- BOAT OF THE YEAR
- Newsletters
- Sailboat Reviews
- Boating Safety
- Sailing Totem
- Charter Resources
- Destinations
- Galley Recipes
- Living Aboard
- Sails and Rigging
- Maintenance
- Best Marine Electronics & Technology

Sailboat Design Evolution
- By Dan Spurr
- Updated: June 10, 2020
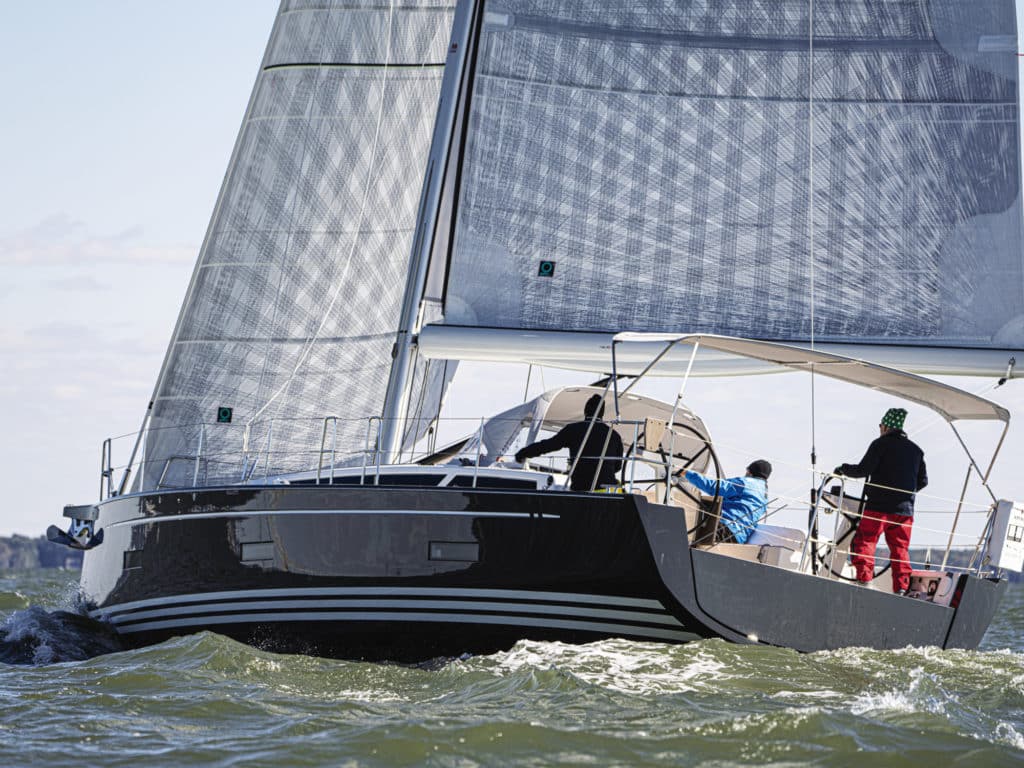

You know the old saying, “The more things change, the more they stay the same”? As a judge for the 2020 Boat of the Year (BOTY) competition at this past fall’s US Sailboat Show in Annapolis, Maryland, I helped inspect and test-sail 22 brand-new current-model sailboats. And I came away thinking, Man, these aren’t the boats I grew up on. In the case of new boats, the saying is wrong: “Nothing stays the same.”
OK, sure, today’s boats still have masts and sails, and the monohulls still have keels. But comparing the Hinckley Bermuda 40, considered by many to be one of the most beautiful and seaworthy boats of the 1960s, ’70s and even ’80s, with, say, the Beneteau First Yacht 53, which debuted at the show, is pretty much apples and oranges.
To get a better sense of what has happened to yacht design, boatbuilding and equipment over the past three, four or even six decades, let’s take a closer look.
Design Dilemmas
At the risk of oversimplification, since the fiberglass era began in the late 1940s and ’50s, the design of midsize and full-size yachts has transitioned from the Cruising Club of America rules, which favored all-around boats (racers had to have comfortable interiors) with moderate beam and long overhangs, to a succession of racing rules such as the IOR, IMS and IRC. All of them dictated proportions, and each required a measurer to determine its rating.

As frustration grew with each (no handicap rule is perfect), alternatives arose, such as the Performance Handicap Racing Fleet, which essentially based one’s handicap on past performance of the same boats in the same fleet. Also, one-design racing became more popular, which spread beyond identical small boats to full-size yachts, popularized in part by builders such as J/Boats and Carroll Marine. The ethos there was: Who cares about intricate rating rules? Let’s just go out and sail fast and have fun!
And that might best sum up the design briefs for the monohulls in this year’s BOTY competition: good all-around performance with comfortable, even luxurious accommodations. Gone are interiors that noted naval architect Robert Perry called “the boy’s cabin in the woods,” deeply influenced by stodgy British designers of the past century and their now-old-fashioned (though sea-friendly, one should note) concepts of a proper yacht, drawn and spec’d by the same guy who designed the hull, deck and rig. Today, dedicated European interior designers are specially commissioned to inject modernity, home fashion colors and textures, amenities, and more light—even dubiously large port lights in the topsides.

Overhangs, bow and stern, have virtually disappeared. Why? It seems largely a matter of style. Plus, the bonus of increased usable space below, not to mention a longer waterline length for a given length overall, which translates to more speed. Former naval architect for C&C Yachts and Hunter Marine, Rob Mazza, recalls that 19th-century pilot cutters and fishing schooners operating in offshore conditions generally had plumb bows, so in a sense, bow forms have come full circle.
Today’s boats are carrying their wide beam farther aft. Gone are the days of the cod’s head and mackerel tail. Wide, flat canoe bodies are decidedly fast off the wind, and might even surf, but they pay a comfort penalty upwind.
These boats have lighter displacement/length (D/L) ratios, which means flatter bottoms and less stowage and space for tanks. The Beneteau 53 has a D/L of 118, compared with the aforementioned Bermuda 40 of 373. Among entries in this year’s BOTY, the heaviest D/L belonged to the Elan Impression 45.1, with a D/L of 195. Recall that when Perry’s extremely popular Valiant 40 was introduced in 1975, the cruising establishment howled that its D/L of 267 was unsuitable for offshore sailing. My, how times have changed!
Perhaps more important, one must ask: “Have the requirements for a good, safe bluewater cruiser actually changed? Or are the majority of today’s production sailboats really best-suited for coastal cruising?”
The ramifications of lighter displacement don’t end there; designers must consider two types of stability: form and ultimate. As weight is taken out of the boat, beam is increased to improve form stability. And with tanks and machinery sometimes raised, ballast might have to be added and/or lowered to improve ultimate stability.
What else to do? Make the boat bigger all around, which also improves stability and stowage. Certainly the average cruising boat today is longer than those of the earlier decades, both wood and fiberglass. And the necessarily shallower bilges mean pumps must be in good shape and of adequate size. That’s not as immediate an issue with a deep or full keel boat with internal ballast and a deep sump; for instance, I couldn’t reach the bottom of the sump in our 1977 Pearson 365.

And how do these wide, shallow, lighter boats handle under sail? Like a witch when cracked off the wind. We saw this trend beginning with shorthanded offshore racers like those of the BOC Challenge round-the-world race in the early 1980s. As CW executive editor Herb McCormick, who has some experience in these boats, says, “They’ll knock your teeth out upwind.” But route planning allows designers to minimize time upwind, and cruisers can too…if you have enough room and distance in front of you. Coastal sailors, on the other hand, will inevitably find even moderate displacement boats more comfortable as they punch into head seas trying to make port.

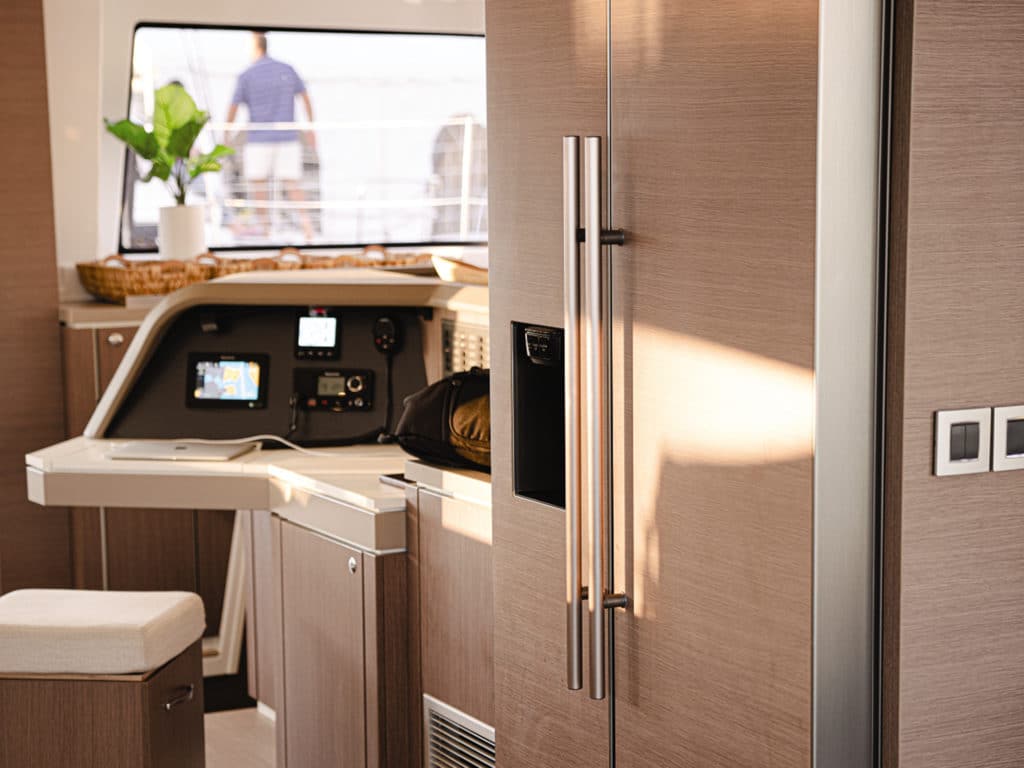
A wide beam carried aft permits a number of useful advantages: the possibility of a dinghy garage under the cockpit on larger boats; easy access to a swim platform and a launched dinghy; and twin helms, which are almost a necessity for good sightlines port and starboard. Of course, two of anything always costs twice as much as one.
Some multihulls now have reverse bows. This retro styling now looks space-age. Very cool. But not everyone is sold on them. Canadian designer Laurie McGowan wrote in a Professional BoatBuilder opinion piece, “I saw through the fog of faddishness and realized that reverse bows are designed to fail—that is, to cause vessels to plunge when lift is required.” Mazza concurs: “Modern multihulls often have reverse stems with negative reserve buoyancy, and those are boats that really can’t afford to bury their bows.”

McGowan also cites another designer critiquing reverse bows for being noticeably wet and requiring alternative ground-tackle arrangements. The latter also is problematic on plumb bows, strongly suggesting a platform or sprit to keep the anchor away from the stem.
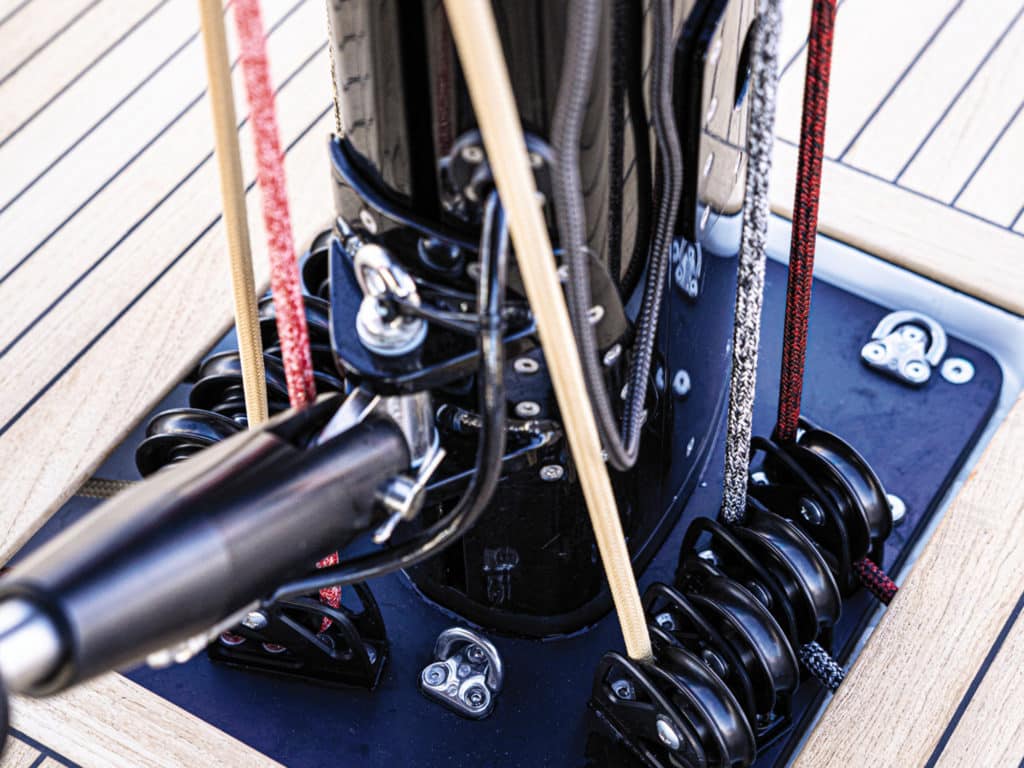
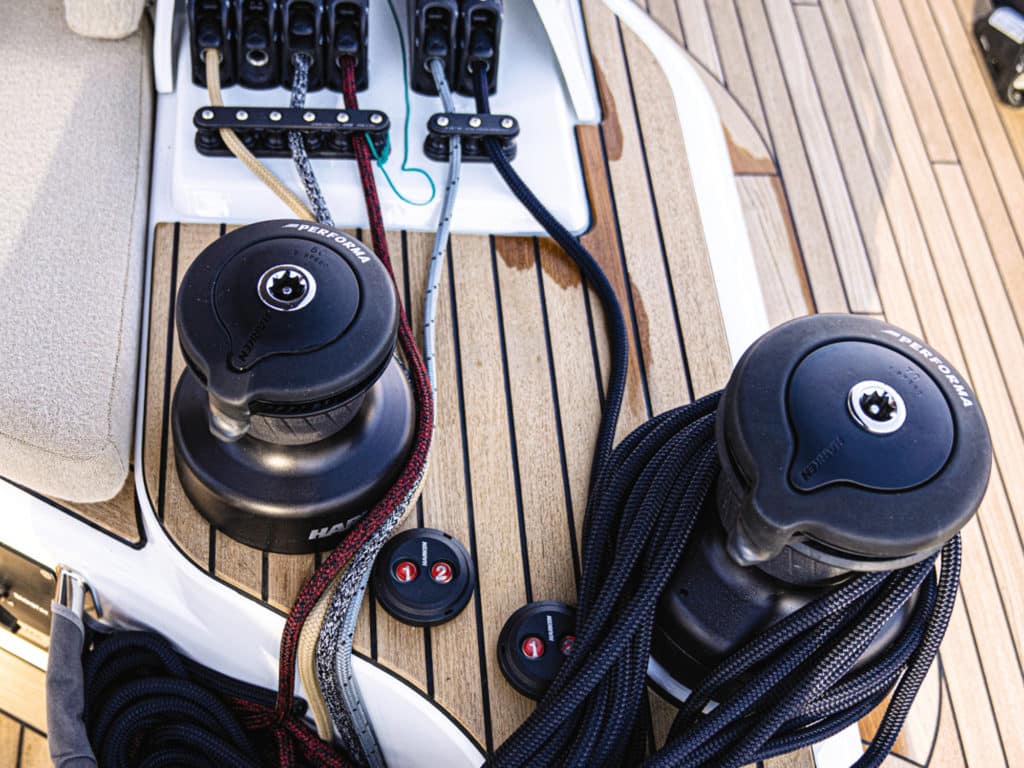
Rigging Redux
If there was a boat in Annapolis with double lower shrouds, single uppers, and spreaders perpendicular to the boat’s centerline, I must have missed it. I believe every boat we sailed had swept-back spreaders and single lowers. An early criticism of extreme swept-back spreaders, as seen on some B&R rigs installed on Hunter sailboats, was that they prevented fully winging out the mainsail. The counter argument was that so many average sailors never go dead downwind in any case, and broad reaching might get them to their destinations faster anyway—and with their lunch sandwiches still in their stomachs.
That issue aside, the current rigging configuration may allow for better mainsail shape. But as Mazza points out, it’s not necessarily simple: “By sweeping the spreaders, the ‘transverse’ rigging starts to add fore-and-aft support to the midsection of the mast as well, reducing the need for the forward lowers. However, spreader sweep really does complicate rig tuning, especially if you are using the fixed backstay to induce headstay tension. Swept spreaders do make it easier to sheet non-overlapping headsails, and do better support the top of the forestay on fractional rigs.”
Certainly, the days of 150 percent genoas are over, replaced by 100 percent jibs that fit perfectly in the foretriangle, often as a self-tacker.
Another notable piece of rigging the judges found common was some form of lazy jacks or mainsail containment, from traditional, multiple lines secured at the mast and boom; to the Dutchman system with monofilament run through cringles sewn into the sail like a window blind; to sailmaker solutions like the Doyle StackPak. This is good news for all sailors, especially those who sail shorthanded on larger boats.
Construction Codas
Improvements in tooling—that is, the making of molds—are easily evident in today’s boats, particularly with deck details, and in fairness. That’s because many of today’s tools are designed with computer software that is extraordinarily accurate, and that accuracy is transferred flawlessly to big five-axis routers that sculpt from giant blocks of foam the desired shape to within thousandths of an inch. Gone are the days of lofting lines on a plywood floor, taken from a table of offsets, and then building a male plug with wood planks and frames. I once owned a 1960s-era sailboat, built by a reputable company, where the centerline of the cockpit was 7 degrees off the centerline of the deck—and they were one piece!

Additive processes, such as 3D printing, are quickly complementing subtractive processes like the milling described above. Already, a company in California has made a multipart mold for a 34-foot sailboat. Advantages include less waste materials.
Job training also has had an impact on the quality of fiberglass boats. There are now numerous schools across the country offering basic-skills training in composites that include spraying molds with gelcoat, lamination, and an introduction to vacuum bagging and infusion.

The patent on SCRIMP—perhaps the first widely employed infusion process—has long ago expired, but many builders have adopted it or a similar process whereby layers of fiberglass are placed in the mold dry along with a network of tubes that will carry resin under vacuum pressure to each area of the hull. After careful placement, the entire mold is covered with a bag, a vacuum is drawn by a pump, and lines to the pot of resin are opened. If done correctly, the result is a more uniform fiberglass part with a more controlled glass-to-resin ratio than is achievable with hand lay-up. And as a huge bonus, there are no volatile organic compounds released into the workplace, and no need for expensive exhaust fans and ductwork. OSHA likes that, and so do the workers.
However, sloppy processes and glasswork can still be found on some new boats. Surveyor Jonathan Klopman—who is based in Marblehead, Massachusetts, but has inspected dozens, if not hundreds, of boats damaged by hurricanes in the Caribbean—tells me that he is appalled by some of the shoddy work he sees, such as balsa cores not vacuum-bagged to the fiberglass skins, resulting in delamination. But overall, I believe workmanship has improved, which is evident when you look behind backrests, inside lockers and into bilges, where the tidiness of glasswork (or lack thereof) is often exposed. Mechanical and electrical systems also have improved, in part due to the promulgation of standards by the American Boat & Yacht Council, and informal enforcement by insurance companies and surveyors.

We all know stainless steel isn’t entirely stainless, and that penetrations in the deck are potentially troublesome; allowing moisture to enter a core material, such as end-grain balsa, can have serious consequences. The core and fiberglass skins must be properly bonded and the kerfs not filled with resin. Beginning in the mid-1990s, some builders such as TPI, which built the early Lagoon cruising catamarans, began using structural adhesives, like Plexus, to bond the hull/deck joint rather than using dozens of metal fasteners. These methacrylate resins are now commonly used for this application and others. Klopman says it basically should be considered a permanent bond, that the two parts, in effect, become one. If you think a through-bolted hull/deck joint makes more sense because one could theoretically separate them for repairs, consider how likely that would ever be: not highly.
Fit-and-Finish
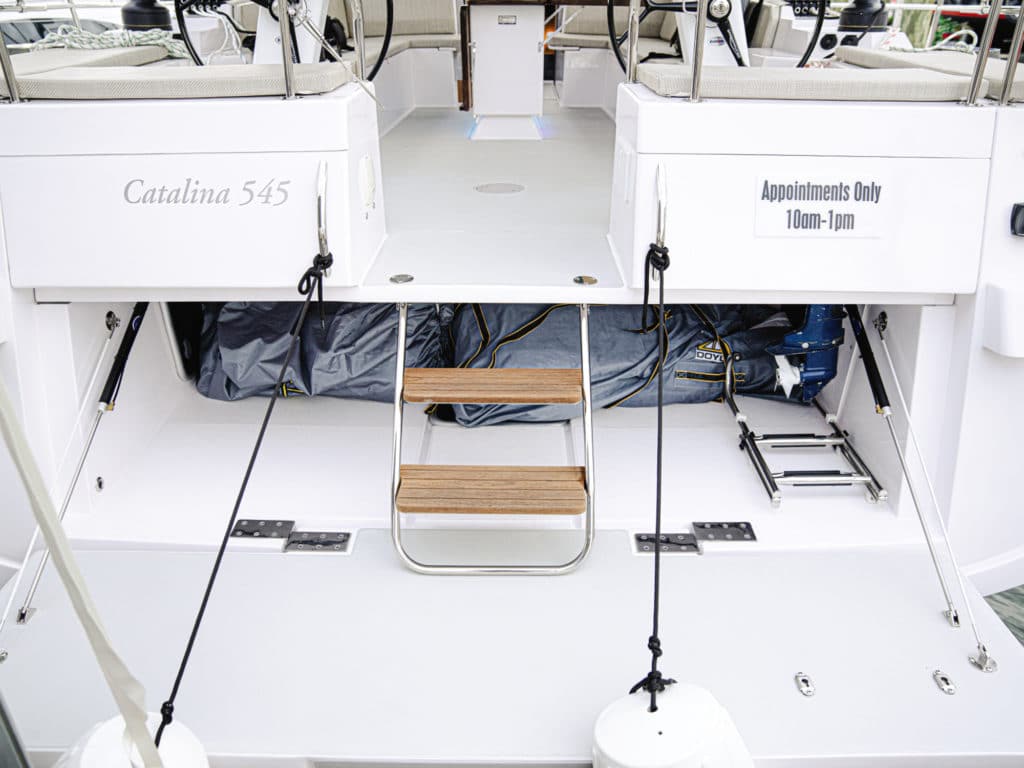
Wide transoms spawned an unexpected bonus; besides the possibility of a dinghy “garage” under the cockpit on larger boats, swim platforms are also possible. In more than one BOTY yacht, the aft end of the cockpit rotated down hydraulically to form the swim platform—pretty slick.
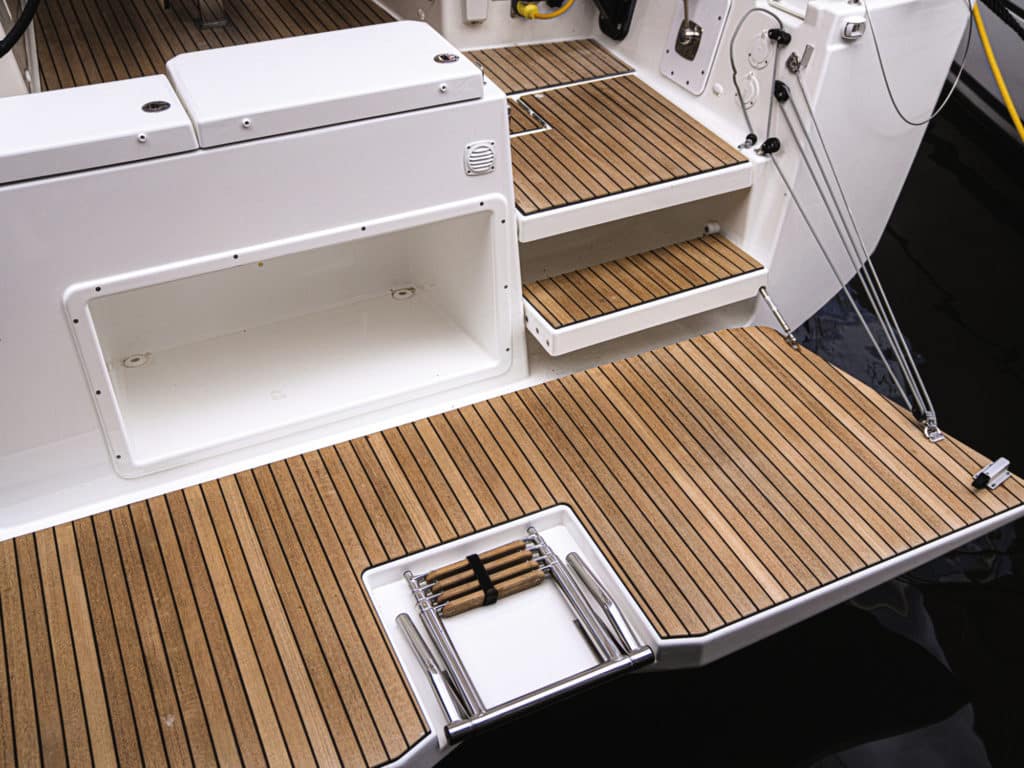
Teak decks are still around, despite their spurning for many years by owners who didn’t want the upkeep. In the 1960s and ’70s, they were considered a sign of a classy boat but fell from favor for a variety of reasons: maintenance, weight and threat of damaging the deck core (the bung sealant wears out and water travels down the fastener through the top fiberglass skin into the core). Specialty companies that supply builders, like Teakdecking Systems in Florida, use epoxy resin to bond their product to decks rather than metal fasteners. And the BOTY judges saw several synthetic faux-teak products that are difficult to distinguish from real teak—the Esthec installed on the Bavaria C50 being one example.

LPG tanks no longer have to be strapped to a stanchion or mounted in a deck box because decks now often incorporate molded lockers specifically designed for one or two tanks of a given size. To meet ABYC standards, they drain overboard. In tandem with these lockers, some boats also have placements or mounts for barbecues that are located out of the wind, obviating the common and exposed stern-rail mount.
Low-voltage LED lights are replacing incandescent bulbs in nearly all applications; improvements in technology have increased brightness (lumens), so some even meet requirements for the range of navigation lights. Advances in battery technology translate to longer life, and depending on type, faster charging. And networked digital switching systems for DC-power distribution also are becoming more common.
Last, I was surprised at how many expensive yachts exhibited at Annapolis had nearly the least-expensive toilets one can buy. Considering the grief caused by small joker valves and poorly sealed hand pumps, one would think builders might install systems that incorporate higher-quality parts or vacuum flushing, and eliminate the minimal hosing that famously permeate odors.
Dan Spurr is an author, editor and cruising sailor who has served on the staffs of Cruising World, Practical Sailor and Professional Boatbuilder. His many books include Heart of Glass , a history of fiberglass boatbuilding and boatbuilders .
Other Design Observations
Here are a few other (surprising) items gleaned from several days of walking the docks and sailing the latest models:
- Multihulls have gained acceptance, though many production models are aimed more at the charter trade than private ownership for solitary cruising. You’d have to have been into boats back in the ’60s and ’70s to remember how skeptical and alarmist the sailing establishment was of two- and three-hull boats: “They’ll capsize and then you’ll drown.” That myth has been roundly debunked. Back then, the only fiberglass-production multihulls were from Europe, many from Prout, which exported a few to the US. There are still plenty of European builders, particularly from France, but South Africa is now a major player in the catamaran market.
- The French builders now own the world market, which of course includes the US. Other than Catalina, few US builders are making a similar impact. In terms of volume, Groupe Beneteau is the largest builder in the world, and they’ve expanded way beyond sailboats into powerboats, runabouts and trawlers.
- Prices seem to have outpaced inflation, perhaps because, like with automobiles, where everyone wants air conditioning, electric windows and automatic transmissions, today’s boats incorporate as standard equipment items that used to be optional. Think hot- and cold-pressure water, pedestal-wheel steering, and full suites of sailing instruments and autopilots.
- More: design , print may 2020 , Sailboats
- More Sailboats

Leopard 40 Prelude Listed For Sale

“Heirloom Quality” Hinckley For Sale

For Sale: 2019 Leopard 43 PC

Meet the Wauquiez 55

It’s Time to Rethink Your Ditch Kit

8 Ways to Prevent Seasickness
- Digital Edition
- Customer Service
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Use
- Email Newsletters
- Cruising World
- Florida Travel + Life
- Sailing World
- Salt Water Sportsman
- Sport Fishing
- Wakeboarding
Many products featured on this site were editorially chosen. Cruising World may receive financial compensation for products purchased through this site.
Copyright © 2024 Cruising World. A Bonnier LLC Company . All rights reserved. Reproduction in whole or in part without permission is prohibited.

The global authority in superyachting
- NEWSLETTERS
- Yachts Home
- The Superyacht Directory
- Yacht Reports
- Brokerage News
- The largest yachts in the world
- The Register
- Yacht Advice
- Yacht Design
- 12m to 24m yachts
- Monaco Yacht Show
- Builder Directory
- Designer Directory
- Interior Design Directory
- Naval Architect Directory
- Yachts for sale home
- Motor yachts
- Sailing yachts
- Explorer yachts
- Classic yachts
- Sale Broker Directory
- Charter Home
- Yachts for Charter
- Charter Destinations
- Charter Broker Directory
- Destinations Home
- Mediterranean
- South Pacific
- Rest of the World
- Boat Life Home
- Owners' Experiences
- Interiors Suppliers
- Owners' Club
- Captains' Club
- BOAT Showcase
- Boat Presents
- Events Home
- World Superyacht Awards
- Superyacht Design Festival
- Design and Innovation Awards
- Young Designer of the Year Award
- Artistry and Craft Awards
- Explorer Yachts Summit
- Ocean Talks
- The Ocean Awards
- BOAT Connect
- Between the bays
- Golf Invitational
- Boat Pro Home
- Pricing Plan
- Superyacht Insight
- Product Features
- Premium Content
- Testimonials
- Global Order Book
- Tenders & Equipment
Retro revival: The best modern classic yachts
Livingstone.
Many people love classic design, but old yachts, cars and aircraft often come with inevitable issues in terms of performance and comfort, not to mention a never-ending maintenance list. The modern classic offers an alternative to owning a classic superyacht , drawing inspiration from the magnificent lines of yachts from the first half of the 20th century, and yet concealing modernity beneath the waterline and within. We round up some of the best modern classic yachts in the world...
It is not just the name of the 24 metre Livingstone that recalls a bygone era - this steel-hulled cruiser from Hartman Yachts oozes 1930s charm with a canoe stern and a decorative aluminium funnel. However, these classic flourishes belie her high-tech equipment, such as an extendable passarelle that can emerge from the beautifully curved transom in a matter of seconds.
The massive modern classic Nero stretches more than 90 metres in length. Built in China by Corsair Yachts , her owner was inspired by J.P. Morgan's Corsair yachts from the 1930s. An apt replica, she resembles a small, classic cruise liner – with a smoke stack included.
Accommodating 12 guests, Nero is one of the most expensive charter yachts . Superyacht Nero is available for charter in the Mediterranean and the Caribbean , with a talented chef on board who has received some bizarre requests in his time.
More about this yacht
Yachts for charter.
She may look like she was born in a different era, but the 48.7 metre yacht Clarity was launched by Turkish yard Bilgin Yachts as recently as 2015. Styled in-house, this modern classic was based on a simple but ambitious premise: to build a yacht with a design that will last forever.
Her full-displacement hull has a bilge keel and bulbous bow for all-ocean seakeeping, while modest 707hp Caterpillar engines yield a serene cruising speed of around 10 knots befitting of Clarity ’s graceful appearance.
Photo: Eray Altay
The 38.8 metre Truly Classic Atalante was launched by Claasen in 2015 and combines retro good looks and modern performance . She features design from renowned modern classic designer Andre Hoek , who takes his inspiration from famous designers of old, such as William Fife , Charles Nicholson and Nathanael Herreshoff .
Atalante was built for the owner of a 27.5 metre Truly Classic of the same name, who enjoyed the smaller version so much that he ordered a larger, faster version.
“ Atalante represents the best of both worlds," said Hoek. "She performs like a modern thoroughbred and blends this with the timeless appeal of a classic yacht.”
The 28.9 metre Ardis II was built by De Cesari for superyacht and jewellery house owner Carlo Traglio . The mahogany motor yacht can often be seen moored in Porto Cervo, Sardinia .
Traglio spent much of his childhood on the classic 50 metre schooner Xarifa , before owning the Perini Navi 80 yacht Malizia . His experience of classic yachts acted as inspiration for building Ardis II , which can accommodate up to eight guests in four cabins. She is fitted with modern MTU diesel engines and is capable of 25 knots.
Launched in 2015 by Rossinavi , the 40 metre motor yacht Taransay was built to replicate yachts of the early 1930s . Taransay's owner is said to have been inspired to build a modern classic yacht after chartering the real classic Ocean Glory , launched in 1935.
Rossinavi married Taransay 's classic styling with modern propulsion – two Caterpillar C18 Acert engines deliver a top speed of 14 knots, and she has a range of 3,500 nautical miles at 10 knots. She also has spacious interiors and deck spaces thanks to a roomy 7.6 metre beam.
Eleonora E is an exact replica of the schooner Westward and an excellent example of a modern classic paying tribute to the original. She was built at the GraafShip yard in the Netherlands and was launched in March 2000. Since then, Eleonora E — currently available for charter — has successfully participated in a number of classic sailing regattas.
The 46 metre Sycara IV was a show-stopper when she was launched by Burger in 2009, displaying the US builder's diversity as it waded into retro yacht waters. With exteriors by Bruce King and interiors by Ken Freivokh and Craig Beale , the fantail stern yacht makes you do a double take as she could easily fit in alongside classic Trumpys .
But this modern classic has a shallow draft and was designed for cruising the Bahamas and the Great Lakes in style. Sycara IV has modern touches with a spacious on-deck master stateroom, telescoping bowsprit and corrosion resistant aluminium hull.
Tempus Fugit
This modern classic yacht is a head turner on the racecourse, blending speed and style thanks to her highly varnished wooden hull. The 27.43 metre Tempus Fugit , from Arkin Pruva , was designed by Rob Humphreys to pay homage to J Class yachts , but she is beamier, offering more comfortable living accommodations below and in the cockpit during races.
And race she does — Tempus Fugit was a surprise contender at regattas when she came onto the scene, holding her own against classic yachts and modern carbon crafts as well.
The beautiful, modern classic ketch Elfje is owned by philanthropist Wendy Schmidt . Schmidt had a very hands-on role in designing Elfje with Hoek Naval Architects and is proud of its environmental credentials, from its racing design to sustainable materials. Expect to hear a lot more about Elfje , a sailing superyacht of the ages , as she's been busy on the racecourse since her launch.
Sponsored listings
- New Sailboats
- Sailboats 21-30ft
- Sailboats 31-35ft
- Sailboats 36-40ft
- Sailboats Over 40ft
- Sailboats Under 21feet
- used_sailboats
- Apps and Computer Programs
- Communications
- Fishfinders
- Handheld Electronics
- Plotters MFDS Rradar
- Wind, Speed & Depth Instruments
- Anchoring Mooring
- Running Rigging
- Sails Canvas
- Standing Rigging
- Diesel Engines
- Off Grid Energy
- Cleaning Waxing
- DIY Projects
- Repair, Tools & Materials
- Spare Parts
- Tools & Gadgets
- Cabin Comfort
- Ventilation
- Footwear Apparel
- Foul Weather Gear
- Mailport & PS Advisor
- Inside Practical Sailor Blog
- Activate My Web Access
- Reset Password
- Pay My Bill
- Customer Service

- Free Newsletter
- Give a Gift

Cal 2-46: A Venerable Lapworth Design Brought Up to Date

Rhumb Lines: Show Highlights from Annapolis

Open Transom Pros and Cons

Mailport: Charley Morgan, Locker Safety, Fast Bottom Paint

Do-it-yourself Electrical System Survey and Inspection

Install a Standalone Sounder Without Drilling

The Tricked Out Tillerpilot

Resolving Common Steering Problems

Top-notch Wind Indicators

The Everlasting Multihull Trampoline

In Search of the Snag-free Clew

The Cruising Sailor’s Argument for High-tech Fibers

Breaking Point: What Can Go Wrong With Your Yanmar?

Rudder Mods for Low-speed Docking

Using Heat to Bend PVC Pipe

Mildew-resistant Caulks for Boats

Can We Trust Plastic Boat Parts?

Repairing Molded Plastics

Mailport: Marine plywood, fuel additives, through bolt options, winch handle holders

The Day Sailor’s First-Aid Kit

Choosing and Securing Seat Cushions

Cockpit Drains on Race Boats

Rhumb Lines: Livin’ the Wharf Rat Life

Resurrecting Slippery Boat Shoes

Shoe Goo’s Gift to Sailors

PS Advisor: Tank Monitor and Camera Mount Hacks

Marine Toilet Maintenance Tips

Learning to Live with Plastic Boat Bits

The Ultimate Guide to Caring for Clear Plastic

Preventing Mildew in Marine Fabrics

Gearing Up for Winter Sailing
- Sailboat Reviews
Practical Sailor Takes a Look at Trends in Modern Boat Design
Is the quest for speed and interior comfort trumping smart design in todays sailboats.

Practical Sailor editors have noticed the increasing tendency in newer-model sailboats to be ill-mannered in gusty conditions. Establishing balance between the sails and the hull is one of the main factors in quality boat design. For correct trim, many things must be considered: the ballast package location, the combined longitudinal center of gravity (LCG), and the longitudinal center of buoyancy. At the same time, to maintain a balanced helm, the keel must promote sufficient lead (the fore and aft distance between the center of effort and the center of lateral resistance). To highlight how these boat design principles play out, Practical Sailor looks at classic sailboats such as the Bill Shaw-designed Pearson 32, Ericson 41, Valiant 40, and Peterson 44, and compares their keel/sail ratios and lead values to more modern sailboat designs such as the Catalina, Hunter, Tartan, and Beneteau.
In the course of taking out boats for testing, Practical Sailor editors have observed an increased tendency for new-model sailboats to be ill-mannered in gusty conditions. We have been watching this trend for several years, and it seems to be becoming more usual than unusual.
In a typical situation, we will be sailing the test boat on the wind in 12 or so knots of breeze and everything is fine. Then, the breeze picks up to about 15 knots and the helm loads up. OK, thats to be expected, so we flatten the main, drop down the traveler, and that takes care of it.
Then we get a puff. Were already on the point of needing to reef, so in the puff, were overcanvassed. Instead of just heeling farther, the boat begins to round up. Fighting it with the helm is hard work, and easing the main so it luffs doesn’t help much.

Photo by Ralph Naranjo
We take in a reef, which usually means we roll in a bit of the jib or a bit of the main, or both, and the helm lightens up. We trim to the new wind and sail along, a bit slower now in the light spots, but then the next gust comes along, and the helm immediately loads up again.
In the worst case weve experienced, the boat rounded up so quickly that it tacked, even though the helm was hard over in the opposite direction. To prove that wasnt a fluke caused by a temporary diversion into a parallel universe, it did the same thing on the other tack.
Practical Sailor editors are old enough to remember a generation of cruising boats that didnt behave in this manner. For sure, there have always been twitchy boats, but most, when hit by a gust, would heel a little more, put some pressure on the wheel or tiller, and once the boat picked up speed, the pressure would come right off. A boat like that will sail for a long time with a loose lashing on the helm.
So, where does this bad habit come from? Several trends in modern cruising yacht design can share the blame. One of them is builders inclination to tilt their designs toward the performance end of the cruisers spectrum. Many recent and current cruising boats, if suitably fitted out with racing sails and the hardware and software to tweak them, could put up an impressive show on the race course.
The sensitivity to trim that accompanies such potential isn’t always suited to cruising shorthanded or with a family, when balance and good manners are key both to enjoyment and, to a degree, safety.
Establishing Balance
Many factors contribute to the balance of a sailboat. The obvious and principal pair are the sails and the hull. When working up a new design, the architect develops these in close association, but both are in turn influenced by other aspects of the boats design as it evolves.
In the standard approach, the designer works up preliminary drawings to express the basic requirements of the design brief, which normally include a desired length, displacement, cabin arrangement, and sailplan to provide the desired performance.
He then sketches out the hull lines (the matrix of contours that define its three-dimensional shape and its volume) to enclose the interior and meet expressed performance goals. The preliminary lines also serve as a basis on which to perform a number of calculations, one of them being the location of the center of buoyancy (CB).
With everything roughed out, the designer then “weighs” every item that will go into the complete boat, from the hull laminate to the toothbrush holder, but excluding the ballast. He combines these weights and their locations on the three axes, X, Y, and Z, to calculate the center of gravity (CG) of the whole package. Computer programs have helped to speed up this process and make volume calculations more accurate, but the process hasn’t changed much.
For the boat to float on its desired lines, the ballast package must then be designed and located to bring the combined longitudinal CG (LCG) of hull and ballast to the same fore-and-aft location as the CB (LCB). Once everything has been resolved satisfactorily, the designer can finalize the lines, carry out the necessary calculations, and establish shape and locations for the keel and the sailplan.
On most boats of current design, the ballast also constitutes the fin keel, and in that role, its location determines the center of lateral resistance (CLR), which in conjunction with the center of effort (CE) of the sailplan, influences how the boat balances under sail.
Even as boat design procedures have evolved from three-dimensional modeling using half hulls, through two-dimensional modeling using pen on vellum, to three-dimensional virtual modeling on computers, the fundamental principles have remained constant. One of the fundamental values used for predicting the proclivities of a boats helm is the dimension termed “lead.” Lead, pronounced “leed,” is the fore and aft distance between the CE and the CLR, expressed as a percentage of the waterline length (DWL).
“Skenes Elements of Yacht Design,” as revised by Francis S. Kinney, and other references for yacht design provide rules of thumb for calculating lead from the sailplan and the hull profile. (See illustration above).
Looking at the diagram, its easy to see how lead is an elusive quantity. First of all, no boat sails with the sailplan as shown-the sails are never flat and on centerline. The traditional range for lead places the CE forward of the CLR by 14 to 19 percent of DWL. This value is lifted from “Skenes,” for years the first reference for any designer. Since that book was written and updated, hull forms have changed, and with them, optimum values for lead.
On designs with fin keels, lead is often calculated with reference to the keel alone. One feature remains constant whatever the design. Moving the centers closer together-reducing lead-increases the tendency to weather helm. Moving them apart reduces that tendency. If the lead is too great, the result may be lee helm, which is generally considered undesirable-and is in fact, rare.
In Kinneys prime years, the 1960s to the 1980s, the basic working sailplan of a sloop included a 150-percent genoa, which would have the effect of moving the CE closer to the CLR. Many designs today have headsails with short or even no overlap and very often a full-battened mainsail with lots of roach. The different aerodynamic characteristics of such rigs might well affect optimum lead, something which designers can only determine through experience. (If a boatbuilder offers an in-mast furling mainsail as an option, its effect on lead will differ from that of the “classic” sailboat.)
The effective CLR can also be very different from that calculated. On a deep-bodied, full-keel hull, that difference simply might be the difference between the geometric center and the center of hydrodynamic pressure of the whole profile.
A sharp bow with a pronounced “chin” might well move the effective CLR forward. On a modern, fin-keeled boat with a shallow, broad canoe body like that of a dinghy, the keel makes a proportionately larger contribution to lateral resistance, so the location of the keel will strongly influence where that resistance operates.
Obviously the rudder, too, is part of the lateral plane, but if our objective is to sail with light to neutral pressure on the helm, under normal conditions, it should not be making a significant contribution to lateral resistance. Its role is to provide a means to change the boats direction and to compensate for the constant fluctuations in the forces applied to the boat in the normal course of sailing. A certain amount of pressure in the form of weather helm helps by providing positive feedback to the helmsman on the state of balance. That said, on many racing hulls, the rudder is designed to contribute lift and has an active role in driving the boat to windward. (It is worth noting that those wide-bodied race boats also tend to have twin rudders.)
Then and Now
Even in the age of computer modeling, yacht design remains a series of compromises. At the moment, it seems the pendulum has swung to a point where high-volume, wide-beam shapes dominate. With them come large rigs to overcome skin drag and its negative effect in light air. As a result, theres a need to sail the vessel as flat as possible or suffer the consequences.
The sailplan and outboard profiles of boats from different eras represent the shift in yacht design that has occurred during recent decades. The modern boats have longer proportional waterlines, indicating higher potential speed. It also means that the boats immersed volume, or displacement, has been distributed over a greater length.
Given two boats of similar displacement like the classic Pearson 32 and the modern Tartan 3400 (above), the Tartan winds up with a shallower canoe body. This also contributes to its being potentially faster and, if both boats had the same draft, would give the keel a slight advantage in span, and therefore effectiveness to windward.
So far so good, but a shallower canoe body forces the cabin sole upward, especially if the belowdecks accommodations are to take full advantage of the wide beam favored in the modern hull. To achieve comparable headroom with its older counterpart, the cabintop has to go up, too, and to ensure sitting headroom on the settees under the sidedeck, so does the freeboard.
Ultimately, the whole deck moves upward. To ensure the boom doesn’t sweep everybody out of the cockpit during an unplanned jibe, the boom too goes up. If sail area is not to be compromised, the entire mainsail goes up, and with it, its center of effort. The bigger the boat, the less pronounced these differences become as the proportions become more relaxed.
Differences are visible, too, between the boats keels; the modern Tartans is smaller in area. While it might be claimed that less wetted surface promises higher sailing speeds in light air, some builders accept a smaller keel to simplify the manufacture of the hull.
In a perfect world, the designer draws a keel to suit the boats sail area and other characteristics, places it to obtain the desired sailing performance, then massages the needed ballast to both fit the keel and trim the boat correctly. The volume of the ballast is usually less than that of the keel, and the builder has to do some intricate laminating work to mold a keel to receive ballast internally or a stub to which to bolt it externally.
On many production boats today, the keels are bolted directly to the bottom of a fair canoe body, a practice which eliminates much labor. The consequence is that the area of the keel is determined by the weight, and therefore the volume, of the ballast. To achieve the desired hydrodynamic properties and mechanical strength-it mustnt bend under the influence of normal sailing loads-a given volume of ballast can be formed into a limited range of shapes. Placing ballast in a bulb at the bottom aids the keels efficiency by creating an endplate effect and raises stiffness by placing ballast low, but it means that the keels lateral plane is sharply reduced.
For a more dramatic representation of how changes in keel design can affect helm balance, compare a Cruising Club of America (CCA) design like the Ericson 41 above, to a modern equivalent with comparable sail area like the Beneteau 46.

When sailing, two boats are subjected to similar forces on the sails. Resisting that side force are the immersed hull, the keel, and the rudder. If the hulls offer similar resistance, the remaining force is shared between the keel and rudder. If one keel is smaller than the other (as is clearly the case here), the effect is to increase the share taken by the rudder.
When the sails are trimmed properly and all is in balance, the rudder will carry a small load. If however, you hit a gust, the rudder must pick up a high proportion of the added side thrust until balance is restored, usually by some adjustment to sail trim.
Simply put, boats of the general modern type are not forgiving in changeable conditions, say, for example when the apparent wind is in the 12- to 18-knot range. At the higher end, youd want to be reefed; at the lower end, probably not.
On a day when you expect the wind to soften rather than harden, youd rather not put in the reef, so that you can maintain speed in the lulls. In the puffs, you want your hands free to ease the traveler and flatten the jib, which is hard to do if the helm is a handful. Compounding the problem on most boats, the mainsail controls are usually not within reach of the helm.
On racing boats, such sensitivity isn’t an issue. On the contrary, sufficient crew are on hand to make adjustments on the fly as quickly and often as needed to keep the boat sailing at her fastest.
Cruising boats are often sailed shorthanded and by crews who are not looking for a constant physical workout. An autopilot might be doing most of the steering, and good balance is helpful in protecting it from having to work too hard-or from being overpowered.
Another striking difference between the older and newer designs is visible in the plan (overhead) view. By 1980, cruising-boat hulls were already becoming beamy relative to boats of the 1960s and 1970s. The current trend is to carry the beam aft, so that in the region of the rudder, its as much as 85 percent of the maximum beam, far wider than the 55 percent to 60 percent once considered acceptable. The principal beneficiary of this extra breadth is the boats interior-builders often offer twin double cabins aft where a generation ago they might have squeezed in a quarter berth and a cockpit locker. The cockpit, too, becomes roomier, and the transom, scooped and sculpted, is transformed into a swim platform and dinghy dock.

Photo by Jarrod Scanlon
All this additional boat aft adds weight aft, in both construction materials and outfit. To compensate, the ballast-that is to say, the keel-has to be fitted farther forward.
The full beam aft does provide a significant boost to the boats ability to carry sail. As the boat heels, the center of buoyancy moves quickly outboard, away from the center of gravity. This lengthens the righting arm, giving a positive contribution toward stability, but it also moves the immersed centerline of the hull away from the static centerline along which both the keel and the rudder are attached. Depending on the hulls shape, this can create a distortion in the immersed volume, which can in turn affect the dynamics acting on it.
Effect of Keel Area
Another factor entering the equation is the area of the keel. This, too, is apparent when comparing the drawings of the older and newer generation boats. Many of the standard tracts on the design of sailing yachts are, lets say, vague on what keel area is adequate or even desirable, although many designers have come up with their own formulas.
Because the keel is reacting in the water to forces generated on the sails by the wind, it makes sense that the area of a fin keel should be related in some way to sail area.
When naval architect Dave Gerr took over as director of the Westlawn Institute of Marine Technology, he found the course materials for sailing yacht design had little detailed explanation on this topic, a gap he subsequently filled. Briefly, he recommends no fin keel should be less that 2.5 percent of the sail area (mainsail 100 percent foretriangle) and need be no more than 5 percent. The smaller value is appropriate for a racing boat with a full crew aboard to trim and tweak the sails to every change in the wind. The larger area is suited to cruising boats, which need to be more forgiving to shorthanded crews.
Current Design Trends
In the past, racing measurement rules have been criticized because the boats designed to compete under them have become type-formed, sometimes with unwelcome consequences in how they handle. We might just as easily level criticism at present-day marketing and manufacturing methods for doing the same to cruising boats.
Lets face it, but for a few differences in sailplans and keel shapes, modern cruising sailboats are quite generic below the sheerline. They are all beamy; they carry their beam aft; they have long waterlines; they have dinghy-like underbodies; and they have spade rudders. The forces that have created this shape have at least as much to do with how many people can sleep and shower in them comfortably as with how the boats will sail.
Dishing out the hull shape in this manner makes it fairly easy to push through the water, but arranging the keel, rudder, and sails so they work in concert has become a more complex problem, exacerbated by having to compensate for extra weight of accommodations aft, something thats less of an issue in raceboats.
The byproduct of these design parameters is zesty performance, a bonus for the marketing department, but speed for its own sake is not the first priority of cruising sailors. In the brochure for the Beneteau 37, the boats polar diagram shows a maximum theoretical sailing speed of over 12 knots in 30 knots of wind. When cruising sailors encounter 30-knot winds, they are more likely to hunker down in the expectation it will blow even harder than they are to set the chute to go surfing. What they want is a boat that will take readily to hunkering, and all the signs indicate those boats are getting fewer in number . . . and they are mostly older designs.
- The Balancing Act
- Pearson 32 vs. Tartan 3400
- Ericson 41 vs. Beneteau 46
- Practical Sailor Design Guide
- The Modern Hull and Helm Balance
RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHOR
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Log in to leave a comment
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell My Personal Information
- Online Account Activation
- Privacy Manager
- Yachting World
- Digital Edition

Anna: The modern classic yacht that conceals some serious technology
- January 21, 2020
Anna is a custom 65ft Spirit of Tradition yacht with some very high-tech features concealed beneath her classic exterior, reports Alison Langley
When approaching Anna moored at the dock, it’s hard to immediately tell whether she is a restored classic or a recently built replica. In fact, neither is true; Anna is a new build designed to include both the virtues of a classic yacht and the technical achievements of a modern cruiser.
Anna ’s story began two decades ago when owner Tony Merck began thinking about stepping up from small classic daysailers, like the Herreshoff 12 1⁄2 and the Bjarne Aas-designed International One-Design, into a larger cruiser that could maintain a classic aesthetic.
Merck had watched the birth of the Spirit of Tradition genre and had followed boats like the Pedrick-designed carbon beauty Savannah , as well as the Joel White-designed W-Class day racers. But his ambitions lay less with recreating an early 20th Century racer. Instead he admired the sturdy, able cruisers from past designers such as Fife and Alden, while he also loved the modern construction and high specification of this new generation of classics.

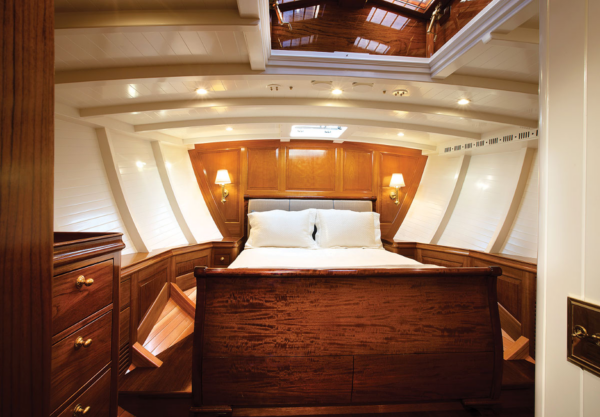
Anna ‘s classically sumptuous cockpit
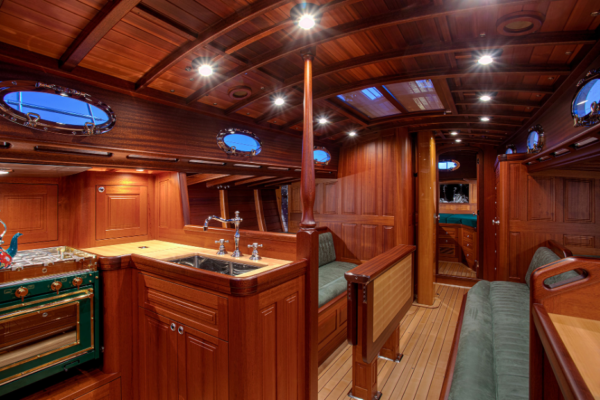
In the summer of 2015, Tony approached Robert Stephens of Stephens Waring Yacht Design and work began on proposal sketches for the boat that would become Anna at their design offices in Belfast, Maine. Stephens has had a lot of experience with modern wood construction, having worked in the Spirit of Tradition genre since before it even had a name.
Tony and his wife Ann knew they wanted her to be built in Maine, but were not set on a yard. Robert Stephens and business partner Paul Waring took Tony on a guided tour of five top Maine yards before deciding to go with Lyman Morse, of Thomaston. Coincidently, Tony had played soccer and rebuilt old cars with yard founder Cabot Lyman in prep school some 50 years before.
Systems expertise
Lyman-Morse is well-respected in the custom boat world, but were not then as well known for building wooden boats as many other Maine yards with expertise in cold-moulded wood construction . Lyman-Morse did, however, have a reputation for high-quality glassfibre and carbon boats, but won the job thanks to their systems expertise and a modern approach to construction, including the integration of old-school hand craftsmanship with cutting-edge equipment like five-axis CNC machines.
Article continues below…

Marilee: The inside story of the 1926 Herreshoff NY40’s remarkable restoration
When the New York Yacht Club commissioned the new NY40 one-design class in 1916 Nathanael Herreshoff’s objective was to design…

Revolver: Bruce Ritchie’s gentleman’s racer blends traditional and modern craftsmanship
“I wasn’t expecting this,” said Michael Ritchie when his 83-year-old father Bruce showed him the lines he had drawn up…
I was hired by Ann Merck and Lyman-Morse early in the project to photograph the entire project from start to finish, and make a coffee table book about Anna as a surprise gift for Tony. Project manager Lance Buchanan made sure my visits were timed so I could capture the build at the right moments.
Anna was built using a wood composite cold-moulding system. Her hull is planked in four layers of wood – an inner layer of tongue-and-groove Douglas fir strip planking, screwed and glued to the laminated Douglas fir frames. That’s followed by two layers of diagonal veneers, and a final layer of longitudinal strip planking, the whole sheathed in two layers of biaxial/mat glassfibre and epoxy.
Her deck is built as a sandwich, separate from the hull: plywood laid over a temporary mould, covered with CoreCell foam, then another ply skin, with a laid teak weatherdeck. Once interior components were in place the deck/cockpit/deckhouse assembly was installed as a unit.

Anna ‘s wineglass transom
Modular build
Lyman-Morse built Anna ’s interior in modules, allowing them to fabricate the galley, head, and main saloon off the boat and then lift each completed section into the hull. When each module was installed, the bulkheads mated against the curvature of the hull perfectly, with no trimming or additional tweaking required. Anna ’s construction adage became, literally, ‘measure once, cut once’.
Since Anna ’s design brief called for a classic ambience, that meant that hundreds of feet of hydraulic lines, electrical wires, and even halyards needed to be concealed beneath the yacht’s joinery. The designers at Lyman-Morse and Stephens Waring worked closely to come up with innovative ways to hide these wiring runs and mechanical spaces. By creating a complete 3D model of Anna they were able to plan these tiny crevices before construction began.
Stephens Waring brought in interior designer Martha Coolidge to contribute her fine eye to the style and detail of the interior, which was painstakingly developed with a combination of hand-coloured sketches, computer renderings and tactile examples. “I think we went through 17 iterations of the brass light-switch covers!” recalls Stephens.

8,212ft of tongue and groove (Douglas fir) planks were used for the inner layer of the hull
Anna is intended for easy daysailing, and her deck layout reflects this. A roller-furling boom from Southern Spars makes simple work of the large, high aspect ratio mainsail. A self-tacking jib will be the go-to sail for most of her career. Anna ’s captain, Jim Murphy, enjoys sailing with guests aboard. “I love to call ‘Ready about’ and watch the guests ask ‘What happens now?’ and see their faces when I say ‘Nothing’, and just spin the wheel,” he comments with a grin.
But ease of sailing has not dulled the experience. Murphy explains: “Under sail, Anna is like a wonderful dancer. Her motion, her response to the sea and helm are like no other boat that I have sailed. An absolute joy.” For Anna ’s forays onto the racecourse, she switches to the ‘race jib’, a 100% working jib that fits on the furling headstay. A Code Zero and masthead asymmetric round out her inventory.
Hidden high tech
Anna ’s traditional style masks lots of high-tech systems. Sail handling systems are all push-button: electric winches, roller-furling boom and jib, and hydraulics to drive the sail controls. Two hidden systems maintain her classic lines while adding 21st Century functionality: a below deck anchor deployment system, and a side-boarding platform that eases access from a tender and provides a swimming ‘porch’.

A hydraulic boarding platform enables easy access to the water for all generations. The step-stool ladder deploys automatically
Beneath the saloon is a state-of-the-art engine room with turbodiesel motor, lithium ion batteries and multi-compressor air conditioning. A touchscreen nav plotter in the raised saloon disappears into the furniture with a touch of a button. Her deck saloon windows are power-operated at rear and sides, allowing airflow and communication with people sitting in the cockpit at the push of a button.
Following her launch in April 2018, Anna has completed two sailing seasons, split between Rhode Island, Maine , and Nova Scotia , with a good mix of day sailing, Spirit of Tradition racing, and overnight sails. She’s earned silverware in both Sprit of Tradition races and design awards but, more importantly, she’s fulfilled the ambition her owners had 20 years earlier to expand their world of classic sailing.
Specification
LOA: 19.96m (65ft 6in) LWL: 14.58m (47ft 10in) Beam: 5.13m (16ft 10in) Draught: 2.28m (7ft 6in) Displacement: 25,855kg (57,000lb) Sail area: 190m 2 (2,040ft 2 ) Built: 2018 Design: Stephens Waring Yacht Design Builder: Lyman-Morse Boatbuilding Co
About the author

First published in the January 2020 edition of Yachting World.
Messing about in boats since 1975. Online Since 1997.
Home | Intro | Our Design Process | Stock Design Info | Motor Yacht Designs | Sailing Yacht Designs | Prototype Designs Plans List | Articles | Our CAD Design Stream | Maxsurf | News..! | SITE MAP..! | Site Search | Design Team | Contact Us Please see the AVAILABLE BOAT PLANS web page
Please see the AVAILABLE BOAT PLANS web page. Home | Intro | Our Design Process | Stock Design Info | Motor Yacht Designs | Sailing Yacht Designs | Prototype Designs Plans List | Articles | Our CAD Design Stream | Maxsurf | News..! | SITE MAP..! | Site Search | Design Team | Contact Us
- All Web Site Graphics, Layout, and Written Content at this Domain Created by Michael Kasten.
- All Graphic and Written Materials at this Domain Copyright © 1989 - 2023 Michael Kasten.
- All Content Registered with US Library of Congress and US Copyright Office.
- Copyright Violations will be Prosecuted. All Rights Reserved.
Sign-Up for News & Stories
Stephens Waring Yacht Design
Spirit of Tradition Yachts Designed In Maine
Home » News » SWD News & Stories » 7 Trends in Sailing Yacht Interior Design
7 Trends in Sailing Yacht Interior Design
Posted on March 14, 2023 and filed under SWD News & Stories

Interior designer Martha Coolidge, working with Stephens Waring Design, fine-tuned the style of the woodwork detail, panel layouts, light fixtures, and other elements of 65-ft ANNA’s appearance. Photo credit: Alison Langley
There’s some irony when it comes to looking at the hottest interior design trends for custom sailing yachts: much of the inspiration for today’s designs draw from the past – combined with modern innovation.
Interior designs that emphasize simplicity, balance, and natural materials are hardly revolutionary. Quite the opposite. But there is a new take and balance between old and new, iconic and innovative, that seems to provide the perfect balance for creating incredible interior spaces.
We’re exploring the top 7 trends in custom yacht design for 2023.
Natural Light and Connection Between Interior and Exterior Spaces
The use of larger windows is a trend that has been gaining popularity in yacht design in recent years, as yacht owners increasingly want to maximize their views of the surrounding environment and bring more natural light into their living spaces.
One way that yacht designers are incorporating larger windows is by using high-strength glass materials that can withstand the harsh marine environment. For example, tempered glass or laminated glass with multiple layers can provide the necessary strength and durability to withstand the wind, waves, and impact from flying debris.
In addition to using strong glass materials, yacht designers are also using innovative engineering techniques to maximize the size and placement of windows. Lightweight structural materials such as carbon fiber and titanium in the yacht’s construction, allow for larger windows without compromising the yacht’s structural integrity. In the photo of ANNA, above, the white-painted transverse structural knees are part of a carbon fabrication that strengthens the cabin and carries the mainsheet loads while blending into the classic joinery.
M ulti Functionality and Flex Spaces
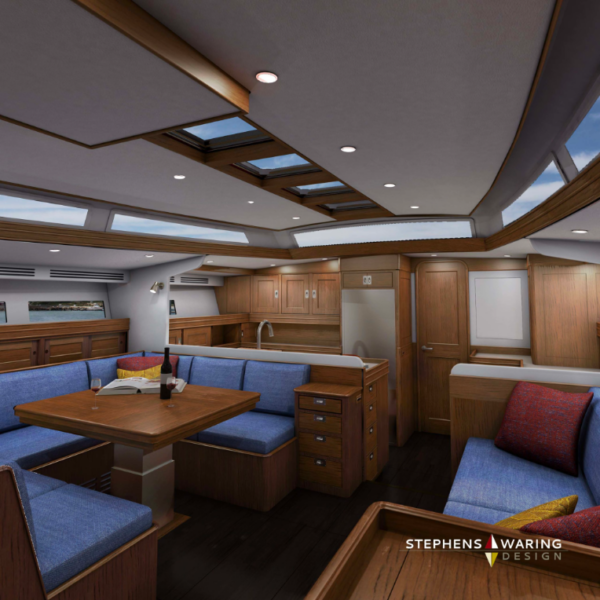

The design for 68-ft CIRRUS comes from blending 40’s & 50’s era style. The large saloon is designed to provide long-term comfort and versatility with innovative vertical storage and a vaulted ceiling that includes panoramic angled glass as well as overhead skylights. Design by Stephens Waring under construction at Jim Betts Enterprises.
Owners are spending more time aboard their vessels and are adding to the list demands and programmatic needs. These include home-office, fitness centers, gourmet kitchens, and gathering places for family and friends to spend longer durations of time together.
Because space is at a premium on a yacht, designers are creating multi-functional spaces that can serve multiple purposes. For example, a seating area that can be converted into a bed or a dining table that can be lowered to create additional seating. Clever storage solutions are also being incorporated into yacht design to make the most of available space.
Old World Charm Meets Modern Sensibilities: Spirit of Tradition

44-ft ITALMUS blends a 1940’s vernacular into the stylistic details and overall aesthetic of the yacht. The interior styling and design is aimed to mirror the era with a theme of highly crafted raised paneling and elegant joinery detail of select quarter sawn mahogany and finished in satin varnis. Design by Stephens Waring, built by Van Dam Classic Boats. Photo credit: Billy Black
Yacht designers have always had a particular reverence for heritage and history. The notion of heading out to sea conjures images of bygone eras past. Capturing that essence requires a balance that avoids becoming kitsch or contrived. While mid-century design may be considered the hot design trend of 2023, as designers steeped in a Spirit of Tradition design philosophy, we feel we’ve never left the genre.
Spirit of Tradition designs embody some historically identifiable link, particularly expressed in the shape and aesthetic exhibited in the design form of the hull and superstructure. Equally important, a Spirit of Tradition vessel must embrace modern development in materials, construction methods, mechanical systems and naval architecture science. Without the Spirit in development, we’re left with only Tradition.
Natural Materials

Douglas fir deck beams, traditional raised and v-groove paneling, bright varnish and white painted surfaces make it a light, airy enclave. Interior design by Martha Coolidge and Stephens Waring Design. Boat construction by Lyman-Morse. Photo credit: Alison Langley
Yacht owners by their very nature are drawn to water and the natural world, so it makes sense to incorporate natural elements such as wood, stone, and other organic materials in design. These materials create a sense of warmth and connect the interior spaces to the natural surroundings.
As experts in wooden boat design, we have long touted the benefits of timber for structural elements. However, incorporation of hardwoods, as well as a growing trend in sustainable timbers, have become increasingly popular with owners looking to achieve aesthetic, durability, and sustainability objectives in interior design.
Other natural materials such as leather and wool are also being incorporated to add texture and comfort. These finishes not only look beautiful, but they are also durable to withstand the harsh marine environment.
Renovation and Restomods

The owner of Marilee (built in 1926) had the bold vision to create an interior that reflected the yacht’s century-long provenance while creating an open space below. The team worked with Paul Waring of Stephens Waring Yacht Design, to create a traditional and properly constructed interior with an updated layout for relaxed, modern day use. Photo credit: Alison Langley
The popularity of restomods has been well established in the world of classic cars, but it has only recently grown in popularity in the world of yachting. Fortunately, this is changing with plenty of success stories to point to. Restomods are ideal for owners looking for cost-effective transformations that maintain sentimental connections to vessels and deliver stunning customized spaces that can be more cost effective than new custom builds. They are also popular with owners who inherit family boats, but need more utility and comfort for future generations.
Historical interiors often lack the ergonomics and amenities most owners seek today. Good restoration projects embrace as much of the original charm and character of the original design as possible while improving comfort and livability. Upgrades to electrical systems, electronics and navigation, plumbing and propulsion systems are low hanging fruit. The interior design aesthetics requires a careful and complementary approach which honors the original character while updating comfort, utility, and aesthetics.
Flexible Spaces for a Crew Cabin

65-ft ANNA’s design includes a unique pocket door system. The design provides an easy way to expand square footage when the cabin is not needed or to private a comfortable extra cabin or crew quarters when extra hands or guests are aboard. Design by Stephens Waring. Construction by Lyman Morse Photo credit: Alison Langley
Owners often struggle with the balance between the desire for a larger vessel with larger interior spaces and the challenge of maintaining a total vessel size (and cost) which is manageable.
As we get older the idea of managing and skippering our own vessel can come at the expense of enjoyment. Hiring crew alleviates some of the operational challenges and burdens, but it also means sharing interior space with others.
Flexible crew cabins provide a cost effective way to optimize space for when crew is and isn’t aboard. One solution is the installation of pocket doors on sleeping quarters. This converts square footage from private berths (crew quarters) to main salon gathering space when doors are opened and transforms the space to private rooms for guests and crew when needed.
Smart technology

Yacht owners are increasingly interested in incorporating smart technology into their vessels. This includes lighting, climate control, entertainment systems, and security features that can be controlled remotely. Smart technology allows yacht owners to control the environment on board and manage energy consumption more efficiently. It also adds an extra layer of security by allowing the owner to monitor their yacht from afar.
Related Articles:
A Clients Dream Crystalized in Spirit of Tradition Style

Pushing the Edge of Accommodations Design

Boat Renovations and Restorations 101

Yacht Philosophy: How to Make Small Spaces Feel Big

site by: slickfish studios
Switch to the dark mode that's kinder on your eyes at night time.
Switch to the light mode that's kinder on your eyes at day time.
From The First Superyacht To Modern Yacht Design: A Look At How Luxury Vessels Have Changed Over the Years
Discover just how far has modern yacht design evolved over the last centuries, from the steam-powered vessels of yesteryear to their streamlined successors..
September 3, 2020, 1:56 pm Comments Off on From The First Superyacht To Modern Yacht Design: A Look At How Luxury Vessels Have Changed Over the Years
Modern yacht design has evolved tremendously since the world’s first ‘superyacht’, Cleopatra’s Barge, emerged from Retire Becket’s shipyard in Salem, Massachusetts, to gasps of admiration from the awe-struck crowds that had gathered on the docks.
The 25m, 192t brigantine had been built at the cost of $50,000 for a wealthy merchant named Captain George Crowninshield Jr. who then went on to sail America’s first-ever pleasure boat across the Atlantic to Europe in 1817.
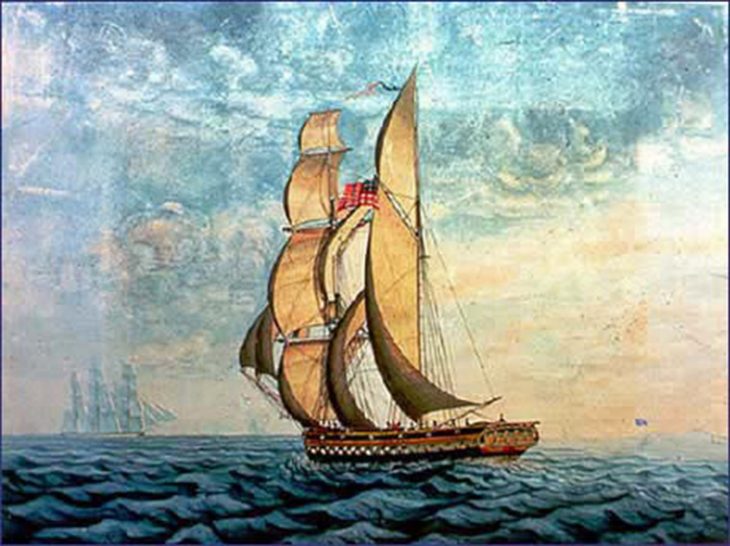

Cleopatra’s Barge was particularly noteworthy as it was opulently furnished, with reports of exotic cabin fittings and beautiful multi-coloured stripes on her elegant hull. No one had ever seen anything like her; and so the first superyacht was born.
Fast forward more than 200 years and there are now said to be more than 5,500 superyachts in the world, of all shapes and sizes (a superyacht is simply defined as a pleasure boat over 24m) and each and every one an example of stunning luxury yacht design.
From luxurious barges to modern yacht design: what’s changed (and what hasn’t)
The first sailing yachts date back to the 1600s, when they became popular modes of transport for the Dutch navy. The word yacht came from the Dutch word ‘jacht’, meaning to hunt, as the sailing boats were built to be light and fast so that they could hunt down and chase pirates.
Originally working vessels, yachts then became the playthings of royalty, with Charles II using a yacht to sail from England to Holland in 1620.
Sail yachts were swapped for steam yachts in the mid 19th century by the wealthy and well-to-do, with the first British royal yacht the Victoria & Albert being completed in 1843. These steam yachts were usually motored by one or two steam engines, and whilst they carried rigging for sails, this was usually just for show.
In fact, these ‘ superyachts ’ became a real indicator of wealth amongst leading families in America, with names such as the Vanderbilts, Goulds, Morgans, Bennetts and Hearsts all competing to come up with the best luxury yacht design . One of the most famous steam yachts at the time was the North Star, built in 1852 for the then richest man in the United States, Cornelius Vanderbilt.
Steam yachts remained the queen of the oceans for almost a century, with two world wars halting technical developments somewhat. Indeed, many superyachts were commandeered to transport freight during the first and second world wars with some, such as the legendary Christina O, serving as a frigate in World War II before being transformed into a luxury vessel. Christina O was bought by Aristotle Onassis in 1954 for $34,000. The Greek shipping magnate then spent $4 million on the refurbishment, which famously included a bronze-edged swimming pool with a mosaic dance floor that rises up at the push of a button.

Luxury yacht design in the 1980s
The late 20th century saw a huge increase in the number and size of superyachts for sale, sparked by an improvement in communications equipment and a growth in the number of wealthy people able to buy their own vessel. New technological advances meant it was possible to easily travel anywhere in the world on larger superyachts, with room for whole families, staff and dedicated crew.
All of a sudden, modern yacht designs had to incorporate home cinemas, fully functional gyms, helipads and water toys galore to cater to wealthy families and their friends. Multi-deck superyachts became popular, such as ‘ Al Salamah ’, a 139m vessel with five decks built by Lurssen in 1999. At the time of her construction, Al Salamah was the third largest yacht in the world, boasting accommodation for 36 guests, a cinema, an onboard hospital, two full-time beauticians, a business centre and a spa. Yet the 162m superyacht ‘Dubai’, by Platinum Yachts, dwarfed Al Salamah when she was completed two years later with her eight decks, on which you can find a helipad, two 33ft chase boats, a squash court and 20 jet skis.

Modest modern yacht designs – a legacy of the financial crisis
When the financial crisis struck in 2008, the superyacht industry was impacted on a global scale, with fewer buyers, charter clients and investors almost overnight. Less became more in luxury yacht design , with the superyacht community choosing smaller, more inventive and innovative vessels over larger multi-decks.
Sailing superyachts are also seeing a resurgence, partly due to the growth of sailing regattas, events which bring the yachting community together for days of weeks filled with fun and excitement.
Once considered a ‘jolly’ where the apres-sailing was taken more seriously than the sailing, many owners are now wanting to compete on superyachts which can actually take home the prize. Composite hulls are increasingly popular, with lifting keels and other features to ensure the yachts are race-fit.
Another modern yacht design that has emerged since the early 21st century is the expedition superyacht, where vessels are designed not only to look elegant but be capable of travelling to the ends of the earth, even in unfavourable conditions.
‘Cloudbreak’ by Abeking & Rasmussen is a good example of an explorer superyacht that was completed in 2016. Boasting all the traditional toys such as a helicopter, spa and cinema room, this 75m exploration yacht named after a mythical wave in Fiji also has a chalet-like fireplace for chilly evenings, a winter garden on the upper deck and zero speed stabilisers to reduce rolling motion in faraway seas.

Environmentally-friendly luxury modern designs
A concern for the environment and a need for sustainability is very much at the forefront of new modern yacht designs, with owners and shipbuilders both looking to use eco-friendly technologies wherever possible.
Ground-breaking technologies include hybrid propulsion systems which use multiple energy sources to lower carbon emissions and reduce noise pollution to the marine wildlife. An example of a yacht which uses such a system is the award-winning Black Pearl, a 106m yacht delivered by Oceanco in 2018. Her hybrid propulsion system combines wind power with two electric propulsion motors, and its controllable pitch propellers generate enough energy to take the Black Pearl across the Atlantic without any fuel at all.
Another brilliant green innovation can be seen on French designer Julien Cadro’s ‘ Ecoo ’ superyacht, which has an Avatar styled hull made out of bamboo fibre instead of steel, while superyacht designer Dan Lenard has designed a yacht made from abandoned performance yacht parts. Eco sailors looking for the perfect superyacht will unfortunately not yet be able to buy one of Lenard’s new recycled boats, however. The designer has only built the 33ft sailboat so he can sail single-handedly across the Atlantic and raise awareness of the state of the world’s oceans.
reading time

The Garden House in the City by Christos Pavlou Architecture

Casa 1/3 by Momento
- Motorcycles
- Car of the Month
- Destinations
- Men’s Fashion
- Watch Collector
- Art & Collectibles
- Vacation Homes
- Celebrity Homes
- New Construction
- Home Design
- Electronics
- Fine Dining
- Baja Bay Club
- Costa Palmas
- Fairmont Doha
- Four Seasons
- Four Seasons Private Residences Dominican Republic at Tropicalia
- Jacob Cohën
- 672 Wine Club
- Sports & Leisure
- Health & Wellness
- Best of the Best
- The Ultimate Gift Guide
5 Beautiful Wooden Boats That Blend Classic Design With Modern Technology
Now that's good wood., michael verdon, michael verdon's most recent stories.
- This Electric Flying Car Could Take You to Work Next Year—and Then Fit in Your Garage
- This African Safari Takes You on a Land Adventure and a River Cruise—Here’s What It Was Like
- Sikorsky’s S-76 Helicopter Has Transported Big Spenders for Decades, and It’s Not Dead Yet
- Share This Article

From one of the largest single-masted wooden sailing yachts in the UK to a mahogany 30-footer with an Art Deco–themed interior, this quartet of vessels showcases just what’s possible with timber, the most classic of boatbuilding materials.

The 111-foot Geist , launched last July by Spirit , is the largest single-masted wooden sailing yacht built in the UK since the 1930s, when the America’s Cup yacht Shamrock V ruled the seas. But Geist is much more than a giant sloop. Her eco-conscious owner mandated systems like the first-of-its-kind electric propulsion by Torqeedo—a 100 kw motor fed by BMW lithium-ion battery banks, which recharge while Geist is sailing—while her Rhoades Young interior elevates wood to its maximum potential, showing off sustainably sourced sipo mahogany, teak and walnut in a series of continuously flowing curves. Even her sails are made of recyclable materials.
Navy Destroyer

Hacker Boat Company traces its roots to John Hacker, who crafted boats for the rich and famous during the Roaring Twenties. The Ticonderoga, N.Y., facility builds modern triple-cockpit runabouts that nonetheless appear straight from the docks of J. D. Rockefeller. The recently launched Restless is a custom project, a modern thoroughbred based on the 1923 Miss APBA race boat; she uses a foot pedal rather than a throttle for acceleration, on her way to a top speed of 65 mph. The Hacker team achieved the striking navy hull by combining a double-planked mahogany layup with a fiberglass skin, while the owners chose the same Cuoio leather favored by Ferrari to pair with the boat’s mahogany topsides.

Jakob Boesch built his first boat in the 1890s, and more than a century later his family continues to merge new technologies with old-world Swiss craftsmanship. Boesch ’s new, 28-foot 860 has a classically styled mahogany hull with up to 11 layers of wood laid at right angles, sealed with six layers of epoxy and finished with six layers of varnish. Propulsion choices include modern options like twin 150 kw electric engines for quiet, emissions-free operation. The runabout’s meticulously crafted silhouette disguises a beast of a machine designed for precise handling, tow sports and speed. Equipped with twin 380 hp Ilmor gas engines, the 860 can hit 48 mph, leaving fiberglass towboats in its wake.

Fiber Class

Unlike the rest of the list, the Hood 57 LM isn’t a proper wooden boat. The hull is what manufacturer Lyman-Morse calls “wood composite,” a combination of strip-planked fir and fiberglass, though its 1950s New England look—including the superstructure’s teak veneer—and pioneering construction suggest the potential for a modern-retro segment; it offers high-tech features such as a carbon-fiber flybridge roof and electric windows. A tough, lightweight boat designed to run offshore, its twin 1350 Volvo IPS pod drives deliver a top speed of 43 mph, while the interior, with its open salon and two generous staterooms, is as spacious as any fiberglass competitor.

Van Dam , which has been building mahogany boats since 1977, moved away from traditional 1920s-style runabouts to focus on original designs such as Catnip . The 30-footer has an Art Deco–themed interior, with stunning metalwork—including an array of semicircular gauge housings, windshield frames with slatted openings and a mirror-like stainless rudder—complementing an expanse of varnished mahogany. With twin 385 hp Ilmor inboards, Catnip has a top end of 57 mph, and since Van Dam won’t build any boat twice, she’s also unique.
Read More On:
More marine.

Tiara’s New 54-Foot Yacht Has a Deck That Transforms Right in Front of You

This Sleek 162-Foot Explorer Yacht Just Became Bering’s New Flagship

The World’s Largest Cruise Ship Has a Full Floor of Luxury Suites—Here’s a Look Inside

How Italy’s Most Stylish City Inspired Tankoa’s New 230-Foot Hybrid Superyacht

Culinary Masters 2024
MAY 17 - 19 Join us for extraordinary meals from the nation’s brightest culinary minds.
Give the Gift of Luxury
Latest Galleries in Marine

Bering B165 in Photos

Tankoa Milano Superyacht in Photos
More from our brands, wwd list: the top 10 ubiquitous faces of fashion month, dartmouth basketball team votes to unionize in college sports first, netflix top 10: ‘avatar: the last airbender’ remains at no. 1 but suffers a viewership decrease, ‘priceless’ artifacts returned to nepal from belgian collector, this best-selling magnetic rowing machine is $185 off on amazon today.

Home Modern classic
Welcome to Leonardo Yachts. In close collaboration with the leading designers in the yachting world such as Hoek Design and Dykstra Naval Architects, we build daysailers that embody the true essence of a modern classic yacht. Our modern classic sailing yachts combine the timeless appeal of a classic yacht with the cutting edge technology of a modern cruiser. Enjoy the exceptional comfort and unrivaled performance or our Spirit of Tradition yachts, without making compromises on beauty and elegance. Our modern classic sailing yachts truly are the ideal combination of old and new…
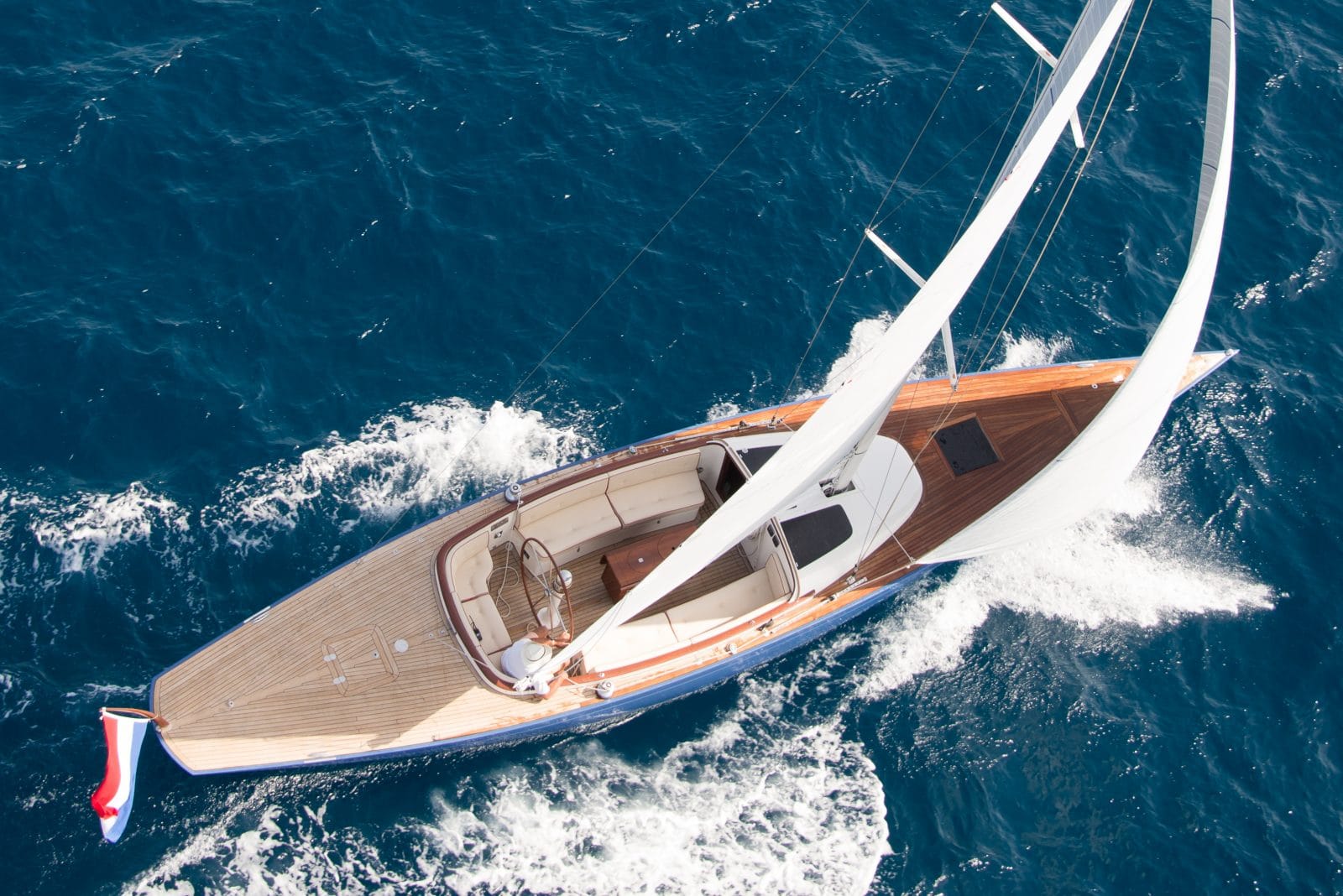

Like a true modern classic yacht, our Eagles all have a classic look with the characteristic long overhangs, classic yacht lines and high gloss mahogany varnished exterior woodwork. The looks are completed by the Edson classic steering pedestal with Ritchie stainless steel compass and the stainless steel 7 spoke steering wheel with high gloss varnished mahogany rim. The interior of our modern classic sailboats can be made in different styles from matt varnished mahogany for a truly classic look or a classic styled white interior with mahogany or teak finish. But also light oak is possible or full teak wood, whatever your preference would be.
The classic lines and looks are integrated in a modern sailing yacht. The designs are made with the latest technology giving the yachts very good and easy to handle sailing characteristics. The modern keels in fin shape can be even upgraded for more performance to a bulb shaped deep draft keel making them fast and easily manouvrable. The modern technology can also be found in the electric package for the winches by which adjusting the sails becomes as easy as pushing a button. The sails from North Sails also hold the latest technology with the 3Di design, making the sails very shape stable to increase the sailing performance. To complete a race set-up, a carbon mast and boom can be added to get the most out of the speed. Standard, our modern classic yachts are delivered with Volvo Penta engines, but off course electric propulsion is available for all models.If you share our passion for modern classic sailing, we would be honoured to help fulfil your aspirations. Together we build the most beautiful Spirit of Tradition boats ever seen.
Get in touch and explore all our options.
Yachting Monthly
- Digital edition

25 of the best small sailing boat designs
- Nic Compton
- August 10, 2022
Nic Compton looks at the 25 yachts under 40ft which have had the biggest impact on UK sailing

There’s nothing like a list of best small sailing boat designs to get the blood pumping.
Everyone has their favourites, and everyone has their pet hates.
This is my list of the 25 best small sailing boat designs, honed down from the list of 55 yachts I started with.
I’ve tried to be objective and have included several boats I don’t particularly like but which have undeniably had an impact on sailing in the UK – and yes, it would be quite a different list if I was writing about another country.
If your favourite isn’t on the best small sailing boat designs list, then send an email to [email protected] to argue the case for your best-loved boat.
Ready? Take a deep breath…

Credit: Bob Aylott
Laurent Giles is best known for designing wholesome wooden cruising boats such as the Vertue and Wanderer III , yet his most successful design was the 26ft Centaur he designed for Westerly, of which a remarkable 2,444 were built between 1969 and 1980.
It might not be the prettiest boat on the water, but it sure packs a lot of accommodation.
The Westerly Centaur was one of the first production boats to be tank tested, so it sails surprisingly well too. Jack L Giles knew what he was doing.
Colin Archer

Credit: Nic Compton
Only 32 Colin Archer lifeboats were built during their designer’s lifetime, starting with Colin Archer in 1893 and finishing with Johan Bruusgaard in 1924.
Yet their reputation for safety spawned hundreds of copycat designs, the most famous of which was Sir Robin Knox-Johnston ’s Suhaili , which he sailed around the world singlehanded in 1968-9.
The term Colin Archer has become so generic it is often used to describe any double-ender – so beware!
Contessa 32

Assent ‘s performance in the 1979 Fastnet Race makes the Contessa 32 a worth entry in the 25 best small sailing boat designs list. Credit: Nic Compton
Designed by David Sadler as a bigger alternative to the popular Contessa 26, the Contessa 32 was built by Jeremy Rogers in Lymington from 1970.
The yacht’s credentials were established when Assent , the Contessa 32 owned by Willy Kerr and skippered by his son Alan, became the only yacht in her class to complete the deadly 1979 Fastnet Race .
When UK production ceased in 1983, more than 700 had been built, and another 20 have been built since 1996.
Cornish Crabber 24

It seemed a daft idea to build a gaff-rigged boat in 1974, just when everyone else had embraced the ‘modern’ Bermudan rig.
Yet the first Cornish Crabber 24, designed by Roger Dongray, tapped into a feeling that would grow and grow and eventually become a movement.
The 24 was followed in 1979 by the even more successful Shrimper 19 – now ubiquitous in almost every harbour in England – and the rest is history.
Drascombe Lugger

Credit: David Harding
There are faster, lighter and more comfortable boats than a Drascombe Lugger.
And yet, 57 years after John Watkinson designed the first ‘lugger’ (soon changed to gunter rig), more than 2,000 have been built and the design is still going strong.
More than any other boat, the Drascombe Lugger opened up dinghy cruising, exemplified by Ken Duxbury’s Greek voyages in the 1970s and Webb Chiles’s near-circumnavigation on Chidiock Tichbourne I and II .

The 26ft Eventide. Credit: David Harding
It’s been described as the Morris Minor of the boating world – except that the majority of the 1,000 Eventides built were lovingly assembled by their owners, not on a production line.
After you’d tested your skills building the Mirror dinghy, you could progress to building a yacht.
And at 24ft long, the Eventide packed a surprising amount of living space.
It was Maurice Griffiths’ most successful design and helped bring yachting to a wider audience.

You either love ’em or you hate ’em – motorsailers, that is.
The Fisher 30 was brought into production in 1971 and was one of the first out-and-out motorsailers.
With its long keel , heavy displacement and high bulwarks, it was intended to evoke the spirit of North Sea fishing boats.
It might not sail brilliantly but it provided an exceptional level of comfort for its size and it would look after you when things turned nasty.
Significantly, it was also fitted with a large engine.

Credit: Rupert Holmes
It should have been a disaster.
In 1941, when the Scandinavian Sailing Federation couldn’t choose a winner for their competition to design an affordable sailing boat, they gave six designs to naval architect Tord Sundén and asked him to combine the best features from each.
The result was a sweet-lined 25ft sloop which was very seaworthy and fast.
The design has been built in GRP since the 1970s and now numbers more than 4,000, with fleets all over the world.

Credit: Kevin Barber
There’s something disconcerting about a boat with two unstayed masts and no foresails, and certainly the Freedom range has its detractors.
Yet as Garry Hoyt proved, first with the Freedom 40, designed in collaboration with Halsey Herreshoff, and then the Freedom 33 , designed with Jay Paris, the boats are simple to sail (none of those clattering jib sheets every time you tack) and surprisingly fast – at least off the wind .
Other ‘cat ketch’ designs followed but the Freedoms developed their own cult following.
Hillyard 12-tonner

The old joke about Hillyards is that you won’t drown on one but you might starve to death getting there.
And yet this religious boatbuilder from Littlehampton built up to 800 yachts which travelled around the world – you can find them cruising far-flung destinations.
Sizes ranged from 2.5 to 20 tons, though the 9- and 12-ton are best for long cruises.

The innovations on Jester means she is one of the best small sailing boat designs in the last 100 years. Credit: Ewen Southby-Tailyour
Blondie Hasler was one of the great sailing innovators and Jester was his testing ground.
She was enclosed, carvel planked and had an unstayed junk rig.
Steering was via a windvane system Hasler created.
Hasler came second in the first OSTAR , proving small boats can achieve great things.

Moody kicked off the era of comfort-oriented boats with its very first design.
The Moody 33, designed by Angus Primrose, had a wide beam and high topside to produce a voluminous hull .
The centre cockpit allowed for an aft cabin, resulting in a 33-footer with two sleeping cabins – an almost unheard of concept in 1973 –full-beam heads and spacious galley.
What’s more, her performance under sail was more than adequate for cruising.
Finally, here was a yacht that all the family could enjoy.
Continues below…

What makes a boat seaworthy?
What characteristics make a yacht fit for purpose? Duncan Kent explores the meaning of 'seaworthy' and how hull design and…

How boat design is evolving
Will Bruton looks at the latest trends and innovations shaping the boats we sail

How keel type affects performance
James Jermain looks at the main keel types, their typical performance and the pros and cons of each

Boat handling: How to use your yacht’s hull shape to your advantage
Whether you have a long keel or twin keel rudders, there will be pros and cons when it comes to…
Nicholson 32

Credit: Genevieve Leaper
Charles Nicholson was a giant of the wooden boat era but one of his last designs – created with his son Peter – was a pioneering fibreglass boat that would become an enduring classic.
With its long keel and heavy displacement, the Nicholson 32 is in many ways a wooden boat built in fibreglass – and indeed the design was based on Nicholson’s South Coast One Design.
From 1966 to 1977, the ‘Nic 32’ went through 11 variations.

Credit: Hallberg-Rassy
In the beginning there was… the Rasmus 35. This was the first yacht built by the company that would become Hallberg-Rassy and which would eventually build more than 9,000 boats.
The Rasmus 35, designed by Olle Enderlein, was a conservative design, featuring a centre cockpit, long keel and well-appointed accommodation.
Some 760 boats were built between 1967 and 1978.

Credit: Larry & Lin Pardey
Lyle Hess was ahead of his time when he designed Renegade in 1949.
Despite winning the Newport to Ensenada race, the 25ft wooden cutter went largely unnoticed.
Hess had to build bridges for 15 years before Larry Pardey asked him to design the 24ft Seraffyn , closely based on Renegade ’s lines but with a Bermudan rig.
Pardey’s subsequent voyages around the world cemented Hess’s reputation and success of the Renegade design.

Would the Rustler 36 make it on your best small sailing boat list? Credit: Rustler Yachts
Six out of 18 entries for the 2018 Golden Globe Race (GGR) were Rustler 36s, with the top three places all going to Rustler 36 skippers.
It was a fantastic endorsement for a long-keel yacht designed by Holman & Pye 40 years before.
Expect to see more Rustler 36s in the 2022 edition of the GGR!

It was Ted Heath who first brought the S&S 34 to prominence with his boat Morning Cloud .
In 1969 the yacht won the Sydney to Hobart Race, despite being one of the smallest boats in the race.
Other epic S&S 34 voyages include the first ever single-handed double circumnavigation by Jon Sanders in 1981

Credit: Colin Work
The Contessa 32 might seem an impossible boat to improve upon, but that’s what her designer David Sadler attempted to do in 1979 with the launch of the Sadler 32 .
That was followed two years later by the Sadler 29 , a tidy little boat that managed to pack in six berths in a comfortable open-plan interior.
The boat was billed as ‘unsinkable’, with a double-skinned hull separated by closed cell foam buoyancy.
What’s more, it was fast, notching up to 12 knots.

Credit: Dick Durham/Yachting Monthly
Another modern take on the Contessa theme was the Sigma 33, designed by David Thomas in 1979.
A modern underwater body combined with greater beam and higher freeboard produced a faster boat with greater accommodation.
And, like the Contessa, the Sigma 33 earned its stripes at the 1979 Fastnet, when two of the boats survived to tell the tale.
A lively one-design fleet soon developed on the Solent which is still active to this day.

A replica of Joshua Slocum’s Spray . Credit: Alamy Stock Photo
The boat Joshua Slocum used for his first singlehanded circumnavigation of the world wasn’t intended to sail much further than the Chesapeake Bay.
The 37ft Spray was a rotten old oyster sloop which a friend gave him and which he had to spend 13 months fixing up.
Yet this boxy little tub, with its over-optimistic clipper bow, not only took Slocum safely around the world but has spawned dozens of modern copies that have undertaken long ocean passages.

Credit: James Wharram Designs
What are boats for if not for dreaming? And James Wharram had big dreams.
First he sailed across the Atlantic on the 23ft 6in catamaran Tangaroa .
He then built the 40ft Rongo on the beach in Trinidad (with a little help from French legend Bernard Moitessier) and sailed back to the UK.
Then he drew the 34ft Tangaroa (based on Rongo ) for others to follow in his wake and sold 500 plans in 10 years.

Credit: Graham Snook/Yachting Monthly
The Twister was designed in a hurry.
Kim Holman wanted a boat at short notice for the 1963 season and, having had some success with his Stella design (based on the Folkboat), he rushed out a ‘knockabout cruising boat for the summer with some racing for fun’.
The result was a Bermudan sloop that proved nigh on unbeatable on the East Anglian circuit.
It proved to be Holman’s most popular design with more than 200 built.

Credit: Alamy Stock Photo
Laurent Giles’s design No15 was drawn in 1935 for a Guernsey solicitor who wanted ‘a boat that would spin on a sixpence and I could sail single-handed ’.
What the young Jack Giles gave him was a pretty transom-sterned cutter, with a nicely raked stem.
Despite being moderate in every way, the boat proved extremely able and was soon racking up long distances, including Humphrey Barton’s famous transatlantic crossing on Vertue XXXV in 1950.
Wanderer II and III

Credit: Thies Matzen
Eric and Susan Hiscock couldn’t afford a Vertue, so Laurent Giles designed a smaller, 21ft version for them which they named Wanderer II .
They were back a few years later, this time wanting a bigger version: the 30ft Wanderer III .
It was this boat they sailed around the world between 1952-55, writing articles and sailing books along the way.
In doing so, they introduced a whole generation of amateur sailors to the possibilities of long-distance cruising.
Westerly 22

The origins of Westerly Marine were incredibly modest.
Commander Denys Rayner started building plywood dinghies in the 1950s which morphed into a 22ft pocket cruiser called the Westcoaster.
Realising the potential of fibreglass, in 1963 he adapted the design to create the Westerly 22, an affordable cruising boat with bilge keels and a reverse sheer coachroof.
Some 332 boats were built to the design before it was relaunched as the Nomad (267 built).
Enjoyed reading 25 of the best small sailing boat designs?
A subscription to Yachting Monthly magazine costs around 40% less than the cover price .
Print and digital editions are available through Magazines Direct – where you can also find the latest deals .
YM is packed with information to help you get the most from your time on the water.
- Take your seamanship to the next level with tips, advice and skills from our experts
- Impartial in-depth reviews of the latest yachts and equipment
- Cruising guides to help you reach those dream destinations
Follow us on Facebook , Twitter and Instagram.
- 2024 BOAT BUYERS GUIDE
- Email Newsletters
- Boat of the Year
- 2024 Freshwater Boat and Gear Buyers Guide
- 2024 Boat Buyers Guide
- 2024 Water Sports Boat Buyers Guide
- 2023 Pontoon Boat Buyers Guide
- Cruising Boats
- Pontoon Boats
- Fishing Boats
- Personal Watercraft
- Water Sports
- Boat Walkthroughs
- What To Look For
- Best Marine Electronics & Technology
- Watersports Favorites Spring 2022
- Boating Lab
- Boating Safety
Six Amazing Boat Hull Designs
- By Dean Travis Clarke
- Updated: October 25, 2016
The American boating consumer bears a remarkable psychological profile when it comes to wants and needs.
A cursory glance at the lines of most boats proves that profiles haven’t changed dramatically over the past 60 or so years. Certainly, construction methods such as resin infusion and injection molding have altered business as usual, and ingredients have also changed to include all manner of space-age composites, epoxies, paints, computer mapping for engines that produces vastly greater horsepower from smaller blocks, and so on. Even propulsion has changed with the advent of pod drives and big outboards. But here’s the weird part: Any time a designer or builder introduces a model that looks significantly different, whether it is Euro-styled or functionally clunky, it fails. It doesn’t matter how well the boat performs, the typical boater rejects it because it doesn’t look like what he knows. We, as an enthusiast niche involving boats, are horribly set in our aesthetic ways.
Look at how well multihulls handle heavy seas. When it comes to seakeeping ability, efficiency and performance, the catamaran has a lot going for it, as anyone who happened to catch some of the most recent America’s Cup racing can attest. And yet, to date, production multihulls have enjoyed only moderate acceptance by boaters.
Here are six of the latest hull-design innovations and technologies being used elsewhere in the maritime world that we will likely never accept for our recreational boats — even though they all work well.
Wave-Piercing Hulls Most accounts cite wave-piercing technology as coming on the scene around the start of the 20th century. However, it has been employed as far back as the times of the Phoenicians and ancient Romans. The design concept consists of a bow with little buoyancy, a hull that slopes inward from the waterline and, ergo, a large reduction in wave-making resistance. While it works well in heavy seas, the drawbacks include reduced interior volume forward and a very wet ride because the waves come up and over the bow as a matter of course. Wave piercers fell out of favor for a period of time due to these same drawbacks but have recently enjoyed a resurgence of popularity because of their dramatic fuel-efficiency gains.
Stepped Hulls OK, this hull form has achieved a certain level of acceptance in our recreational boats, mostly in performance boats or offshore center consoles. But why isn’t it more popular? The stepped bottom has been around as a V-bottom refinement since at least 1912. Steps are grooves in the hull stretching outward from the keel to the chines. Most hulls sport one or two steps per side. And a vessel should really be capable of cruising in excess of about 30 knots for a stepped hull to be worthwhile. Steps work by allowing air to be “injected” against the running surface, breaking contact between part of the hull and the water, which in effect turns the running surface into numerous short, wide planes, rather than one long, narrow one.
How much the hull surface contacts the water directly determines the amount of drag a hull suffers. Steps (also called vents) decrease the amount of hull contacting the water (called the wetted surface), thereby decreasing drag, increasing speed for the same horsepower, and increasing fuel efficiency. It all sounds good. But steps also come with potential drawbacks. Though modern deep-V designs have enough deadrise to counteract the problem in most cases, stepped hulls have been known to suffer from transom slide in sharp turns at speed. They also require attention to loading and trim because the steps need the proper angle of attack to function correctly; they don’t offer an advantage in flat, calm water; and they require a special trailer.
Most owners of stepped-hull vessels are experienced and want to travel at high speeds in moderate to heavy seas, and/or achieve good economy and range. Yet to date, performance and center console builders aside, only Regal Boats, with its FasTrac hulls, and Formula have committed to using steps in production cruisers and sport boats.
Asymmetrical Twin Hulls This unique design concept comes from the drawing board of Larry Graf, the pioneer who put power catamarans on the map here in the U.S. when he founded Glacier Bay Boats in 1987. His new company, Aspen Powerboats, employs a cat design where one hull is narrower (35 percent) than the other. His patent calls it a Power Proa, and it relies on a single engine in only the wider of the two hulls. The hull shapes, alignment and placement compensate for the offset propulsion thrust, allowing the vessel to run straight and true. With only one set of running gear in the water, inherent appendage drag is reduced by 20 percent. Combined with the efficiency of the hull designs, overall fuel efficiency of the Aspen rises to an impressive 70 percent over monohulls of comparable size. Aspen won an award for the best 30- to 39-foot catamaran in the world in 2014.
SWATH A quick glance might lead you to believe that a SWATH (small waterplane area twin hull) vessel is a catamaran. And it is but only to the extent that it has two hulls in the water with a bridge across the top. But that’s where the hulls’ similarities end.
Consider a submarine. Once under the surface, it runs stable, with no roll or pitching from wave action. All that wave energy remains on the sea surface. That basically explains how a SWATH design functions.
If you’ve ever dived under a wave at the beach to avoid being smacked by it, you know that the water beneath the wave is calmer. SWATH minimizes a vessel’s volume where the water meets the air (which is where all the wave energy is at its peak). The bulk of the vessel’s displacement and buoyancy runs beneath the waves, affording amazing stability, even in big seas and at high speeds. Please think of high speeds as a relative term here, as this is not a planing hull. What SWATH does provide, however, are a wide, stable deck and unsurpassed ride quality, especially in rough seas.
Drawbacks to SWATH designs include the fact that each hull must be custom designed. Draft runs deeper than standard hulls (especially planing hulls). The underwater “torpedoes” providing buoyancy must run parallel to the water’s surface, which requires a fairly complex trim-control system. And the underside of the deck must be far enough above the sea surface to avoid waves slamming up into it. Finally, SWATH vessels cost more to design and build than conventional hulls.
Hydrofoils Once the strict province of commercial ferries and a few high-speed military vessels, the most recent America’s Cup has spurred hydrofoil acceptance to new heights. Will it catch on with powerboats?
The hydrofoil design acts exactly like an airplane wing, providing more lift than the drag coefficient the vessel produces, thereby lifting the entire hull out of the water. Only the hydrofoils remain in the water, unaffected by surface wave action. In fact, hydrofoils cut inherent resistance to zero while the hull is out of the water. In the case of power-driven boats, you still suffer drag from the propulsion system (prop, shaft or the like).
The most significant disadvantage to this system on recreational boats is definitely the deployment of the foils. Unless you want the added draft of these struts sticking down below your hull all the time, you must be able to extend and withdraw them — a complex engineering feat. There is at least one recreational powerboat employing hydrofoils: Twin Vee builds a catamaran with foils that don’t actually lift the hulls completely out of the water. It does improve fuel economy and ride stability nonetheless. Still, boats ride more smoothly in a sea and go much faster with hydrofoils. With the dramatic acceptance of this technology in sailing, is it only a matter of time before recreational powerboats incorporate foils into their designs?
Ulstein X-Bow The Norwegian Ulstein Group has been designing offshore vessels since 1917. Presently, it has the notoriety of creating the most advanced bow design in history. The Ulstein X-Bow looks like it might be upside down, but it’s proven itself in more than 100 offshore support vessels to date. The X-Bow allows higher speeds and smoother rides in even the worst seas. Gone are the slamming and vibration that occur when the bow of a ship drops off a wave. It functions better on all points of sea, and its lower hydrodynamic drag substantially decreases fuel consumption. The X-Bow has proven so successful that Ulstein is in the process of creating an X-Stern design now.
You won’t ever see this on small recreational boats, but you can nod knowingly when someone points one out on a mega-yacht in the near future.
- More: Boats
Boat Test: 2024 Highfield Sport 800
Boat test: 2024 boston whaler 210 vanatge, mercury racing unleashes new 60 apx outboard at dubai boat show, boat test: 2024 scarab jet 195 id, best marine flare guns & visual distress signals, honda announces the new seabrook boat line.
- Digital Edition
- Customer Service
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Use
- Cruising World
- Florida Travel + Life
- Sailing World
- Salt Water Sportsman
- Sport Fishing
- Wakeboarding
Many products featured on this site were editorially chosen. Boating may receive financial compensation for products purchased through this site.
Copyright © 2024 Boating. A Bonnier LLC Company . All rights reserved. Reproduction in whole or in part without permission is prohibited.

CLASSIC > 100'
Dating back to 1987, the Hoek range of classic yachts consists of custom-designed and custom-built projects developed in close partnership with owners. Ranging in size from 33 to 262 feet, these sloops, schooners and ketches all have their own distinctive interiors, sail plans and layouts. What all Hoek classics have in common is the way they combine a classic hull shape and above-water styling with a modern underwater configuration. The first designs with a wing keel and spade rudder were the 70-foot sloop Joss and the 70-foot ketch Kim; their unprecedented performance and manoeuvrability were seen as a true breakthrough in yachting. Hoek Design became the frontrunner in the ‘classic above/modern below’ approach to yachting. And, as shown by designs such as the 37 feet Wallynano and Athos (203 feet), a broad range and an ongoing commitment to perfection enable us to maintain a leading position to this day.
So with a perfectly good boat already on the shore at Tahoe and a few weeks all by myself, what else is a man supposed to do except start building a new boat? As it happened I tried my hand at rowing, and found it immensely calming – much like I’ve heard cycling described by its fans – an introvert’s dream. However the Mixer, at 12 feet and about 120 pounds, is a bit of hassle to get to the water. Worth it for sailing, but not for an impulse row. I also have an Intex inflatable kayak – 80 bucks of Amazon (I know, I could have built a lovely Michalak Toto , I missed that trick). The Intex kayak gets more use than anything. I even use it after work sometimes to go for a paddle in the lagoon at Foster City, CA. I leave it in my car, I can blow it up in seconds, carry it to the water, hop in, and paddle my way to inner Zen. As it happens, I went for a paddle this evening, because the bridge across the bay was jammed up and I needed a Zen-recharge before getting my traffic-on.
So how about combining those things? A boat I could row, or sail, and would be light enough to carry, to put on the top of my SUV, or inside my wife’s minivan. I do not want to deal with the DMV again this decade, so my vessel had to be small enough – less than 8 feet. So the choices: A plywood lapstrake tender, maybe an Oughtred design, a Michalak-designed dink (I already have the plans for Tween ), a nuthatch pram. I also have the plans for Storer’s Mk2 and Oz RV.
Long story short: the PDR is too big to carry, its just too wide. The prams are a shade ugly – not really my cup of tea. Lapstraking looks far too complicated for my video-game-generation attention span and physical skill levels. But Michalak - one of my all-time favorite human beings, by the way, and you can tell him that – happened to mention in his sales pitch for the Weevee that – and I quote: “I can't help but think that WeeVee was not suitable for sailing by anyone except the skateboard crowd.”
Well now you’re talking my language, Jim Michalak, I consider myself a firm member of the skateboard crowd (actually more of a snowboarder, but same thing). Anyway, with such a description as that, I was sold.
The hardest part about building a Michalak is waiting for unspeakably slow plan delivery mechanism – the mail carrier. Seriously, is this how everything used to happen? How did you cope without everything being digital? An 8 day wait is simply beyond my tolerance level. I used the Tween plans to start on the rudder and leeboard (both turned out to be a different size, never mind, they’ll work).
When the plans arrived, I started immediately. I got the plywood home on the top of my SUV, somewhat against relevant vehicle code. I had it marked out within the half hour, did a terrible job with the jigsaw holding the sheets on a thigh, at one point resting a lose end on my forehead. Skill – epoxy cures all – a few little wavy bits don’t matter (see why I didn’t tackle the lapstrake now?). Within the first evening I had all the major panels cut out and the framing on.
I’d already cut the gunnels out of two 10 foot 4x1s. Weevee has an awesome I-Beam gunnel which I love. Check out the duckworks page to see more. The next day, I put the pieces together – I wired in some parts, but mostly used up a roll of duct tape to hold it all together (nod to Storer for that tip – works well – I only used wire on two very highly-stressed parts).
I’d seen an episode of “How Its Made” about making CLC canoes, and I’d seen them apply a very neat bead of thickened epoxy straight onto a plywood joint – none of this “wetting out” nonsense. I copied them using a pastry bag (thanks wifey!) and very exceptionally happy with the results. The seams on my Mixer were a long, drawn out, incredibly messy affair taking a whole weekend. On the Weevee, about 1.5 hours. I used 1 inch fiberglass tape – because it was only 8 bucks a roll from Amazon – but I used two layers on all inside seams. Outside I used the fiberglass cloth leftover from the Mixer job (I had plenty left over because of a brain-fart in the whole yards-versus-feet affair).
Outside the hull I also didn’t wet out first – I put on the glass then drenched it in resin, smoothing it as best I could. It all turned out drippy and runny, but the glass was firmly on, the bits all attached together, and I was happy – only 4 evenings I think to this point. I think I had this goal of building it in less than 20 hours, to less than 100 dollars. The hull just squeaked in under that, the rig took a few hours longer (the rudder and leeboard took a day or so each, I think). However, I decided early on I wasn’t even going to bother trying to “fair” it. I spent about 35 hours on my Mixer purely on what I termed “sanding and fairing” in my log – time wasted in my opinion – it looks rough as hell close up – but the thing is, I don’t care in the slightest. I decided for this boat I wasn’t going to paint it, just varnish it, warts and all. It even has the pencil lines marking out the stations visible on the bottom. To me it just adds character.
I thought long and hard about adding bulkheads and decks. Michalak’s hand-wavy “use foam blocks when sailing to avoid swamping” gave me some mild nightmares. I just didn’t want to add all that extra weight, and void the whole point of the boat. Instead, I made some cleats out of excess gunnel material. I bought two very nice 55L dry bags. I bulk out the dry-bags with balloons, fasten them tight, and lash them into the bow and stern. I tried it in my backyard pool, it works well.
I took it out rowing, and found that I had forgotten to add the skeg. Every bodily movement, voluntary or otherwise, caused the boat to change direction. The leverage applied by the oars versus the drag on the water is laughable – the whole boat will pivot easily around a single powerful oar-stroke. I decided to push on to hanging the rudder, I couldn’t figure out an easy way of attaching the skeg straight, and having it on at an angle is basically a lifetime of regret in the waiting. I didn’t put a sink-weight on the rudder, since on the mixer it doesn’t always hold it down, instead I put a cleat on the side of the rudder and I’ll cleat it up or down with a single line.
The centerboard went on next – quite easy – except for the cut right through the gunnel. The leeboard can double as a rowing seat, but obviously not as a sailing seat. A wet bum is in my future. Although, I did buy a floating cushion to help.
I was originally going to use the old 12 foot mast from my Mixer with a 55 square foot leg-o-mutton sprit sail. But when I put the boat in my pool and slotted the mast in place, the weight of the mast pulled the whole boat over on its side. With my 60 pound eldest son acting as ballast, it balanced ok, so I was more or less ok with it. A recent capsize of my Mixer has knocked some sense into me though, so I switched strategy and I’m starting with a tiny 8 foot mast and 21 square foot leg-o-mutton sprit sail. Even the skateboard crowd have rudimentary learning capabilities when given adequate stimuli.
So there we are. It fits on my car, I can lift it up and carry it around easily – although when hoisted on my shoulder its just wide enough to clang on that bone on the outside of the ankle, which ruins my Zen somewhat. Due to its insane instability, coupled with the evil genius that it clearly is, as a pun on the design name and due to the fact that it looks like a giant bug, I’ve called it Doctor Weevil.
And now the screw-ups. I’m including this, because there are many folks like me who haven’t really got any discernible woodworking skills or training, but who could – and should – find the courage to give it a go anyway. Store-bought boats are too damn expensive, and its killing – or already killed – sailing. We need to fight back against this corporate growth-oriented profit-at-all-costs non-sense and educate people that with some effort, some determination and a little bit of peace and quiet, a person (man or woman, black or white, terrestrial or alien) can build a boat and have a great time on the water.
- I didn’t put the spreaders in during construction – I don’t know why not, I think I forget then couldn’t be bothered to backtrack. I also took the temp form outa step too early. The excuse for this was to get the seams neater. Its about 2 inches narrower than it should be. On the positive side, I did the neatest saw-cuts of my whole life when trimming down the bottom to fit.
- The mast partner hole in the bow pad was cut exactly one half-inch too far to the right. I don’t know how I did it, but I only noticed when I was squaring up the epoxy-covered, fiberglass-tape-goopy mess that holds the mast step in place. I couldn’t be bothered to backtrack and fix it, so I gooped it upright where it sat and lamented my mistake with a beer. I rationalize: the boat is called Doctor Weevil, you have to expect weird stuff like that.
- The force of the gunnels pulling outwards on the sides, right at the ends of the hull, pulled the outer layer of ply away from the core. I only noticed when I was varnishing. I pumped as much thickened epoxy into the gaps as I could, and assume its fine.
- I got medium-large amounts of epoxy resin on my arms and legs, gluing my luscious thick body hair into what looked like giant nose-booger-wipes. I did this the day before a rather important management meeting at which I had to appear sensible and make deep and thoughtful contributions about the strategy and direction of the business unit that I co-run. I only noticed the epoxy at lunch time (this is California, I wear shorts and a polo short every day). It wouldn’t come off at all. Well it would, but only with my actual skin, and I didn’t feel that deal was worth it. I didn’t mention it and neither did the executives. One can only give so much of a fuss about ones appearance when there’s a boat half built at home.

For Sailors, By Sailors
The latest events, creating a sustainable association, introducing the laser class.
Welcome to The Laser Class, established by concerned sailors with a desire to celebrate the iconic One-Design Laser boat and to reconstitute the original Laser Class as a world-class organization that represents and serves its community.
Join us today! Membership of the Association is free until 2022. You will also get a Members Card giving you access to exclusive discounts from our partners.
Sounds good? Join now!
- Latest News

Classic Yacht Register
* vessels in the registry are currently being updated, so some links are not active until the process is completed..

Classic Yacht Register of Heritage
The Classic Yacht Register of Heritage is a database of the worlds Vintage, Classic and Grand Prix (Spirit of Tradition) sailboats. The Registry includes surviving, and destroyed vessels, and inclusion is either by vessel’s historical significance, invitation or request.
The wonderful stories and racing histories of these magnificent craft are important to the overall valuation of each vessels historical record, so please provide as much information as possibly including any home videos that you may have.
Provenance (The Wall of Remembrance) – An important classification within each vessels profile that recognizes the dedicated stewardship, preservation, and celebrity of all the men and women that have cared for and sailed on these legendary vessels. All helping to preserve and add to the historical significance of these vessels for future generation to come.
Reunions – If you wish to be reunited with the vessel that you were once associated with, please let us know and we will do our best to reunite all for a special celebration. Please view the video “Banzai – A Celebration of Life” for one of our reunions. Banzai Reunion.
Wartime Registry of Civilian Sailing Vessels – Dedicated to the Men and Women of the Coastal Picket Patrol – “Semper Paratus,” where civilian sailing vessels and their civilian crews were commissioned into service to defend the front lines of American and European Shores. Wartime Registry.
Related posts:
- SSL Finals – Photo finish
- Tropical Storm Florence Rescue Efforts
- Palm Beach Boat Show – It’s a wrap
- Boats Removed from Honolulu, Falls of Clyde Remains
Leave a Comment Cancel
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Email Address:
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .

- Find A School
- Certifications
- North U Sail Trim
- Inside Sailing with Peter Isler
- Docking Made Easy
- Study Quizzes
- Bite-sized Lessons
- Fun Quizzes
- Sailing Challenge
ASA Sailing Schools in California
Directory of American Sailing Association sailing schools located in the state of California where you can take beginning to advanced sailing lessons.
California has been divided into the following regions
Northern California
Southern california, afterguard sailing academy oakland, northern california, (510) 535-1954 afterguard.net.

San Francisco Bay is the best place in the world to learn to sail. We do not have make up – it is all here. So the place is fantastic as a general learning location. Our school has two locations to sail from. Oakland Estuary has wind from each of two shores year round plus is protected from the higher winds of weather and seasons. Smooth flat waters of a Riviera zone to start for all intro courses up through ASA-101. Then our classes venture out to the Central SF Bay. By mid ASA level we leave from Treasure Island …
More Information
Delta Sailing School Isleton, Northern California
(916) 966-1855 deltasailingschool.com.

Delta Sailing School offers classes and club membership in the beautiful, laid back, natural environment of the spectacular California Delta. With over 1,000 miles of waterway, we have lots of space for sailing and enjoying this peaceful gem that not too many people have discovered yet. We are convenient to Sacramento, the Foothills, the Valley and the San Francisco Bay Area. Learn to sail in steady winds and warm temperatures. Our instructors are enthusiastic and supportive, professional, experienced and fun. They love to teach sailing, and it shows! Our Basic Keelboat Class is limited to four students giving each person …
Modern Sailing School & Club Sausalito, Northern California
(415) 331-8250 modernsailing.com.

Since 1983, Modern Sailing School & Club has been introducing people to sailing from our headquarters in Sausalito, California. Even if you have never set foot on a boat, we can teach you everything you need to know to build a strong foundation in this rewarding and life long sport.
Modern Sailing School & Club Berkeley, Northern California
Our East Bay location at the Berkeley Marina is situated at the end of “The Slot,” the center of action in San Francisco Bay’s famous wind patterns. Unique to our Berkeley location, our fleet of nimble and sporty J/24s and J/80s provide you with the option of taking your first courses on either the Sportboat or the Cruising Boat learning path.
Monterey Peninsula Yacht Club Monterey, Northern California
(831) 372-9686 www.mpyc.org.

Pacific Sail Santa Cruz, Northern California
(831) 423-7245 www.pacificsail.com.

Pacific Yachting & Sailing is a premiere Sailing School located in Santa Cruz, California. We are one of the only schools in Northern California located on the Monterey Bay and Pacific Ocean. We also offer a fleet of 14 sailing yachts from 28-46 feet for Bareboat Charter, Instruction, Skippered Charters and Team Building Regattas. Our knowledgeable and supportive Captains will provide you with the education needed to experience the ultimate pleasure and respect for sailing on the Pacific Ocean and other locations, worldwide. All of our instructors are US Coast Guard licensed American Sailing Association (ASA) certification. They all have …
Sail Monterey Monterey, Northern California
(831) 372-7245 montereysailing.com.

Sail Monterey is the only full service sailing charter, sailing school, and rental business in Monterey. Learn to sail in the Monterey Bay National Marine Sanctuary! Our 8-12 knot prevailing winds from the Northwest make the Monterey Bay an ideal place to start your sailing adventure!
SailTime – San Francisco Emeryville, Northern California
(415) 869-2861 www.sailtime.com.

Hi! I am Captain Lisa of SailTime San Francisco Bay. Sailing has been my passion ever since I can remember back to when I was 7 years old on a Sunfish with my father and the family dog! I spent many years sailing catamarans before I got serious and started sailing bigger boats. Along the way I took classes, read, studied and did a lot of sailing. The excellent training I have received both with an instructor and with on water experience has made me the confident sailor that I am today. Never stop learning or sailing! I was a …
Spinnaker Sailing Redwood City, Northern California
650-363-1390 spinnakersailing.com.

Spinnaker Sailing in Redwood City is the perfect sailing club providing, sailing instruction and sailing activities for those living on the San Francisco Peninsula, South Bay and East Bay locations. Students who graduate from Spinnaker Sailing School not only received the internationally recognized certification from ASA but the confidence to sail anywhere in the world.
Spinnaker Sailing – San Francisco San Francisco, Northern California
(415) 543-7333 www.spinnaker-sailing.com.

Spinnaker Sailing has been in business for 35 years. and is located in one of the Best Marinas on the West Coast, South Beach Harbor. This location is perfect as the breeze is fresh, the water is flat and it’s only 3 minutes from the boats berth to our teaching grounds…no long channels.
Stillwater Yacht Club Pebble Beach, Northern California
(559) 917-0559 www.sycpb.org.
Stillwater Yacht Club currently owns two Santana 22s, three FJs, Laser Picos, stand-up paddle boards and five Kayaks for our adult members to enjoy free of cost. Lessons are available by appointment at a nominal fee. Members may take the boats out on Carmel Bay upon demonstrating competent sailing skills. One Santana 22 is berthed in Monterey Harbor and use involves additional fees to offset slip expenses. Stillwater Yacht Club is a certified American Sailing Association school, qualifying sailors for a certificate in basic keelboat operation.
Tradewinds Sailing School & Club Richmond, Northern California
(510) 232-7999 www.tradewindssailing.com.

Tradewinds Sailing School has a program for sailors at any level who are serious about gaining the foundation knowledge of sailing and continuing on to become a competent sailor.
Aventura Sailing Academy Dana Point, Southern California
(949) 493-9493 aventurasailing.com.

Aventura Sailing Academy is Dana Point Harbor’s Premier Sailing Club and Academy. For over 44 years we have been successfully teaching students, from the beginner to the advanced. We are a West Coast leader in producing well trained Sailors.
USCG Master Class 100T Captain Ric Dahlin (Director of Academy) is also a Collegiate level sailing instructor, and as a professional educator, Aventura’s classroom and lectures have been providing “best in class” sailing instruction with top results. All of our Certified ASA instructors are friendly and dedicated to your sailing instruction. Aventura Academy’s classes are challenging, fun and engaging but most importantly highly effective.
Blue Pacific Yachting Marina del Rey, Southern California
(310) 305-7245 bluepacificyachting.com.

Let Blue Pacific Yachting help you realize the joys of sailing. Learn to sail in a safe and supportive environment under the expert guidance of our certified instructors. Students gain hands-on experience and acquire the knowledge and confidence to sail aboard a modern, mid-sized, fully-equipped yacht.
Bluewater Sailing Marina del Rey, Southern California
(310) 823-5545 bluewatersailing.com.

Sailing lessons in Marina del Rey, the Pacific Ocean and beyond. In addition to our ASA courses, we offer year-round innovative sailing possibilities that are tons of fun with many opportunities to get out on the water and meet others in our vast community of sailors with all levels of experience.
California Sailing Cooperative Marina del Rey, Southern California
(909) 861-5673 www.californiasailingcoop.org.

California Sailing Cooperative (CSC), founded in 1994, is a non-profit club and school offering comprehensive sailing instruction, including ASA certifications, at an affordable cost on a well maintained Catalina 36. The teaching team, headed by Training Director Capt. Charlie Hentges, consisting of CSC’s ASA certified instructor/skippers and club mates, all of whom have completed at least 3 ASA courses. CSC earned the 2012 ASA “School of the Year” award.. CSC’s training philosophy permits members to work on their ASA certifications at their own comfort level, setting their own time table, thus combining expert instruction with at-sea experience. Every sail is …
Freeman Marine Institute Newport Beach, California
(916) 792-8478.
Freeman Marine Institute is devoted to excellence in teaching, learning, and helping students gain access to the amazing world of Sailing.
Harbor Sailboats San Diego, Southern California
(619) 291-9568 www.harborsailboats.com.

Harbor Sailboats is San Diego’s Premier Sailing Club, offering award winning instruction aboard Southern California’s most modern fleet of sailboats. Founded in 1969, Harbor Sailboats offers ASA sailing courses from Basic Keelboat to Advanced Coastal Cruising. In addition to offering the International Proficiency Certificate for European/Mediterranean chartering, Harbor Sailboats also offers learn to sail vacations. Spend the week aboard a luxurious sailing yacht while a certified instructor prepares you for a lifetime of confident sailing.
Learn to Sail San Diego San Diego, Southern California
(619) 316-6430 www.learntosailsandiego.com.

We offer live aboard and learn to sail courses in beautiful San Diego. All of our classes are private, so only you and your friends or family will be on board our Beneteau 36s7.
Leo Robbins Community Sailing Center Ventura, Southern California
(805) 658-4746 www.cityofventura.net.
Quality instruction, award winning instructors, affordable pricing and scheduling.
Los Angeles Yacht Club San Pedro, Southern California
(310) 831-1203 www.layc.org.

Offering beginning and advanced ASA certification courses, Los Angeles Yacht Club’s mission is to bring its sailing heritage and tradition to everyone. Our ASA certified instructors will teach you to sail our 22’ Capris safely and confidently over five, 4-hour lessons. Classes are offered Tuesday through Sunday in a group setting, with no more than three students per boat. Private and family lessons are also available.
Marina Sailing – Channel Islands Oxnard, Southern California
(805) 985-5219 www.marinasailing.com.

Marina Sailing is Southern California’s oldest and largest sailing charter and instruction company. Started in 1962, our six locations along the coast offer a wide range of boats from 22 to 50 feet, including monohulls, catamarans, and powerboats.
Marina Sailing – Long Beach Long Beach, Southern California
(562) 432-4672 www.marinasailing.com.

Marina Sailing – Marina del Rey Marina del Rey, Southern California
(310) 822-6617 www.marinasailing.com, marina sailing – newport beach newport beach, southern california, (949) 548-8900 www.marinasailing.com, marina sailing – redondo beach redondo beach, southern california, (310) 318-2772 www.marinasailing.com, marina sailing – san diego san diego, southern california, (619) 221-8286 www.marinasailing.com, naos yachts marina del rey, southern california, (310) 821-8446 naosyachts.com.

The Naos Yachts team consists of offshore, coastal and dinghy racers, as well as long distance cruisers. Our instructors are all ASA certified and we provide instruction on brand new Beneteau yachts and Lagoon catamarans.
Newport Beach Sailing School Newport Beach, Southern California
(949) 209-9931 www.newportbeachsail.com.

The Newport Beach Sailing School is unique in that we specialize in private and semi-private sailing instruction off the coast of Southern California. Our motto is ‘The best value in private sailing lessons.’ We are dedicated to providing highly personalized instruction, and the classes are scheduled according to your availability.
Redondo Beach Recreation Redondo Beach, Southern California
(310) 318-0610 ext. 3399 www.redondo.org, sail channel islands oxnard, southern california, (805) 750-7828 www.sailchannelislands.com.

COASTAL CRUISING AND BAREBOAT TRAINING in Channel Islands NationalPark. That’s what I do. That and cruises for up to four people just for the fun of it. In terms of ASA qualifications, I only do private lessons – just you and your crew. And if your crew is a spouse who just needs a vacation, that’s fine, too.
San Luis Yacht Club Avila Beach, California
(805) 546-3132.

Learn to sail in the San Luis Yacht Club flagship, the 30 ft. Bermuda sloop “Second Wind”, on beautiful Avila Bay, California. These classes bring participants, ages 16 and up, to ASA 101 (beginner level) standard. Classes cover basic sailing theory, parts of the boat, crew communications, tacking, jibing, sail trim, crew overboard recovery, safety and more. Fee includes a textbook and tests. Upon successful completion of class and passing the ASA 101 Exam, an additional $39 will be collected by the instructor for students wishing to get certified. The certificate is internationally recognized and can be used to help …
Santa Barbara Sailing Center Santa Barbara, Southern California
(805) 962-2826 www.sbsail.com.

The Santa Barbara Sailing Center offers award winning instruction in one of the finest training locations in the world. We average 10-15 knots of wind right outside The Santa Barbara Harbor for our ASA 101 & 103 courses. During our 104 & 106 courses, we average 20-25 knots of wind at The Channel Islands National Park and Marine Sanctuary. Training Vessels include Catalina 22’s, 28’s, 32’s, 36’s, 42’s & 50’s. All instructors all USCG licensed & ASA certified. We offer world renowned Corporate Regattas which emphasizes Team Building.
Seaforth Boat Rentals San Diego, Southern California
(888) 834-2628 www.seaforthboatrental.com.
At Seaforth Boater Education we offer sailing classes and lessons for every level of sailor, from beginner to advanced. If you are just starting out, we offer the Amercian Sailing Association’s Basic Keelboat Sailing course designed to teach the beginner the fundamentals of sailing. If you have been sailing for a while in the bays and are interested in getting more out of your sailing, take a look at our 3-Day or 4-Day ASA 103/104 Combo Class where you can learn more advanced coastal sailing techniques. All of our classes are designed to allow you to get the most out …
South Bay Sailing Redondo Beach, Southern California
(310) 937-3180 www.southbaysailing.com.
South Bay Sailing has been offering a wide range American Sailing Association Certification Courses, Charters, Rentals, Youth Lessons/Camps, Social Events and much more since 2005. Learn basic through advanced sailing skills or just enjoy the day on the water with a twist of performance aboard one of our J/80s or our Farr 40. And why not hold your next team building regatta on actual race boats! No matter what sailing option you choose, our ASA certified sailing instructors will have you on the open ocean minutes after your departure. South Bay Sailing has always prided itself in making sailing accessible …
West Coast Multihulls San Diego, Southern California
(619) 365-4326 charter-catamaran.com.

Catamarans and trimarans are not just another income stream for West Coast Multihulls, they are our passion. If your sailing goal is to become a proficient confident multihull sailor, we are the school for you. Our staff and Instructors have decades of multihull, training, sailing and live-aboard experience to draw from and share with you. We sail out of beautiful San Diego, CA with sailing classes offered year-round from the Sunroad Resort Marina. San Diego enjoys a comfortable, moderate climate with light to moderate winds throughout the year. We are the only catamaran and trimaran specialists in California. West Coast …

- Learn To Sail
- Mobile Apps
- Online Courses
- Upcoming Courses
- Sailor Resources
- ASA Log Book
- Bite Sized Lessons
- Knots Made Easy
- Catamaran Challenge
- Sailing Vacations
- Sailing Cruises
- Charter Resources
- International Proficiency Certificate
- Find A Charter
- All Articles
- Sailing Tips
- Sailing Terms
- Destinations
- Environmental
- Initiatives
- Instructor Resources
- Become An Instructor
- Become An ASA School
- Member / Instructor Login
- Affiliate Login

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Xc45 was the first cruising yacht X-Yachts ever built, and designed to give the same X-Yachts sailing experience for sailors who'd spent years racing 30/40-footer X- and IMX designs, but in ...
After a 30 year absence, a veteran marine journalist returns to the US Sailboat Show and discovers the many changes in cruising boat design and construction. By Dan Spurr. Updated: June 10, 2020. The X-Yachts 46 displays the wide beam, twin wheels and open transom that define many 2020 models. Jon Whittle.
The 90 metre Athena, built by Royal Huisman, is inspired by classic schooner yachts, but has a modern twist.This modernity is appreciated in Athena's sail plan and rig, which benefits from in-mast and in-boom furling.. The three-masted schooner Athena flies some 2,500 square metres of sail, which can be set and stowed at just a press of a button(s) thanks to the 55 Rondal captive winches on board.
Ulstein Verft's 290-Foot Motor Yacht 'Olivia O'. Olivia O is a yacht that means business. Robust in every way, she is owned by a commercial shipping magnate with a love for industrial boats ...
8. Svea. Svea, the newest addition to the now nine-strong J Class fleet, is one of the most outstanding new yachts of modern times - a harmonious meeting of historic and modern design; a blend ...
To highlight how these boat design principles play out, Practical Sailor looks at classic sailboats such as the Bill Shaw-designed Pearson 32, Ericson 41, Valiant 40, and Peterson 44, and compares their keel/sail ratios and lead values to more modern sailboat designs such as the Catalina, Hunter, Tartan, and Beneteau. ****.
Website of Berckemeyer Yacht Design. Individual modern and classic sailing yachts... dreams get true! CURRENT BM YACHTS. BM23 classic; BM24 classic; WOY 26; LA28 daysail; BM30 Bristol; ... BM YACHTS. BM31 Miura2; BM32 classic; BM34 Cape; BM35 Bristol; GERMAN 39; BM39 Artic; BM39 Bristol;
Design: Stephens Waring Yacht Design ... Video: See inside 9 of the most amazing modern sailing superyachts. Lagoon 46 first look: Updating this catamaran is a significant step for the yard.
Award winning 'modern-classic' yacht design. Custom designed motor and sailing yachts for blue water. Messing about in boats since 1975. Online Since 1997. ... Modern Classic Yacht Design. My specialty is custom yacht design, from concept to launch. Strength, safety, comfort, performance, style, grace... the essential attributes of a yacht. ...
A 165-metre-long submarine, a tetrahedron-shaped hydrofoil and a vessel by Zaha Hadid feature in this roundup of yacht designs that have sought to disrupt the high-end boat industry.
There's some irony when it comes to looking at the hottest interior design trends for custom sailing yachts: much of the inspiration for today's designs draw from the past - combined with modern innovation. Interior designs that emphasize simplicity, balance, and natural materials are hardly revolutionary. Quite the opposite.
Some of the bigger names pushing the realms of possibility in this segment, include Greenline, Silent Yachts, Candela Boats and newcomer Alva Yachts (a new builder making waves in electric-powered catamarans, powerboats and sailing vessels). As an early adopter Greenline Yachts has a wide range of hybrid boats and yachts currently on the market ...
Modern yacht design has evolved tremendously since the world's first 'superyacht', Cleopatra's Barge, emerged from Retire Becket's shipyard in Salem, Massachusetts, to gasps of admiration from the awe-struck crowds that had gathered on the docks. The ... Sail yachts were swapped for steam yachts in the mid 19th century by the wealthy ...
The 111-foot Geist, launched last July by Spirit, is the largest single-masted wooden sailing yacht built in the UK since the 1930s, when the America's Cup yacht Shamrock V ruled the seas. But ...
The designs are made with the latest technology giving the yachts very good and easy to handle sailing characteristics. The modern keels in fin shape can be even upgraded for more performance to a bulb shaped deep draft keel making them fast and easily manouvrable. The modern technology can also be found in the electric package for the winches ...
Sailing Yachts. CLASSIC 100' - 33' classic daysailer - 36' Josephine II - 38' Eagle 38 - 47' Elsa - 54' Eagle 54 - 55' Tintagel - 56' Bartelli II - 57' Jenny - 60' Schwanensee - 65' D'Oude Liefde ... Hoek Design modern yachts can be broadly separated into two groups. The contemporary styled designs such as Skipper, Aphrodite I, Aphrodite II and ...
Each British vessel took around 46,000 hours to build, 90,000 hours to design, 75- to 100 thousand hours to CNC machine, and weighs around 6,450 tonnes. The yachts also include 17,300 individual ...
Assent 's performance in the 1979 Fastnet Race makes the Contessa 32 a worth entry in the 25 best small sailing boat designs list. Credit: Nic Compton. Designed by David Sadler as a bigger alternative to the popular Contessa 26, the Contessa 32 was built by Jeremy Rogers in Lymington from 1970. The yacht's credentials were established when ...
The design concept consists of a bow with little buoyancy, a hull that slopes inward from the waterline and, ergo, a large reduction in wave-making resistance. While it works well in heavy seas, the drawbacks include reduced interior volume forward and a very wet ride because the waves come up and over the bow as a matter of course.
Dating back to 1987, the Hoek range of classic yachts consists of custom-designed and custom-built projects developed in close partnership with owners. Ranging in size from 33 to 262 feet, these sloops, schooners and ketches all have their own distinctive interiors, sail plans and layouts.
Michalak Weevee Build. by Tom Geary - Fremont, California - USA. My wife and kids go to the family cabin in Tahoe every year for about 6 weeks - all of July and half of August. I stay at home like a good husband and father, working during the day and cleaning the house from top to bottom in the evening. Really though, I drink beer and watch ...
Welcome to The Laser Class, established by concerned sailors with a desire to celebrate the iconic One-Design Laser boat and to reconstitute the original Laser Class as a world-class organization that represents and serves its community. Join us today! Membership of the Association is free until 2022.
project info: project title: Boat-Building in Shichahai architecture: JieJie Studio location: Beijing, China lead architect: Guanyu Ming design team: Jincan Cao, Jiawei Li project area: 120 square ...
A modern yacht with the styling of a classic sailer this beautiful sailing yacht and technological wonder sleep 10 guests and boasts a media lounge, diving facilities with a decompression chamber. ... The boat, design number 822, was conceived by the then eighty-year-old William Fife III, alongside his nephew Robert Balderton Fife who had only ...
Pacific Yachting & Sailing is a premiere Sailing School located in Santa Cruz, California. We are one of the only schools in Northern California located on the Monterey Bay and Pacific Ocean. We also offer a fleet of 14 sailing yachts from 28-46 feet for Bareboat Charter, Instruction, Skippered Charters and Team Building Regattas.