected weather changes.
Some Facts About How To Sail A Sailboat:
- ✅ Sailing a boat is a combination of art and skill, relying on the sailor’s feel and the forces of wind and water. (Source: ASA)
- ✅ There are several ways to get started with learning how to sail a boat, including taking a formal course at a sailing school or using online resources like the free ASA sailing course and Sailing Challenge App. (Source: ASA)
- ✅ Familiarizing yourself with the language of sailing, including sailing terms and points of sail, is important for effective communication and navigation while sailing. (Source: ASA)
- ✅ Understanding the different parts of a sailboat, such as the mast, sails, keel, rudder, and lines, is necessary for preparing a sailboat for sailing. (Source: WikiHow)
- ✅ Safety is a crucial aspect of sailing, and it is recommended to have an experienced sailor show you the rigging and sails before venturing out on your own. (Source: WikiHow)
Frequently Asked Questions
Faq 1: what are the different ways to learn how to sail a sailboat.
There are multiple ways to learn how to sail a sailboat. You can jump in a boat with a friend, take a formal course at a sailing school, or learn on your own with a small sailboat.
FAQ 2: What are the basic steps involved in sailing a sailboat?
The basic steps of sailing involve gaining specific knowledge and skills. This includes understanding basic sailing terms, familiarizing yourself with the parts of the boat, rigging the boat, learning basic sailing techniques, maneuvering the boat, docking or anchoring, utilizing various equipment, and tying knots.
FAQ 3: Where can I find resources to learn how to sail a sailboat?
There are several resources available to help beginners learn how to sail a sailboat. You can take advantage of online courses provided by organizations like the American Sailing Association (ASA). ASA also offers the Sailing Challenge App, which allows users to virtually sail their own vessel while learning basic sailing principles. Another option is to find a sailing school near you and enroll in a beginning sailing course, such as ASA 101.
FAQ 4: What are some important sailing techniques and practices to learn?
Some important sailing techniques and practices to learn include setting the mainsail and jib correctly for steering the boat and gaining speed, changing tacks by either “coming about” or jibing, steering from the windward side of the tiller or wheel for better visibility, understanding the correct trim of the sails using telltales, and following sailing rules of the road such as giving way to less maneuverable boats and boats on starboard tack.
FAQ 5: How can I improve my sailing skills?
Practice and experience are important for honing sailing skills in different conditions. It is recommended to continue learning and expanding your knowledge through resources like books, courses, and lessons. Seeking guidance from experienced sailors or instructors can also help improve your skills. Being part of the sailing community and participating in sailing events or club activities can provide valuable opportunities to learn and grow as a sailor.
FAQ 6: What are some important safety considerations when sailing a sailboat?
Safety is emphasized throughout the sailing process. It is important to wear appropriate clothing, apply sunscreen, and consider medication for motion sickness. When boarding a boat, finding stability and using handholds for support is crucial. The skipper should take charge and assign tasks before getting underway. Following safety guidelines, having proper equipment on board, and being knowledgeable about sailing safety can ensure a fun and secure sailing experience.
About the author
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Latest posts

The history of sailing – from ancient times to modern adventures
History of Sailing Sailing is a time-honored tradition that has evolved over millennia, from its humble beginnings as a means of transportation to a beloved modern-day recreational activity. The history of sailing is a fascinating journey that spans cultures and centuries, rich in innovation and adventure. In this article, we’ll explore the remarkable evolution of…

Sailing Solo: Adventures and Challenges of Single-Handed Sailing
Solo Sailing Sailing has always been a pursuit of freedom, adventure, and self-discovery. While sailing with a crew is a fantastic experience, there’s a unique allure to sailing solo – just you, the wind, and the open sea. Single-handed sailing, as it’s often called, is a journey of self-reliance, resilience, and the ultimate test of…

Sustainable Sailing: Eco-Friendly Practices on the boat
Eco Friendly Sailing Sailing is an exhilarating and timeless way to explore the beauty of the open water, but it’s important to remember that our oceans and environment need our protection. Sustainable sailing, which involves eco-friendly practices and mindful decision-making, allows sailors to enjoy their adventures while minimizing their impact on the environment. In this…
17 Sailboat Types Explained: How To Recognize Them
Ever wondered what type of sailboat you're looking at? Identifying sailboats isn't hard, you just have to know what to look for. In this article, I'll help you.
Every time I'm around a large number of sailboats, I look around in awe (especially with the bigger ones). I recognize some, but with most of them, I'll have to ask the owner. When they answer, I try to hide my ignorance. The words don't make any sense!
So here's a complete list with pictures of the most common sailboat types today. For each of them, I'll explain exactly where the name comes from, and how you can recognize it easily.
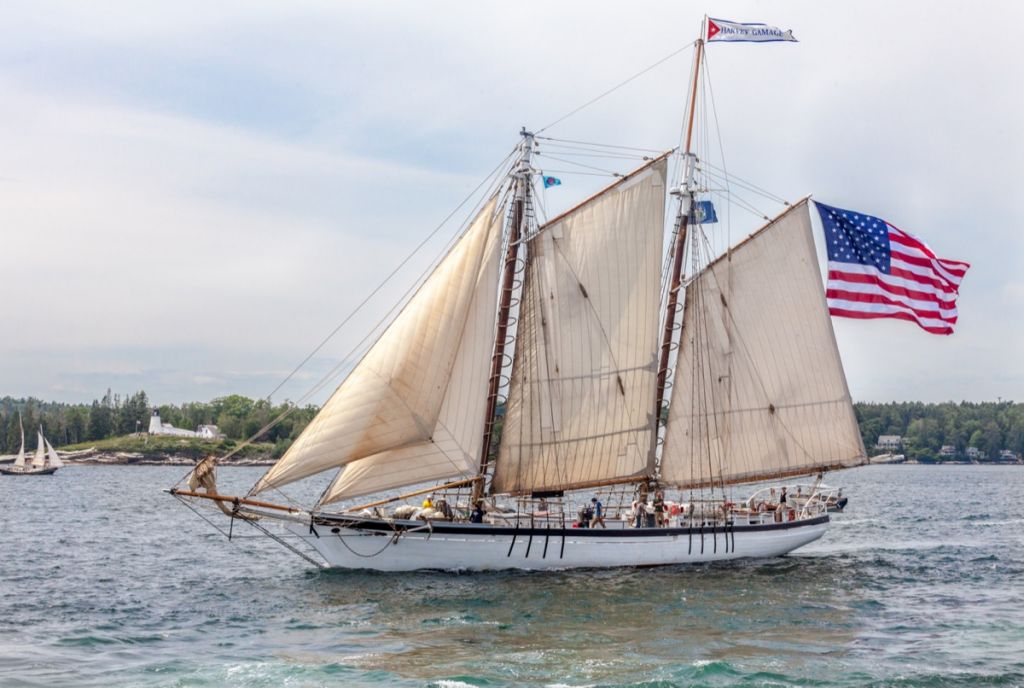

So here's my list of popular sailboat types, explained:
Bermuda sloop, sailing hydrofoil, dutch barge, chinese junk, square-rigged tall ship, in conclusion, how to recognize any sailboat.
Before we get started, I wanted to quickly explain what you should look for when you try to identify a sailboat.
The type of sailboat is always determined by one of these four things:
- The type of hull
- The type of keel
- The number of masts
- And the type of sails and rig
The hull is the boat's body. There are basically three hull types: monohull, catamaran, and trimaran. Simply said: do I see one hull, two hulls (catamaran) or three hulls (trimaran)? Most sailboats are monohulls.
Next, there is the keel type. The keel is the underwater part of the hull. Mostly, you won't be able to see that, because it's underwater. So we'll leave that for now.
The sail plan
The last factor is the number of masts and the sail plan. The sail plan, simply put, is the number of sails, the type of sails, and how the sails are mounted to the masts (also called rigging ).
Sailboat are mostly named after the sail plan, but occasionally, a sail type is thrown in there as well.
So now we know what to pay attention to, let's go and check out some sailboats!

Dinghies are the smallest and most simple sailboats around.
They are your typical training sailboats. Small boats with an open hull, with just one mast and one sail. Perfect for learning the ways of the wind.
On average, they are between 6 and 20 ft long. Mostly sailed single-handed (solo). There's no special rigging, just the mainsail. The mainsail is commonly a Bermuda (triangular) mainsail. Dinghies have a simple rudder stick and no special equipment or rigging.
Dinghies are great for learning how to sail. The smaller the boat, the better you feel the impact of your trim and actions.
How to recognize a sailing dinghy:
- short (8ft)
- one Bermuda sail
- open hull design
- rudder stick
Common places to spot them: lakes, near docks

If you'd ask a kid to draw a sailboat, she'll most probably draw this one. The Bermuda Sloop is the most popular and most common sailboat type today. You'll definitely recognize this one.
How to recognize a Bermuda Sloop:
- triangular mainsail (called a Bermuda sail)
- a foresail (also called the jib)
- fore-and-aft rigged
- medium-sized (12 - 50 ft)
Fore-and-aft rigged just means "from front to back". This type of rigging helps to sail upwind.
Any sailboat with one mast and two sails could still be a sloop. Even if the sails are another shape or rigged in another way. For example, here's a gaff-rigged sloop (more on the gaff rig later):

If you want to learn all about sail rigs, check out my full Guide to Understanding Sail Rig Types here. It has good infographics and explains it in more detail
The Bermuda sloop has a lot of advantages over other sailboat types (which is why it's so popular):
- the Bermuda rig is very maneuverable and pretty fast in almost all conditions
- it's really versatile
- you can sail it by yourself without any problems
- it's a simple setup
Common places to spot a sloop: everywhere. Smaller sloops are more common for inland waters, rivers, and lakes. Medium-sized and large sloops are very popular cruising boats.

Cutters have one mast but three or more sails. Most cutters are Bermuda rigged, which means they look a lot like sloops.
How to recognize a cutter:
- looks like a sloop
- two or more headsails instead of one
- commonly one mast
- sometimes an extra mast with mainsail
Cutters have more sail area, which makes them faster, but also harder to sail single-handed. There's also more strain on the mast and rigging.
Common places to spot a cutter: everywhere. Cutters are very popular for cruising.
They mostly have a Bermuda rig, which means triangular sails. But there are also gaff cutters and naval cutters, and some have two masts.
Here's an example of a two-masted naval cutter with an extra gaff mainsail and top gaff:

The Hydrofoil is a pretty new sailboat design. It's a racing sailboat with thin wing foils under the hull. These lift up the hull, out of the water, reducing the displacement to nearly zero. The foils create downforce and keep it from lifting off entirely.
This makes the hydrofoil extremely fast and also impressive.
The hydrofoil refers to the keel type. There are both monohull and multihull hydrofoils.
How to recognize a hydrofoil:
- it flies above the waterline and has small fins
Common places to spot a hydrofoil: at racing events

Famous catamaran: La Vagabonde from Sailing La Vagabonde
A catamaran is a type of cruising and racing multihull sailboat with two hulls. The hulls are always the same size.
Most catamarans have a standard Bermuda rig. The catamaran refers to the hull, so it can have any number of masts, sails, sail types and rig type.
How to recognize a catamaran:
- any boat with two hulls is called a catamaran
Common places to spot catamarans: coastal waters, The Caribbean, shallow reefs
The advantages of a catamaran: Catamarans heel less than monohulls and are more buoyant. Because of the double hull, they don't need as deep a keel to be stable. They have a smaller displacement, making them faster. They also have a very shallow draft. That's why catamarans are so popular in the Caribbean, where there's lots of shallow water.
Catamarans are nearly impossible to capsize:
"Compared with a monohull, a cruising catamaran sailboat has a high initial resistance to heeling and capsize—a fifty-footer requires four times the force to initiate a capsize than an equivalent monohull." Source: Wikipedia

How to recognize a trimaran:
- any boat with three hulls is called a trimaran
Trimarans have three hulls, so it's a multi-hull design. It's mostly a regular monohull with two smaller hulls or floaters on the sides. Some trimarans can be trailered by winching in the auxiliary hulls, like this:

This makes them very suitable for long-term cruising, but also for regular docking. This is great for crowded areas and small berths, like in the Mediterranean. It sure is more cost-effective than the catamaran (but you also don't have the extra storage and living space!).
Common places to spot Trimarans: mostly popular for long-term cruising, you'll find the trimaran in coastal areas.

Gaffer refers to gaff-rigged, which is the way the sails are rigged. A gaff rig is a rectangular sail with a top pole, or 'spar', which attaches it to the mast. This pole is called the 'gaff'. To hoist the mainsail, you hoist this top spar with a separate halyard. Most gaffers carry additional gaff topsails as well.
Gaff rigs are a bit less versatile than sloops. Because of the gaff, they can have a larger sail area. So they will perform better with downwind points of sail. Upwind, however, they handle less well.
How to recognize a gaffer:
- sail is rectangular
- mainsail has a top pole (or spar)
Since a gaffer refers to the rig type, and not the mast configuration or keel type, all sailboats with this kind of rigging can be called 'gaffers'.
Common places to spot a gaffer: Gaffers are popular inland sailboats. It's a more traditional rig, being used recreationally.

Schooners used to be extremely popular before sloops took over. Schooners are easy to sail but slower than sloops. They handle better than sloops in all comfortable (cruising) points of sail, except for upwind.
How to recognize a schooner:
- mostly two masts
- smaller mast in front
- taller mast in the back
- fore-and-aft rigged sails
- gaff-rigged mainsails (spar on top of the sail)
Common places to spot a schooner: coastal marinas, bays

How to recognize a ketch:
- medium-sized (30 ft and up)
- smaller mast in back
- taller mast in front
- both masts have a mainsail
The ketch refers to the sail plan (mast configuration and type of rig). Ketches actually handle really well. The back mast (mizzenmast) powers the hull, giving the skipper more control. Because of the extra mainsail, the ketch has shorter masts. This means less stress on masts and rigging, and less heel.
Common places to spot a ketch: larger marinas, coastal regions
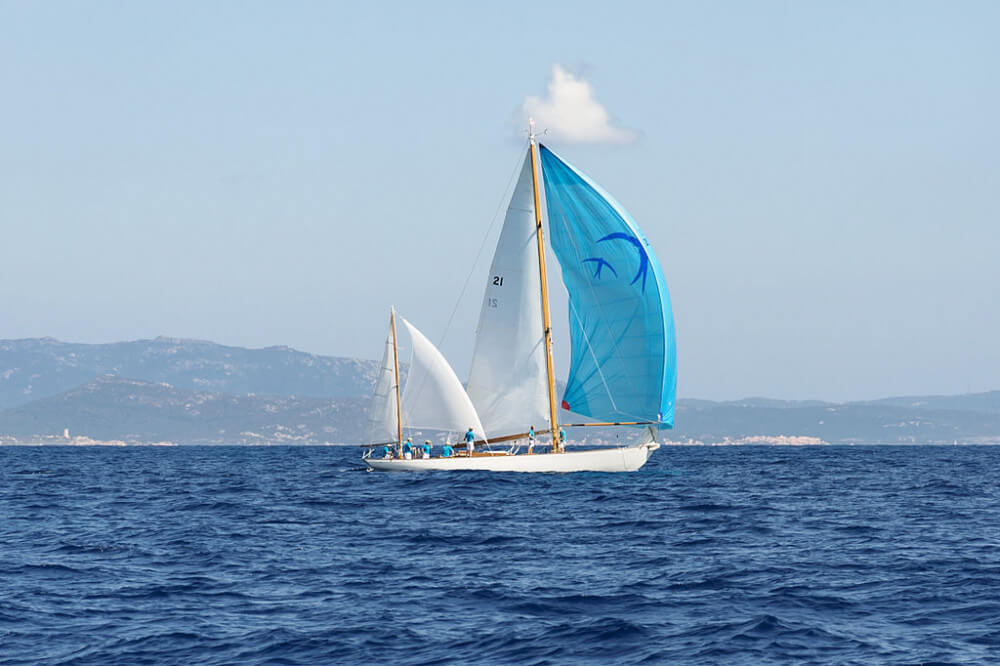

How to recognize a yawl:
- main mast in front
- much smaller mast in the back
- back mast doesn't carry a mainsail
The aft mast is called a mizzenmast. Most ketches are gaff-rigged, so they have a spar at the top of the sail. They sometimes carry gaff topsails. They are harder to sail than sloops.
The yawl refers to the sail plan (mast configuration and type of rig).
Common places to spot a yawl: they are not as popular as sloops, and most yawls are vintage sailboat models. You'll find most being used as daysailers on lakes and in bays.

Dutch Barges are very traditional cargo ships for inland waters. My hometown is literally littered with a very well-known type of barge, the Skutsje. This is a Frisian design with leeboards.
Skutsjes don't have a keel but use leeboards for stability instead, which are the 'swords' or boards on the side of the hull.
How to recognize a Dutch Barge:
- most barges have one or two masts
- large, wooden masts
- leeboards (wooden wings on the side of the hull)
- mostly gaff-rigged sails (pole on top of the sail, attached to mast)
- a ducktail transom
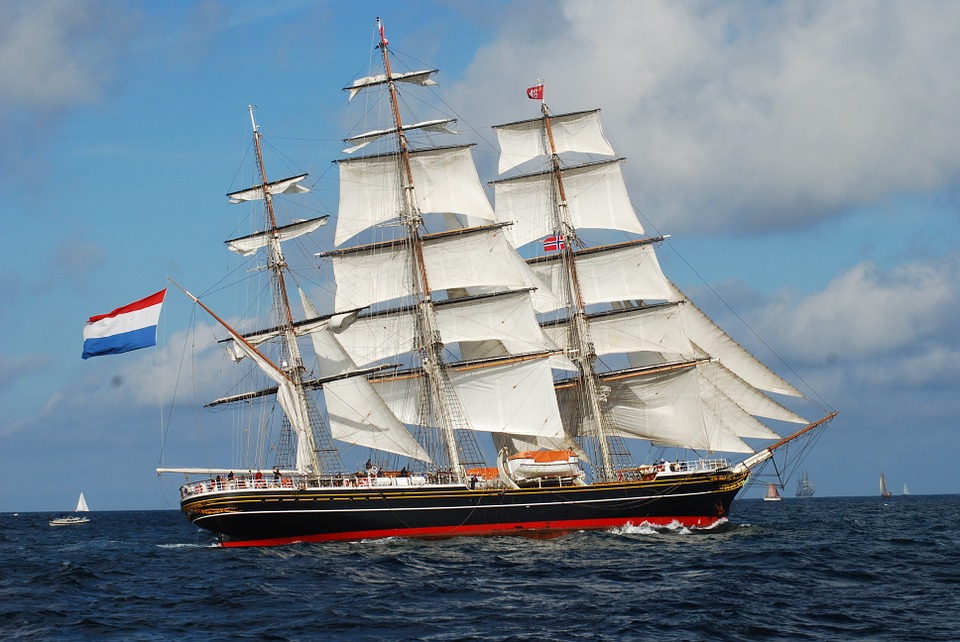

The clipper is one of the latest sailboat designs before steam-powered vessels took over. The cutter has a large cargo area for transporting cargo. But they also needed to be fast to compete with steam vessels. It's a large, yet surprisingly fast sailboat model, and is known for its good handling.
This made them good for trade, especially transporting valuable goods like tea or spices.
How to recognize a Clipper:
- mostly three masts
- square-rigged sails
- narrow but long, steel hull
Common places to spot a clipper: inland waters, used as houseboats, but coastal waters as well. There are a lot of clippers on the Frisian Lakes and Waddenzee in The Netherlands (where I live).

This particular junk is Satu, from the Chesapeake Bay Area.
The Chinese Junk is an ancient type of sailboat. Junks were used to sail to Indonesia and India from the start of the Middle Ages onward (500 AD). The word junk supposedly comes from the Chinese word 'jung', meaning 'floating house'.
How to recognize a Chinese junk:
- medium-sized (30 - 50 ft)
- large, flat sails with full-length battens
- stern (back of the hull) opens up in a high deck
- mostly two masts (sometimes one)
- with two mainsails, sails are traditionally maroon
- lug-rigged sails
The junk has a large sail area. The full-length battens make sure the sails stay flat. It's one of the flattest sails around, which makes it good for downwind courses. This also comes at a cost: the junk doesn't sail as well upwind.

The cat rig is a sail plan with most commonly just one mast and one sail, the mainsail.
Most sailing dinghies are cats, but there are also larger boats with this type of sail plan. The picture above is a great example.
How to recognize a cat rig:
- smaller boats
- mostly one mast
- one sail per mast
- no standing rigging
Cat-rigged refers to the rigging, not the mast configuration or sail type. So you can have cats with a Bermuda sail (called a Bermuda Cat) or gaff-rigged sail (called a Gaff Cat), and so on. There are also Cat Ketches and Cat Schooners, for example. These have two masts.
The important thing to know is: cats have one sail per mast and no standing rigging .
Most typical place to spot Cats: lakes and inland waters

Famous brig: HMS Beagle (Charles Darwin's ship)
A brig was a very popular type of small warship of the U.S. navy during the 19th century. They were used in the American Revolution and other wars with the United Kingdom. They carry 10-18 guns and are relatively fast and maneuverable. They required less crew than a square-rigged ship.
How to recognize a brig:
- square-rigged foremast
- mainmast square-rigged or square-rigged and gaff-rigged

How to recognize a tall ship:
- three or four masts
- square sails with a pole across the top
- multiple square sails on each mast
- a lot of lines and rigging
Square-rigged ships, or tall ships, are what we think of when we think of pirate ships. Now, most pirate ships weren't actually tall ships, but they come from around the same period. They used to be built from wood, but more modern tall ships are nearly always steel.
Tall ships have three or four masts and square sails which are square-rigged. That means they are attached to the masts with yards.
We have the tall ship races every four years, where dozens of tall ships meet and race just offshore.
Most common place to spot Tall Ships: Museums, special events, open ocean

This is a bonus type since it is not very common anymore. As far as I know, there's only one left.
The Trabaccolo is a small cargo ship used in the Adriatic Sea. It has lug sails. A lug rig is a rectangular sail, but on a long pole or yard that runs fore-and-aft. It was a popular Venetian sailboat used for trade.
The name comes from the Italian word trabacca , which means tent, referring to the sails.
How to recognize a Trabaccolo:
- wide and short hull
- sails look like a tent
Most common place to spot Trabaccolo's: the Marine Museum of Cesenatico has a fully restored Trabaccolo.
So, there you have it. Now you know what to look for, and how to recognize the most common sailboat types easily. Next time you encounter a magnificent sailboat, you'll know what it's called - or where to find out quickly.

I loved this article. I had no idea there were so many kinds of sailboats.
i have a large sailing boat about 28ft. that im having a difficult time identifying. it was my fathers & unfortunately hes passed away now. any helpful information would be appreciated.
Jorge Eusali Castro Archbold
I find a saleboat boat but i can find the módem…os registré out off bru’x, and the saleboat name is TADCOZ, can you tell me who to go about this matter in getting info.thank con voz your time…
Leave a comment
You may also like, guide to understanding sail rig types (with pictures).
There are a lot of different sail rig types and it can be difficult to remember what's what. So I've come up with a system. Let me explain it in this article.

The Ultimate Guide to Sail Types and Rigs (with Pictures)

How Much Sailboats Cost On Average (380+ Prices Compared)
Own your first boat within a year on any budget.
A sailboat doesn't have to be expensive if you know what you're doing. If you want to learn how to make your sailing dream reality within a year, leave your email and I'll send you free updates . I don't like spam - I will only send helpful content.
Ready to Own Your First Boat?
Just tell us the best email address to send your tips to:

Types of Sailboats: A Complete Guide

Last Updated by
Daniel Wade
June 15, 2022
Learning the different types of sailboats can help you identify vessels and choose the right boat.
In this article, we'll cover the most common kinds of sailboats, their origins, and what they're used for. We'll also go over the strengths and weaknesses of each design, along with when they're most useful.
The most common kind of sailboat is the sloop, as it's simple to operate and versatile. Other common sailboat types include the schooner, cutter, cat, ketch, schooner, catamaran, and trimaran. Other sailboat variations include pocket cruisers, motorsailers, displacement, and shoal-draft vessels.
The information found in this article is sourced from boat reference guides, including A Field Guide to Sailboats of North America by Richard M. Sherwood and trusted sources in the sailing community.
Table of contents
Distinguishing Types of Sailboats
In this article, we'll distinguish sailboats by traits such as their hull type, rig, and general configuration. Some sailboats share multiple characteristics with other boats but fall into a completely different category. For example, a sailboat with a Bermuda rig, a large engine, and a pilothouse could technically be called a sloop, but it's more likely a motorsailer.
When discerning sailboat type, the first most obvious place to look is the hull. If it has only one hull, you can immediately eliminate the trimaran and the catamaran. If it has two or more hulls, it's certainly not a typical monohull vessel.
The next trait to consider is the rig. You can tell a lot about a sailboat based on its rig, including what it's designed to be used for. For example, a long and slender sailboat with a tall triangular rig is likely designed for speed or racing, whereas a wide vessel with a complex gaff rig is probably built for offshore cruising.
Other factors that determine boat type include hull shape, overall length, cabin size, sail plan, and displacement. Hull material also plays a role, but every major type of sailboat has been built in both wood and fiberglass at some point.
Sailboat vs. Motorsailer
Most sailboats have motors, but most motorized sailboats are not motorsailers. A motorsailer is a specific kind of sailboat designed to run efficiently under sail and power, and sometimes both.
Most sailboats have an auxiliary engine, though these power plants are designed primarily for maneuvering. These vessels cannot achieve reasonable speed or fuel-efficiency. Motorsailers can operate like a powerboat.
Motorsailers provide great flexibility on short runs. They're great family boats, and they're popular in coastal communities with heavy boat traffic. However, these features come at a cost. Motorsailers aren't the fastest or most efficient powerboats, and they're also not the most agile sailboats. That said, they make an excellent general-purpose sailing craft.
Monohull vs. Multi-hull: Which is Better?
Multihull sailboats are increasingly popular, thanks to advances and lightweight materials, and sailboat design. But are they better than traditional sailboats? Monohulls are easier to maintain and less expensive, and they offer better interior layouts. Multihulls are more stable and comfortable, and they're significantly easier to control. Multihull sailboats also have a speed advantage.
Monohull Sailboats
A monohull sailboat is a traditionally-shaped vessel with a single hull. The vast majority of consumer sailboats are monohulls, as they're inexpensive to produce and easy to handle. Monohull sailboats are proven and easy to maintain, though they lack the initial stability and motion comfort of multi-hull vessels.
Monohull sailboats have a much greater rig variety than multi-hull sailboats. The vast majority of multihull sailboats have a single mast, whereas multi-masted vessels such as yawls and schooners are always monohulls. Some multi-hull sailboats have side-by-side masts, but these are the exception.
Catamaran Sailboats
The second most common sailboat configuration is the catamaran. A catamaran is a multihull sailboat that has two symmetrical hulls placed side-by-side and connected with a deck. This basic design has been used for hundreds of years, and it experienced a big resurgence in the fiberglass boat era.
Catamarans are fast, efficient, and comfortable. They don't heel very much, as this design has excellent initial stability. The primary drawback of the catamaran is below decks. The cabin of a catamaran is split between both hulls, which often leaves less space for the galley, head, and living areas.
Trimaran Sailboats
Trimarans are multi-hull sailboats similar to catamarans. Trimarans have three hulls arranged side-by-side. The profile of a trimaran is often indistinguishable from a catamaran.
Trimarans are increasingly popular, as they're faster than catamarans and monohulls and considerably easier to control. Trimarans suffer from the same spatial limitations as catamarans. The addition of an extra hull adds additional space, which is one reason why these multi-hull vessels are some of the best-selling sailboats on the market today.
Sailboat Rig Types
Rigging is another way to distinguish sailboat types. The rig of a sailboat refers to it's mast and sail configuration. Here are the most common types of sailboat rigs and what they're used for.
Sloops are the most common type of sailboat on the water today. A sloop is a simple single-mast rig that usually incorporates a tall triangular mainsail and headsail. The sloop rig is easy to control, fun to sail, and versatile. Sloops are common on racing sailboats as they can sail quite close to the wind. These maneuverable sailboats also have excellent windward performance.
The sloop rig is popular because it works well in almost any situation. That said, other more complex rigs offer finer control and superior performance for some hull types. Additionally, sloops spread their entire sail area over just to canvases, which is less flexible than multi-masted rigs. The sloop is ideal for general-purpose sailing, and it's proven itself inland and offshore.
Sloop Features:
- Most popular sailboat rig
- Single mast
- One mainsail and headsail
- Typically Bermuda-rigged
- Easy to handle
- Great windward performance
- Less precise control
- Easier to capsize
- Requires a tall mast
Suitable Uses:
- Offshore cruising
- Coastal cruising
Cat (Catboat)
The cat (or catboat) is a single-masted sailboat with a large, single mainsail. Catboats have a thick forward mast, no headsail, and an exceptionally long boom. These vessels are typically gaff-rigged, as this four-edged rig offers greater sail area with a shorter mast. Catboats were popular workboats in New England around the turn of the century, and they have a large following today.
Catboats are typically short and wide, which provides excellent stability in rough coastal conditions. They're hardy and seaworthy vessels, but they're slow and not ideal for offshore use. Catboats are simple and easy to control, as they only have a single gaff sail. Catboats are easy to spot thanks to their forward-mounted mast and enormous mainsail.
Catboat Features:
- Far forward-mounted single mast
- Large four-sided gaff sail
- Short and wide with a large cockpit
- Usually between 20 and 30 feet in length
- Excellent workboats
- Tough and useful design
- Great for fishing
- Large cockpit and cabin
- Not ideal for offshore sailing
- Single sail offers less precise control
- Slow compared to other rigs
- Inland cruising
At first glance, a cutter is difficult to distinguish from a sloop. Both vessels have a single mast located in roughly the same position, but the sail plan is dramatically different. The cutter uses two headsails and often incorporates a large spar that extends from the bow (called a bowsprit).
The additional headsail is called a staysail. A sloop only carries one headsail, which is typically a jib. Cutter headsails have a lower center of gravity which provides superior performance in rough weather. It's more difficult to capsize a cutter, and they offer more precise control than a sloop. Cutters have more complex rigging, which is a disadvantage for some people.
Cutter Features:
- Two headsails
- Long bowsprit
- Similar to sloop
- Gaff or Bermuda-rigged
- Fast and efficient
- Offers precise control
- Superior rough-weather performance
- More complex than the sloop rig
- Harder to handle than simpler rigs
Perhaps the most majestic type of sailboat rig, the schooner is a multi-masted vessel with plenty of history and rugged seaworthiness. The schooner is typically gaff-rigged with short masts and multiple sails. Schooners are fast and powerful vessels with a complex rig. These sailboats have excellent offshore handling characteristics.
Schooners have a minimum of two masts, but some have three or more. The aftermost large sail is the mainsail, and the nearly identical forward sail is called the foresail. Schooners can have one or more headsail, which includes a cutter-style staysail. Some schooners have an additional smaller sale aft of the mainsail called the mizzen.
Schooner Features:
- At least two masts
- Usually gaff-rigged
- One or more headsails
- Excellent offshore handling
- Precise control
- Numerous sail options (headsails, topsails, mizzen)
- Fast and powerful
- Complex and labor-intensive rig
- Difficult to adjust rig single-handed
- Offshore fishing
Picture a ketch as a sloop or a cutter with an extra mast behind the mainsail. These vessels are seaworthy, powerful, excellent for offshore cruising. A ketch is similar to a yawl, except its larger mizzen doesn't hang off the stern. The ketch is either gaff or Bermuda-rigged.
Ketch-rigged sailboats have smaller sails, and thus, shorter masts. This makes them more durable and controllable in rough weather. The mizzen can help the boat steer itself, which is advantageous on offshore voyages. A ketch is likely slower than a sloop or a cutter, which means you aren't likely to find one winning a race.
Ketch Features:
- Headsail (or headsails), mainsail, and mizzen
- Mizzen doesn't extend past the rudder post
- Good offshore handling
- Controllable and mild
- Shorter and stronger masts
- Easy self-steering
- Slower than sloops and cutters
- Less common on the used market
A dinghy is a general term for a small sailboat of fewer than 28 feet overall. Dinghys are often dual-power boats, which means they usually have oars or a small outboard in addition to a sail. These small boats are open-top and only suitable for cruising in protected waters. Many larger sailboats have a deployable dinghy on board to get to shore when at anchor.
Dinghy Features:
- One or two people maximum capacity
- Easy to sail
- Works with oars, sails, or an outboard
- Great auxiliary boat
- Small and exposed
- Not suitable for offshore use
- Going from anchor to shore
- Protected recreational sailing (lakes, rivers, and harbors)
Best Sailboat Type for Stability
Stability is a factor that varies widely between sailboat types. There are different types of stability, and some sailors prefer one over another. For initial stability, the trimaran wins with little contest. This is because these vessels have a very high beam-to-length ratio, which makes them much less prone to rolling. Next up is the catamaran, which enjoys the same benefit from a wide beam but lacks the additional support of a center hull section.
It's clear that in most conditions, multihull vessels have the greatest stability. But what about in rough weather? And what about capsizing? Multihull sailboats are impossible to right after a knockdown. This is where full-keel monohull sailboats excel.
Traditional vessels with deep displacement keels are the safest and most stable in rough weather. The shape, depth, and weight of their keels keep them from knocking over and rolling excessively. In many cases, these sailboats will suffer a dismasting long before a knockdown. The primary disadvantage of deep-keeled sailboats is their tendency to heel excessively. This characteristic isn't hazardous, though it can make novice sailors nervous and reduce cabin comfort while underway.
Best Sailboat Type for Offshore Cruising
The best sailboat type for offshore cruising is the schooner. These graceful aid robust vessels have proven themselves over centuries as durable and capable vessels. They typically use deep displacement keels, which makes them stable in rough weather and easy to keep on course.
That said, the full answer isn't quite so simple. Modern multihull designs are an attractive option, and they have also proven to be strong and safe designs. Multihull sailboats are an increasingly popular option for offshore sailors, and they offer comfort that was previously unknown in the sailing community.
Many sailors cross oceans in basic Bermuda-rigged monohulls and take full advantage of a fin-keel design speed. At the end of the day, the best offshore cruising sailboat is whatever you are comfortable handling and living aboard. There are physical limits to all sailboat designs, though almost any vessel can make it across an ocean if piloted by a competent skipper and crew.
Best Sailboat Type for Racing The modern lightweight Bermuda-rigged sailboat is the king of the regatta. When designed with the right kind of hull, these vessels are some of the fastest sailboats ever developed. Many boats constructed between the 1970s and today incorporate these design features due to their favorable coastal and inland handling characteristics. Even small sailboats, such as the Cal 20 and the Catalina 22, benefit from this design. These boats are renowned for their speed and handling characteristics.
Related Articles
I've personally had thousands of questions about sailing and sailboats over the years. As I learn and experience sailing, and the community, I share the answers that work and make sense to me, here on Life of Sailing.
by this author
Learn About Sailboats
Most Recent

What Does "Sailing By The Lee" Mean?
October 3, 2023

The Best Sailing Schools And Programs: Reviews & Ratings
September 26, 2023
Important Legal Info
Lifeofsailing.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon. This site also participates in other affiliate programs and is compensated for referring traffic and business to these companies.
Similar Posts

Affordable Sailboats You Can Build at Home
September 13, 2023

Best Small Sailboat Ornaments
September 12, 2023

Discover the Magic of Hydrofoil Sailboats
December 11, 2023
Popular Posts

Best Liveaboard Catamaran Sailboats
December 28, 2023

Can a Novice Sail Around the World?
Elizabeth O'Malley

4 Best Electric Outboard Motors

How Long Did It Take The Vikings To Sail To England?

10 Best Sailboat Brands (And Why)
December 20, 2023

7 Best Places To Liveaboard A Sailboat
Get the best sailing content.
Top Rated Posts
Lifeofsailing.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon. This site also participates in other affiliate programs and is compensated for referring traffic and business to these companies. (866) 342-SAIL
© 2024 Life of Sailing Email: [email protected] Address: 11816 Inwood Rd #3024 Dallas, TX 75244 Disclaimer Privacy Policy
No products in the cart.
Sailing Ellidah is supported by our readers. Buying through our links may earn us an affiliate commission at no extra cost to you.
The Different Parts Of A Sailboat Explained
A sailboat consists of hundreds of parts, each with its specific term and function. From stern to bow, keel to mast, each part and its equipment plays a vital role in making the vessel seaworthy and able to sail.
In this guide, I’ll show you most of the components so you can better understand what they are and their function. We’ll begin with the main components, move to the basic features, and finish with our interior and equipment.
The main parts of a sailboat
The main parts of a sailboat are the key components that make it a vessel able to sail. You’ll notice that the structure has several distinct differences from powerboats.
We can categorize the main parts into the following:
- Hull: The main structure, or “body” part of a boat.
- Keel: The heavy fin at the bottom allows stability under sail.
- Rudder: The fin sticking down at the stern, allowing us to steer the vessel.
- Mast: The “spars” or “poles” holding the sails.
- Rigging: The standing rig is the wires that supports the mast. The running rigging is all the lines that control the sails.
- Boom: The horizontal spar supporting the bottom of the mainsail.
- Sails: The canvas used to harness the energy of the wind.
Let’s dig a bit deeper into each of the components.
Hull – The main structure
A sailboat’s hull is the vessel’s main body or structure. The shape is vital to the boat’s performance and stability, and you have probably seen boats in many different forms. Older vessels are typically narrow, with a rounded underbody and a small stern. Modern designs have a flatter belly and broad stern supporting dual helm stations.
One of the hull’s primary functions is to displace water and provide buoyancy to keep the boat afloat. The hull is also the structure that holds the vessel’s living compartments and all its equipment. The main structure must be strong enough to withstand the forces of the water and any rough weather conditions that Mother Nature might throw at it.
Fiberglass (GRP), steel, aluminum, and wood are the most commonly used hull materials, each with pros and cons.
You can learn more about hull materials and their strengths in this article .
A monohull is a type of sailboat that has a single hull. Monohulls are classified into two categories based on weight and shape: planing and displacement hulls.
Sailboats with more than one hull are called multihulls. There are two types of multihulls: catamarans, which have two, and trimarans, which have three. These boats are typically designed with planing hulls.
Keel – The fin under the boat
The keel of a sailboat is a structural fin that extends downward from the bottom of the hull. There are several types of keels, each with unique characteristics and advantages. They all serve the same fundamental purpose of stabilizing the boat when we sail by adding lateral resistance in the water and weight at the vessel’s bottom.
Standard keel designs include:
- Lifting Keel
Some sailboats have a retractable centerboard functioning as their keel, allowing them to take the boat into shallower areas.
Rudder – To steer the boat
The rudder is a flat surface that sits perpendicular to the waterline. It is connected to the boat by a pivot point, allowing it to swivel left and right. When the steering wheel or tiller is turned, the rudder moves, creating drag in the water causing the boat to turn. The size and shape of the rudder can vary depending on the size and type of boat.
The most commonly seen rudder designs:
- Full skeg-supported
- Semi skeg-supported
Skeg-supported rudders are structurally one of the most reliable and robust constructions, but they are less efficient than a balanced rudder performance-wise. Balanced rudders pivot around their vertical center, giving less drag in the water and higher maneuverability at the cost of being a more vulnerable construction.
Twin rudders are often seen on modern performance sailboats with a wide stern. When the sailboat heel over , the leeward rudder gets better track through the water than a single rudder placed at the vessel’s center line. Contrary to some misconceptions, they can’t be controlled individually, even if the boat has two steering wheels.
Mast and Rigging – Supporting the sails
The mast is the long vertical spar that extends upward from the deck of a sailboat and holds the sails. It is the tallest part of the boat and is typically made of wood, aluminum, or carbon fiber. The mast is held in place by stays and shrouds, which form the sailboat’s standing rigging.
Depending on the rig the boat is manufactured with, there are several different types of masts. For example, a sloop-rigged sailboat will have only one main mast, while a ketch-rigged vessel will have a smaller additional mizzen mast placed further aft from the main mast.
There are two types of rigging:
- The Standing rigging consists of the stays and shrouds that keep the mast or masts in place.
- The Running rigging is the lines we use to hoist, lower, and control the sails.
Pro Tip: “S par” is a general term for a pole made of a solid material like wood, metal, or composite and is used to support a boat’s sail. The mast, boom, spreaders, and poles are defined as spars.
Boom – Supporting the mainsail
The boom is a horizontal beam extending from the mast and supporting the mainsail’s tack and clew (bottom two corners). It is attached to the mast by a hinge called a Gooseneck .
We use the boom to control the shape and angle of the mainsail to optimize its efficiency and power. Some booms also have a Vang or Rod-Kicker installed to assist in trimming the mainsail.
Sails – The canvas used to harness the energy of the wind
Most vessels have at least two sails, depending on the rig type and boat setup.
The Mainsail flies behind the mast, on top of the boom. Although it may not always be the largest sail on the vessel, we commonly refer to it as “the main.”
The Headsail(s ), located in front of the mast, are often of different sizes and shapes, and many sailboats have more than one. The Jib and Genoa are two of the most common types.
Different types of sails are used for various sail plans and situations, and you can learn more about them in this guide .
Now that we had a look at the main parts of the boat, let us dive deeper and look at the rest of the vessel.
The starboard and port side of the boat
Learning about the boat’s components is very important, but we must also know how to orient ourselves on the vessel. Using the words “left and right” on onboard often leads to confusion.
If you refer to something on the left side of the boat, the person facing you will be confused. He won’t know if you are referring to his or your left. This is where the terms “Port” and “ Starboard ” make better sense.
When facing the front of the boat or the bow , your left side of the boat is the port side, and the right-hand side is the starboard . If you turn around and face the back of the boat or the stern , your right-hand side will be the port side.
- A red light identifies the port side of a vessel.
- A green light identifies the starboard side of a vessel.
Windward and Leeward
- The windward side of the boat is the side facing the wind. If the wind comes from your right-hand side while facing forward, the starboard side is windward. This will be the boat’s high side as the wind heels the boat over.
- The leeward side of the boat is the side opposite to the wind. This will be the lower side of the ship while sailing as the wind heels the boat over.
Windward and leeward are two of the most important aspects to understand when sailing and navigating. Not only to identify equipment and gear on each side of the boat but to avoid collisions when sailing close to other vessels. There are rules on the water dictating which boat is “Stand On” and which has to “Give Way” depending on whether you are the windward or the leeward vessel in the situation.
Read this article to access a free course on navigation rules .
Basic parts of a sailboat
The boat’s bow is the front part, typically shaped like a “V” to cut through the waves. Larger vessels often have a locker for their anchor chain in this section, holding the anchor at the front.
The midship section is the center of the boat. Some refer to this part as amidships.
The stern is the rear or back part of the boat. It is also referred to as the aft . I’ve had French crew calling the stern the butt of the vessel, which is funny but also correct!
The beam is the widest part of the boat. Also referred to as the sides on the middle.
The transom is a flat surface across the stern of the boat.
The waterline is the part where the hull (body) of the boat meets the water. Many vessels have a painted stripe to mark the waterline, indicating how loaded the ship is. If you have too much stuff on board, the waterline goes underwater, and it is time to do some housekeeping!
The freeboard is the vertical part of the ship side between the water and the deck. When you see a blue boat like Ellidah, the freeboard is the blue part.
The deck is the “floor” of the boat when you are outside. You have probably heard the term “All hands on deck!” The front deck is the deck space in front of the mast. Side decks are the decks on the boat’s sides.
The mid-deck is between the cockpit and the mast. The aft deck is the deck behind the cockpit. Sailboats with aft cockpits often don’t have any aft decks, but some have a swimming platform instead.
The cockpit is the boat’s steering position and where you will find the helm.
The helm is the position the helmsman uses to steer the boat. Smaller sailboats often use a tiller to navigate, while most bigger yachts have one or two steering wheels.
Main parts below deck (inside the boat)
Let us look at the interior to highlight and learn about the parts we have below the deck.
The Companionway
The companionway is the “front door” of the boat. This is where the steps lead from the cockpit or deck down below. It is usually opened and closed using a hatch, two doors, or a plate.
The Galley
The galley is the boat’s kitchen. This is where sailors prepare their delicious meals.
The Saloon
The saloon is basically the boat’s living room, usually where you find the settee and dinette. This is where delicious meals from the galley are served together with refreshing beverages in good company.
The settee is the sofa or couch in a boat. It is also used as a sea berth to sleep in when sailing.
The dinette is the area where you can sit down at a table and eat your dinner. It’s also perfect for consuming rum and a game of cards in good company.
A cabin is often used as a bedroom in a boat but is not necessarily where you sleep. Many boats have more than one cabin.
A berth is a place in the boat where you can sleep. This doesn’t necessarily have to be a bed and can often include the sleeping space in the saloon. Sea-berth usually refers to a sleeping position where you are tucked well in and can sleep when the boat is heeling over and moving around.
The head is the toilet on a boat. If your skipper tells you to go and clean the head, getting out the shampoo won’t do you any good!
Nav station
The navigation station is usually a chart table and a console with mysterious instruments like radios, switchboards, and complicated electronics. This is where adventures are planned and the skipper’s favorite seat onboard.
The bilge is a space in the bottom of the hull where water collects and sometimes a storage space for all sorts of things. It usually contains a bilge pump to pump out water that finds its way into the boat in various places.
A v-berth is a bed in the front cabin shaped like a V.
A bulkhead is a wall inside the boat, usually supporting the structure.
Hardware and Equipment
Sailboats come equipped with a variety of different hardware and equipment. While the specific items may vary from boat to boat, there are some essentials that nearly every sailboat has.
A winch is a metal drum that gives you a mechanical advantage and is used to control and tighten lines. These can be operated by turning a line around it and pulling manually or by a winch handle to get more force.
Most modern winches are so-called “self-tailing,” which means they lock the line on so you can winch the line without holding on to it. Some boats even have electrical winches operated by a button.
A cleat is a fitting used to fasten a rope. Most boats have at least 6 of these. One on each side on the bow, midship and stern. These are used to secure the boat to a mooring buoy or key. Many ships have more cleats than this for various lines and ropes, and they can be used for anything as they are strong points fitted to the hull.
The sprayhood is the boat’s windshield that protects the people in the cockpit from sea spray. Some vessels have a canvas sprayhood that can be folded down or removed. Others have solid sprayhoods, often called a hard dodger or a doghouse .
The bimini is the cockpit’s “roof.” It protects you from the elements and shelters you from spray, rain, and burning sun rays! A bimini can be made of canvas or hard material. A hard bimini can also be called a hardtop .
Dinghy
A dinghy is a little boat you use to get from the mothership to shore when you are at anchor, also called a tender or annex . It can be everything from a small inflatable rubber kayak to a RIB or even a solid boat.
An essential and valuable piece of kit as it is the daily driver for most cruisers. It is like the car of a land crab, used for all commuting on the water and hauling important stuff like beer, rum, and food onboard. Dinghies often have electric or petrol engines, which we call outboards.
Dinghies are also great to use for watersports, such as wakeboarding!
Like Captain Ron said in the movie, fenders are the rubber bumper things you hang off your boat to prevent it from scratching against something like the pontoon or another ship. It is conveniently also used to sit on or as a backrest while relaxing on deck.
A boat hook is a long stick with a hook at the end. Used to grab lines, items, and stuff that is too far to reach by hand, like cushions flying overboard. It is also convenient as a tool to push the boat away from another craft or the key. Most vessels have them on board.
The guard rail can be a flexible wire or a solid metal rail surrounding the boat to prevent us from falling overboard. Some also use a net as an addition for increased safety.
The pushpit is a metal guard rail around the stern of the boat. This is where the guard rail is secured on the stern: a common place to mount the BBQ, life raft, and the outboard for the dinghy.
The pulpit is the metal guardrail on the bow. This is where the guard rail is secured onto the bow.
The stanchions are the metal bars that keep the guard rail in place around the boat between the pushpit and the pulpit.
An arch is a typical structure made of stainless steel on the back of a boat and is often used to mount a variety of items like antennas, radars, solar panels, wind generators, etc. It is also convenient to use for lifting the dinghy and its outboard.
Ground Tackle
The ground tackle consists of several things:
- Your anchor
- Your anchor chain
- The link between the two
- The connection between the chain and your boat
It includes all equipment holding your boat to the ground. Larger boats sometimes have two anchors on the bow.
A windlass is a winch that hoists and lowers the anchor and chain. Most boats have one on the bow and some on the stern. These incredible things can be electrical or manual (some are both) and are essential to anchor your boat when not in a port or marina.
VHF stands for “Very High-Frequency Radio.” It broadcasts on the VHF network and allows you to communicate with others around you. Sadly, you won’t be able to tune in to your favorite radio show on these.
Still, they are essential for contacting other boats and port authorities. It is also the radio you will transmit an emergency mayday over in case of emergency. VHF radios sometimes require a license, depending on the country you are in.
Chartplotter
A Chartplotter is a navigation computer that shows various information on a screen, like charts, routes, radar images, etc. It is another vital piece of equipment that helps you navigate and maneuver the boat.
Final words
I hope this guide has been helpful and not too overwhelming for you. We’ve covered many of the parts of a sailboat and its terms and functions, but this article only touches on the basics. If you want to keep learning about sailing, I have written several other guides to help you get started.
Now that you have a basic understanding of sailboats, it’s time to take the next step and dive into a sailboat’s standing rigging .
Sharing is caring!
Skipper, Electrician and ROV Pilot
Robin is the founder and owner of Sailing Ellidah and has been living on his sailboat since 2019. He is currently on a journey to sail around the world and is passionate about writing his story and helpful content to inspire others who share his interest in sailing.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Learn about the different types of sails and rigs on a sailboat, from mainsail and headsail to spinnaker and gennaker. See pictures and diagrams of sail shapes, parts, and functions for various conditions and configurations.
Learn about the 8 types of sails for sailboats, from mainsails and headsails to spinnakers and gennakers. Find out how to use different sails for different wind and weather conditions and sailboat types.
Learn about the common sails on a sailboat, such as mainsail, headsail, jib, genoa, spinnaker, and storm jib. Find out how to choose the ideal sail based on wind conditions, boat size, and performance.
Learn about different kinds of sails and how they are used on sailboats depending on the wind conditions. Find out the advantages and disadvantages of mainsail, headsail, genoa, spinnaker, and gennaker sails.
Learn about the different sails on a sailboat, such as mainsail, headsail, spinnaker, gennaker, and more. Find out how they are used, rigged, and shaped for different wind conditions and sail plans.
Learn about the different types of sails on a sailboat, their shapes, functions, and combinations. Explore sail anatomy, materials, and configurations for various wind conditions and sail plans.
Mainsails are essential for providing the boat with forward propulsion and play a significant role in steering and balancing the vessel. There are two primary types of mainsails: full-batten and partial-batten. Full-batten mainsails have horizontal battens that run the entire width of the sail, providing additional support and shape.
Learn about the most popular types of sails on sailboats, such as mainsail, headsail, genoa, spinnaker, and gennaker. Also, discover the different sail and mast configurations, such as sloop, fractional rig sloop, cutter, ketch, schooner, yawl, and cat.
Another important sail on a sailboat is the headsail. This sail is located at the front of the boat and is used to catch the wind from the side. Headsails come in many different shapes and sizes, including genoas, jibs, and spinnakers. Choosing the right headsail can make a big difference in how the boat performs, especially in heavy wind ...
In the era of the "golden age of sail," different sail plans were used on sailing vessels to optimize their performance and accommodate smaller crews. Fore and Aft Rig. The fore-and-aft rig, consisting of sails aligned along the length of the boat, includes popular designs like schooners and sloops.
Learn about different types of sails and rigs for sailboats, from the common sloop to the dual masted ketch and schooner. Find out how to use them to improve your sailing performance and enjoyment.
https://improvesailing.com/sails - If you want to learn the different sail types for sailboats, this video is for you. I've done a ton of research to learn ...
Short answer types of sails for sailboats: Sailboats typically use four primary types of sails: mainsails, genoas/jibs, spinnakers, and staysails. Mainsails are the largest and provide forward propulsion. Genoas/jibs enable efficient sailing upwind. Spinnakers are used for downwind sailing and maximizing speed. Stay-sails provide stability in heavy wind conditions. Understanding the Basics ...
Spinnakers are large, lightweight sails designed for sailing downwind, with the wind coming from behind the boat. They are typically used in racing or when cruising in light wind conditions to maximize speed and performance. Spinnakers come in two main types: symmetrical and asymmetrical. Symmetrical spinnakers are used for sailing directly ...
The Ultimate Guide to Different Types of Sails: Exploring the Basics. Sailing is a timeless activity that has captivated individuals for centuries. Whether you're a seasoned sailor or new to the world of sailing, understanding the different types of sails is essential knowledge that can greatly enhance your experience on the water.
Short answer sailboat types of sails: There are several types of sails used in sailboats, including the mainsail, jib, genoa, spinnaker, and staysail. Each sail type serves a specific purpose and is designed to perform optimally under different wind conditions and points of sail. Introduction to Sailboat Types of Sails: A Comprehensive GuideIntroduction to Sailboat
BOAT RIG TYPES. The type of rig of a sailboat is a deciding factor in the kind and number of sails you can use on your vessel. Let's quickly look at the main rig types of modern sailboats. Sloop. A sloop is the most common type of rig you see out on the water. It features one mast and two sails (a mainsail and a genoa). Cutter
The function of the ketch's mizzen sail is different from that of the yawl. It's actually used to drive the boat forward, and the mizzen sail, together with the headsail, are sufficient to sail the ketch. The mizzen sail on a yawl can't really drive the boat forward. Schooner. Schooners have two masts that are fore-and-aft rigged.
Learn the different types of sails on a sailboat, such as mainsail, headsail, genoa, spinnaker, gennaker, and more. Find out how they are placed, shaped, and used in different wind conditions and points of sail.
Sailboat Types There are many different types of boats for sailing, differentiated by three distinctive characteristics: Hull Type (monohull, catamaran or trimaran); Keel Type (fin keel, wing keel, bilge keel, daggerboard, or centerboard); Mast Configuration and Sails (sloop, fractional rig sloop, ketch, schooner, yawl, cutter, cat); Let's explore those different types in a little more detail.
When it comes to sailing, understanding the different types of sails is absolutely crucial. Let's take a look at the primary sail types that you should know about. 1. Main Sail: Undoubtedly the most significant sail on a sailboat, the main sail is situated at the back of the vessel. Its main purpose is to harness the power of the wind and ...
Understanding the different parts of a sailboat, such as the mast, sails, keel, rudder, and lines, is necessary for preparing a sailboat for sailing. (Source: WikiHow) Safety is a crucial aspect of sailing, and it is recommended to have an experienced sailor show you the rigging and sails before venturing out on your own.
one mast. triangular mainsail (called a Bermuda sail) a foresail (also called the jib) fore-and-aft rigged. medium-sized (12 - 50 ft) Fore-and-aft rigged just means "from front to back". This type of rigging helps to sail upwind. Any sailboat with one mast and two sails could still be a sloop.
The most common kind of sailboat is the sloop, as it's simple to operate and versatile. Other common sailboat types include the schooner, cutter, cat, ketch, schooner, catamaran, and trimaran. Other sailboat variations include pocket cruisers, motorsailers, displacement, and shoal-draft vessels. The information found in this article is sourced ...
The main parts of a sailboat. Hull - The main structure. Keel - The fin under the boat. Rudder - To steer the boat. Mast and Rigging - Supporting the sails. Boom - Supporting the mainsail. Sails - The canvas used to harness the energy of the wind. The starboard and port side of the boat. Windward and Leeward.