The Only 50 Sailing Terms You'll Need To Know (With Pictures)
Ever get confused by all those odd sailing terms? Starboard, tack, jib… Well, no worries. In this article, I'll go over the most important sailing terms for beginners.
This is a great resource for beginning sailors that need an overview of the most important sailing terms without drowning in it . For a comprehensive list, check out this Wikipedia glossary of nautical terms . There are A LOT of nautical terms there. But no one in his or her right mind will read through that entire page (it has 48.434 words!). There are a lot of obscure words listed that no one really uses anyways. So in this article, I've filtered out the most important ones to get you up to speed quickly. I've also added pictures so you'll know what we're talking about.
Let's jump straight in. For the sake of good manners, I have categorized them by topic. If you are looking for a specific term, just ctrl+f your way directly to it.
Here are the only 50 sailing terms you'll need to know:


Orientation
Parts of the boat, parts related to sails, other terms.
...because it isn't as easy as 'left', 'right', 'front' and 'back'. No, no.
Port is the left side of the boat. It's as simple as that. I'm not entirely sure why don't they just call it 'left' these days. The name came to existence because centuries ago, you always docked your big boat with the harbor (port) being on the left side. And the word stuck with us till today.

Starboard is the right side of the boat. If in a car, you say 'look to your right', on a boat, you say 'look to the starboard'. Again, you might as well just call it 'right'. Oh, wait… you wouldn't seem as cool if you did. Alright, let's keep calling it starboard.

The bow is the front of the boat. The word likely comes from the Middle Dutch 'boech' (nowadays spelled 'boeg'). If you call it 'front' instead, you will get your message across just as well. But it won't get you the admiring looks from those around you.

Stern is the back of the boat. That is where you, as a captain, will spend most of your time. Whether you will force your crew to call it 'stern' or let them use the word 'back', like the dry land creatures they are, is up to you. After all, you are the captain.

The windward side of the boat is the side facing into the wind. So if the wind is coming from the right side, the windward side is on the right. Unlike some of the previous ones, this term actually makes sense - at times you need to talk about a direction not fixed in relation to the boat, but rather relative to the direction of the wind.

Leeward side of the boat is the lee side. If the wind is coming from the right side, the leeward side is on the left. Note that neither windward nor leeward specify the angle of the wind. Thus even if the wind was coming 20 degrees right off of the direction of the boat, so almost from the front, left would still be considered the leeward side.

Since there are gadgets and parts on the boat that you won't see anywhere else, it only makes sense they all have their own special name. You want to know these because unlike the direction terms where you can do with 'left' and 'right', you don't want to call a tiller 'that stick thing back there'.
Helm is the boat's steering wheel. In this case, I forgive those who came up with this name, since it is shorter than 'steering wheel' and thus saves valuable time that we can spend on sailing. Though I doubt linguistic economy was the reason.
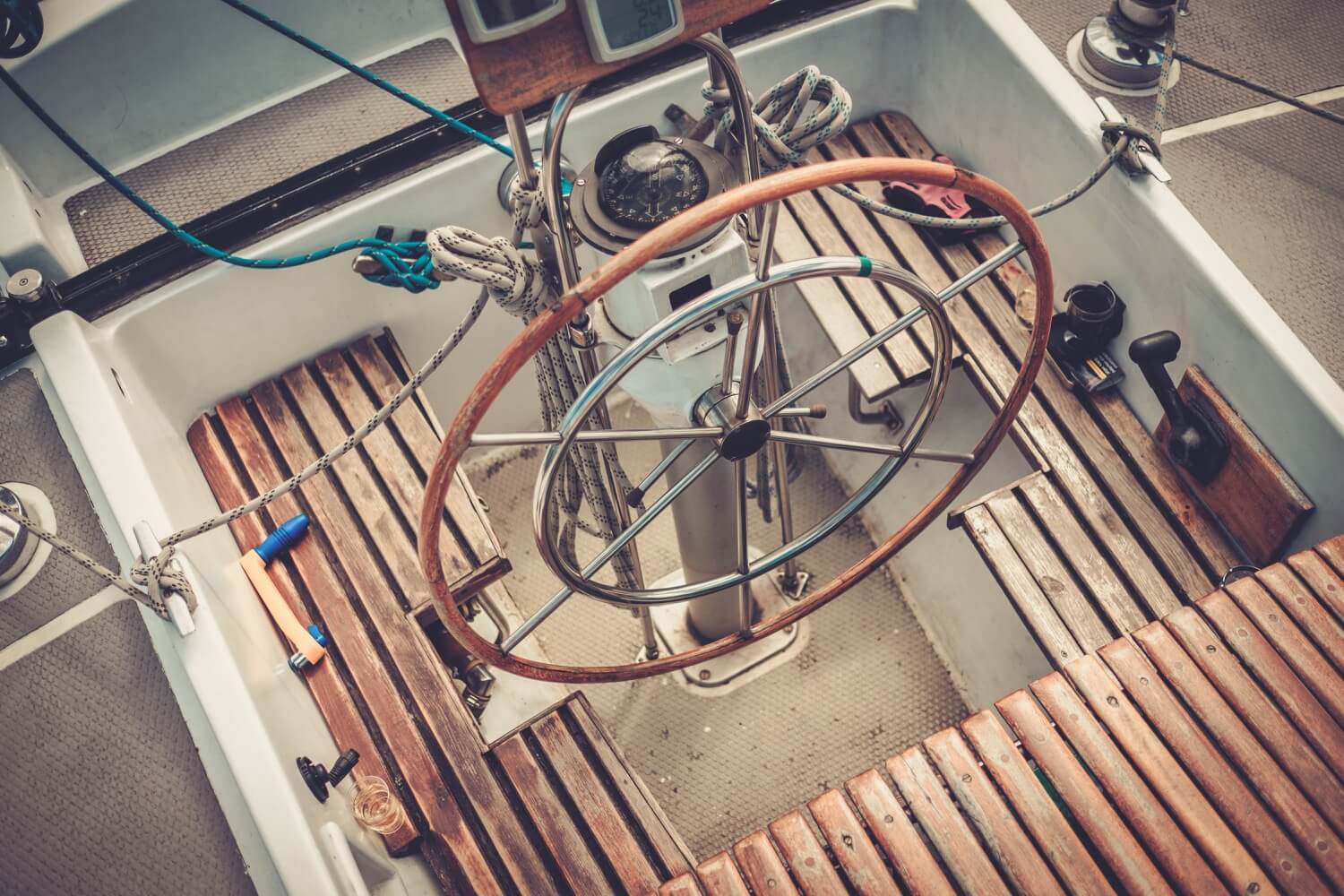

Tiller is the long stick that operates your boat's rudder. A steering stick, if you will. It has the same function as a helm does, but it is usually used on smaller boats, where a helm would take up too much space. Or by people who prefer it to a helm, since a tiller offers a bit more in terms of response.

The rudder is the long, flat piece of metal or wood that sits underwater below the back of your boat. Connected to a tiller or a helm, it is used to control the direction of your exciting voyage. By the way, since aerodynamics and hydrodynamics work in similar ways, a plane is also operated by a rudder. Though that one isn't underwater. Hopefully.

Hull is the boat's body. Whatever the shape or size, whether opened on top (like a dinghy) or closed by a deck, (like a traditional sailboat) it's all called a hull. Structures sitting on top of the deck, like a deck salon or cabins, aren't considered a part of the hull anymore.

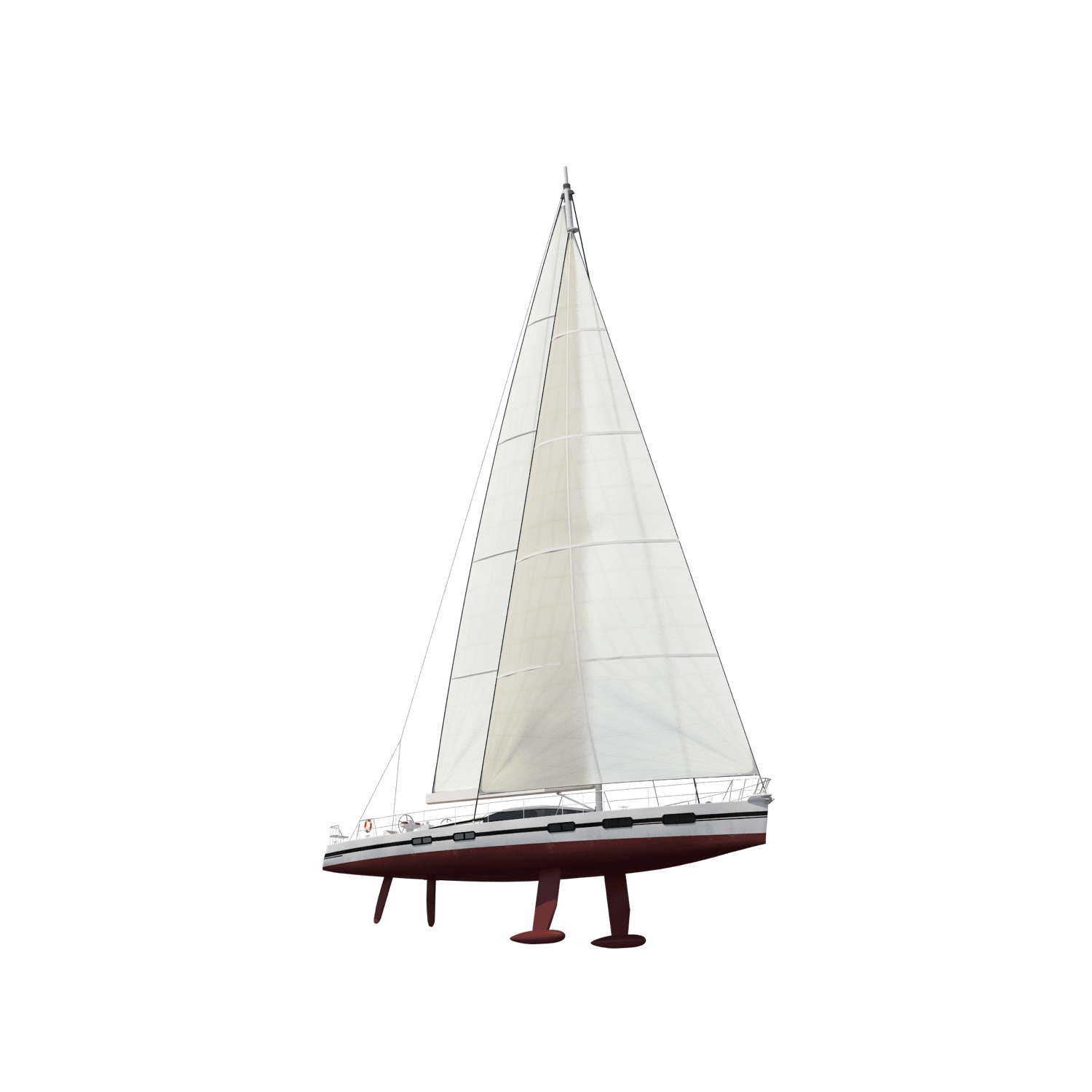
The keel is an underwater fin below the boat's belly. The sizes and shapes vary, sometimes it is relatively short and goes deep, (fin keel) sometimes it runs from the front all the way to the back (full keel or ballast keel). It is there mainly for stability and to help maintain forward direction when sailing.

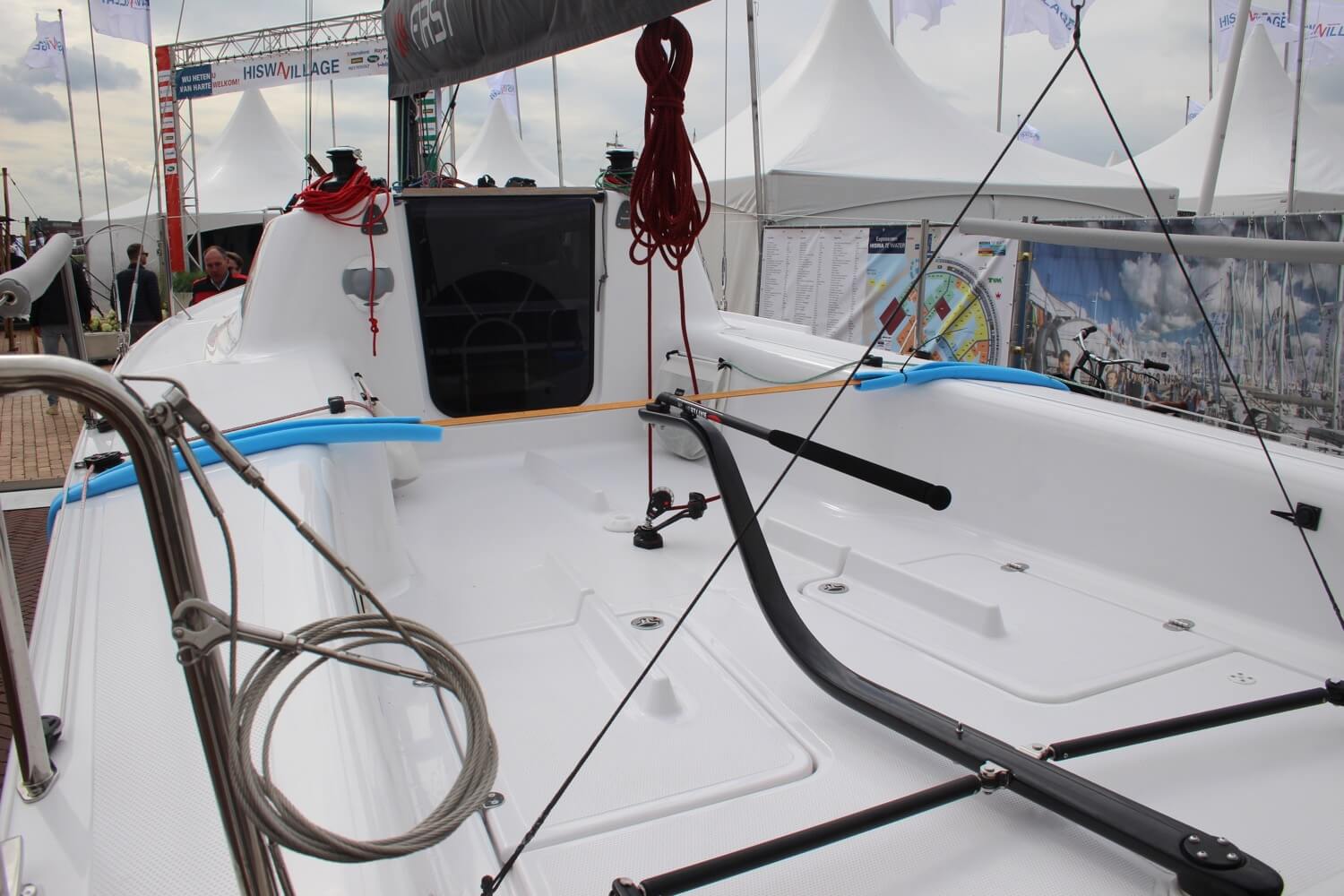
The cockpit is the area where a boat is operated from. On sailboats, it is usually in the back and it is an open area without a roof, though this varies. You will find the rudder control and winches there. In 'smaller' (below 70 ft or so) sailboats this area oftentimes doubles as a deck dining place with a table and seating.
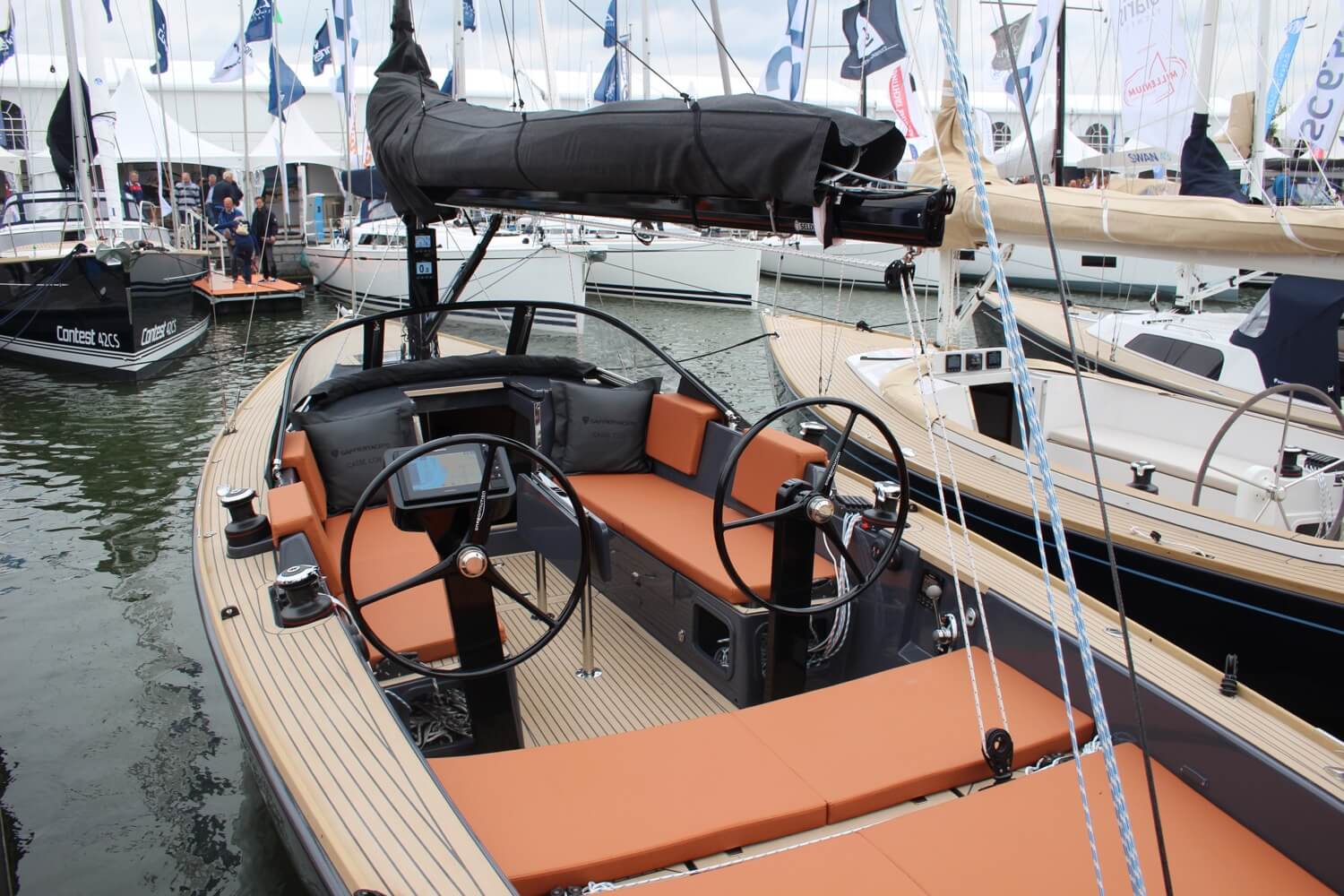

The bimini is a sun roof or shade that is covers the cockpit, and is generally attached to a steel frame which runs over the cockpit.
This is where things tend to get confusing. There are a whole lot of parts and a whole lot of names for them. It pays off for you and your crew to know them though, as during the stormier moments, you all want to be on the same boat (ha, ha) linguistically, as every second counts.
Lines are ropes. Not much more to add here. I suppose a 'line' sounds a bit fancier than a 'rope'. One thing this article will teach you is that if there is the slightest crack in the wall of your boat, linguistic elitism will leak its way in.

This one is quite self-explanatory. The mainsail is the main, largest sail of the boat, attached to the mast on the side and the boom at the bottom. It has a triangular shape and serves as the most important sail, the first one you should get acquainted with if you are just starting out.

The jib is the front sail of your boat, sometimes also called the genoa. That is as long as you are sailing on the traditional sloop - the classical two sail setup you see the most often. The jib is wrapped around the line that goes from the top of your mast to the boat's bow.

Spinnaker is the third type of sail you are the most likely to encounter on your travels. It goes in front of your boat and has a half balloon or kite-like shape. This is because it is constructed specifically for sailing downwind. Its purpose is to grab as much backwind as it can and drag your boat forward. It is not attached to the boat most of the time like the mainsail or the jib, instead, it is stored separately and used only when needed.

The mast is the tall, vertical pole that goes from the floor of your salon, through the deck, meters above your boat. All the sails are attached to it, also radars and lights, giving sailboats radio and visual visibility far greater than that of equally sized motorboats. Take that, ya noisy stinkies!
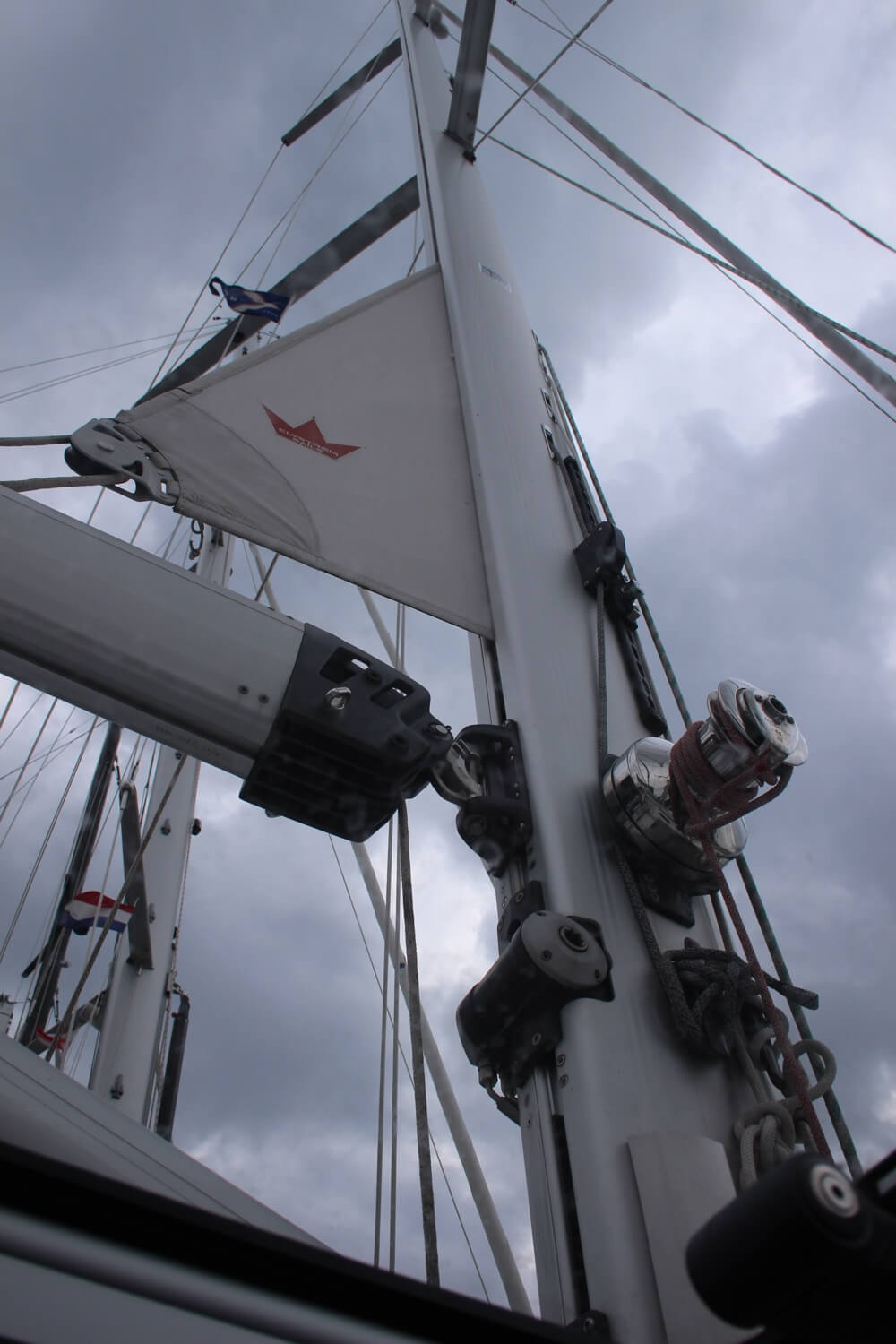

The boom is the horizontal pole right above the deck, attached to the mast at the right angle. The bottom of the mainsail is attached to it, it is used to determine its shape and direction. It is also where the mainsail is often stored, folded and covered with a protective sheet. The boom is also among the top causes of injuries on a sailboat, as in certain winds it tends to swing with force powerful enough to knock a few grown men overboard. Stay away from its reach at all times when under sail.
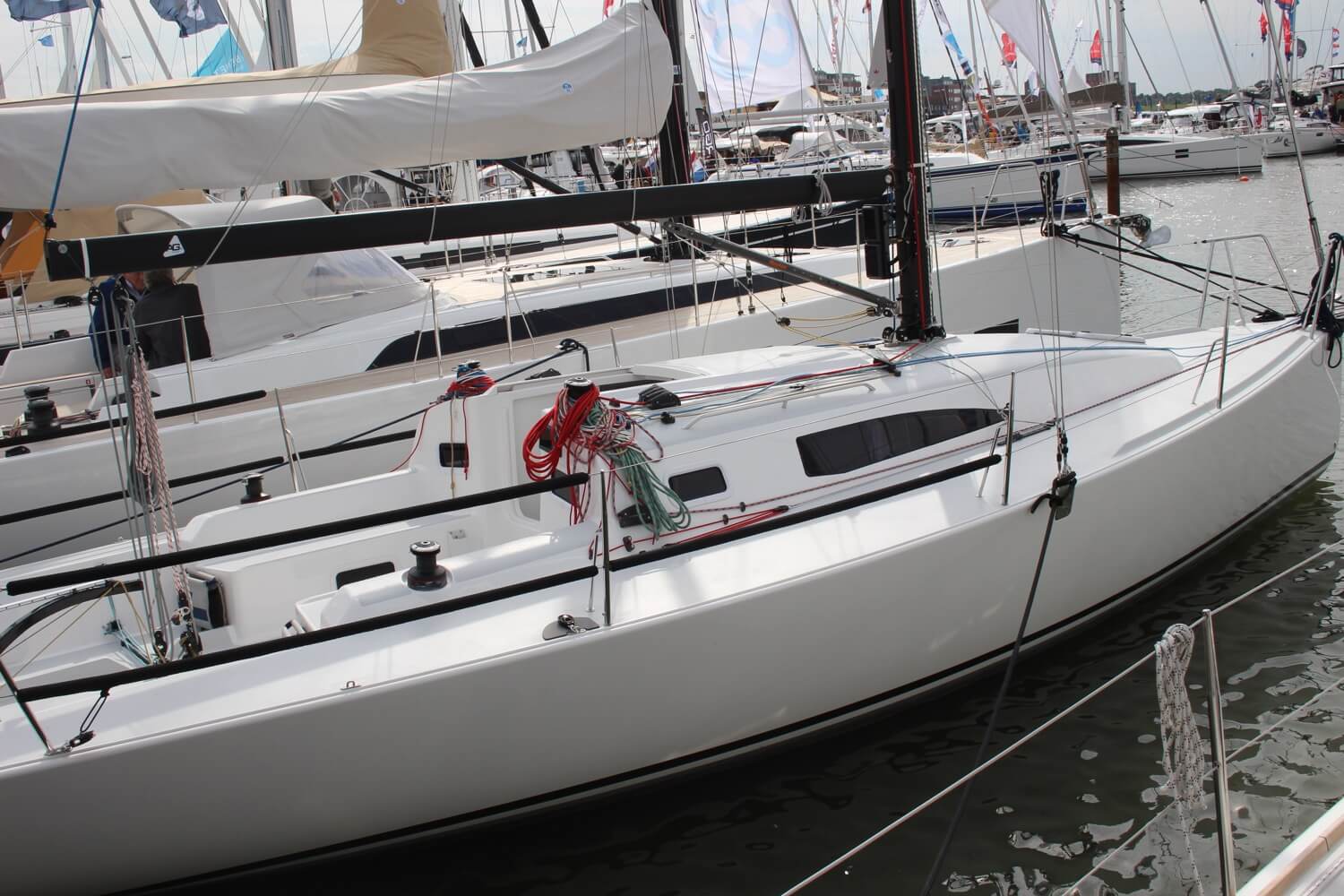

The forestay is the cable going from the top of the mast to the very front of the bow. It is there to hold the mast in place. Sometimes you will find people refer to it as the 'headstay'. It is often made of steel, so it is safe to hold on to it when you are pretending to be Jack on the bow of the Titanic's, the boat hits a wave and you lose your balance.
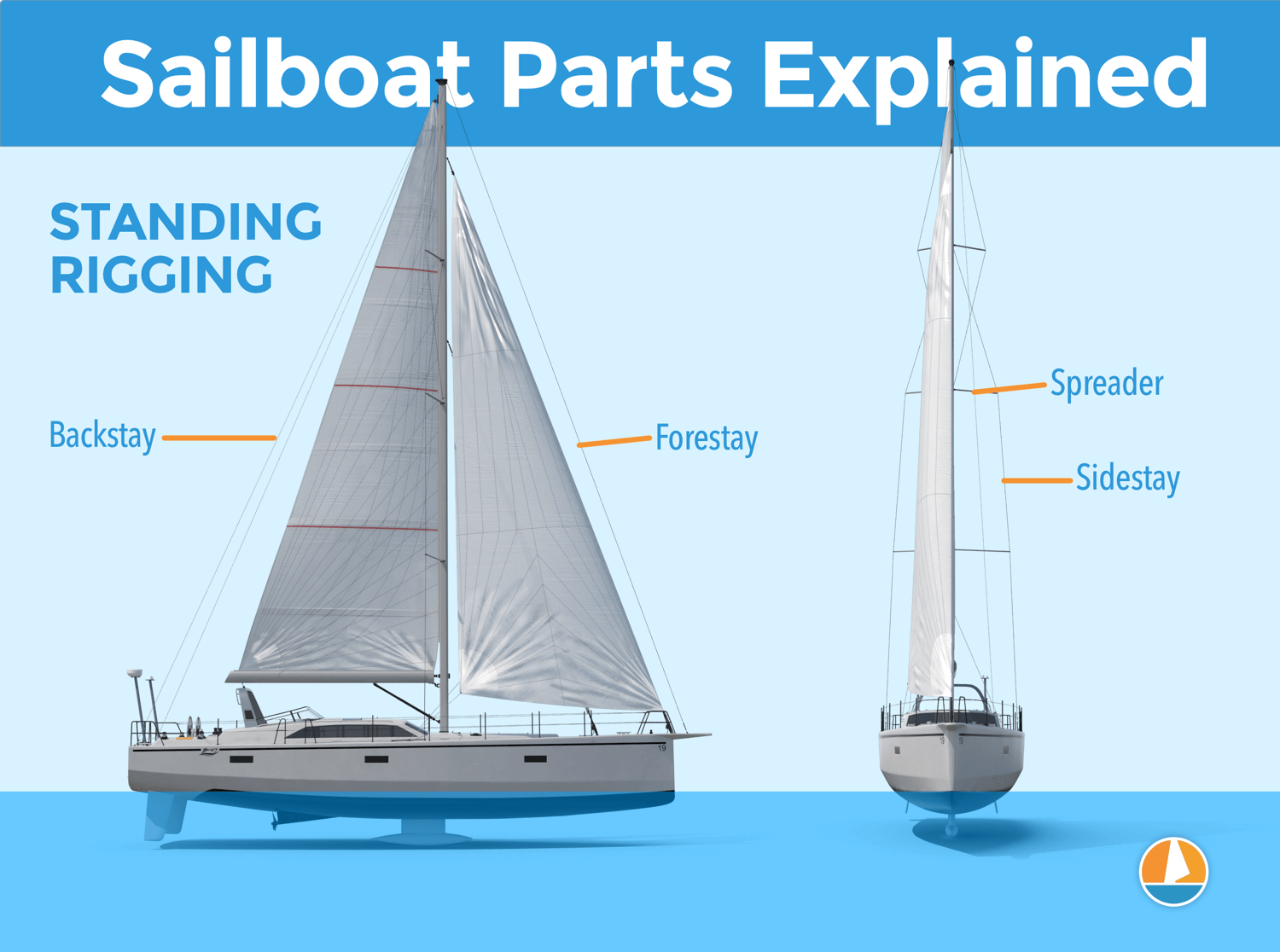
This diagram is from our guide on sailboat parts , which I really recommend for beginners. It walks you through all the most important sailboat parts in normal words.
The backstay is the cable going from the top of the mast to the very back of the boat. In many cases it is doubled at the bottom, each end attached to one corner of the back of the boat so that they don't interfere with space and provide more stability for the mast. Just as with forestay, these are made of steel.
Shrouds are the cables going from the top of the mast to the left and right side of the boat. Sometimes there are four, two on each side. Together with forestay and backstay, they make sure your mast withstands all the forces exerted on it when the wind pushes the sails.
The foot of a sail is its bottom edge. If you imagine a sail as a triangle, the base is called the foot. You probably won't use this term while sailing, but when researching proper sail trim, it is likely you will stumble upon it.
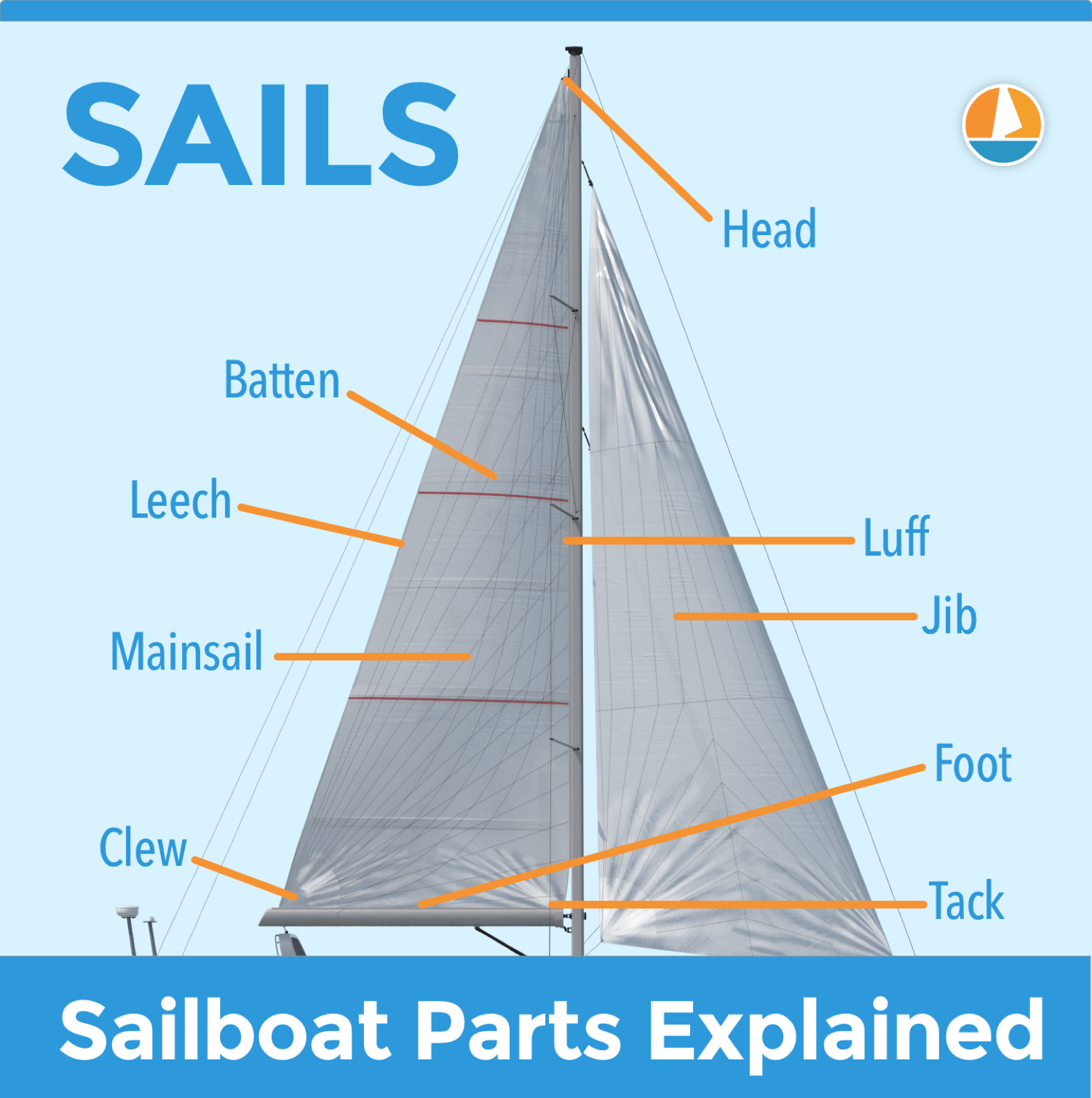
This diagram is again from our guide on sailboat parts , which I really recommend for beginners. If you're looking for a good starting point to learn your sailboat ins and outs, this article is perfect for you.
Leech of a sail is its back side edge. Thus it is the part closest to you when you are standing at the helm. Just as with the foot, this is a term quite often used when describing sail trimming techniques, since the shape of the leech determines the shape of the whole sail.
Luff of a sail is its front side edge. Thus the part the furthest from you when you are standing at the helm. For mainsail, it is the edge that is right next to the mast, for the foresail it is the edge right next to the forestay. Just as with foot and leech, the shape of these edges determines the overall shape of the sail so you will most likely encounter these terms in trimming lessons and tutorials.
The head of a sail is its top corner. On a traditional sloop, you will have the 'main head' and the 'jib head'. There is usually a reinforcing patch of some kind on these corners, as you will find a hole in them to which a line is attached.
It's also something else entirely, but more on that later ...
Halyard is the line attached to the sail head. On your boat, you will most likely have two. The 'main halyard' which is what you use to hoist your mainsail if it is folded on the boom, and the 'jib halyard' which holds the jib head up.
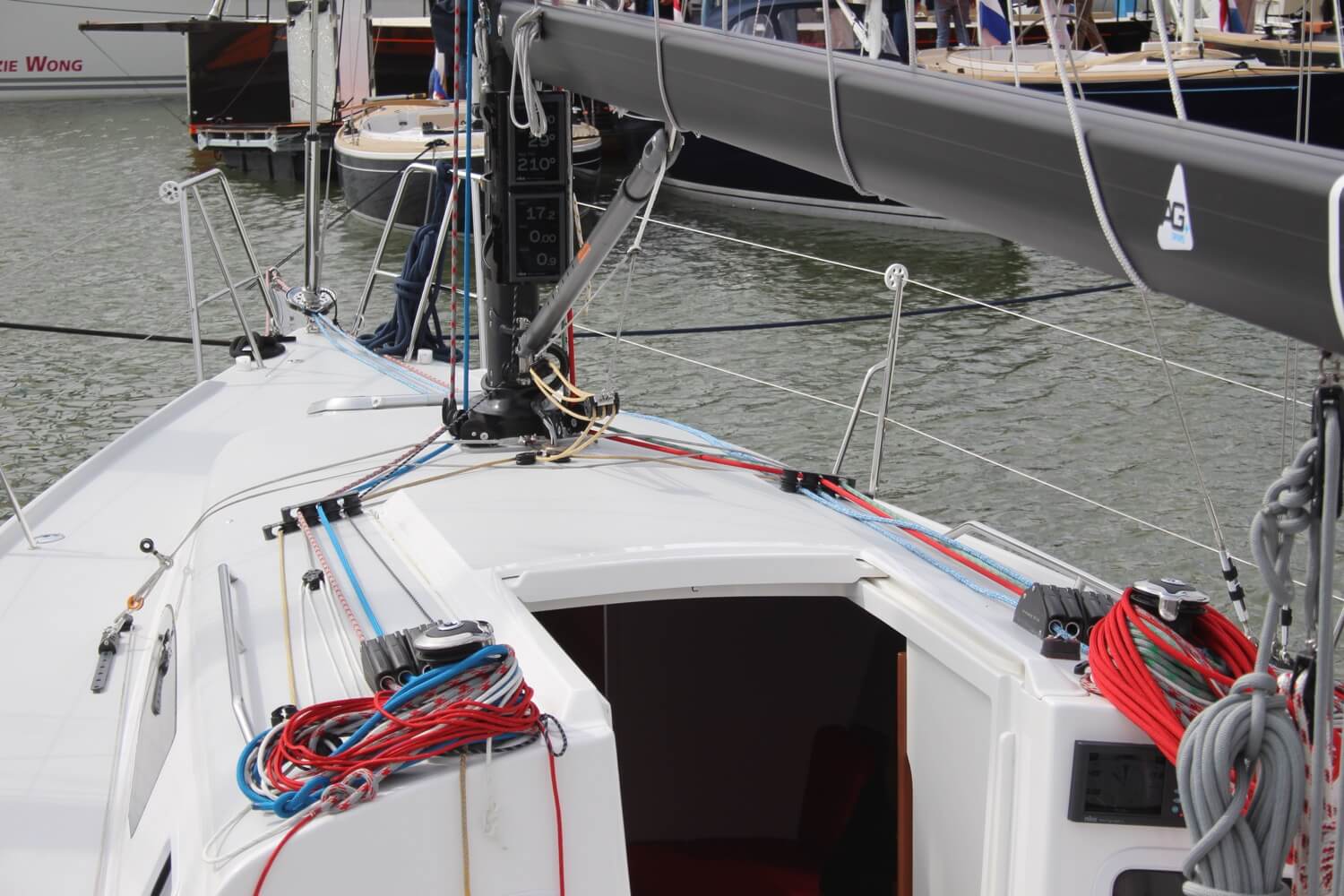

Clew of a sail is its back corner. The line attached to the 'main clew' will be used to hoist your mainsail if it is wrapped inside of the mast. The line attached to the 'jib clew' will be used to open the jib on most sailboats since jibs are most often wrapped around the luff.
Telltales are light, usually cotton or wool pieces of ropes attached to a sail, showing you the airflow around it. These are important because they help you determine if your trim is effective or not. Because of the material they are made of, you might sometimes encounter them being called 'woolies'.
Vang, or a 'boom vang' is a device pulling the boom down. This is important because it controls the tension of the mainsail, influencing its shape greatly. You won't find it on every boat though. Holiday cruisers often don't have it, as it is a piece of equipment focused on performance and thus not necessary for your average trip.
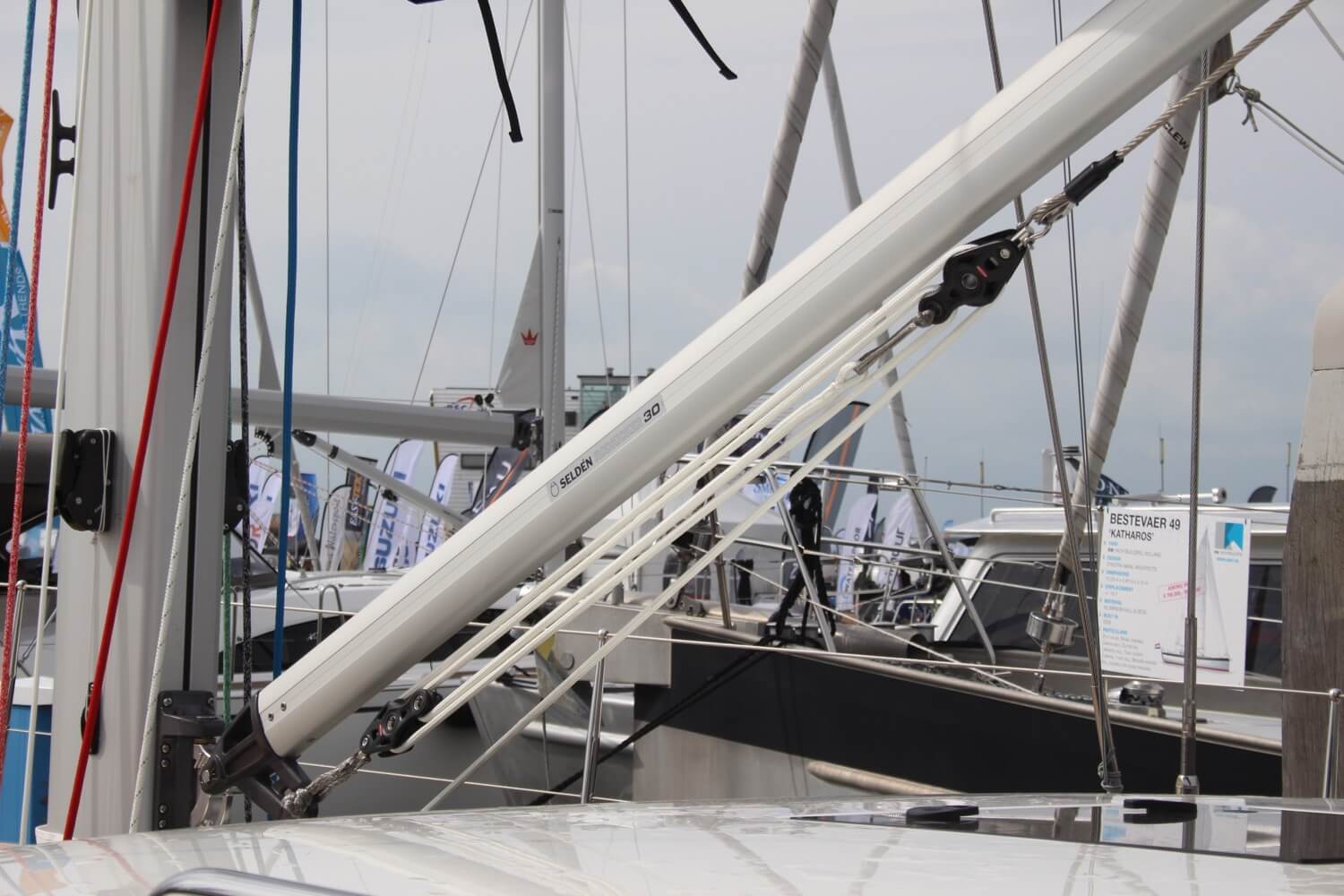

Topping Lift
The topping lift is a line that is attached to the aft (back) end of the boom and runs to the top of the mast. It supports the boom whenever you take down the mainsail.
Also referred to as a 'horse', the traveler is a side to side track to which the boom is attached, allowing the control of the extent to which the boom goes off the centerline. This is important especially if the wind is blowing from behind and you need to control the angle of the mainsheet.
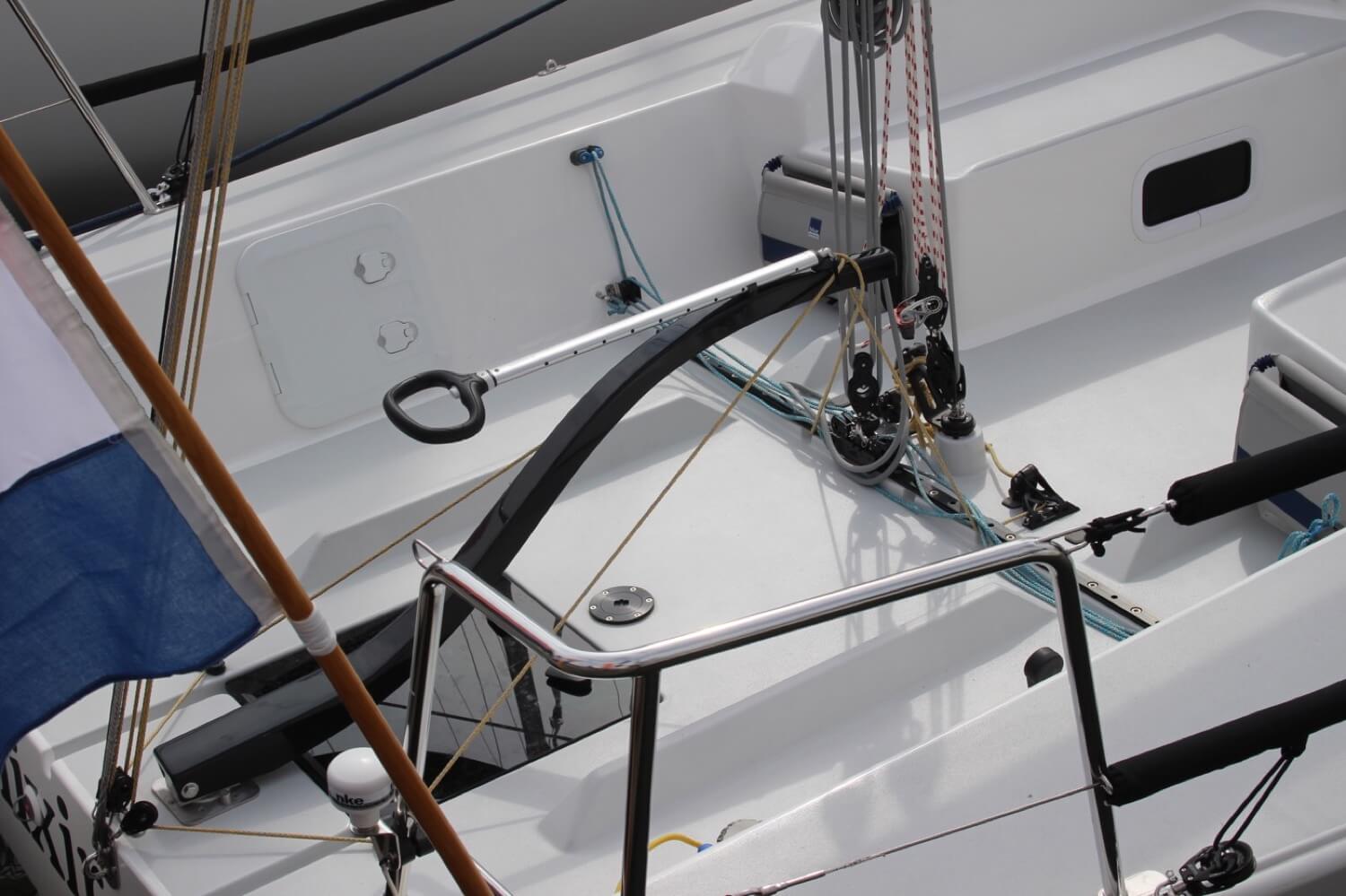

Outhaul is the line attached to the mainsail or the jib clew, allowing the control of the foot tension. This is important for determining the sail shape - for instance in stronger winds, you want the foot to be more tense to achieve a more effective airflow as opposed to slower winds where you can allow the foot to arch more.
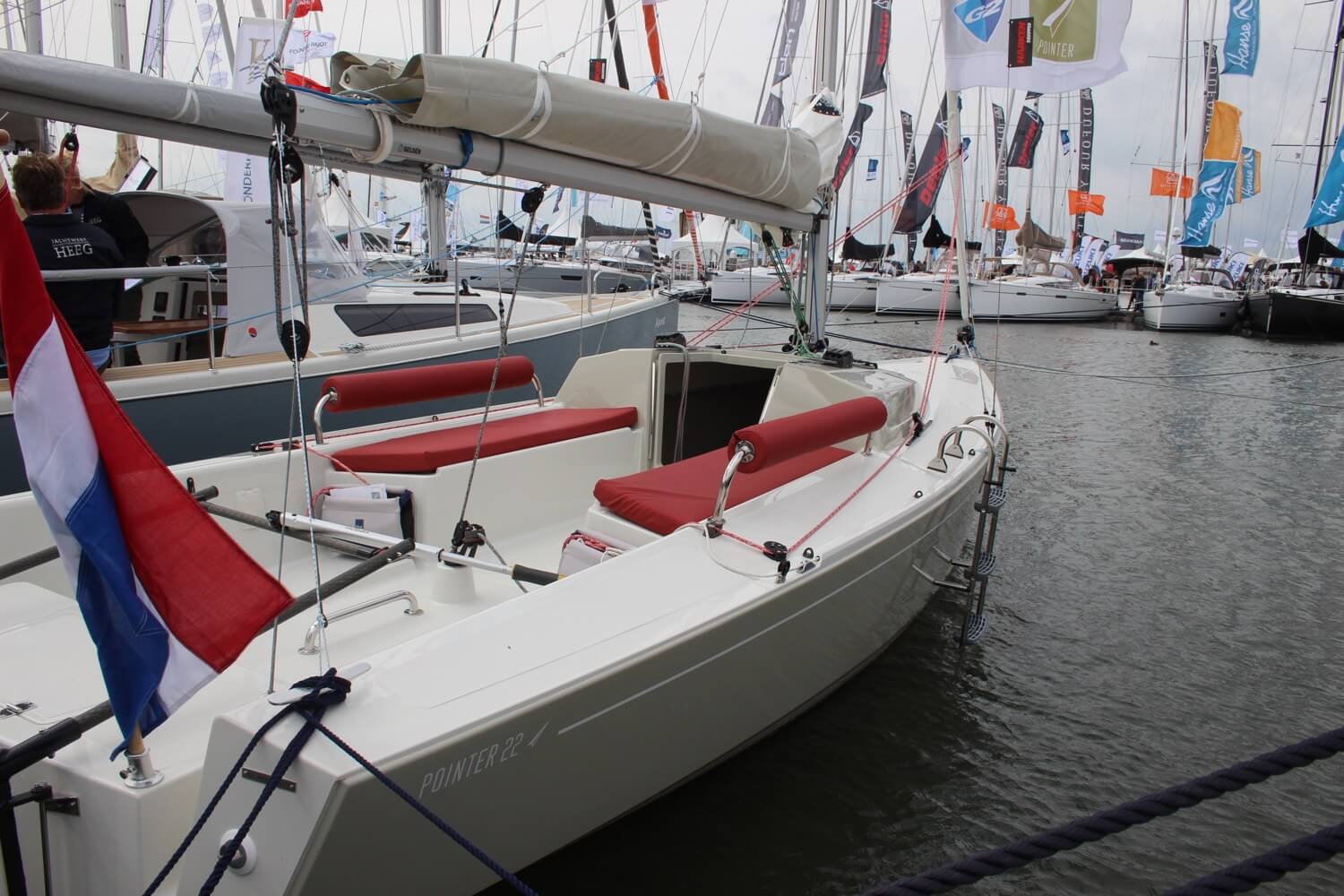

Reefing is reducing the sail area to lessen the power exerted on it by the wind. You may want to reef if the wind is getting too strong for your boat, or if it is changing too rapidly, as an overpowered boat is difficult to control. Fun fact: they say that when you feel you need to reef because the wind got too strong, it is already too late to reef.

A batten is a slat placed horizontally in the body of the sail to support its shape. You will not find them on all sailboats, it is a performance-enhancing element that many cruisers lack. It helps tremendously as without it, sails tend to belly out and lose their shape under certain conditions.
The cleat is a piece of fitting where a line can be secured and immobilized, even if under great tension. It usually consists of two cogwheel-like pieces fastened close to each other, in the middle of which the rope is placed, unable to move thanks to friction. This type is great as it allows for a quick release. Sometimes though, it is a simple piece of metal or plastic where the rope is tied.
...and then there are all those things that just float around you when sailing, those little things that are the reason for you having to carry a dictionary in your pocket.
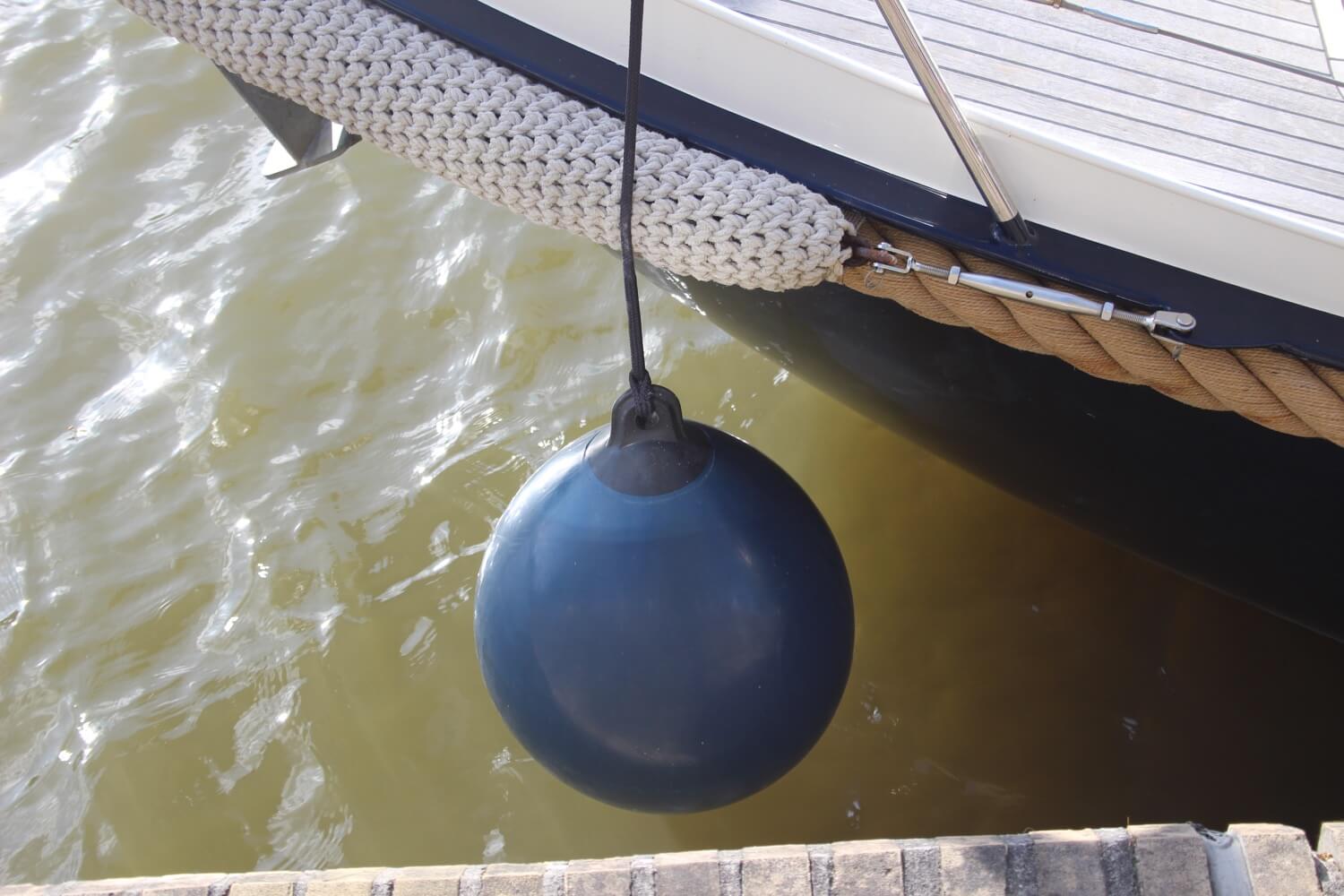
Fenders are bumpers allowing some contact with other boats or piers while docked, without scraping the paint. They are often balloon-shaped, made of rubber or some relatively soft material. They are usually attached to the boat's railing and you move them around as you need.

The beam is the width of the boat. Could be just called width, I know. The word comes from the fact that there are transverse reinforcing beams in the boat hull and deck. Next time you are choosing your charter boat for holidays, you will know what this attribute means.
True wind is the actual direction and speed of the wind. This is different than the apparent wind, which is wind direction and speed relative to the boat. Apparent wind is a combination of the true wind and the headwind, which is the wind the boat experiences solely by being in motion.
The berth is a sleeping space on a boat. Thus if a boat has eight berths, it means eight people can comfortably sleep on it. Note that this often includes the salon couches, so a berth is not necessarily a space in an actual bed for one person.

Boat's draft is the distance from the water surface to the deepest point of the boat. In other words, the draft is the minimum water depth you can go to and not scrape your hull or keel. Better double this number when sailing, just to be safe, as hitting the seabed can have disastrous consequences.
Tacking is zig-zagging towards your destination. It is necessary in case your destination is in the direction of the wind since sailboats can not go directly into it. Since the closest to the wind direction you can sail is around 45 degrees, you have to change direction left and right from your desired course.

This diagram is from our guide on sailing into the wind for beginners , which explains in 7 simple steps how to get good upwind sailing performance.
Bareboat is a boat without a skipper. You will encounter this term in boat charters and it means you rent the boat without any crew, thus you need to operate it yourself. It is the best way to sail unless you enjoy living in close proximity to a sea wolf who you also have to feed.
The chart is a nautical map. It differs from classical maps as it depicts information relevant for a sailor - water depth, navigational hazards, seabed material, anchorages and so on. Formerly made of paper, these days made of ones and zeros. As is everything in this digital world.
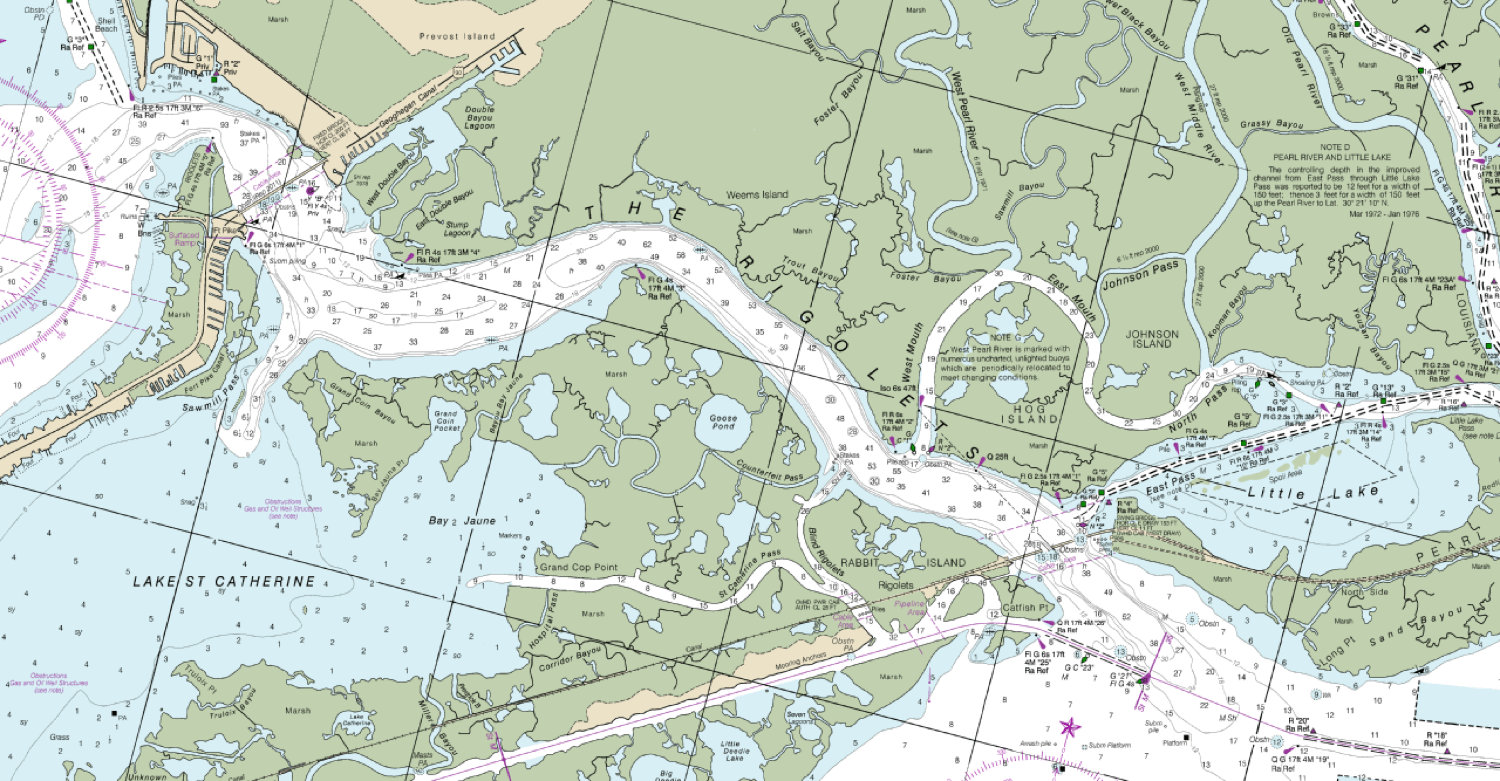
We have a guide that explains all the different chart types clearly for beginners - read it here .
Galley on a boat is its kitchen. Also a medieval warship, but if you find this term in a boat's description, war is not likely what they have in mind.

Heads on a boat is the bathroom. Though in all my years of sailing I have never ever heard anybody use this term instead of a 'bathroom'. I suppose saying that you are going to use the heads just sounds odd.

A knot is the unit of speed of boats. It is equal to one nautical mile per hour. That is 1.852 kilometers per hour or 1.5078 miles per hour. Though a bit confusing and annoying at times, you will have to get used to this, since most of your boat's instruments will use this unit. It dates all the way back to the seventeenth century when boat's speed was measured with a rope with knots tied on it.

Mooring is attaching the boat to a buoy that is anchored to the seabed. This is usually a cheaper option to docking in a marina. It also means larger space between the boats anchored in the same area, thus more privacy. Though you will have to use your dinghy to get to shore instead of just stepping on the pier directly from your deck.

A salon on a boat is its living room. On smaller boats, it is usually in the same room as the boat's kitchen and the captain's corner with navigation instruments.

A skipper is the captain of a sailboat. If you ask me, the word 'captain' is much better than a skipper, which to me sounds like a small boy who sits on the shore the whole day, skipping stones. But hey, who am I to talk.
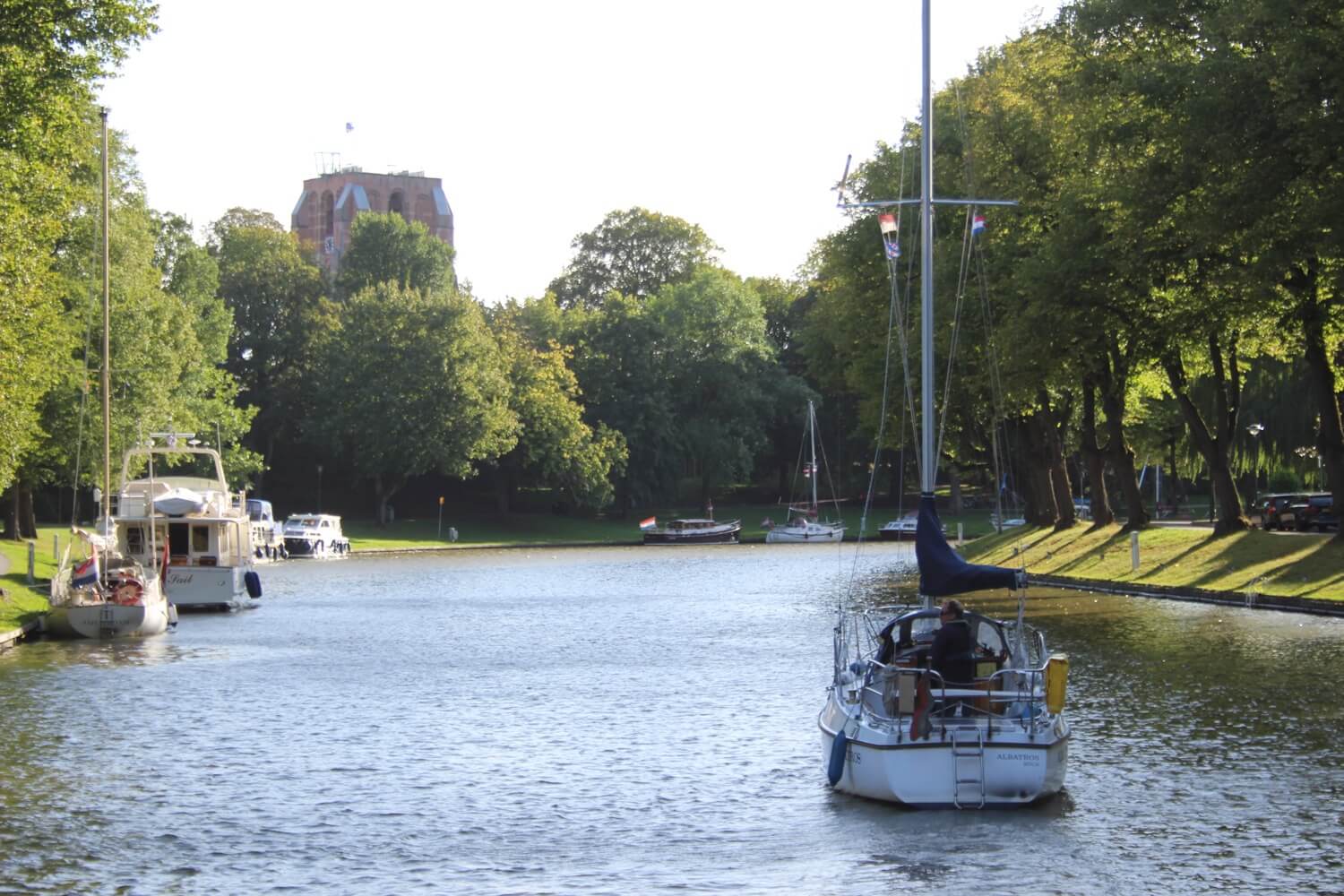

A monohull is a classical boat with a single hull. A boat with two hulls is called a catamaran, or a 'cat'. Although rare, there are also trimarans, boats with three hulls. Multihulls with four or more hulls do happen but they are an unnecessary freak of nature.

So there you have it. Fifty sailing terms you will encounter the most when traveling or learning. I know you might think some of them are a bit unnecessary since they have a perfectly fine 'real world' equivalent. I agree. But until the tradition changes, you might want to get some of these under your skin.
A boat's freeboard is the distance from the upper deck to the waterline. Classic yachts have low freeboards, so they appear to lay deeper in the water, as opposed to more modern yachts, which have a higher freeboard. It literally means 'free-board' : the amount of visible board.
The lunch hook is a light anchor setup that is used to moor small yachts temporarily. It typically uses a lightweight anchor on a short scope that takes little effort to set. The lunch hook is only used when the crew is on board and will be monitoring the anchor.
In naval architecture and ship design: “Head” = WC = Bathroom. A toilet is still a toilet. The toilet is in the head. In olden day, the toilet was a hole in the head.
Hi Rich, you’re absolutely right. I’ve corrected the error. Thanks for pointing it out.
A nautical mile is one minute of a degree, so if you travel 60 nautical miles that means you have gone 1 degree around the “globe”. (Note: arc length not actual length.) This is the original definition. As such the average was agreed upon and the lengths given a standardization. Which you mentioned.
As such 1 knot is to travel one nautical mile in an hour.
Also 1.5078. I think you made a mistake as it should be 1.1508 miles to a nautical mile.
Thanks for the information. Sorry about being a pedantic mathematics teacher.
So, where is the “nautical mile” calculated from, the equator or one of the tropic lines?
Just to clarify a nautical mile. If you draw an imaginary line from the North Pole or South Pole to the center of the Earth and draw another line from the center of the Earth to any point on the equator, it forms a right angle, which is 90 degrees. This equates to latitude. The equator is 0 degrees and the poles are 90 degrees. Your latitude is the angle that you are north or south of the equator. Each degree of latitude is divided into 60 minutes. A minute of latitude is the same distance matter where you are on Earth. It is 6,076 feet. This is the length of a nautical mile. A statute mile is 5,280 feet, so a nautical mile is 1.1508 statute miles.
Thank you very clear and well explained. Hopefully I’ll remember The Fifty
KöhnSharkösz
Really? No gunwale? No transom? Those or basic terms to the Washington State Boater Education Card required to operate watercraft here. Definitely more of a “need to know” than bimini.
Thank you, those definitions and explanations were clear, thorough, and helpful. I’m really glad I found my way (somehow) to your webpage.
Leave a comment
You may also like, 17 sailboat types explained: how to recognize them.
Ever wondered what type of sailboat you're looking at? Identifying sailboats isn't hard, you just have to know what to look for. In this article, I'll help you.

How Much Sailboats Cost On Average (380+ Prices Compared)

The Ultimate Guide to Sail Types and Rigs (with Pictures)

Sailboat Parts Explained: Illustrated Guide (with Diagrams)

How To Live On a Boat For Free: How I'd Do It
Own your first boat within a year on any budget.
A sailboat doesn't have to be expensive if you know what you're doing. If you want to learn how to make your sailing dream reality within a year, leave your email and I'll send you free updates . I don't like spam - I will only send helpful content.
Ready to Own Your First Boat?
Just tell us the best email address to send your tips to:

Sailing Terminology List: 300+ Sailing Terms

There’s a massive amount of sailing terms that any sailor will eventually learn with time and it can seem daunting essentially learning a new language.
Need to know sailing terminology will help you out when communicating with your crew members and captains of other vessels, so having a sailing terminology list handy can do a lot of good.
That’s why I put together this list of common sailing terms that’ll help you out the next time you head out on the water.
Aback – A foresail when against the wind, used when tacking to help the vessel turn. Abaft – Toward the stern, relative to some object. Abeam – On the beam, a relative bearing at right angles to the ship’s keel. Aboard – On or in a vessel. Adrift – A boat drifting without being propelled. Aft – At or towards the stern or behind the boat. Aground – A boat whose keel is touching the bottom. Amidships – The middle section of a vessel with reference to the athwartships plane, as distinguished from port or starboard. Apparent wind – The wind felt aboard a moving boat. Astern – Behind the stern of the boat. Athwartships – Across the boat from side to side.
Backstay – The standing rigging running from the stern to the top of the mast, keeping the mast from falling forward. Bail – To empty the boat of water. Ballast – Weight in the keel of a boat that provides stability. Barometer – An instrument that measures air pressure, an aid to forecasting the weather. Batten – A thin wood or fiberglass slat that slides into a pocket in the leech of a sail, helping to maintain an aerodynamic shape. Beam – The width of a boat at its widest point. Beam reach – Sailing in a direction at approximately 90 degrees to the wind. Bear away – To “fall off” or head away from the wind. Bearing – The direction from one object to another expressed in compass degrees. Beating – A course sailed upwind. Below – The area of a boat beneath the deck. Bend – To attach a sail to a spar or a headstay or to attach a line to a sail. Bight – A loop in a line. Bilge – The lowest part of a boat’s interior where water on board will collect. Bitter end – The end of a line. Blanket – To use the sail or object to block the wind from filling a sail. Block – A pulley on a boat. Boat hook – A pole with a hook on the end used for grabbing hold of a mooring or retrieving something that has fallen overboard. Boltrope – The rope that is sewn into the foot and luff of some mainsails and the luff of some jibs by which the sails are attached to the boat. Boom – The spar extending directly aft from the mast to which the foot of the mainsail is attached. Boom vang – A block and tackle system, which pulls the boom down to assist sail control. Bottom – The underside of a boat. Bow – The forward part of the boat. Bowline – A line running from the bow of the boat to the dock or mooring. Bow spring – A line running from the bow of the boat parallel to the dock or mooring that stops the boat from moving forward along the dock. Bowline – A knot designed to make a loop that will not slip and can be easily untied. Breast line – A short line leading directly from the boat to the dock. Broach – An uncontrolled rounding up into the wind, usually from a downwind point of sail. Broad reach – Sailing in a direction with the wind at the rear corner (the quarter) of the boat. Approximately 135 degrees from the bow of the boat. Bulkhead – A wall that runs athwartships on a boat, usually providing structural support to the hull. Buoy – A floating navigation marker. Buoyancy – The ability of an object to float. Bulwark – A solid side wall, often about waist high, from the outside edge of the deck to prevent someone from falling overboard. Burdened vessel – The vessel required to give way for another boat when the two may be on a collision course. By the Lee – A sailboat running with the wind coming over the same side of the boat as the boom.
Cabin – The interior of the boat. Can – In the U.S., it’s an odd-numbered green buoy marking the left side of the channel when returning to harbor. Capsize – To tip or turn a boat over. Cast off – To release a line when leaving a dock or mooring. Catamaran – A twin-hulled vessel with a deck or trampoline between the hulls. Catboat – A boat with only a mainsail and an unstayed mast located at the bow. Centerboard – A pivoting board that can be lowered and used like a keel to keep a boat from slipping to leeward. Centerline – The midline of the boat running from bow to stern. Chafe – Wear on a line caused by rubbing. Chainplates – Strong metal plates which connect the shrouds to the boat. Channel – A (usually narrow) lane, marked by buoys, in which the water is deep enough to allow a vessel safe passage. Chart – A nautical map. Charter – To rent a boat. Chock – A guide mounted on the deck through which dock lines and anchor rode are run. Chop – Rough, short, steep waves. Cleat – A nautical fitting that is used to secure a line. Clew – The lower aft corner of a sail. The clew of the mainsail is held taut by the outhaul. The jib sheets are attached to the clew of the jib. Close hauled – The point of sail that is closest to the wind when the sails are hauled close to the centerline of the boat. Close reach – Sailing in a direction with the wind forward of the beam (about 70o from the bow). Coaming – The short protective wall that surrounds the cockpit or hatch. Cockpit – The lower area of the deck in which the steering and sail controls are located. Coil – To loop a line neatly so it can be stored, or a reel of line. Come about – To alter course so as to cause the bow of the boat to pass through the eye of the wind. Companionway – The steps leading from the cockpit or deck to the cabin below. Compass – The magnetic instrument which indicates the direction in which the boat is headed. Compass rose – The circles on a chart which indicate the direction of true and magnetic north. Course – The direction in which the boat is being steered. Crew – Besides the skipper, anyone on board who helps run the boat. Cunningham – A line running through a grommet a short distance above the tack of the mainsail which is used to tension the luff of the main. Current – The horizontal movement of water caused by tides, wind, and other forces. Cutter – A single-masted boat rigged with both jib and staysail.
Daysailer – A small sailboat. Dead downwind – Sailing in a direction straight downwind. Deck – The mostly flat area on top of the boat. De-power – Reducing the power in the sails by luffing, easing the sheets, or stalling. Dinghy – A small sailboat or rowboat. Displacement – The weight of the boat; therefore the amount of water that it displaces. Dock – The quay or pontoon where a boat may be tied up. Dockline – A line used to secure a boat to the dock. Dodger – A canvas protection in front of the cockpit of some boats that are designed to keep spray off the skipper and crew. Downhaul – A line used to pull down on the movable gooseneck on some boats to tension the luff of the mainsail. Draft – The depth of a boat’s keel from the surface of the water.
Ease – To let out a line or sail. Ebb – An outgoing tide.
Fairlead – A fitting that guides sheets and other lines in a way that reduces friction and therefore chafe. Fairway – The center of a channel. Fake – Lay out a line on the deck using large loops to keep it from becoming tangled. Fall off – Alter course away from the wind. Fast – To secure something. Fathom – A measure of the depth of water. One fathom equals six feet. Fender – An inflated rubber or plastic bumper used to protect a boat by keeping it from hitting the dock. Fend off – To push off. Fetch – The distance of open water to windward between the shore and the boat. Fid – A tapered spike used to open the lay of a rope when splicing. Flood – An incoming tide. Following sea – Wave pattern hitting the stern of the boat. Foot – The bottom edge of the sail. Fore – Another word for “forward”. Forepeak – An accommodation or storage area in the bow below the deck. Foresail – A jib or genoa. Forestay – The standing rigging running from the bow to the mast top and to which the foresail is secured. Forward – Towards the bow. Fouled – Another word for “tangled”. Fractional rig – When the forestay is attached to the mast some distance below the top. Foul weather gear – Water resistant clothing. Freeboard – The height of the hull above the water’s surface. Full – Not luffing. Furl – To fold or roll up a sail.
Gaff – On some boats, a spar along the top edge of a four-sided fore and aft sail. Genoa – A large foresail whose clew extends aft of the mast. Give way vessel – The vessel required, by the regulations, to give way in a collision situation. G.M.T. – Greenwich Mean Time. The time at the prime meridian in Greenwich, London, England. Now referred to as Universal Time Coordinated U.T.C. Gooseneck – The strong fitting that connects the boom to the mast. Great Circle – A line drawn on a chart which is accurate over a long distance, a section of the Earth which intersects the center of the Earth. Grommet – A reinforcing ring set in a sail. Ground tackle – Collective term for the anchor and rode (chain and line). Gudgeon – A fitting attached to the stern into which the pintles of a rudder are inserted. Gunwale – The edge of the deck where it meets the topsides. Gybe – Another alternative spelling of “jibe”.
Halyard – A line used to raise or lower a sail. Hank – A snap hook which is used to secure the luff of a foresail to the forestay. Hard a-lee – The call given to the crew that will initiate the action of tacking. Hard over – To turn the helm or tiller as far as possible in one direction. Hatch – A large covered opening in the deck. Haul in – To tighten a line. Head – The toilet on a boat as well as the top corner of a sail. Headboard – The small reinforcing board affixed to the head of a sail. Headed – A wind shift which causes the boat to head down or causes the sails to be sheeted in. Heading – The direction of the boat expressed in degrees. Head down – Changing course away from the wind. Head off – Another word for “head down”. Head up – Changing course towards the wind. Headsail – A jib/genoa attached to the forestay. Headstay – The standing rigging running from the bow to the top of the mast. Head to wind – When the bow of the boat is dead into the wind. Headway – Forward progress. Heave – To throw. Heave to – To hold one’s position in the water by using the force of the sails and the rudder to counteract each other. Holding ground – The seabed or bottom ground in an anchorage. Hove to – A boat that has completed the process of heaving to with its aback, its main trimmed, and its rudder positioned to hold the vessel close to the wind. Heavy weather – Strong winds and large waves. Heel – The lean of the boat caused by the wind. Helm – The tiller. Helmsman – The person responsible for steering the boat. Hull – The body of the boat, excluding the rig and sails. Hull speed – The theoretical maximum speed of a sailboat determined by the length of its waterline.
Inboard – Inside of the rail of the boat. In irons – A boat that is head to wind and unable to move or maneuver.
Jackstay – A wire or webbing strap attached at the front and back of a vessel along the deck to which a safety harness line may be clipped. Jib – The small forward sail of a boat that is attached to the forestay. Jibe – To change the direction of the boat by steering the stern through the wind. Jibe oh – The command given to the crew when starting a jibe. Jiffy reef – A quick reefing system allowing a section of the mainsail to be pulled down and tied to the boom. Jury rig – An improvised temporary repair.
Kedge – A smaller anchor than the main or bower anchor. Often used for maneuvering or kedging off. Kedge off – To use an anchor to pull a boat into deeper water after it has run aground. Keel – The heavy vertical fin beneath a boat that helps keep it upright and prevents it from slipping sideways in the water. Ketch – A two-masted sailboat on which the mizzen (after) mast is lower than the mainmast and is located forward of the rudderpost. Knockdown – A boat heeled so far that one of its spreaders touches the water. Knot – One nautical mail per hour.
Land breeze – A wind that blows over the land and out to sea. Lash – To tie down. Lay – To sail a course that will clear an obstacle without tacking. Lazarette – A storage compartment built into the cockpit or deck. Lazy sheet – The windward side jib sheet that is not under strain. Lead – To pass a line through a fitting or block. Lee helm – The boats tendency to turn away from the wind. Lee shore – Land which on the leeward side of the boat. Leech – The after edge of a sail. Leeward – The direction away from the wind that is the direction that the wind is blowing to. Leeward side – The side of the boat or sail that is away from the wind. Leeway – The sideways slippage of the boat in a downwind direction. Lifeline – Rope or wire supported by stanchions. Lift – The force that results from air passing by a sail or water past a keel that moves the boat forward and sideways. Line – A rope. L.O.A. – The maximum Length Overall fore and aft along the hull. Lubber line – A line on a magnetic compass to help the helmsman steer the correct course. Luff – The leading edge of a sail as well as the fluttering of a sail caused by aiming too close to the wind. Lull – A decrease in wind speed for a short duration. L.W.L. – The length fore and aft along the hull measured at the waterline.
Magnetic – In reference to the magnetic north rather than true north. Mainmast – The taller of two masts on a boat. Mainsail – The sail hoisted on the mast of a sloop or cutter or the sail hoisted on the mainmast of a ketch or yawl. Mainsheet – The controlling line for the mainsail. Marlinspike – A pointed tool used to loosen knots. Mast – The vertical spar in the middle of a boat from which the mainsail is set. Masthead – The top of the mast. Maststep – The fitting in which the foot of the mast sits. Mizzen – The small aftermost sail on a ketch or yawl hoisted on the mizzenmast. Mizzenmast – The shorter mast aft of the main mast on a ketch or yawl. Mooring – A permanently anchored ball or buoy to which a boat can be tied.
Nautical mile – Standard nautical unit of distance equal to one minute of arc of the Earth’s latitude or 6080 feet. Navigation rules – Laws established to prevent collisions on the water. No-go zone – An area into the wind in which a sailboat cannot produce power to sail. Nun – A red even numbered buoy marking the right side of a channel when returning to port.
Offshore wind – Wind blowing away from the shore and out to sea. Offshore – Away from or out of sight of land. Off the wind – Not close-hauled point of sail. On the wind – Sailing upwind in a close-hauled point of sail. Outboard – Outside the rail of a boat. Outhaul – The controlling line attached to the clew of a mainsail used to tension the foot of the sail. Overpowered – A boat that is heeling too far because it has too much sail up for the amount of wind.
Painter – The line attached to the bow of a dinghy. Pay out – To ease a line. P.F.D. – A Personal Flotation Device such as a life jacket. Pinching – Sailing too close to the wind. Pintle – Small metal extension on a rudder that slides into a gudgeon on the transom. Point – To steer close to the wind. Points of sail – Boat direction in relation to the wind. Port – The left-hand side of the boat when facing forward, a harbor, or a window in a cabin on a boat. Port tack – Sailing on any point of sail with the wind coming over the port side of the boat. Prevailing wind – Typical or consistent wind direction. Puff – An increase in wind speed. Pulpit – A guardrail at the bows of a vessel.
Quarter – The sides of the boat near the stern.
Rail – The outer edges of the deck. Rake – The angle of the mast. Range – The alignment of two objects that indicate the middle of a channel. Reach – One of the several points of sail across the wind. Ready about – The command given to the crew to prepare to tack. Ready to jibe – The command given to the crew to prepare to jibe. Reef – To reduce the area of a sail. Reeve – To pass a line through a ring or block. Rhumb line – A straight line drawn on a Mercator chart, which intersects all meridians at the same angle. Rig – The design of a boat’s masts, standing rigging and sail plan. Rigging – The wires and lines used to support and control sails. Roach – The sail area aft of a straight line running between the head and clew of a sail. Rode – The line and chain attached from the boat to the anchor. Roller-furling – A mechanical system to roll up a headsail around the headstay. Rudder – A vertical blade attached to the bottom of the hull which is used to steer the boat. Run – Point of sailing when the wind is coming from dead astern. Running rigging – The lines used to control the sails.
Sail ties – Lengths of line or webbing used to secure sails when they are dropped or to secure the unused portion of a reefed sail. Schooner – A two-masted boat whose foremast is the same height or shorter than its mainmast. Scope – The length of anchor rode paid out in relation to the maximum depth of water. Scull – To propel a boat with a single oar fixed in a notch through the transom. Scupper – A cockpit or deck drain. Sea breeze – A wind that blows from the sea onto the land. Seacock – A valve which opens and closes a hole used as an intake or discharge from the boat. Secure – The make safe or tie down. Set – The direction of the current as well as to trim the sails. Shackle – A metal fitting at the end of a line used to attach the line to a sail or another fitting. Shake out – To remove a reef. Sheave – The wheel inside a block or fitting over which the line runs freely. Sheet – A line used to control a sail by pulling it in or easing it out. Shoal – An area of shallow water. Shroud – Standing rigging at the side of the mast. Singlehanded – Sailing alone. Skeg – A vertical fin in front of the rudder. Sloop – A single-masted sailboat with mainsail and headsail. Sole – The floor in a cockpit or cabin. Spar – A pole used to attach a sail on a boat, for example, the mast, the boom, or a gaff. Spinnaker – A large downwind headsail not attached to the head stay. Splice – The joining of two lines together by interweaving their strands. Spreader – A support strut extending athwartships from the mast used to support and guide the shroud from the top of the mast to the chainplate. Spring line – A dock line running forward or aft from the boat to the dock to keep the boat from moving fore or aft. Squall – A fast moving short intense storm. Stanchions – Stainless steel or aluminum supports at the edge of the deck which holds the lifelines. Standing rigging – The permanent rigging of a boat, including the forestay, backstay, and shrouds. Starboard – The right-hand side of the boat when looking forward from the stern. Starboard tack – Sailing on any point of sail with the wind coming over the starboard side of the boat. Stay – A wire support for a mast, part of the standing rigging. Staysail – Any sail which is attached to a stay. Steerage way – The minimum speed of the boat through the water that allows the rudder to function efficiently. Stem – The foremost tip of the boat. Stern – The aft part of the boat. Stern spring – A line running from the stern of the boat parallel to the dock or mooring that stops the boat from moving backward along the dock. Stow – To store properly. Swamped – Filled with water.
Tack – To alter course so as to cause the bow of the boat to pass through the eye of the wind. Tackle – A series of blocks and line that provide a mechanical advantage. Tail – To hold the end of a line so as to keep it under tension on a winch. Telltales – Short lengths of yarn or cloth attached to the sails which indicate when the sail is properly trimmed. Tide – The rise and fall of water level due to the gravitational effects of the sun and the moon. Tiller – A long handle attached to the rudder which is used to steer the boat. Toe rail – A low rail around the outer edge of the deck. Topping lift – A line used to hold the boom up when the mainsail is lowered or stowed. Topsides – The sides of a boat between the waterline and the deck. Transom – The vertical surface of the stern. Trim – To adjust the sail controls to create optimum lift from the sails. Trimaran – A three-hulled vessel. True wind – The actual speed and direction of the wind as you would feel when standing still. Tune – To adjust the boats standing rigging. Turnbuckle – A mechanical fitting attached to the lower ends of stays allowing the standing rigging to be adjusted.
Underway – A boat that is not attached to the ground by either anchor or mooring lines. Upwind – Towards the direction of the wind. U.S.C.G. – United States Coast Guard. U.T.C. – Universal Time Coordinated. As the modern term for Greenwich Mean Time, this is the standard reference time which is used internationally for navigational information.
Vang – A block and tackle system, which pulls the boom down to assist sail control. Veer – A clockwise change in the wind direction. Vessel – Any sailboat, powerboat, or ship.
Wake – Waves caused by a boat moving through the water. Waterline – The horizontal line on the hull of a boat where the surface of the water should be. Weather helm – The tendency of the boat to head up towards the wind, this increases as the sailboat becomes overpowered. Whip – To bind together the strands at the end of a line. Whisker pole – A pole temporarily mounted between the mast and the clew of the jib. Used to hold the sail out and keep it full when sailing downwind. Winch – A deck-mounted drum with a handle offering a mechanical advantage when used to trim sheets. Windward – Towards the wind. Windward side – The side of the boat closest to the wind. Wing-and-wing – Sailing downwind with the jib set on the opposite side to the mainsail. Working sails – The mainsail and the standard jib. Working sheet – The leeward sheet that is under tension.
Yard – The horizontal spar from which a square sail is suspended. Yawl – A two-masted vessel on which the mizzenmast is mounted aft of the rudderpost.
Get the very best sailing stuff straight to your inbox
Nomadic sailing.
At Nomadic Sailing, we're all about helping the community learn all there is to know about sailing. From learning how to sail to popular and lesser-known destinations to essential sailing gear and more.
Quick Links
Business address.
1200 Fourth Street #1141 Key West, FL 33040 United States
Copyright © 2024 Nomadic Sailing. All rights reserved. Nomadic Sailing is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means to earn fees by linking to Amazon.com and affiliated sites.


Sailing Terms: A Complete Guide

Last Updated by
June 15, 2022
Learning sailing terms when you first get into boating can be a daunting task.
Some sailing terms are logical, like 'fore' means forward or front of the boat, while others might as well be in a different language. Athwartship, for example. Nothing in our daily lexicon gives any clues as to what that might mean. Like it or not, it's time to dust off the old noodle and get to memorizing some new vocab words!
Knowing the difference between a clew and a tack, a luff and a leech, will help you communicate with your sail maker regarding which part of your sail needs resewn. If you need to have your rigging adjusted, you must know the difference between your shrouds and your stays, your standing rigging vs. your running rigging.
By educating yourself in the correct names of all parts of your sailboat, you can avoid situations in which you may need to use terms such as ‘thingy’ or ‘that round part at the end of that thing’. While even the most seasoned sailor occasionally troops over the vernacular, it is always beneficial to have as wide a nautical vocabulary as possible. Many in the sailing community get by without knowing the entire sailing dictionary, but if you’re interested in avoiding vocabulary embarrassment, check out the list I’ve compiled of sailing terms that every sailor ought to know.
I’ve been sailing on and off throughout my life and I know from experience that it is incredibly helpful to know the correct terms for each part of your sails, rigging, and boat.
Sailors are among the kindest, most helpful people you’ll ever meet. But, if you’re looking for help on why you’re not getting the most speed out of your mainsail and you know don’t know the correct terms for each part of the sail, it may be hard to get advice from you fellow sailor on why ‘the back of the mainsail is flappy’. They would be more likely to give useful advice if you’re able to tell them that you’re struggling to keep wind in the roach of your mainsail. Check out my list of sailing terms and see if a few don’t stick. I’ve done my best to include pictures when possible.
Table of contents
Sailing Terms
Abeam : When an object, craft or island is abeam your vessel, that means that it is off the side of your boat. It is 90 degrees from the centerline of your boat.
Abaft : Toward the stern. “Honey, have you seen my boat shoes?” “They’re abaft the navigation table!” This is the opposite of forward.
Aft : In the stern of the boat. For example, the back cabin is referred to as the aft cabin.
Apparent wind : The wind direction and speed which the crew observes to be blowing in combination with the true wind. This is often different from the true wind direction and speed due to the boat's motion.
Astern : The area behind the boat. If you go astern, you are going in reverse.
Athwartship : Directionally perpendicular to the centerline of the boat.
Backing (a sail) : Forcing the sail to take wind into its opposite side by pulling the sail to the opposite side of the boat.
Backstay : The wire that runs from the back of the boat to the mast head. This prevents the mast from falling forward.
Bailer : Any scoop-like container that is used to remove water from within a vessel’s hull.
Ballast : Weight which adds stability to the vessel. The weight usually is composed of lead or iron and placed low in the boat's hull, such as within the keel.
Batten : a thin, flexible strip (often fiberglass) that is inserted into the main sail to help it stay open to the wind. The batten runs from the back edge of the sail (leech) toward the front edge (luff).
Beam : The width of the vessel at its widest point.
Beam reach : Sailing with the wind blowing perpendicular to the direction the boat is traveling.
Bearing off or Bearing away : Steering the boat away from the direction in which the wind is blowing.
Bend : a knot which connects two ropes.
Berth : A slip, a mooring, or a bed within the boat.
Bight : A bend or loop in a rope. When a rope forms a bight, it has changed direction 180 degrees.
Bilge : The lowest area within a boats hull. This area collects water which is then pumped overboard by a bilge pump.
Bimini : The covering over the cockpit. Usually constructed from a stainless steel frame covered with canvas or fiberglass. It provides protection from sun and rain, but not wind.
Binnacle : The pedestal centrally located in the cockpit that generally holds the steering wheel and navigational instruments.
Block : A pulley.
Boom : This pole runs perpendicular to the mast and holds the bottom of the mainsail in place. Its position is adjustable side to side as needed for the wind direction.
Boom vang : A tackle which ensures that the boom does not lift upward from wind pressure in the mainsail.
Boot Top or Boot Stripe : The stripe of tape or paint between the boat's underwater (bottom) paint and it’s above water (topside) paint.
Bow : Front end of the boat
Bowsprit : The forward most protruding pole or platform which some boats possess. This spar allows for the sails and rigging to be attached further forward.
Broach : When a boat sailing downwind accidentally ends up sideways to the waves and heels over dangerously. This can be caused by large seas or poor steering.
Broad reach : Sailing with the wind coming off your stern quarter. If you’re standing at the helm facing the bow, the wind is blowing halfway between the side and the back of the boat.
Bulkhead : The walls in a boat which run athwartship, or perpendicular to the centerline of the vessel.
Capsize : When a vessel tips over past 90 degrees.
Catamaran : A vessel with two hulls.
Centerboard : A retractable keel which helps the sailboat maintain course and stability underway. When raised, the vessel is able to enter shallow waters.
Centerline : An imaginary line that runs from the center of the bow to the center of the stern.
Chainplate : A metal plate that is secured to the boat's hull to which wires supporting the mast are attached. The chainplates may be exterior or interior, visible or hidden.
Chandlery : A store that sells boat supplies and parts.
Cleats : The wooden or metal piece to which ropes are secured.
Chock : A fitting that a line passes through to change direction without chafing.
Clew : The lower back corner of a sail. This is where the foot and leech of the sail meet.
Close-hauled : Sailing as close to the direction the wind is coming from as possible with the sails pulled in tight. (See Points of Sail for infographic.)
Close Reach : Sailing between close hauled and beam reach. (See Points of Sail for infographic.)
Coamings : The lip around a hatch or window which stops water from entering. Also the raised area around the cockpit to keep out water.
Cockpit : The area from which steering occurs. This can be in the center of the boat or in the back of the boat.
Companionway : The doorway into the cabin.
Cotter pin : a bendable metal pin which is inserted into a metal rod then bent to lock it in place.
Daybeacons : Markers for navigation which are on posts. These are red or green.
Dead run : Sailing with the wind coming from directly behind the boat. Sails are fully out to catch the wind.
Dead reckoning : Determining a vessel's position by knowing the direction and speed traveled.
Dinghy : A small boat which is used to travel to shore from the main vessel. This can be propelled oars or a motor.
Dodger : The structure at the front of the cockpit which protects the cockpit and companionway from wind and spray. This is generally made of stainless steel frame covered with canvas and plastic windows. It can also be a solid structure with solid windows.
Dismasting : When the mast breaks off the boat. This can occur due to rigging failure or structural failure of the mast.
Displacement : The weight of the water that would otherwise be in the place of the boats hull.
Drogue : A sea anchor which is deployed to help control the drift of a vessel. It can be constructed like a parachute, bucket, or even a rope dragging behind the boat.
Ebb tide : After high tide when the water is receding towards low tide.
EPIRB : Stands for Emergency Position Indicating Radio Beacon. This device transmits a distress signal to emergency services and notifies them of a vessel's location.
Fairlead: A fitting which encloses a line within a smooth ring and helps guide its direction.
Fathom : A measurement of water depth equal to 6 feet.
Fid : A pointed tool used when splicing a line.
Fiddle : The raised edge around a table which prevents objects from falling off as the boat rocks or heels.
Fix : Determining a vessel's location by using the compass bearing of two or more fixed points of reference such as landmarks or buoys.
Fin keel : A fixed, ballasted keel which is centrally located beneath the hull. It does not run the full length of the hull.
Flogging : When a sail flaps noisily because it is not being filled by the wind.
Flood tide : Time period between low tide and high tide when the water is rising.
Foot : The bottom edge of a sail.
Fore : At or near the bow of a vessel.
Forestay : The wire which leads from the bow to the top of the mast. The forward most sail attaches to the forestay either directly or by use of a roller furling system.
Full keel : A fixed, ballasted keel which runs the full length of the hull.
Furling system : A system around which the sail wraps when not in use and is unwrapped for sailing. This may be around the forestay or within the mast.
Freeboard : The distance on a vessel from the waterline to the deck.
Galley : The kitchen on a boat.
Gelcoat : A colored resin which is painted onto the outside surface of a boat and forms a protective glossy layer.
Genoa : A large forward sail which, when fully extended, comes back past the mast. Larger than a jib sail.
Gimbals : Often attached to a boat's stove, it is the fitting which allows an object to maintain an upright position when a vessel heels.
Gooseneck : The point at which the boom attaches to the mast. It allows the boom to move in all directions.
Ground tackle : The anchor, chain, and line used to fix a boat to the bottom when anchoring.
Gunwale : Pronounced “gunnel”. This is the top edge of a boat's hull.
Halyard : The line which attaches to a sail to raise it.
Hanks : The clips that attach the front edge (luff) of a sail to the forestay.
Hatch : An opening window in the cabin roof much like a skylight.
Head : Bathroom on a boat. Also, the uppermost corner on a sail.
Headway : The forward motion of a vessel through the water.
Heave to : A method of controlling a boat’s position to the waves and limiting headway by backwinding the forward sail and keeping the rudder hard over into the wind.
Heel : The tilt that occurs to a boat's hull when the sails are filled with wind.
In-Irons : When a sailboat is bow into the wind with sails flapping. No steerage is possible as the vessel has no forward motion. (See Points of Sail for infographic.)
Jackline or Jackstay : Lines that are run from the bow to the stern. To these safety lines, sailors attach a lanyard connected to their harness so that they may work on deck without fear of being swept overboard in rough seas.
Jib : A triangular forward sail.
Jib sheets : Lines used to control the jib.
Jibing : Pronounced with a long i sound. Steering the boat from one downwind direction to another downwind direction by turning the stern of the boat through the wind. This will cause the sails to move across the boat to the other side, i.e. from port to starboard.
Kedge anchor : A small, lighter second anchor.
Keel : The bottom most part of a boat's structure. This part provides ballast and stability.
Ketch : A sailboat with two masts. The forward mast is the taller mast.
Knot : Regarding speed, one knot is equal to one nautical mile per hour.
Lazyjacks : Light lines that run from the boom to the mast and help contain the mainsail while it’s being lowered to the boom.
Leech : The back edge of a sail. If the sail is square, then this term refers to the outside edges of the sail.
Lee shore : The shore onto which the wind is blowing. On an island, the side of the island facing into the wind is the lee shore.
Leeward : The direction to which the wind is blowing. If the wind is coming from the north, then south is leeward.
Luff : The forward edge of the sail.
Lying a-hull : When a vessel is drifting with all of it’s sails down.
Mainsail : Pronounce main’sil. The primary sail of a boat that is hoisted up or unfurled from the mast.
Mayday : An emergency call put out over a marine radio when there is clear and present danger to the crew of the vessel.
Mizzen : The shorter mast behind the main mast on a ketch.
Monohull : A vessel with a single hull.
Mooring field : An anchorage in which permanently anchored buoys are present to which vessels may be secured.
Multihull : A vessel with more than one hull such as a catamaran or trimaran.
No-sail zone : This is an area 45 degrees to either side of directly into the wind. It is not possible for a boat to sail in this zone as the sails cannot fill with wind. Tacking is necessary. (See Points of Sail for infographic.)
On the hard : When a vessel is out of the water and being stored on land.
Painter : The line which secures the bow of a dinghy to the main boat.
Pan Pan : Pronounced pon-pon. This is an urgent distress radio call which is used when a vessel needs assistance. It is one step below Mayday.
Points of sail : The vessels course in relation to the direction of the wind.
Port : The left side of the boat when facing forward.
Port tack : Sailing with the wind hitting the port side of the vessel and the sails are out on the starboard side.
Pulpit : The metal rails at the bow of the boat which protect the crew from going overboard.
Pushpit : The metal rails at the back of the boat to protect the crew from going overboard.
Quarter : The back corner area of the boat. This area is 45 degrees behind, or abaft, the beam of the vessel.
Reef : reducing the size of the sail in high winds for the safety of the crew and equipment. This is done by either tying or rolling the sail to the boom or forestay.
Rigging : All the wires and ropes used to hold the mast in place and adjust the sails.
Roach : The outer back edge area of the mainsail. If you were to draw a diagonal line from the head of the sail to the clew (back corner), the roach would be outside this diagonal line.
Roller furling : A system which rolls the sail up when not in use. The sail is stored on the roller either at the mast or boom for the mainsail, and at the forestay for the jib or genoa.
Rudder : Steering fin at the back of the boat. Controlled by a steering wheel or tiller from the cockpit.
Running : Sailing in a downwind direction.
Running rigging : The lines, such as sheets and halyards, which control the sails.
Schooner : A sailing vessel with two or more masts. The mainmast is at the back.
Seacock : a valve which can be open or closed to allow water to flow in or out of a through hull fitting.
Scope : The length of chain and line that is between the anchor and the boat.
Scuppers : Deck drains which allow water to flow overboard.
Securite : Pronounced securi-tay. This is a radio call to provide mariners with local marine safety information.
Shackle : A metal U or D shaped link which has a removable pin through the ends.
Sheet : A line or rope which connects to the clew (back corner) of a sail. It is used to control or trim the sail.
Shrouds : Wires or ropes which run from the deck chainplates to the mast. The shrouds prevent the mast from moving side to side.
Skeg : A section of the hull from which the rudder hangs. It provides a variable amount of protection to the rudder depending on its size.
Sloop : A single masted sailboat with a mainsail and a foresail.
Slugs : Fittings on the front edge (luff) of the mainsail that slide into the mast track for hoisting the sail.
Spinnaker : A large, light, often colorful sail that is used off the bow of the boat for sailing downwind (running).
Splice : Connecting two lines together by weaving their strands together.
Spreaders : The horizontal arms extending out from the sides of the mast.
Spring line : Dock lines positioned from the bow to a midship point on the dock or from the stern to a midship point on the dock. This line configuration helps decrease forward and backward motion of the boat while docked.
Stanchions : The metal posts along the outside edge of the deck through which the lifelines run.
Standing rigging : The wires and ropes, such as the shrouds and stays, that are permanently in place and hold up the mast.
Starboard : The right side of the boat when facing forward.
Starboard tack : Sailing with the wind hitting the starboard side of the boat and the sails out on the port side.
Stays : The wires or ropes which run from the bow and stern to the mast top to keep the mast from moving forward or backward.
Steerage way : When a vessel is moving through the water with enough speed to allow the rudder to steer the boat.
Stern : The back end of a boat.
Storm jib : A small, strong forward sail used in heavy winds.
Swing : The circular motion of an anchored boat around it’s anchor due to wind and water movement.
Tack : The forward lower corner of a sail.
Tacking : Turning the boat across the direction the wind is coming from to change course direction. This causes the sails to travel to the other side of the boat.
Tender : Small boat used to transport from shore to the main boat.
Tiller : A bar which controls the rudder and is used to steer the boat from the cockpit. It is used in place of a steering wheel.
Toe rail : The raised lip around the edge of the deck. This can be constructed of wood, fiberglass, or aluminum. It helps prevent items from rolling overboard.
Topping lift : A wire or rope which runs from the back end of the boom to the mast top. This line controls the height of the boom.
Trysail : A small, strong storm sail that is used in place of the mainsail in high winds.
Trim : To adjust the sails.
Winch : A round, drum-like mechanical device used to pull on a line to raise or adjust sails.
Windlass : A winch used to raise and lower the anchor.
Windward : The direction from which the wind is blowing.
Wing on wing : Sailing downwind with the mainsail out on one side and the foresail on the opposite side.
Related Articles
Beth lives on board her 1983 30ft S2 sailboat with her husband, 6 year-old son, and her two fur babies. She has been sailing and boating for most of her life. Beth has been blessed to experience cruising in the Great Lakes, the Bahamas, and in Alaska. She loves to travel and adores living on her tiny boat with her family.
by this author
Most Recent

What Does "Sailing By The Lee" Mean?
Daniel Wade
October 3, 2023

The Best Sailing Schools And Programs: Reviews & Ratings
September 26, 2023
Important Legal Info
Lifeofsailing.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon. This site also participates in other affiliate programs and is compensated for referring traffic and business to these companies.
Similar Posts

How To Choose The Right Sailing Instructor
August 16, 2023

Cost To Sail Around The World
May 16, 2023

Small Sailboat Sizes: A Complete Guide
October 30, 2022
Popular Posts

Best Liveaboard Catamaran Sailboats
December 28, 2023

Can a Novice Sail Around the World?
Elizabeth O'Malley

4 Best Electric Outboard Motors

How Long Did It Take The Vikings To Sail To England?

10 Best Sailboat Brands (And Why)
December 20, 2023

7 Best Places To Liveaboard A Sailboat
Get the best sailing content.
Top Rated Posts
Lifeofsailing.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon. This site also participates in other affiliate programs and is compensated for referring traffic and business to these companies. (866) 342-SAIL
© 2024 Life of Sailing Email: [email protected] Address: 11816 Inwood Rd #3024 Dallas, TX 75244 Disclaimer Privacy Policy
- Paddle Board

A to Z of Nautical Terms: A Complete Glossary of Boat Terminology
Are you a new boat owner? Whether you bought a jet ski or a 40-foot cabin cruiser, you’re going to need to understand the lingo while you’re out on the water. Here’s a glossary of basic nautical terms to have you sounding like a sailor.
Toward the stern of the vessel.
A sail position with the wind striking on its leeward side.
Around or near the stern of the vessel.
At a right-angle to the boat’s center-line.
Lashing the helm to the leeward side to ride out bad weather without the sails set.
The center of the deck of the vessel between the fore-and-aft.
Automatic Identification System.
Apparent Wind
The speed and direction of the wind combined with the boat’s movement and the true wind speed and direction.
To look behind the boat while driving in reverse.
Automatic Radar Plotting Aid.
Athwartships
At a right-angle to the aft-and-fore line of the vessel.
The act of measuring the angular distance on the horizon circle in a clockwise method, typically between a heavenly body and an observer.
When the wind starts to shift in an anti-clockwise direction.
Back a sail
Sheeting the sail to the windward direction, so the wind fills the sail on the leeward side.
The stay supports the aft from the mast, preventing its forward movement.
Baggywrinkle
The teased-out plaited rope wound around the stays or shrouds preventing chaffing.
Iron or lead weights are fixed in a low-access area of the vessel or on the keel to stabilize the boat.
A flexible and lightweight strip feeds into the sail leech’s batten pocket, supporting the roach.
Ballast Keel
A ballast bolted to the keel, increasing the vessel’s stability to prevent capsizing.
The widest point of the vessel or a traverse member supporting the deck. On the beam, objects are at a right-angle to the center-line.
Taking the action of steering the vessel away from the wind.
To tag a zig-zagging approach into the wind or close-hauling with alternate tacks.
The object’s direction from the observer measured in magnetic or true degrees.
To fasten the rope around the cleat using a figure-8 knot.
Securing the sail to the spar before hoisting it or connecting two ropes using a knot.
A sleeping quarters on a boat or a slip occupied by a vessel in a marina or harbor.
The loop or bend in a knot.
The round, lower part of the hull where the water collects.
The pulley fixed inside a plastic or wooden casing with a rope running around a sheave and changing to pulling direction.
Boot-Topping
The narrow-colored stripe is painted between the topside enamel and bottom paint.
The heeling action of the boat when it slews to the broadside while running downwind. Abroach usually occurs in heavy seas.
Broad Reach
The point of sailing the vessel between a run and the beam reach with the wind blowing over the quarter.
The partitioning wall in the vessel athwartship.
A measurement of distance equal to 0.1-sea mile, 185-meters, or 200-yards.
Center-Line
The center of the vessel along the aft-to-fore line.
Center-Board
A board lowers through a slot on the keel for reducing leeway.
The fitting slipping over the boom like a claw. It attaches to the main sheet after you finish reefing the sail.
Chart Datum
The reference level on the charts below which the low tide level. The sounding features below the chart datum. The datum level varies depending on country and area.
The metal, wooden, or plastic fitting used to secure ropes.
Close-Hauled
The skill of sailing close to the wind, also known as beating.
The lower, aft corner of the sail where the leech and foot meet.
Close Reach
The point where you’re sailing between the beam reach and the close-hauled or when the wind blows toward the forward of the beam.
The direction that you steer the vessel in degrees. Mariners can use true or magnetic readings or use a compass to plot the course.
Close-Winded
The act of sailing a boat close to the wind.
The rope loop at either end of the line reef points or an eye in a sail.
The difference between the direction indicated by the magnetic meridian and the compass needle, caused by carrying metal objects aboard the vessel.
Sailing with the wind blowing to the aft, in line with the center-line of the vessel.
Displacement
The displacement hull design displaces boat weight in the water and is only supported by its buoyancy.
The weight of the water displaced by the vessel is equal to the vessel’s weight.
The rope used to pull down the spar or sail.
To float the vessel with the wind or current. Or the distance covered by the boat while drifting in the current, measured in time.
The distance between the lowest point on the keel and the center-line of the vessel measured as a vertical distance.
The sea anchor thrown over the stern of a life raft or boat or to reduce drift.
Digital Selective Calling (a function on Marine radios ).
A retractable keel drawn into the vessel’s hull.
Emergency Position Indication Radio Beacon.
Estimated Position.
Estimated Time of Departure.
Estimated Time of Arrival.
The fitting adjusting the feeding line allows you to change the direction of the lead line.
The raised border on cabin tables, chart tables, preventing objects from falling off the surface.
Measurement of water depth and rope lengths.
- 1 Fathom = 6-feet = 1.83-meters.
The vessel positioning plotted by two or more positioning lines.
The vertical distance between the top of the deck and the waterline.
The closest stay running between the masthead and stemhead, hankering the mainsail.
A large-size headsail is available in various sizes, overlapping the mainsail before hoisting in fresh to light winds on all sailing points.
Two concentric rings pivot at right-angles to keep objects horizontal despite the swaying motion of the boat.
Global Navigation Satellite System.
Global Maritime Distress and Safety System.
To change tack by turning the boat into the eye of the wind.
Booming out the headsail in a windward position using the whisker pole to hold it on the opposite side of the mainsail.
The fitting anchoring the mast to the boom, allowing free movement in all directions.
This metal rail surrounds the boat’s edges, allowing easy gripping to prevent falling overboard.
Turning the stern through the wind to change from one tack to another.
The spinnaker guy controls the steadying rope for the spar through the aft-fore position of the spinnaker pole. The foreguy keeps the spinnaker pole in the forward position.
Global Positioning System.
The rope hoisting the lower sails.
Highest Astronomical Tide.
The fitting for attaching the sail’s luff to a stay.
The deck opening provides the crew with access to the berth or cabin interior.
The streamlined surround of a forestay featuring the groove allows for the sliding attachment of the luff sides of the headsail.
Head-to-Wind
When the bow of the vessel points into the direction of the wind.
The forward motion of the vessel through the water.
The toilet.
The action of backing the jib and lashing the tiller to the leeward side in rough weather conditions. The heave-to encourages the vessel to reduce headway and lie quietly.
When the vessel exaggeratedly leans to one side.
International Maritime Organization.
International Regulations for Preventing Collisions at Sea.
International Telecommunication Union
The lines on weather maps joining places with equal atmospheric pressure.
The temporary device for replacing damaged or lost gear.
The line running from aft-to-fore on both sides of the vessel. The jackstays allow for the clipping attachment of safety harnesses to prevent being lost at sea when falling overboard.
A secondary, smaller, lightweight anchor.
A dual-masted sailboat featuring a mizzen mast that’s slightly smaller than its mainmast, with a stepped forward position of the rudder post/stock.
The center-line of the vessel features the attachment of the ballast keel, allowing for the lowering of the center-board.
Kicking Strap
The line for pulling down the boom or keeping it in the horizontal position when on a run or reach.
A short length of line attached to an important object that you don’t want to lose, such as the jet ski key. The lanyard can connect to your wrist or lifejacket.
The aft edge of the triangular sail. Both side-edges of a square sail.
Lowest Astronomical Tide.
The shore on which the wind is blowing.
The natural tendency of vessels to bear away from the direction of the wind.
Moving in a direction away from the wind. The direction in which the wind is blowing.
The vessel’s leaning to one side due to improper distribution of weight in the boat’s hull.
The leading edge of the sail. Luffing up is turning the head of the boat into the wind.
The sideways motion off course resulting from the wind blowing on one side of the hull and sails.
The instrument for measuring the distance and speed of a boat traveling through the water. It is also the act of recording the details of a voyage in a logbook.
Marinized engine
A car engine or motorbike motor adapted for use in watercraft.
Maritime and Coastguard Agency.
The keel socket locating the base of the mast.
Measured Mile
The distance marked on charts measures one nautical mile between islands at sea or onshore ranges.
The short after-mast on the yawl or ketch.
This imaginary longitudinal line circling the earth, passing through both poles, cutting at right-angles through the equator.
Mean Low Water Neaps.
Mean High Water Neaps.
Mean High Water Springs.
Mean Low Water Springs.
Maritime Mobile Service Identity.
The rope used for pulling out the sail’s foot.
Overall Length (LOA)
The extreme length of the vessel. The measurement from the aftmost point of the stern to the foremost points of the bow. This measurement excludes the self-steering gear, bowsprit, etc.
An emergency call requesting immediate assistance.
The bowline on a tender or dinghy for towing or making fast.
To gradually let out the rope.
The left-hand side of the vessel when looking forward.
Point of Sailing
The angles of the wind allowing for the sailing of the boat. Or the boat’s course relative to its direction and the direction of the wind.
Your vessel is on its port track when the wind is striking the boat’s port side first, and the mainsail is out to the starboard side.
Line of Position/Position Line
The line on charts shows the bearing of the vessel and the position where the boat mist lie. Or two positional lines providing a location fix.
The steel guard rail fitted to the bow to provide additional safety for the crew when working around the boat’s edge.
The steel guard rail fitted around the stern of the boat to prevent the crew from falling overboard.
The section of the vessel midway between the beam and the stern.
The difference in water levels between the high and low tides is the range of tides. Or the distance at which you can see the light.
The act of reducing the sail surface area through folding or rolling additional materials onto the forestay or boom.
Reefing Pennant
The sturdy line allowing you to pull down the leech cringle or luff to the boom while reefing.
When sailing with the wind blowing onto the beam, with all sailing points between close-hauled and running.
Riding Sail
The small sail you hoist to maintain the steerage way during stormy weather.
The imaginary line cuts through all meridians at the same angle. Or the course of the vessel moving in a fixed direction.
Rigging Screw
The deck fitting allowing for tensioning of the standing rigging.
The act of sailing with the wind to the aft of the vessel and with the sails eased into the wide-out, full position.
The curve in a leech sail extending beyond the direct line formed from clew to head.
Running Rigging
All moving lines like halyards and sheets used for trimming and setting sails.
Search and Rescue.
A vessel with two or more masts and the mainmast featured in the aftermost position.
Search and Rescue Transponder.
The toe-rail holes allowing water to drain off the deck.
The room in which the vessel can maneuver clear of submerged dangers.
The shut-off valve for the underwater outlet or inlet passing through the vessel’s hull.
This is French for “radio silence.” You’ll use it when reporting a distress call or incident at sea.
The act of hoisting a sail. Or how the sails fit or the direction of a tidal stream or current.
A procedure word for identifying safety calls.
A steel link featuring a removable bolt crossing the open end. The shackle comes in various designs, from “S” to “U” shapes and more.
The cables or ropes typically fund in pairs, leading from the mast to the chainplates at the deck level. These shrouds prevent the mast from falling to the side, and it’s part of your standing rigging.
The rope attaching to the boom to the sail’s clew allows for the trimming and control over the sail.
Skin Fitting
A through-hull fitting featuring a hole in its skin allows for air and water passing. The seacock is the accessory used for sealing the cavity when not in use.
A boat with a single-masted design for one headsail and one mainsail.
The general term for any metal or wooden pole on board a boat. The pole gives shape to the sails.
Safety of Life at Sea.
Speed Over the Ground
A lightweight, large balloon-shaped sail for running or reacting.
The horizontal struts attach to the mast and extend to the shrouds to assist with supporting the mast.
The act of joining wires or ropes using a weaving process interlacing the fibers in the cable or rope.
The sail will stall if the airflow over the sail surface breaks up, causing the vessel to lose its momentum.
Standing Part
The part of the line you don’t use when making a knot. Or the part of a rope you use to tie around the knot.
The metal post bolted to the deck in an upright position to support the guard railing.
Standing Rigging
The stays and shrouds provide permanent support to the mast.
Starboard Tack
The vessel is on the starboard tack when the boom is out to post, and the wind strikes the boat’s starboard side.
The right-hand side of the vessel when looking forward.
The rope or wire supports the mast in the fore-and-aft direction. It is a part of the standing rigging for your boat.
The sternward movement of the vessel towards the backward direction.
Steerage Way
The vessel has steerage when it reaches sufficient speed, allowing for steering or answering the helm.
The loop of rope or wire attaches the spar to the block to make a sling.
The railing around the vessel’s stern prevents the crew from falling overboard. Modern yachts do not have the elegant wooden railing of older models. Instead, they feature tubular steel or aluminum railings, called Pushpits.
Telegraph Buoy
The buoy marks the position of a submerged cable.
To pull on the end of the rope or cable, wound around a winch.
The compass mounted over the captain’s berth, allowing for the easy reference to what’s going on in the vessel’s helm.
The metal fitting forming eyes at the end of cables, wires, or ropes.
A description for any small boat, usually inflatable models. These boats will take supplies and people between a larger vessel and the shore.
Thermal Wind
The wind occurring from the difference in the heating of the sea and the land by the sun. The sun heats the land faster than the sea, resulting in the onshore wind from the sea replacing the air rising over the land, causing the “sea breeze” phenomenon.
Thumb Cleat
A small cleat featuring a single horn.
The wooden pegs featuring vertical pairs in the gunwale for constraining the oars for rowing.
Topping Lift
The rope linking the mast to the boom end. It supports the boom, allowing for its lowering and raising.
The progress on the vessel’s journey over the ocean. The trajectory line of the boat.
The sides of the hull between the waterline and the deck.
The netting stretching across the hulls of a catamaran.
A watch period or watch duty at the helm of the vessel.
Traverse beams forming part of the stern and fixed to the sternpost of a wooden ship.
Tricolor Lamp
A lamp displaying red in proper port sectors, green in the starboard sectors, and white astern. Some authorities permit the tri-color light on smaller boats instead of conventional stern and bow lights.
Turk’s Head
A decorative knot featuring variable numbers of interwoven strands that form a closed loop.
The direction and velocity of wind measured by stationary observers. Apparent wind is wind experienced by moving objects.
Sturdy steel fittings used for attaching standing rigging to the spar or mast.
The low, forward corner of the sail. Or the action of turning the boat through the wind to get it to blow on the other side of the sails.
Sailing close-hauled to work windward on an alternate course. The wind is on one side then the other.
The low strip of steel, wood, or strapping running along the edge of the deck. You’ll use it in combination with the hand railing to hold your feet to the deck to prevent falling overboard.
The rise and fall of the ocean are caused by the moon’s gravitational effect on the earth and the ocean.
The line moving from the mast had to the spar or the boom used in raising it.
To adjust the sail angle using sheets to achieve optimal efficiency from the sail. Or it describes the action of adjusting the load, influencing the fore-and-aft angle at which it floats.
The course of the boat making good on its travel plan. A fitting of on the boom or mast to the slide on the sail fit. The fitting along which the traveler runs for altering the sheet tension.
The speed and direction of the wind when anchored, stationary on the water, or land.
Turn Buckle
The apparatus used for tightening the standing rigging on the vessel.
A line used in raising something like a spinnaker pole vertically.
The vessel is underway when it releases it fastening to shore when it is not aground or at anchor.
See kicking strap.
The wind will veer when shifting in a clockwise direction. Veering can also mean paying out anchor rope or cable in a controlled manner.
Velocity Made Good
Very High Frequency
The disturbed water left behind (astern) the boat as it moves forward in the water, usually caused by a motor.
Weather Helm
The tendency of the vessel to turn into the wind.
The distance between the radio waves.
Weather Side
The side of the vessel to which the wind is blowing.
World Geodetic Survey of 1984 (most common chart datum).
A mechanical device featuring a cable or line attached to a motor. The winch pulls the boat aboard the trailer and helps with the vessel’s launch from the trailer. The winch also gives more pulling power to withdrawing nets or other apparatus from the water.
Whisker Pole
A lightweight pole used for holding the clew out of the headsail when on a run.
The winch features a vertical handle and a horizontal shaft used in hauling up the anchor chain.
The parts of the vessel that increase the drag on the boat. Examples would be the spars, rigging, etc.
The direction from which the wind blows toward the wind (the opposite way to leeward).
Cross Track Error. The perpendicular distance between two waypoints off track.
A dual-masted vessel with its mizzen stepped aft of its rudder post/stock.

John is an experienced journalist and veteran boater. He heads up the content team at BoatingBeast and aims to share his many years experience of the marine world with our readers.
What to Do If Your Boat Engine Won’t Start? Common Problems & How to Fix Them
How to launch a boat by yourself: complete beginner’s guide, how to surf: complete beginner’s guide to get you started.
Comments are closed.
Type above and press Enter to search. Press Esc to cancel.
A Complete List Of Sailing Terms
Sailing terminology and jargon can be difficult to understand for a complete beginner.
We've compiled a list of sailing terms, vocabulary, lingo, and phrases with their meanings and definitions.
Filter the sailing terms by letter:
A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z
The sailing terms beginning with the letter A are:
- Abaft : Toward the stern of a boat and behind the middle of the boat
- Abandon Ship : An instruction to leave the boat immediately. This is an emergency situation and everyone needs to get off the boat
- Abeam : On a line at right angles to a ship's or an aircraft's length
- Able Seaman : A crew member with experience and expertise in working on deck and handling the sailboat's rigging and equipment
- Aboard : This is a nautical term to describe being on or in a boat
- Above Board : This means anything on or above the boat deck
- Adrift : Not anchored or not securely moored, drifting with the current or wind
- Aft : The aft is the area at the back of the boat. It is also known as the stern
- Aft cabin : This is a sleeping cabin at the aft side (rear) of the boat
- Aftmost : Furthest towards the stern (back) of the boat
- Aground : When the boat is resting on or touching the ground below the bottom of the water
- A-hull : A-hull refers to a situation where a boat is secured to its anchor and is lying in the direction of the wind and waves, with all sails furled and no movement. This is typically done as a safety measure in severe weather conditions when the boat is in danger of capsizing or otherwise being damaged. It is also used as a strategy to wait out a storm or other adverse weather
- Alee : Away from the wind
- All Hands On Deck : This phrase is used to call all crew members to the deck of a sailing vessel, and is often used as a call to action in times of emergency. It is also considered a good omen for a ship to have all hands on deck before setting sail.
- Aloft : Above the deck or in the upper parts of the mast or rigging
- Anchor : A device used to hold or anchor a boat in a specific location on the water
- Anchor Buoy : A buoy attached to an anchor that is used to indicate the location of the anchor on the bottom
- Apeak : When the anchor is at the highest point of the bow when it is rode out
- Apparent Wind : The wind direction and speed observed by the crew in combination with the true wind direction and speed, which can be different due to the boat's motion
- Ashore : To or on the shore or land from the direction of the sea
- Astern : Behind or at the rear of a boat. If a boat is traveling astern, it is going in reverse
- Athwartship : Having a position across a vessel from side to side at right angles to the keel
The sailing terms beginning with the letter B are:
- B & R Rigging : B&R rigging refers to a specific type of rigging system used on sailing boats. The B&R rigging system is a combination of a traditional forestay and backstay system, with a flexible rig that allows for a more efficient sail shape in a wide range of wind conditions
- Back A Sail : Back a sail refers to the action of filling a sail with wind from the opposite direction, or "backwards" direction of the sailboat's forward motion. This is done by adjusting the sail and the direction of the boat so that the wind is blowing into the back of the sail, causing the sail to fill with wind and push the boat in the opposite direction. Backing a sail can be used to slow the boat down, change direction, or to help keep the boat in a specific location
- Backstay : A rope or cable that runs from the mast to the stern of a sailboat. It is used to support the mast and control the shape of the sails
- Baggywrinkle : A soft covering for cables to reduce sail chafe
- Ballast : Ballast refers to the weight placed on the bottom of a sailboat to improve its stability and balance. The weight of the ballast helps to counteract the force of the wind on the sails
- Ballast Keel : A vertical downward extension of the boat's hull, narrowly V-shaped. It is ballasted or weighted for stability and lateral resistance
- Barque : This is a sailboat with 3 or more masts with all the masts being square-rigged except the sternmost, which is fore-and-aft-rigged
- Batten : A batten is a primary structure of a mainsail. It supports the sail's shape
- Beam : The width of the boat, measured at its widest point
- Beam Reach : A point of sail in which the wind is coming from the side of the boat, resulting in the sails being at a 90-degree angle to the centerline of the boat
- Bear Away : Bear away, also known as falling off, means to turn a boat away from the direction of the wind
- Beat : This is sailing in a zig-zag formation toward the wind
- Beaufort Scale : A scale used to measure wind speed and the resulting sea conditions. It is named after Francis Beaufort, an officer in the Royal Navy
- Below Deck : Below deck in boating refers to the interior of a boat, typically the area below the main deck. This area is usually enclosed and protected from the elements, and typically includes living spaces such as cabins, heads (bathrooms), galley (kitchen), and salon (common area).
- Bermuda Rig : A Bermuda rig, also known as a Marconi rig, is a type of sailboat rigging that is characterized by a triangular mainsail and a jib sail. The mainsail is attached to the mast and the boom, with the boom extending out from the mast. The jib sail is attached to the forestay, which is a cable or rope that runs from the bow of the boat to the mast
- Bermuda Sloop : Bermuda sloop is a specific type of sailboat design that originated in Bermuda. It is characterized by a single mast, with a triangular mainsail and a jib sail, and it is the most popular sailboat design in the world. Bermuda sloops are known for their efficiency and ability to sail well in a wide range of wind conditions.
- Berth : A bed or sleeping area on a boat. For example, a 6-berth boat is a boat that can sleep 6 people
- Bight : A bend in a sailing rope
- Bimini Top : A Bimini top is a type of boat cover or canopy that is mounted on the top of a sailboat, typically on the stern or the cockpit area. The Bimini top provides shade and protection from the sun and rain for the passengers and crew on the boat
- Bilge : The lowest part of a boat's interior, typically located near the keel, where water collects and needs to be pumped out
- Binnacle : A binnacle is a housing or container on a boat that is used to protect and secure a vessel's compass. It is typically located near the helm or steering station
- Bon Voyage : This is a French phrase that literally means "good voyage" and is often used as a way to say "good luck" to someone setting out on a journey
- Boom : A boom on a sailboat is a horizontal spar, or pole, that extends out from the mast of a sailboat. The boom is used to support and control the bottom edge, or foot, of a sail. The boom also helps to shape the sail and control the angle at which the wind hits it, allowing the boat to move efficiently through the water
- Bosun : A crew member in charge of maintenance and upkeep of the boat's hull, rigging, and equipment.
- Bow : The bow is the front area of a boat
- Bridge : A room or platform area of a boat from which the boat can be operated
- Brig : A sailing vessel with two square-rigged masts
- Brigantine : A two-masted sailboat, square-rigged on the foremast but fore-and-aft-rigged on the mainmast
- Bulkhead : A bulkhead refers to a vertical wall within the interior of a boat that helps to divide the space and provide structural support. They are typically found below deck on a sailboat
- Bumper : A type of fender used to protect a boat from damage when it is moored or docked.
- Buoy : It is a device or object that is placed in the sea to aid navigation. For racing, it's used to set the race course and for recreational sailing, it is used to mark areas to avoid (among a few other purposes)
The sailing terms beginning with the letter C are:
- Cabin : This is a room inside a boat, typically found below the deck
- Canvas : A boat canvas refers to the various types of fabric or material used on boats to provide protection, shade, and shelter. Types of canvas include Bimini top, sail cover, dodger, etc.
- Capsize : When a boat heels over so far that the keel is lifted out of the water and the boat overturns
- Captain : The person in command of the sailboat. They are responsible for operating the boat safely
- Catamaran : Any vessel with two hulls
- Center-board : A board lowered through a slot in the keel to reduce leeway
- Chart Plotter : An electronic navigation device that plots the location and position of a sailboat on the water
- Cleat : A cleat is a device used on boats to secure ropes or lines. It typically consists of two horizontal arms with holes or slots that can be tightened around a rope by pulling on the line and then making a turn or two around the arms. Cleats are used to secure lines when docking, mooring, or anchoring a boat, and can be found on the deck, gunwale, or cockpit of a boat
- Clew : A clew is the lower aft corner of a sail
- Clipper : A sailboat designed for speed
- Cockpit : An enclosed space on a sailboat's deck where a sailboat is controlled or steered
- Cook : A crew member responsible for preparing and cooking meals for the crew
- Course : This is the direction in which a boat is traveling
- Close-Hauled : A point of sail where the boat is sailing as close to the wind as possible
The sailing terms beginning with the letter D are:
- Dead Reckoning : a method of navigation that involves calculating a ship's position by using information about its speed and direction over a certain period of time
- Deadrise : The angle between the bottom of a boat and the horizontal plane of the water
- Deck : The horizontal surface area on the top of the boat
- Deckhand : A member of the crew responsible for various tasks such as hoisting sails, steering the ship, and maintaining the deck
- Dock : A fixed structure attached to the shore to which a vessel is secured when in port
- Downbound : This is when a vessel is traveling downstream
- Draft : The depth of water a boat requires to float measured from the waterline to the lowest point of the hull
- Drift : The sideways movement of a boat caused by wind or current
- Drogue : A device that is towed behind a boat to slow it down or to keep it from drifting too quickly
- Drowned Out : When the wind is too strong for the sails and the boat can no longer make headway
The sailing terms beginning with the letter E are:
- Ease : To let out or slacken a line or sail
- Emergency Tiller : A backup steering system for a boat, typically used when the regular steering system fails
- Engineer : A crew member responsible for the maintenance and operation of the sailboat's engines and mechanical systems
- Entering A Port : This refers to the process of navigating a boat into a harbor or marina
- External Lead : This refers to the navigation method of determining the position of a boat by measuring the angle between two visible objects on shore or on buoys, using a lead line
- Eye Of The Wind : The direction from which the wind is blowing
- Eye-Splice : A way of creating a permanent loop in the end of a sailing rope
The sailing terms beginning with the letter F are:
- Fair Winds And Following Seas : This phrase is often used as a wish for good luck and smooth sailing
- Fairlead : A fitting through which ropes are led in order to change their direction or reduce friction
- Fathom : A unit of measurement for depth, equal to six feet
- Fender : A device placed between a boat and a dock or another boat to protect the boat from damage
- First Mate : The officer in charge of the deck crew, responsible for navigation and safety
- Foresail : A sail located at the front of a sailboat, also called jib
- Freeboard : The distance from the waterline to the deck of a boat
- Frigate : A type of ship, typically used for naval warfare or as a command ship for a fleet
- Furl : To roll or wrap a sail around a boom or mast in order to take it down
- Fetch : The distance over which a wind has blown without significant obstacle
- Front : The boundary between two different air masses, often associated with changes in temperature and precipitation
The sailing terms beginning with the letter G are:
- Gaff : A spar used to extend the upper edge of a fore-and-aft sail
- Gale : A strong wind with a speed of between 34-47 knots
- Geared Winch : A mechanical winch that is powered by gears and used to raise or lower a sail
- Genoa : A type of jib sail that is larger than a standard jib
- Give-Way Vessel : A vessel required to take action to avoid a collision with another vessel as per the international regulations for preventing collisions at sea (COLREGS)
- Godspeed : This phrase is used to wish someone a safe and successful journey
- Gunwale : The upper edge of the side of a boat
- Gybe : A maneuver in which a boat changes direction by turning its stern through the wind and causing the sail to change sides
- Gyroscopic Compass : A type of compass that uses a spinning wheel to provide stable and accurate heading information
The sailing terms beginning with the letter H are:
- Heading : The direction in which a boat is pointed, usually measured in degrees from true or magnetic north
- Heading Up : This refers to turning the bow of a sailboat towards the wind
- Heavy Weather : Severe weather conditions such as high winds, heavy seas, and storms
- Halyard : A rope or line used to hoist or lower a sail or flag. There is likely 1 halyard for each sail
- Hard Alee : An order to turn the bow of the boat as far as possible in the opposite direction of the wind
- Hatch : An opening in the deck of a boat, used for access to the interior or for ventilation
- Headstay : The cable or rod that supports the forestay, and holds the mast in the forward direction
- Helm : The helm of a sailboat is the steering mechanism of the boat, typically located at the back or the stern of the boat, and is used to control the direction of the boat. The helm is typically a wheel or tiller
- Helmsman : The person who steers the boat
- Helmsman's Seat : A seat located close to the helm, used by the helmsman to steer the boat
- Hiking : When a crew member moves out on the rail of the boat to counteract the heeling force of the wind and keep the boat level
- Hiking Strap : A strap used by a crew member to hold on to while hiking out on the rail of the boat
- Hurricane : A severe tropical storm with winds of 74 mph (119 km/h) or greater
The sailing terms beginning with the letter I are:
- International Regulations for Preventing Collisions At Sea (COLREGS) : A set of rules that govern the behavior of vessels on the water in order to prevent collisions
- Inboard : A motor or engine that is located inside the boat, as opposed to an outboard motor which is mounted outside the boat
- In Irons : A situation when a sailing vessel is stopped or hindered in its progression through the water because the wind is blowing directly onto the sail, preventing the vessel from moving forward
- Inhaul : A line or rope used to adjust the position of a sail
- Inshore : Close to the shore
- Inner Forestay : A rope or cable that supports the mast and holds the jib or genoa sail in place
- Iron Mike : This is a slang term for a sailboat's autopilot
- Irons : When a boat is stopped or hindered in its progression through the water because the wind is blowing directly onto the sail, preventing the vessel from moving forward
- Islands : Natural land formations that are surrounded by water
The sailing terms beginning with the letter J are:
- Jib : A triangular sail located at the front of a sailboat, also known as a foresail
- Jibe : A maneuver in which a boat changes direction by turning its stern through the wind and causing the sail to change sides
- Jib Sheet : A line used to control the angle of the jib sail
- Jumper Stay : An additional stay that supports the mast and is used to tension the headstay
- Jib Tack : The lower forward corner of a jib sail
- Jibing : Turning the boat so that the wind blows on the opposite side of the sail
- Jib Hanks : metal or plastic clips that hold the jib sail to the forestay
- Jib Furling : A system for rolling up a jib sail and securing it to the forestay when not in use
The sailing terms beginning with the letter K are:
- Keel : A long, heavy structural member that runs along the bottom of a boat's hull, providing stability and helping to keep the boat upright
- Knot : A unit of speed, equal to one nautical mile per hour
- Kedge : A small anchor used to hold a boat in a particular position or to move a boat by hauling it on a line
- King Plank : The centerline plank in the bottom of a boat that runs parallel to the keel
- Knees : Strong brackets that are used to support the deck and reinforce the hull-to-deck joint of a boat
- Knockdown : When a boat is hit by a large wave and it's knocked down on its side, causing water to flood the deck
- Kedge Anchor : a small anchor used as a temporary anchor to hold a boat in a particular position
The sailing terms beginning with the letter L are:
- Lazy Jacks : Lines or webbing that are used to guide the mainsail as it is lowered, making it easier to handle
- Leach : The back edge of a sail
- Lead Line : A line with a weight (lead) on the end, used to determine the depth of water beneath a boat
- Leeward : The direction away from the wind
- Luff : The leading edge of a sail, or the flapping or fluttering of a sail caused by wind coming from the wrong angle
- Luffing : When a sail is flapping or fluttering caused by wind coming from the wrong angle
- Lying Ahull : When a boat is allowed to drift without any sail set, used in heavy weather to prevent capsizing
- Life Jacket : A device worn by people on boats to keep them afloat in case of emergency, also known as a personal flotation device (PFD)
- Lifeline : A safety line that runs around the perimeter of a boat, used to prevent crew members from falling overboard
- Log : A device used to measure the speed of a boat through the water
- Long keel : A type of keel that extends the full length of the boat's hull, providing stability and helping to keep the boat upright
The sailing terms beginning with the letter M are:
- Mainsail : The largest sail on a sailboat, located at the back of the boat and controlled by the main sheet
- Main Sheet : A line used to control the angle of the mainsail
- Mast : The tall vertical spar that supports the sails of a boat
- Moor : To tie or anchor a boat in a specific location
- Mooring : A location where a boat can be tied or anchored
- Motor Sailor : A boat with both a sail and an engine propulsion
- Mainsail Halyard : A rope or line used to hoist the mainsail
- Mark : A buoy or other object used as a reference point for navigation
- Mariner's Compass : A type of compass that is used on boats and ships, typically featuring a magnetized needle that points towards magnetic north.
- Man Overboard (MOB) : A situation in which someone falls off a boat and into the water
The sailing terms beginning with the letter N are:
- Nautical Mile : A unit of measuring distance at sea that is used in navigation, equal to 1.85 kilometers
- Navigation Lights : lights required by international regulations to be displayed on boats in order to indicate the boat's position and direction of travel at night
- Navigation : The process of planning, tracking, and controlling the movement of a boat or ship
- Navigator : The officer responsible for charting the sailboat's course, using navigation instruments and maps
- Navigational Aids : Any device or system that helps a boat or ship navigate, such as buoys, lighthouses, and radar.
- Nautical Chart : A map specifically designed for navigation on the water, showing water depths, coastlines, navigational hazards, and other important information
- Natural Navigation : the traditional method of navigation using natural cues such as the stars, sun, moon, and the movement of ocean currents and waves
- Navigation Rules : A set of regulations that govern the movement of boats and ships in order to prevent collisions
- Navigation Software : Computer programs that assist in navigation by providing information such as navigation chart, water depth, weather forecasts and routes
- Navigation Lights : Lights that are required by international regulations to be displayed on boats and ships in order to indicate the vessel's position and direction of travel at night
- Navigational Sextant : An instrument used for measuring the angle between two visible objects, typically the horizon and a celestial body, used for navigation and determining a vessel's position at sea
The sailing terms beginning with the letter O are:
- Outboard : Also called outboard motor, an outboard refers to a motor or engine that is mounted outside the boat, as opposed to an inboard motor which is located inside the boat.
- Overboard : When something falls or is thrown off the boat into the water
- Offshore : Away from the shore
- Off The Wind : Sailing with the wind blowing from behind the boat.
- Outhaul : A line or rope used to adjust the position of a sail.
- Outrigger : An extension or framework that is attached to the side of a boat to increase stability.
- Overfall : A type of wave that forms when the wind and current are opposing, leading to steep, breaking waves.
- Overhead : The highest point in a boat, typically the top of the cabin or the coach roof
- Owner's Cabin : A room in a boat that is reserved for the owner, usually the largest and most comfortable cabin
The sailing terms beginning with the letter P are:
- Paddle : A tool used for propelling a boat through the water, typically consisting of a long shaft with a flat blade on one end
- Piling : A vertical structural member driven into the bottom of a body of water to support a dock or pier
- Porthole : A small window in the hull of a boat that provides light and ventilation to the interior
- Personal Flotation Device (PFD) : A device worn by people on boats to keep them afloat in case of emergency, also known as a life jacket
- Port : The left side of a boat when facing the bow (front)
- Pitch : The up-and-down movement of a boat caused by waves
- Planking : The process of covering a boat's hull with thin wooden planks
- Planking Seam : The joint between two adjacent planks on a boat's hull
- Point Of Sail : This is the direction you are going relative to the direction from where the wind is coming
- Propeller : A device that is attached to the bottom of a boat's hull, used to propel the boat through the water
The sailing terms beginning with the letter Q are:
- Quartering Sea : Waves that are coming from the side of a boat at a 45-degree angle
- Quarterdeck : The area of a sailboat located at the aft (rear) of the main deck, traditionally reserved for the ship's officers on larger boats
- Quartermaster : A crew member responsible for steering the sailboat, and also sometimes responsible for navigation. They are most commonly found on large sailboats and ships
- Quay : A man-made structure built alongside a body of water to provide a place for boats to tie up and load or unload cargo
- Quicksilver : An older term for Mercury, it was used to refer to a liquid in a barometer or thermometer
- Quartering : When a boat is sailing at an angle to the wind, with the wind blowing from the side
- Quartering Wind : A wind that is blowing on the side of the boat
- Quilting : A technique used to make a piece of clothing or sail that involves stitching together multiple layers of material
- Quoins : Blocks of wood or metal used to adjust the tension on a sail
- Quick Release : a device that allows you to quickly release a rope or line under load
The sailing terms beginning with the letter R are:
- Rudder : A flat underwater structure located at the stern of a boat. It is used to steer the boat
- Reef : To reduce the size of a sail by rolling or folding a portion of it and fastening it in place to reduce the sail's wind-catching surface
- Rope : a strong cord made of natural or synthetic fibers, used for a variety of purposes on a boat, including hoisting sails, tying up to a dock, and securing gear
- Running Lights : Lights that are required by international regulations to be displayed on boats and ships in order to indicate the vessel's position and direction of travel at night
- Rigging : The ropes, cables, and chains that are used to support the mast and control the sails of a boat
- Rode : The anchor line and chain used to secure a boat to the sea floor
- Rocker : The curvature of a boat's bottom from the centerline to the keel
- Roller Furling : A system for rolling up a sail and securing it to the mast or boom when not in use
- Roller Reefing : A method of reefing a sail in which the sail is rolled around a foil on the mast or boom
- Right Of Way : The responsibility of a vessel to give way to other vessels as per the international regulations for preventing collisions at sea (COLREGS)
The sailing terms beginning with the letter S are:
- Safe Harbor : A safe harbor is considered a symbol of good luck for sailors
- Sheet : A rope used to control the position of a sail
- Shroud : A rope or cable that runs from the mast to the side of the boat to provide support for the mast
- Starboard : The right side of the boat when facing forward
- Stern : The rear end of the boat
- Starboard Tack : Sailing with the wind coming from the right side of the boat
- Steward/Stewardess : A crew member responsible for the provisioning, cleaning, and maintenance of the sailboat's interior
- Spinnaker : A large, triangular sail used when sailing downwind
- Sail : A sheet of fabric that is attached to a mast and used to propel a boat through the wind
- Skipper : The person in charge of a sailboat
- Spar : A wooden or metal pole that supports a sail
- Shackle : A U-shaped metal fastener with a pin that is used to connect ropes or cables to the boat
- Scull : A method of steering a boat by using a oar or paddle at the stern of the boat
- Shrouds : A set of ropes or cables that run from the top of the mast to the sides of the boat to provide support for the mast
- Scuttlebutt : A nautical term for gossip or rumors
- Sea Room : The amount of space around a boat that is necessary to safely navigate
- Sea State : The condition of the surface of a body of water, often used to describe the roughness of the water during bad weather
- Sextant : An instrument used for navigation at sea, used to measure the angle between two visible objects, typically the horizon and a celestial object, in order to determine the ship's position
- Spinnaker : A spinnaker is a sail designed specifically for sailing off the wind on courses between a reach (wind at 90° to the course) to downwind (course in the same direction as the wind)
- Storm Sail : A sail that is designed for use in heavy weather
- Steering Compass : A compass mounted on or near the helm of a boat that is used to help the helmsman steer the boat
- Shipshape : A term used to describe a boat that is well-maintained and in good condition
- Squall : A sudden, strong wind often accompanied by rain or snow
- Swell : Large ocean waves that are caused by distant storms or winds
The sailing terms beginning with the letter T are:
- Tack : The direction in which a sailboat is moving
- Topsail : A sail set above the main sail on a ship's mast
- Tiller : A handle or lever used to steer a boat
- Trim : The adjustment of a sail's angle to the wind to optimize the boat's speed and direction
- Tacking : The act of turning a sailboat into the wind in order to change direction
- Tender : A small boat used to transport people or goods to and from a larger boat
- Tumblehome : The inward slope of a sailboat's sides above the waterline
- Topsides : The upper side of a ship's hull above the waterline
- Tugboat : A powerful boat used to tow or move other boats or ships
- Thwart : A seat that runs across a boat, typically used in a canoe or rowboat
- Tarpaulin : A heavy-duty waterproof sheet used to cover and protect equipment on a boat
- Telltale : A small flag or ribbon used to indicate the direction of the wind
- Topsheets : The sheets that control the uppermost sails of a square-rigged vessel
- Towing : The act of pulling a boat or ship behind another using a line or cable
- Toe Rail : A narrow rail along the edge of the deck used to prevent water from running onto the deck
- Trough : An elongated area of low pressure often associated with stormy weather
- Thunder Squall : A sudden, severe thunderstorm with high winds and heavy precipitation
The sailing terms beginning with the letter U are:
- Underway : Describes a boat that is not anchored or aground
- Upwind : Sailing towards the direction from which the wind is blowing
- Unfurl : To release and extend a sail from a furled position
- Uphaul : A rope or line used to raise a sail
- Underwater Gear : Equipment or gear used for activities under the water surface, such as diving gear or fishing gear
- Upstream : Against the direction of a current or flow
- Underbody : The bottom of a boat or ship's hull
- Underwater Lights : Lights used to illuminate the underwater area around a boat
- Underwater Soundings : Measurements taken to determine the depth of water beneath a boat
- Unstep : To remove a mast from a boat
- Unbend : To remove a sail from a boat or to remove a rope from a cleat or winch
- Unmoor : To release a boat from its moorings
The sailing terms beginning with the letter V are:
- Veer : To change the direction of the wind
- VHF Radio : A radio used for communication on boats and ships, operating on very high frequency
- Vang : A rope or lever used to control the angle of a sail
- Ventilator : A device used to allow air to flow into a boat
- Vane : A device used to determine wind direction
- Velocity : The speed at which a boat or ship is moving
- Valve : A device used to control the flow of fluids or gases
- VHF Antenna : A type of antenna that is used for VHF radios
- Velocimeter : An instrument used to measure the speed of a boat through the water.
- Visibility : The maximum distance at which an object can be seen
- Vent : A hole or opening on the sailboat that allows air or gases to escape
The sailing terms beginning with the letter W are:
- Wake : The trail of water left behind a sailboat as it moves
- Waterline : The line where the water meets the side of a boat or ship
- Windward : The direction from which the wind is blowing
- Watertight : Describes a boat that is designed to prevent water from entering
- Wharf : A platform or dock used for loading and unloading boats and ships
- Warps : Ropes or lines used to secure a boat or ship to a dock or buoy
- Windlass : A mechanical device used to raise or lower an anchor
- Watertight Bulkhead : A partition that is designed to prevent water from penetrating the interior of a boat or ship
- Watertight Door : A door that is designed to prevent water from penetrating the interior of a boat
- Whipping : A method of securing the end of a rope to prevent fraying
- Watertight Hatch : A hatch that is designed to prevent water from penetrating the interior of a boat or ship
- Waterspout : A type of tornado that forms over water
- Wench : A mechanical device used for hauling or lifting heavy loads on a boat
The sailing terms beginning with the letter X are:
- X-Yachts : A brand of luxury performance sailing yachts
- X-Bow : A type of bow design that features a sharp, vertical bow that is designed to reduce slamming in heavy seas
The sailing terms beginning with the letter Y are:
- Yard : A spar that extends horizontally from the mast of a sailboat, used to support and shape the sails
- Yaw : When a boat deviates from its course, typically caused by wind, waves, or steering issues
The sailing terms beginning with the letter Z are:
- Zephyr : A light breeze often used to refer to a gentle wind in sailing terms
- Zigzag : A course that changes direction frequently, often used to avoid obstacles or to make progress in difficult wind conditions
- Zone of Confidence : The area around a sailboat where the skipper is confident of his/her ability to handle the sailing vessel safely
Frequently Asked Questions About Sailing Terminology
Below are the most commonly asked questions about sailing terminology.
What Are The Most Popular Sailing Terms?
The most popular sailing terms are bow, port, stern, starboard, helm, keel, rigging, rudder, sails, deck, below deck, above deck, inboard, outboard, jib, anchor, skipper, aft, captain, rope, berths, knot, tack, mast, boom, mainsail, heading, furling, visibility, buoy, batten, main sheet, dock, offshore, inshore, nautical mile, man overboard, personal flotation device, reef, life jackets, hull and mooring.
What Are The Least Popular Sailing Terms?
The least popular sailing terms are iron mike, irons, toe rail, zephyr, scuttlebutt, rocker, luffing, shipshape, sea room, zigzag, quartering sea, beat, piling, and quilting.
What Are Sailing Terms For Wind?
Sailing terms for wind are windward, leeward, close-hauled, beam reach, running, tacking, jibing, true wind, apparent wind, fetch, and beaufort scale.
What Are Sailing Terms For Good Luck?
Sailing terms for good luck are bon voyage, all hands on deck, fair winds and following seas, godspeed and safe harbor.
What Are Sailing Terms For The Crew?
Sailing terms that pertain to the crew include captain, first mate, navigator, bosun, deckhand, quartermaster, able seamen, steward/stewardess, engineer and cook.
What Are Sailing Terms For Sails?
Sailing terms for sails are mainsail, jib, genoa, spinnaker, boom, halyard, sheet, clew, tack, reef, leach, and luff.
What Are Sailing Terms For Bad Weather & Storms?
Sailing terms for bad weather and storms are squall, gale, storm, hurricane, trough, front, sea state, swell, thunder squall and fetch.
What Are Sailing Terms For Beginners?
Sailing terms for beginners are hull, mast, sail, boom, rudder, keel, anchor, port, starboard, bow, captain, skipper, stern, deck, cabin, cleat and tack.
What Are Sailing Terms For Parts Of The Sailboat?
Sailing terms for parts of the sailboat are hull, mast, boom, rigging, standing rigging, running rigging, bow, stern, deck, cabin, bow pulpit, stern pulpit, gunwale, keel, rudder, tiller, winch, cleat, chocks and chain plates.

Glossary of Nautical Terms: The Ultimate Guide to 500+ Boating and Sailing Terms
Navigating the world of boating and sailing requires a good understanding of many nautical terms. From the anatomy of a boat to the mechanics of sailing, there are many terms that any boater or sailor needs to know.
Knowing some basic nautical terms is vital for safety, effective communication, and mastering the art of boating and sailing, whether you’re a seasoned sailor or a novice.
In this article, we’ve gathered 500+ nautical terms to cover general boating and sailing jargon. Enhance your knowledge and sail with confidence!
Let’s dive into the fascinating language of boating!
Nautical terms list
A b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z.
Aback – when the wind strikes the sails from the opposite side of the vessel than intended (lee side).
Abaft – toward the stern or rear of the boat.
Abaft the beam – a point on the boat’s side or stern that is behind a line perpendicular to the beam, which is the widest part of the boat.
Abeam – at right angles to the centerline of a boat.
Aboard – on or in a boat.
Abreast – side by side.
Adrift – a boat that is floating without any propulsion or anchor holding it in place.
Aft – toward the back of the ship (stern).
Aground – a boat that has run aground or is stuck on a reef or sandbar.
Ahead – forward of the ship, in forward direction.
Ahoy – a nautical greeting used to call or draw attention.
back to top
Aids to Navigation – navigational tools such as lighthouses, buoys, and beacons, that supplement natural landmarks, to help boats navigate safely.
AIS – Automatic Identification System.
Alee – side of the boat that is sheltered from the wind, opposite to windward.
Aloft – overhead, above the deck of the boat. .
Amidship – at or near the middle part of the boat.
Anchor – a heavy object used to grip to the ground underwater and keep a boat in place.
Anchorage – a suitable place in a body of water where boats can anchor or moor.
Apparent wind – The perceived wind speed and direction experienced the crew on a moving boat.
ARPA – Automatic Radar Plotting Aid.
Astern – behind or towards the rear of a boat. Opposite to ahead.
Athwartships – perpendicular to the centerline of a ship or boat.
Aweigh – the position of an anchor when it is being lifted from the seabed.
Azimuth – horizontal angle between a fixed reference point and the direction or bearing of an object. Typically measured in degrees and clockwise direction.
Back a sail – process of reversing the direction of a sail in order to slow down or stop a boat.
Backstay – a wire or rope that supports the mast from the stern of the boat and prevents its forward movement.
Backwinded – when the wind hits a sail on the opposite side to which it was intended to be set.
Baggywrinkle – protective covering that is placed on the rigging of a sailing vessel to prevent wear and tear from the sails.
Bail – to remove water from a boat using a bucket or other container.
Bailers – devices used for removing water from a boat.
Bale – a large bundle or package of goods or supplies that are tightly bound together for storage or transportation on a boat.
Ballast – a heavy material that is placed in the hull of a ship or boat to increase its stability and control its buoyancy.
Ballast keel – type of keel designed to provide ballast to a sailing vessel, typically a sailboat or yacht.
Bar – a shallow area of water that forms at the entrance or exit of a harbor or river.
Barber hauler – a line or wire attached to the jib or spinnaker sheet used to adjust its angle.
Batten – a thin, flat piece of wood or metal used to reinforce a sail.
Batten down – to secure hatches and other openings on a boat to prevent water from entering.
Beam – the widest part of a boat, usually in the middle.
Beam reach – a point of sail where the wind is blowing perpendicular to the side of the sailboat.
Bear away / Bear off – to steer the boat away from the wind.
Bearing – compass direction of an object relative to the boat’s position and expressed in degrees from true or magnetic north.
Beat – to sail upwind by tacking back and forth (zigzag) at an angle to the wind.
Belay – to secure a rope or line to a cleat or other fitting to prevent it from running out.
Below – lower deck or level of a boat.
Bend – to tie or fasten a rope or line to an object, such as a sail or anchor, using a knot or hitch.
Berth – (1) a place in a harbor where a boat can be docked or moored. (2) a bed or sleeping area on a boat.
Bight – bend or loop in a rope.
Bilge – the lowest part of a boat’s hull where water that enters the boat collects.
Binnacle – a case that holds a boat’s compass.
Bitter end – the end or final part of a line or chain.
Blanketing – a tactical sailing maneuver where one boat blocks the wind from reaching another boat to slowing it down.
Block – a pulley used to change the direction or mechanical advantage of a rope.
Bluewater sailing – to sail on the open ocean as opposed to coastal or lake sailing.
Boat – a craft or vessel designed to float on water and typically propelled by oars, sails, or an engine. Can be used for transportation, recreation, or commercial purposes.
Boat hook – device used for reaching or pulling objects in the water, or for pushing off from docks or other boats.
Boatswain – (pronounced “bosun”) a crew member responsible for the maintenance of the boat and its equipment.
Bobstay – supporting wire stay that runs from the bow of a boat to the end of the bowsprit, helping to hold it steady and secure.
Bollard – a short, thick post used for securing ropes or cables on a ship or dock.
Bolt Rope – a rope sewn onto the edge of a sail, to attach the sail to the rigging of the boat.
Boom – horizontal spar that extends from the mast of a sailboat and holds the foot of the sail.
Boom Crutch – a device used to hold the boom up and in place when the sail is not in use, usually while the boat is anchored or moored. The crutch is stowed when the boat is sailing.
Boom vang – a device on a sailboat that helps control the shape and tension of the mainsail by applying downward force to the boom. Helps to control the sail’s twist, and keep the boom from lifting.
Boot stripe – painted stripe on the hull of a boat that runs the length of the boat at or near the waterline.
Boot tope – a boot stripe at the boat’s designed waterline.
Bow – the front or forward section of the boat.
Bowline – (1) a docking line at the bow or forward part of the boat.(2) knot used to create a fixed loop at the end of a line that will not slip or come undone under load.
Bow thruster – a device used to maneuver a boat in tight spaces.
Bowsprit – a spar extending forward from a ship’s bow, primarily used to anchor the forestay for the jib or other headsails.
Breast line – a dock line going perpendicular from the centerline of the boat to the dock. Used to temporarily hold a boat close to the dock .
Bridge – the area of a ship from which it is navigated and controlled.
Bridle – line or wire attached to the boat at both ends and used to distribute the load.
Brightwork – varnished or polished surfaces such as wood or metal on a boat.
Broach – when a boat suddenly turns broadside to the wind and waves, causing it to heel over excessively and potentially leading to a loss of control.
Broad reach – point of sail where the wind is coming from behind the boat but not directly downwind.
Bulkhead – a dividing wall or partition separating different compartments within a boat.
Bullseye – a block with one or more holes through the center used for leading lines, halyards, or sheets.
Bulwark – vertical extension of the boat’s hull that increases the height of the sides and helps to prevent water from coming on board and to keep the crew in.
Bunk – narrow bed often built into the wall or arranged in tiers to maximize space.
Buoy – a floating device used as a navigational aid or to mark the location of hazards or obstructions.
Burdened vessel – a vessel that, according to navigational rules must give way to a “privileged vessel”. It is more commonly called a “give-way” vessel.
Cabin – an enclosed area on a boat used for living quarters or storage.
Cabin sole – the floor or deck of the cabin on a boat.
Cable – (1) Heavy chain or rope attached to an anchor. (2) A unit of length equal to 120 fathoms or 720 feet (219 meters) in US customary units (USCS).
Can – a type of navigational buoy.
Canvas – material used for sails in the early days. Still used for boat covers, dodgers, biminis, and other accessories.
Capsize – to turn over or flip a boat.
Capstan – a machine used to raise heavy objects such as anchors.
Cargo – goods or materials transported by ship or other means of transport.
Cast off – to untie a boat from a mooring or dock, or to release a line from a cleat or bollard.
Catamaran – a boat with two parallel hulls.
Catboat – sailboat with a single sail mounted on a mast set well forward in the bow of the boat.
Celestial navigation – method of navigating a boat by using the positions of celestial bodies such as stars, the moon, and planets.
Centerboard – a board lowered through a slot in the centerline or keel to help reduce sideways drift. Also spelled centreboard.
Centerline – line at the center of a sailboat, from the bow (front) to the stern (rear), that divides the boat into port and starboard halves.
Chafe – damage to a line, or cable caused by rubbing against a rough surface or another object.
Chafe gear/ Chafing gear – gear used to prevent chafe. Chafe gear materials commonly include rubber, canvas, and leather.
Chain plates – metal plates that are part of the sailboat rigging system, and are used to attach shrouds and stays to the deck.
Chart – a map used for navigation.
Chart datum – level surface provided on a chart and used by boaters to determine water depth at any given point and to ensure safe passage.
Chine – intersection between the bottom and sides of a boat, that creates an angle or ridge along the hull. Not found in round bottom boats.
Chock – a fitting attached to the deck and used to guide anchor, mooring or dock lines.
Clear the decks – to remove or tidy up everything from a boat’s decks to prepare for action or to clean the ship.
Cleat – a fitting on a boat’s deck to which a rope or chain can be tied.
Clew – the lower aft corner of a triangular sail or the lower corners of a four-sided sail.
Close hauled – a point of sail where the boat is sailing as close to the wind as possible.
Close reach – point of sail where the wind is coming over the side of the boat at an angle between a beam reach and a close hauled.
Clove hitch – a type of knot used to attach a line to a post, pole, or another line.
Coaming – raised edge or border around an opening or a raised area on a boat to prevent water from entering the cockpit, hatch, or other openings.
Cockpit – the area of a boat or ship where the steering and navigation equipment is located.
Coil – to arrange a line in a series of circular loops, ready for stowing.
Comms – short for “communications”, referring to communication equipment and systems on a ship.
Companionway – a stairway or ladder leading from one deck to another.
Compass – a navigational instrument used to determine direction relative to the Earth’s magnetic poles.
Compound sheer – curvature of a boat’s deck from the bow to the stern, where the height of the deck changes both horizontally and vertically. .
Container ship – a type of ship designed to transport standardized shipping containers.
Course – the intended direction of a boat’s movement.
Coxswain – the person who steers and directs a small boat.
CQD – a distress signal used in radio communication before the adoption of SOS . A combination of two signals: “CQ” (“sécu“, from the French word sécurité) which means “alert message to all stations”, and “D” to indicate “distress”. See meaning of CQD .
Crane – a machine used for lifting and moving heavy objects on a boat.
Crew – the people who operate a boat.
Cringle – small eye or grommet in a sail used to attach lines or fittings.
Cuddy – small shelter on a boat used for storage or for the crew to take refuge from the weather.
Cunningham – a control line that is used to adjust the tension of the luff (forward edge) of a sail.
Current – the flow of water in a particular direction, often caused by tides or winds.
Cutter rig – a type of sailboat rigging that features two or more head sails, or foresails, mounted on the forestay.
D signal – a signal used in maritime communication to indicate “keep clear, I am maneuvering with difficulty.” It is represented by a yellow and blue square flag (Delta flag).
Daggerboard – similar to a centerboard, it slides up and down in a slot in the hull. Common on catamarans, trimarans, and some small monohull sailing boats.
Davit – a crane-like device used for lowering or raising small boats on a ship.
Dead ahead – Directly in front of the boat and its centerline.
Dead astern – Directly behind the boat or straight aft.
Dead reckoning (DR)/ Deduced reckoning – estimated position based on course, speed, and time from a known past position.
Dead run – when the wind is directly behind a sailboat. The boat is running directly downwind.
Deadhead – a floating log or piece of timber that poses a hazard to navigation.
Deadlight – a type of weather cover designed to fit into a larger opening in a boat’s hull or deck and used to close off an opening in bad weather.
Deck – the horizontal surface of a boat’s hull above the waterline.
Deck plate – a metal or plastic plate that covers an opening in the deck of a boat, providing access to equipment or storage spaces such as the bilge or fuel tank.
Depth sounder – a device used to measure the depth of water.
Deviation – difference between the true north and magnetic north which affects the accuracy of the compass. Is caused by a vessel’s own magnetic field or metallic objects.
Dinghy – small boat often used as tenders to larger boats, to ferry people and supplies to and from shore.
Displacement – (1) the weight of the water displaced by the boat when afloat. (2) the weight of the boat itself, including all the equipment, fuel, and supplies on board.
Displacement hull – a hull design that displaces a volume of water equal to the boat’s weight for improved buoyancy.
Dock – a structure built along the shore or waterfront for boats to moor, tie up, or load and unload passengers or cargo.
Dodger – cover that extends above the cockpit of a boat to provide shelter from wind, spray, and rain.
Double ender – a type of boat or ship that has a pointed bow and stern, which are similar in shape and size, allowing for better stability and maneuverability.
Downhaul – a line used to apply downward tension or pull on a sail or other piece of equipment.
Downwind – when the wind is blowing from behind a vessel or in the same direction the boat is traveling. Sailing away from the wind.
Draft – the depth of a boat’s hull below the waterline.
Drift – distance and direction a vessel is carried off course due to external forces such as wind, waves, or current.
Drogue – sea anchor device that is attached to the boat by a line and deployed overboard to create drag and slow down drift.
Drop keel – a retractable keel that can be lowered and raised as needed.
Dry dock – a structure used for repairing, building, and maintaining boats out of the water.
DSC – Digital Selective Calling, a method of communication used in maritime radio systems.
Ease – to slacken or loosen.
Ebb – the flow of tidewater away from land, usually occurs between high and low tide.
EP – Estimated Position.
EPIRB – Emergency position indicating radio beacon, a device used to alert search and rescue services in case of an emergency.
ETA – Estimated Time of Arrival.
ETD – Estimated Time of Departure.
Fairlead – a fitting on a boat’s deck used to guide ropes or cables.
Fairway – a navigable channel or area of water.
Fall off – to steer a vessel away from the wind. Also known as Head Down.
Fathom – a unit of measurement equal to 6 feet (1.83m), used to measure water depth.
Fender – a cushioning device, placed between boats, or between a boat and a pier, to prevent damage.
Ferry – a boat or ship used to transport passengers and vehicles across a body of water.
Fiddle – a raised guard around the edge of a table, counter, or other flat surfaces to prevent objects from falling off.
Figure Eight Knot – a type of stopper knot, that looks like the number eight, and is used to prevent the end of a rope from passing through a retaining device such as a ring, grommet, or block.
Figurehead – a carved ornament mounted on the bow of a boat.
Fix – the vessel position determined by taking bearings or sightings on three or more objects or landmarks.
Flare – (1) a device used to signal for help or to mark the location of a person or object in the water. (2) the outward curve of a boat.
Fleet – a group of ships.
Float – a buoyant object used for marking channels or hazards in the water.
Flood – the incoming or rising tide. Opposite to ebb.
Flotsam – debris or wreckage from a ship that is floating on the surface of the water.
Fluke – the part of an anchor that digs into the seabed to hold the vessel in place.
Foghorn – a loud horn used to signal in foggy conditions.
Following sea – wave pattern approaching a vessel from astern, following the vessel’s direction of travel.
Force 8 – gale level winds with average speeds of 34 to 40 knots (39 to 46 mph) according to the Beaufort Wind Scale. Level 12 is a hurricane .
Fore – towards the front or bow of a ship.
Forecastle – Sometimes abbreviated fo’c’sle, the forward-most part of the ship, often used as the crew’s living quarters.
Foredeck – the boat’s deck at the bow or front of the vessel.
Foremast – the mast located nearest to the bow (front) on a boat with more than one mast. Usually the second tallest mast.
Forepeak – small compartment at the forward end of a ship, below deck, and used for storage of equipment, sails, or anchors.
Foresail – sail located forward of the mast on a sailing vessel.
Forestay – a stay that supports the mast from the front of the boat.
Foretriangle – the triangular area of sail between the forestay, mast, and deck of a sailing vessel.
Forward – towards the front or bow of a boat.
Fouled – Fouled- entangled or obstructed.
Fractional rig – Fractional rig- sailing rig in which the forestay does not run to the top of the mast but instead attaches at a point below the top, or “fractional” point.
Freeboard – the vertical distance between the waterline and the main deck of a boat.
Furl – to roll up and secure a sail.
Gaff – a spar positioned diagonally across the mast and used to support and control the sail.
Galley – the ship’s kitchen or cooking area.
Gangway – a movable ramp or platform used for boarding or disembarking a boat.
Gasket – a rope used to secure a sail to a spar or mast. Term mainly used in square-rigged ships.
Gear – various pieces of equipment and supplies used to operate and maintain a boat, including sails, lines, winches, anchors , electronics, safety gear, etc.
Genoa – a type of headsail that is larger than the jib and overlaps the mainsail. It is said the sail originated in Genoa Italy, hence its name.
Gimbals – a device used to keep a compass or other instrument level and stable.
Give – a vessel that requires taking action and keeping clear of the Stand-on vessel.
GMDSS – Global Maritime Distress and Safety System.
GMT – Greenwich Meridian Time. Became Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) in 1972.
GNSS – Global Navigation Satellite System.
Go about – to turn the boat through the wind during the tack.
Going to weather – sailing against wind and seas.
Gooseneck – fitting that attaches the boom of a sailboat to the mast. Designed to allow the boom to pivot up and down and side to side.
GPS – Global Positioning System, a satellite-based navigation system used for determining location and navigation path.
Grab rails – cabin fittings for hand-holding and personal safety when moving around the boat.
Great Circles – method of defining the shortest distance between two points on the globe’s surface.
Grog – a mixture of rum and water served to sailors in the 18th century.
Ground tackle – equipment used to anchor a boat. Includes the anchor, anchor chain or rope, and any other equipment required for anchorage.
Grounding – when a boat runs aground on a shallow area or rocks.
Guard rail – also known as a lifeline, is a safety railing system that runs around the perimeter of a boat, to prevent crew and passengers from falling overboard.
Gunwale – the upper edge of a boat’s side.
Guy – a steadying line used to control the end of a spar.
Gybe – another term for jibe.
Half – a flag flown at a lowered position as a sign of mourning.
Halyard – a rope or line used for hoisting or lowering a sail.
Hanks – metal fittings or hooks used to attach a sail to a stay of a sailboat.
Hard alee – a command given on a sailing vessel to turn the helm and have the bow of the boat through the wind as quickly as possible.
Hard Chine – hard or abrupt intersection between the bottom and sides of a boat, that creates an angle or ridge along the hull. Not found in round bottom boats.
Hard over – to turn the steering wheel as fast as possible.
HAT – Highest Astronomical Tide.
Hatch – an opening in a boat’s deck used for access or ventilation.
Hawser – a large rope used for towing or mooring a ship.
Head – (1) the toilet or bathroom on a boat (2) the upper corner or end of a triangular sail.
Head Down – to steer a vessel away from the wind. Also known as Fall Off.
Head to Wind – when the bow of the boat points directly into the wind.
Header – when wind direction changes, causing the boat to head down.
Headfoil – streamlined rod surrounding the forestay, and used to furl and unfurl the headsail.
Heading – the direction in which a boat bow is pointed or aimed. Usually expressed as an angle in degrees relative to the north or another reference.
Headsail – sail located forward of the mast on a sailing vessel. See Foresail.
Headstay – a stay that supports the mast from the front of the boat. See Forestay.
Headway – forward motion or progress made by a vessel through the water. opposite to sternway.
Heave to – to stop a boat’s forward progress.
Heel – the lean of the boat to one side and caused by the winds force on the sails.
Helm – the steering apparatus of a boat, including the wheel or tiller .
Helmsman – crew member at the helm and responsible for steering the boat.
Helmsperson – person who steers the boat. See Helmsmans.
Hike – to lean out over the side of the boat to balance it.
Hike out – the practice of leaning over the windward side of a sailboat in order to keep it balanced and prevent it from tipping over.
Hiking stick – a device used to control the tiller from a certain distance.
Hitch – a knot used to attach a rope or line to an object, such as a post, ring, or hook.
Hoist – to raise something, usually a sail, up a mast or spar using halyards or other lines.
Hold – the interior space of a ship or vessel used for storing cargo or goods.
Hook – slang for anchor.
Hove to – see heave to.
Hull – the main body or frame of a boat.
Hull speed – the maximum speed at which a keelboat can travel through the water.
Icebreaker – a type of ship designed to navigate through ice-covered waters.
IMO – International Maritime Organisation.
In irons – when a sailboat heads directly into the wind, becomes stuck or stalled, and is unable to move forward or steer effectively.
Inboard – inside the hull of a boat, as opposed to outside or outboard.
IOR – International Offshore Rating.
IRPCS – International Regulations for Preventing Collisions at Sea.
Isobars – lines that connect points of equal atmospheric pressure on a weather map.
ITU – International Telecommunication Union.
Jack line – a length of webbing or wire that is secured to a boat’s deck, running fore and aft, that is used to attach a safety harness and tether to the boat.
Jackstay – a line or wire that runs between two points on a vessel to support or guide a load between those points.
Jacobs Ladder – a rope ladder that is used to climb aboard a ship or to climb up to the crow’s nest of a mast.
Jetsam – goods or materials intentionally thrown overboard from a ship in distress to lighten the ship’s load. Different from flotsam, where items are accidentally lost and float at sea.
Jetty – a long structure that extends from the shore into a river or ocean. Used as a platform for fishing or for docking boats. Typically made of concrete, stone, or other materials.
Jib – a triangular sail at the front of a boat.
Jibe – to turn a sailboat so the wind hits the sail from the opposite side by turning the boat’s stern through the wind. Also Gybe.
Jiffy reefing – a technique used to quickly reduce the sail area of a sail in high winds.
Jury – a temporary arrangement or makeshift repair used to replace damaged or lost gear.
Kedge – small, secondary anchor of a boat.
Keel – the centerline structure running along the bottom of a boat’s hull.
Keelson – a longitudinal beam or structure that runs along the bottom of a boat hull, parallel to the keel, typically found in larger vessels.
Ketch – a two-masted sailboat, with the main mast located forward and the smaller mizzen mast aft.
Kicking strap – also known as a boom vang or simply a vang, is a line or mechanical device used to control the boom on a sailboat.
Knot – a unit of speed equal to one nautical mile per hour (1 knot = 1.15 miles per hour = 1.85 kilometers per hour).
Landfall – the first sighting or arrival at land after a voyage at sea.
Lanyard – a line used for securing or attaching equipment on a boat.
LAT – Lowest Astronomical Tide.
Latitude – a measure in degrees of a boat’s position north or south of the equator.
Launch – (1) to put a boat into the water from a dry dock or trailer (2) a small, open motorboat used for short trips to and from shore or ship.
Lazarette – small storage compartment on a boat, typically located aft and below the cockpit or deck.
Lazy jac k – lines used to help control the mainsail of a sailboat when it is being lowered.
Lead – term used to indicate the direction in which a line runs.
Lee – the sheltered side of a boat, away from the wind.
Lee cloths – pieces of fabric or netting used to create a barrier along the side of a berth (sleeping area) to prevent the user to slide out due to boat movement.
Lee helm – condition where the boat tends to steer away from the wind.
Lee shore – a coast or shoreline located to the lee (downwind) of a boat. It is generally recommended to keep a safe distance from lee shores when navigating in windy or rough conditions.
Leech – the rear edge of a sail, typically the edge of the sail that is not attached to a mast, spar, or another rigging.
Leech Line – a line used to tighten the leech.
Leeward – the direction away from the wind. Opposite to Winward.
Leeway – the sideways drift of a boat caused by wind force or currents.
Life Jacket – A buoyancy aid that helps a person float and stay afloat in the water, reducing the risk of drowning. Also known as a Personal Flotation Device (PFD) .
Lifeline – a line or cable used to prevent crew members from falling overboard.
Lifesaving equipment – devices used to save lives in case of an emergency, such as lifeboats, life rafts, and life jackets .
Light – a navigational aid used to indicate the location of hazards or to guide ships into port.
Lighthouse – a tower or structure with a bright light used to guide ships at sea.
Line – a rope or cable used on a boat for various purposes, such as securing cargo or tying up to a dock.
List – the leaning or tilting of a boat to one side due to uneven weight distribution.
Log – (1) device used to measure a boat’s speed and distance traveled (2) a record of the details of a voyage. See logbook.
Logbook – a record of a boat’s activities, including its course, speed, and events.
Longitude – a measure, in degrees, of a boat’s position east or west of the Prime Meridian.
Lubber’s line – reference line or mark on a boat’s compass that helps the user determine the boat’s heading or direction of travel.
Luff – the edge of a sail closest to the wind.
Mainsail (Main) – the largest and most important sail on a sailboat, is typically attached to the mast and boom.
Mainsheet – the line that controls the position and tension of the mainsail. It is typically attached to the aft end of the boom and runs aft to the cockpit.
Manning – the act of providing personnel to operate a ship.
Mariner – a person who navigates or operates a ship.
Marlinspike – a tool used for working with ropes and knots. Has a pointed end for separating strands, and a flattened end for splicing.
Mast – a tall vertical pole that supports the sails.
Mast step – fitting or structure on a sailboat that supports the bottom of the mast and attaches it to the hull.
Masthead rig – type of rig in which the forestay attaches to the mast at the very top of it, or masthead.
Mayday – distress signal used in radio communications to signal a life-threatening emergency on board.
MCA – Maritime and Coastguard Agency (UK).
Measured mile – one nautical mile, typically marked with buoys or other navigational aids, used to measure the speed and performance of a boat.
Meridian – a line of longitude that runs north-south and passes through both the North and South Poles.
MHWN – Mean High Water Neaps.
MHWS – Mean High Water Springs.
Midship – Approximately the central section of a boat, typically the widest part of the hull.
Mizzen – the aft-most mast on a ship.
MLWN – Mean Low Water Neaps.
MLWS – Mean Low Water Springs.
MMSI – Maritime Mobile Service Identity.
Mooring – the act of securing a boat to a dock or buoy.
Motor – when sails and motor are used simultaneously on a sailboat.
Nautical mile – a unit of distance used in navigation, equal to one minute of latitude. A nautical mile is slightly more than a standard mile. 1 nautical mile = 1.15 miles = 1.85 kilometers.
Navigation – the process of planning and directing the course of a boat.
Navigation Rules – set of regulations that govern the safe navigation of vessels on the water, including rules for preventing collisions , signaling, and right of way.
Navigator – a person who plans and directs the course of a boat.
Nun – a navigation aid used to indicate the edge of a navigable channel or the location of a hazard.
Oar – a long, narrow paddle used to row a boat.
Offing – refers to the open sea, particularly a safe distance from the shore.
Old salt – experienced sailor who has spent a significant portion of their life at sea.
Onboard – on or in the ship.
Outboard – (1) away from the centerline of a boat (2) a detachable engine mounted on the stern of a boat.
Outhaul – a line that controls the tension and position of the sail along the boom.
Overall length (OAL) – the maximum length of a vessel, measured from the outermost point at the bow to the outermost point at the stern, including any protrusions or extensions.
Overboard – over the side of the ship.
P Flag – also called Blue Peter flag, is a nautical signal flag that indicates a ship is preparing to leave port. It is a blue flag with a white square in the center.
Paddle – a flat blade used for propelling a small boat through the water.
Painter – a rope or cable used to secure or tow a small boat to a larger ship or dock.
Pan Pan – radio call to request assistance from other vessels or authorities. Unlike Mayday, Pan-pan is used when there is no immediate danger to life or the vessel’s safety.
Pay out – to let out a rope or cable gradually. Opposite to paying out is “taking in” or “reeling in”.
Pedestal – column or base used to elevate and secure equipment, such as the steering wheel and controls, for easy access and stability.
Pennant – long, narrow, triangular flag that is typically used on boats and ships for signaling or identification purposes.
PFD – personal flotation device, also known as a life jacket.
Pier – raised structure that extends from the shore over the water and is used for docking boats, as well as for recreational activities.
Piling – a vertical support used to anchor a dock or pier.
Pilot – a person who navigates a ship through difficult or unfamiliar waters.
Pitch – the angle of a ship’s hull relative to the horizontal plane.
Planing – when a boat rises up and glides over the surface of the water, rather than displacing water as a traditional boat would.
Point of sail – the direction that a sailing vessel is traveling relative to the wind, e.g. beam reach, broad reach, upwind, downwind, etc.
Polaris – a star located in the constellation Ursa Minor, commonly known as the North Star or Pole Star. Used for centuries as a navigational aid.
Port – the left side of a boat when facing forward.
Port tack – sailing with the wind coming from the port side of the boat, and the sail is set to the starboard side of the boat.
Preventer – a line used to prevent the boom from accidentally jibing (moving suddenly and dangerously from one side to the other).
Privileged vessel – vessel that has the right of way over other vessels in certain situations as defined by navigation rules.
Proa – a traditional outrigger canoe with a single sail and a long, narrow hull.
Propeller – a device used to propel a boat through the water.
Pulpit – safety railing located at the bow of a boat that helps prevent people from falling overboard.
Q flag – a yellow flag that is flown by boat to indicate that it is healthy and to request free pratique (permission to enter a port or receive officials from shore).
Quarter – the side of a ship between the stern and amidships.
Quay – pronounced as “key” or “kee.” Is a wharf used for loading and unloading cargo or passengers from ships.
Radar – a device that uses radio waves to detect the presence and location of objects, used for navigation and collision avoidance .
Ratchet – a mechanism that allows a rope to be tightened in one direction only.
Reach – point of sail where the wind is coming from the side of the boat, at an angle between a close-hauled course (where the boat is sailing as close to the wind as possible) and a run (where the wind is coming directly from behind the boat). The three types of reach are close reach, beam reach, and broad reach, depending on the angle of the wind relative to the boat.
Ready about – to signal to the crew that the boat is about to tack, or turn into the wind.
Reef – to reduce the size of a sail by folding or rolling a portion of it.
Reeling in – to retrieve a fishing line or reel.
Rhumb line – a line that crosses all meridians of longitude at the same angle. Also called a loxodrome.
Rigging – the system of ropes, cables, and other devices used to support and control the sails of a boat.
Right of way – the privilege of a vessel to maintain its course over others based on established navigational rules. it is determined by the vessel type, position, course, speed, and other factors.
Roach – the curved portion of the sail that extends beyond a straight line drawn between the head and clew.
Rocker – upward curvature of a boat’s keel to the bow and stern.
Rode – the line or chain attached to the anchor and used to hold the boat in place while at anchor.
Roller reefing – to shorten the sail area by wrapping a sail around a boom or forestay.
Rope – cordage or line used aboard a vessel, including halyards, sheets, dock lines, and anchor lines. In nautical terminology, Line is frequently used instead of rope.
Rudder – a flat plate or blade attached to the stern of a boat and used to steer it.
Run aground – to ground a boat on a shallow area or rocks.
Run/running – to sail with the wind aft or directly behind the boat, which is the most downwind point of sail.
Running lights – lights required to be displayed on a boat underway between sunset and sunrise. Consist of red and green sidelights and a white stern light .
Running rigging – the lines such as sheets or halyards used to adjust the position of the sails.
Sail – a piece of fabric attached to a mast or spar and used to capture the wind to propel a boat.
Sail trim – the adjustments made to the sails on a sailboat to optimize their performance in different wind and sea conditions.
Sampan – a flat-bottomed boat typically used in China and Southeast Asia for transportation and fishing.
Samson post – a vertical post or bitt located on the deck or hull of a ship used for securing mooring lines or tow lines.
SAR – Search and Rescue.
SART – Search and Rescue Transponder.
Sat Nav – short for “satellite navigation” refers to the use of GPS to determine a boat’s position and navigate from one location to another.
Schooner – a sailing ship with two or more masts and fore-and-aft sails on the mainmast.
Scope – the ratio between the length of an anchor rode and the water depth. A higher scope, such as 7:1 or 10:1, means that more rode is paid out and the anchor is more securely set in the bottom, providing greater holding power for the boat.
Scull – a method of propulsion in a small boat where a single oar is moved back and forth behind the boat, with the oar pivoting at the stern rather than the side of the boat.
Scupper – a hole or channel in a boat’s deck that allows water to drain off.
Scuttle – to intentionally sink a boat by creating holes in the hull or opening its seacocks to let water in. Also refers to a small hatch or opening in a ship’s deck or hull that is used for ventilation, drainage, or access to equipment.
Scuttlebutt – a drinking fountain on a boat, or gossip among sailors.
Sea anchor – a device used to slow down or stabilize a boat in heavy seas.
Sea chest – a compartment in the ship’s hull for pumping seawater.
Sea Cock – a valve fitted to a boat’s hull which allows water to enter or exit through a hose or pipe. Used for draining water from the bilge or for providing water to the engine or other onboard systems.
Sea level – the level of the ocean’s surface used as a reference point for measuring elevation.
Sea room – a safe distance or area available for a boat to maneuver and navigate safely in open waters without colliding with other vessels, obstacles or running aground.
Seafarer – a person who travels by sea, especially for work or adventure.
Seamanship – skills, knowledge, and practices for operating a boat, as well as maintaining and caring for it.
Seaworthy – a boat’s capability to withstand harsh conditions and challenges of the sea.
Sécurité – term (french) used in marine radio communication to indicate a message that is about to be transmitted concerning the safety of navigation or important meteorological warnings.
Seelonce – term (French) used in marine radio communication to indicate that a distress call is being made and that all other radio traffic should cease.
Self – a feature in boats where any water that enters the cockpit is automatically drained or pumped out.
Set – (1) the trim of a sail (2) the direction in which a vessel is moving in relation to its intended course or direction (3) dropping an anchor and allowing it to settle.
Sextant – a navigational instrument used to determine a boat’s position by measuring the angles between the horizon and celestial objects such as the sun and stars.
Shackle – metal fastener with a removable pin or bolt used to connect two parts of a chain or rigging together or to attach a line or cable to an object.
Sheave – grooved wheel or roller of a block pulley used to guide and redirect lines.
Sheet – a line used to adjust the position of a sail.
Ship – a large seagoing vessel.
Ship’s bell – a bell used to mark time aboard a ship.
Shipshape – in good order and condition.
Shipwreck – the remains of a sunken ship.
Shore – the land bordering a body of water, typically where it meets the water.
Shroud – a rope or cable used to support the mast of a boat.
Skeg – a structural extension of the keel that runs aft beneath the boat’s hull.
Skipper – the captain or person in charge of a ship or boat.
Slack – to loose or not taut lines or cables. Lack of tension or looseness in a sail or other piece of equipment.
Sloop – a sailing vessel that has a single mast with one mainsail and a headsail.
Snubber – a device used to relieve tension on a boat’s anchor chain, prevent the chain from chafing against the boat’s bow, and reduce shock loads on the anchor and chain.
SOG – Speed Over the Ground.
SOLAS – Safety of Life at Sea. An international treaty established in 1914 that sets minimum safety standards for ships.
Sole – the floor or bottom surface of a boat’s cabin or cockpit.
Sonar – a device that uses sound waves to detect the presence and location of underwater objects, used for navigation and detecting hazards.
SOS – Morse code distress signal used as an international standard for emergency situations. Listen to an SOS signal .
Soundings – measurements of the depth of water in a particular area.
Spar – a long, slender pole used to support sails on a boat.
Speed log – a device used to measure a boat’s speed through the water.
Spinnaker – a large sail used for downwind sailing.
Splice – join two ropes to form a permanent loop in a single rope. Involves weaving the strands of the rope together to create a strong, permanent bond.
Spreaders – horizontal struts that are attached to a sailing boat’s mast to keep the mast from bending and to help control the shape of the sails.
Spring line – a line used to control the position of a boat while it is docked.
Squall – a sudden, sharp increase in wind speed, regularly accompanied by rain, thunder, and lightning.
Square knot – also known as a reef knot, is a basic knot used to join two ropes of equal size.
Stall – when the sail loses its ability to generate lift or control due to a lack of airflow.
Stanchion – vertical pole or post, made of metal or plastic, used to support a railing or guardrail.
Stand – a vessel that has the right-of-way and requires keeping her course and speed.
Standing part – the part of a line that is not actively used to perform a task, such as tying a knot or securing a line to a cleat.Opposite to the working end.
Standing Rigging – fixed lines or wires on a sailboat that support the mast and keep it in place. This includes the forestay, backstay, and shrouds. Different from the running rigging, which is used to control the sails and is adjusted frequently.
Starboard – the right side of a boat when facing forward.
Starboard tack – sailing with the wind coming from the starboard side of the boat, and the sail is set to the port side of the boat.
Stay – a line or wire that supports a mast from the bow (forestay), stern (backstay), or either side (sidestays).
Staysail – a type of sail that is set on a stay instead of a mast.
Steerage way – when a boat moving forward has enough water flowing over its rudder(s) to enable it to be steered effectively.
Stem – the forward-most part of a boat’s bow that curves upward to provide a shape for the hull to cut through the water efficiently.
Stern – the rear or aft part of a boat.
Stern line – a line used to secure the stern of a vessel to a dock, pier, or other mooring point.
Sternpost – the vertical post at the back of the ship’s hull.
Sternway – the reverse or backward motion of a boat.
Stores – the supplies or provisions needed for a vessel’s operation during a voyage.
Stow – to pack or store cargo or equipment on a ship.
Strake – a continuous line of planking or plating along the hull of a boat.
Sump pump – a device used to remove water that has accumulated in a pit or shower basin.
Swell – a long, rolling wave caused by wind or distant storms .
Tabernacle – a hinged support structure that enables a mast to be lowered and raised easily. Is a useful feature for sailboats that need to pass under low bridges or power lines.
Tack – (1) the lower forward corner of the sail. (2) To turn a sailboat’s bow through the wind so that the wind catches the opposite side of the sail. (3) noun used to indicate the direction the sailboat is sailing with respect to the wind e.g. port tack or starboard tack.
Tackle – a system of ropes and pulleys used to hoist or move heavy objects on a boat.
Taffrail – the rail or railing around the stern of a vessel, and is primarily used for safety.
Taking in – furling or reefing a sail to reduce its area.
Tang – metal fitting used to attach standing rigging, such as shrouds and stays, to a mast or spar.
Telltales – thin strips of cloth or yarn that are attached to a sail, used to indicate airflow and sail trim.
Tender – small boat used to ferry people and supplies to and from shore. Also called dinghy .
Thwart – a crosswise seat in a boat.
Tidal range – the difference in water level between high tide and low tide in a particular area.
Tide – the periodic rise and fall of water level caused by the gravitational pull of the moon and sun.
Tiller – a handle or lever used to steer a boat.
Toe rail – a narrow strip of wood, metal, or fiberglass molding along the edge of a sailboat’s deck near the hull, mainly used to secure a foothold for crew moving around the deck.
Tonnage – the total weight or volume of cargo that a vessel can carry, and usually expressed in either gross tonnage (GT) or net tonnage (NT).
Topmast – a mast situated above the lower mast on a ship.
Topsail – a sail set on the top of a ship’s mast.
Topside – the upper part of a boat’s hull.
Track – a device or structure that allows a sail or other object to move along a fixed path.
Trampoline – netting that is stretched between the hulls of a catamaran or trimaran, providing a stable and comfortable surface for passengers to relax on.
Transom – the flat, vertical surface at the stern of a boat.
Trapeze – wire and equipment used on a sailing boat to allow crew members to hang out outboard to counterbalance the force of the wind on the sails.
Traveler – device that allows the mainsail to be moved horizontally along the boat.
Trim – to adjust the sails or ballast to maintain a boat’s stability and speed.
Trimaran – a type of multihull boat consisting of a main hull and two smaller outrigger hulls called amas, attached to the main hull with lateral struts.
True north – the direction of the North Pole.
True wind – actual speed and direction of the wind experienced when there is no other movement or influence.
Tuning – process of adjusting the rigging and sails of a sailboat to optimize performance and balance in different wind and sea conditions.
Turnbuckle – device used for adjusting the tension or length of lines, cables, tie rods, and other tensioning systems.
Turning mark – buoy or other fixed object used in sailing or boat racing to mark a course change.
Turtling – when a boat capsizes, with the mast pointing down towards the sea bottom.
Underway – a boat that is in motion.
Unmoor – to release a boat from its moorings.
Uphaul – a line used to hoist a sail, flag, or spar up to the masthead.
Upwind – the direction that is facing or heading towards the wind. See beat.
V berth – bed in “V shape” typically found in the forward cabin of a boat. .
V bottom – also known as a V-hull, is a type of boat hull design that features a V-shaped hull that slices through the water.
Vang – see boom vang and kicking strap.
Veer – (1) change of wind direction clockwise. (2) To pay out or let out more line or chain, allowing a vessel to move farther away from its anchor point.
Vessel – a general term for any type of watercraft.
VHF – Very High Frequency.
Victuals – food or other provisions.
Vittles – see victuals.
VMG (Velocity Made Good) – speed at which a sailboat can make progress towards its destination while accounting for the effects of wind direction and currents.
Wake – the trail of disturbed water left behind by a moving ship.
Warship – a ship equipped for combat.
Watch – period of time during which one or more crew members are responsible for operating a vessel.
Waterline – the line where a boat’s hull meets the water.
Wavelength – distance between two consecutive points of the same phase on a radio wave.
Way – the forward movement of a boat through the water.
Waypoint – a predetermined location on a boat’s course.
Weather deck – the uppermost deck exposed to the elements on a ship.
Weather helm – the tendency of a boat to turn into the wind when the helm is released.
Wheel – a circular steering device used to steer a boat.
Whisker pole – also known as a spinnaker pole, is a horizontal spar used for jibing and holding out the clew of a jib or spinnaker.
Winch – mechanical device used to wind in or let out a cable or rope under tension.
Wind rose – a graphic tool used to visualize the distribution of wind directions and speeds at a particular location over a specific period of time.
Windage – the effect of wind on a boat or parts of it, that can cause it to drift or experience a lateral force.
Windlass – a mechanical device used on a boat to help with the raising and lowering of heavy equipment such as an anchor or sails.
Windward – the direction from which the wind is blowing. Opposite to Leeward.
Working end – the part of a line that is actively used to perform a task, such as tying a knot or securing a line to a cleat. Opposite to the standing part.
XTE (Cross Track Error) – perpendicular distance between a vessel’s actual position and its intended track.
Yacht – a pleasure boat used for cruising or racing.
Yard – a horizontal spar attached to a mast used to support a sail.
Yaw – movement or rotation of a vessel around its vertical axis that occurs when the boat is underway.
Yawl – a type of sailboat with two masts, with the smaller mizzen mast located aft the rudder post.
Zincs – type of sacrificial anodes used to protect boats and other underwater structures from corrosion.
As an Amazon Associate, we earn from qualifying purchases. Read more
© 2024 BestBoatTips.com - All rights reserved
Sail away with these essential sailing terms (or risk walking the plank)
Welcome to our guide to sailing terms! Whether you are a seasoned sailor or new to the sport, understanding the terminology used on the water is essential for safe and effective navigation. In this glossary, we will cover some of the most common and important terms you need to know to communicate with your crew and understand the mechanics of your vessel. From bow to stern and hull to hull, we've got you covered. So grab your captain's hat and let's set sail on a voyage of language learning.
FAQ Sailing Terms
One reason why sailing terms are so different is that sailing has a long history dating back thousands of years, and the terminology that is used has developed over time to reflect the unique aspects of this activity. Another reason is that sailing involves a variety of different types of boats, each with its own set of equipment and terminology. For example, a small sailboat like a dinghy will have different parts and use different terms than a large sailboat like a yacht.
No products in the cart.
Sailing Ellidah is supported by our readers. Buying through our links may earn us an affiliate commission at no extra cost to you.
150+ Nautical Terms: Illustrated Guide
Sailing and nautical terms have been refined over centuries, forming a unique glossary that can leave even the most seasoned wordsmiths scratching their heads.
Today, we’ll look at the terminology of words and names used at sea to help you through even the saltiest conversations.
Terms for the components a sailboat consists of
Let’s start with terms for the parts a sailboat is put together from. These refer to each component and explain what they are.
The main parts
Mast : The mast is the big, tall spar that holds up the sails! Some boats have more than one mast.
Mainsail: The mainsail is the sail behind the mast and on top of the boom. Often just referred to as “the main.”
Boom: The spar that sticks out behind the mast.
Rudder: The rudder is also a fin sticking down under the boat but is located back towards the stern and connected to the wheel or tiller, enabling you to steer the vessel.
Headsail: The sail(s) in front of the mast. Many boats have more than one headsail and can be of different sizes and shapes.
Spreader: The fins or wings that space the shrouds out from the mast.
Hull: This is the body or structure of the boat. Monohulls have one hull, catamarans have two hulls, and trimarans have three hulls – you get the point.
Keel : This is the heavy fin sticking down under the middle of the boat, allowing it to sail. There are many different keel designs, but they are all heavy, and their job is to keep the vessel stable and track through the water under sail.
Helm: This is the position where you steer the boat. Usually, this is a wheel, but it can also be a tiller on many vessels.
Cockpit: The cockpit is the boat’s steering position and where you will find the helm.
Transom: The flat surface across the stern of the boat.
Bow and Stern: The bow is the front part of a boat, while the stern is the rear end.
Midship: By some called amidships – The center of the boat.
Beam: The widest part of the boat. It is also referred to as the sides on the middle of the vessel.
Waterline: This is the part where the hull (body) of the boat meets the water. Many ships have a painted stripe to mark the waterline, indicating the boat’s load. If you have too much stuff on board, the waterline goes underwater, and it is time to do some housekeeping!
Freeboard: The vertical part of the ship side between the water and the deck.
Deck: The deck is the “floor” of the boat when you are outside. You have probably heard the term “All hands on deck!”
Spar: The general term for a pole made of a solid material like wood or metal used to support a boat’s sail. The mast, boom, spreaders, etc., are defined as spars.
Gooseneck: This fitting connects the boom to the mast and allows it to move horizontally and vertically.
You can read more about the different parts of a sailboat in this article.
The standing rigging which holds the sails
Forestay: The forestay is a wire that runs from the bow to the top of the mast. Some boats, like the Cutter rig, can have several additional inner forestays in different configurations.
Furling system: Most sailboats have their headsail on a furling system, a tube running along the forestay from the bottom furler drum to the masthead swivel.
Backstay/Aft stay: The wire that runs from the aft of the boat up to the top of the mast.
Shrouds: On most common cruising boats, there are usually four shrouds on each side to support the mast from sideways motion. The shrouds are generally made of wire but can also be rods or Dyneema lines. The cap shrouds run from the masthead through the tips of the spreaders down to the deck. The intermediate shrouds run from the lower part of the mast, through the lower spreaders, and to the deck. The lower shrouds run from the mast under the lower spreaders down to the deck – one forward and one aft on both sides. This is called continuous rigging .
Turnbuckle: The fitting that connects the shrouds to the chainplate on the deck. These are adjustable, allowing tensioning of the rig.
Chainplate: A fixed strong point bolted on the deck. Usually reinforced with a backing plate underneath.
You can read more about the standing rigging in this article .

The running rigging which operates the sails
Line: The running rigging on a sailboat often consists of lines, a type of rope with a smooth surface that works well when used on a winch.
Halyard: This is the line you use to hoist and lower the sail.
Sheets: The sheet is the line you use to control a sail . The mainsheet controls the angle of the mainsail and is attached between the boom and the mainsheet traveler . The two headsail sheets are connected to the sail’s clew (lower aft corner) and run back to each side of the cockpit.
Outhaul: The outhaul is attached to the clew of the mainsail and used to adjust the foot tension.
Topping lift: A line attached to the boom’s end runs through the masthead and down to the deck or cockpit. Used to lift and hold the boom and also function as a spare main halyard.
Downhaul: A line used to lower with. Typically used to lower the mainsail when reefing and lowering the spinnaker and whisker poles.
Reef line: Depending on your setup, these lines are used to reduce the sail area of the mainsail.
Shaking a reef: When we sail with a reefed sail and want to increase the sail area back to full, we call it shaking the reef.
Equipment used to operate the running rigging
Block: A pulley with a sheave wheel. These are used to change the direction of a pull on a line or rope and give a mechanical advantage.
Mainsheet Traveler: The traveler is a horizontal track attached to the mainsheet through a series of blocks. The traveler enables you to adjust the boom from side to side or lock it at an angle.
Cars: The cars are pulleys or blocks attached to a track on the side decks that your headsail sheets run through. They are used to control the angle of the sheet between the clew and the deck.
Jammer: The jammer is used to lock a line in place. Most sailboats use these for locking the halyards, mainsheet, outhaul, reef lines, traveler lines, boom vang lines, etc.
Spinnaker Pole: A spar used to wing out a headsail when sailing off the wind, particularly the Spinnaker.
Whisker Pole: Similar to the spinnaker pole, but typically built lighter and attached to a track on the mast. These can be found in fixed lengths or adjustable lengths.
Boom Vang/Rod Kicker: A compression pole is used to tension the boom downwards.
You can read more about the running rigging in this article.
Deck gear and hardware
In-mast furling: A furling system that furls the mainsail in and out of the mast as opposed to the traditional way where the mainsail is secured to the boom and is hoisted and lowered on a track behind the mast.
In-boom furling: A furling system that furls the mainsail in and out of the boom.
Stack Pack: Also called Lazy Bag or Lazy Pack . A bag with a zip attached to the boom where the mainsail is stored when unused.
Lazy Jacks: A set of lines running from the stack pack to the mast guides the mainsail up and down from the Stack Pack and prevents it from falling on the deck.
Masthead: Not to be confused with the term masthead rigging. Out of context, the masthead is the top of the mast.
Winch: A metal drum that gives you a mechanical advantage when tightening lines.
Sprayhood: The windshield of the boat that protects the people in the cockpit from sea spray. Some ships have canvas spray hoods that can be folded down or removed. Others have solid sprayhoods, often called a hard dodger or a doghouse .
Bimini: The cockpit’s roof protects you from the elements and provides shelter from spray, rain, and burning sun rays! A bimini can be made of canvas or hard material. The hard bimini is usually called a hardtop .
Outboard: Short-term for an outboard engine, which usually belongs to the dinghy.
Cruisers: What we sailors often call ourselves. Especially those of us living onboard. Although salty, we are definitely handy to have on board as we are also electricians, mechanics, plumbers, and you name it.
Fenders: Like Captain Ron said in the movie, the rubber bumper things you hang off the side of your boat to prevent it from scratching against something like the key side or another boat. Conveniently also used to sit on or as a backrest while relaxing on the deck.
Boat Hook: A long stick with a hook at the end. Used to grab lines, items, and stuff that is too far to reach by hand, like cushions flying overboard. It is also convenient as a tool to push the boat away from another ship or the key. Or to push mud or clay off the anchor . Or catch a wild flying halyard. Most vessels have them on board, and you want one or two. (They tend to get lost at sea).
Guard Rail: This can be a flexible wire or a solid metal rail surrounding the boat to prevent us from falling overboard. Some also use a net as an addition for increased safety.
Pushpit: The metal guard rail around the stern of the boat. This is where the guard rail is secured on the stern. A common place to mount the BBQ, life raft, and the outboard for the dinghy.
Pulpit: The metal guardrail on the bow. This is where the guard rail is secured onto the bow.
Stanchion: The metal bar that keeps the guard rail in place around the boat between the pushpit and the pulpit.
Arch: A big structure usually made of stainless steel on the back of a boat. Often used to mount a variety of items like antennas, radars, solar panels, wind generators, etc.
Ground Tackle: This consists of your anchor , your anchor chain, the link between the two, and the connection between the chain and your boat. The ground tackle is basically the system that holds your boat to the ground.
Windlass: The winch that hoists or lowers the anchor and chain. Most boats have one on the bow, and some have one on the stern, too. These incredible things can be electrical or manual (some are both) and are essential to anchor your boat when not in a port or marina. Try to haul the anchor manually once – you’ll put a windlass on the top of your wish list pretty quickly…
VHF Radio: Very High-Frequency Radio that broadcasts on the VHF network and makes you able to communicate with others around you. Sadly, you won’t be able to tune in to your favorite radio show on these. Still, they are invaluable at sea for communication.
Chart Plotter: A navigation computer that shows various information on a screen, like charts, routes, radar images, etc.
Parts below the decks
Companionway: The “front door” of the boat. This is where the steps lead from the cockpit or deck down below. It is usually opened and closed using a hatch, two doors, or a plate.
Galley: The kitchen of a boat is never to be called a kitchen. Always use the term galley when you are onboard!
Saloon: This is the boat’s living room and usually where you find the settee and dinette.
Settee: The couch in a ship.
Dinette: This is the area where you can sit down at a table and eat your dinner. It’s also perfect for consuming rum in good company and a game of cards.
Cabin: These are the “rooms” onboard but might not necessarily be the “bedrooms.”
Head: There are no bathrooms on a boat, only heads. If your skipper tells you to go and clean the head, getting out the shampoo won’t do you any good.
Nav station: Usually a chart table and a console with mysterious instruments like radios, chart plotters, radar screens, and all sorts of complicated electronics. This is often where adventures are planned and the skipper’s favorite seat onboard. (At least, that is my favorite and where all this content is created!).
Bilge: The space in the bottom of the hull where water collects and sometimes a storage space for all sorts of things. It usually contains a bilge pump to pump out water that finds its way into the boat in various places. You may have heard the phrase: “Treasures of the bilge.” Now you get it!
Berth: A place in the boat where you can sleep. This doesn’t necessarily have to be a bed and can often include the sleeping space in the salon. The term sea-berth usually refers to a sleeping position where you are tucked well in and can sleep when the boat is heeling over and moving around.
V-berth: The bed in the front cabin is shaped like a V.
Bulkhead: A wall inside the boat, usually supporting the structure.
Terms used for directions and navigation
Port and Starboard : Port refers to the left side of the boat when facing the bow (front), while starboard signifies the right side.
Windward and Leeward : The windward side refers to the side of a boat facing the wind, while the leeward side is the side sheltered from the wind. These sailing terms also apply to geographic features, like islands or coastlines, that offer protection from the wind.
Chart : A nautical chart is a map specifically designed for marine navigation, depicting water depths, shoreline features, navigational aids, and potential hazards.
Compass : A compass is an essential navigational instrument that indicates magnetic north, allowing sailors to determine their heading and steer their vessels accordingly.
Course : The course is a vessel’s intended direction of travel, expressed in degrees from true or magnetic north.
Heading : The heading is the actual direction a vessel points, also expressed in degrees from true or magnetic north.
Latitude : Latitude is a geographic coordinate that specifies a location’s distance north or south of the equator, measured in degrees, minutes, and seconds.
Longitude : Longitude is a geographic coordinate that specifies a location’s distance east or west of the Prime Meridian, measured in degrees, minutes, and seconds.
Waypoint : A waypoint is a specific location, defined by its latitude and longitude, that serves as a reference point for navigation.
Bearing: The angle between the observer’s position and a distant object, measured in degrees from true or magnetic north.
Fix : A fix precisely determines a vessel’s position using various navigational methods, such as bearings, GPS, or visual landmarks.
Dead Reckoning : Dead reckoning is a method of estimating a vessel’s current position based on its previous position, speed, and course over time.
Tide : Tides are the regular rise and fall of sea levels caused by the gravitational forces exerted by the Moon and Sun.
Current : Current refers to the horizontal movement of water in a particular direction. Currents can significantly affect a vessel’s speed and course, so make sure to consider them when sailing and navigating.
Buoy: A buoy is a floating device anchored in a body of water, such as an ocean, sea, lake, or river, to serve various purposes, including navigation, marking channels, identifying hazards, or indicating mooring locations.
The names of different sails and their parts
Mainsail: The mainsail is the sail behind the mast and on top of the boom.
Genoa : A Genoa is a headsail that extends past the mast and overlaps the mainsail.
Jib : A Jib is a headsail that does not overlap the mainsail.
Staysail: A staysail is usually found on cutter rigs and is the sail set on the inner forestay.
Yankee: A yankee headsail is used similarly to a Genoa or Jib but has a high-cut clew and is often used on cutter-rigged boats together with a staysail.
Mizzen sail: A mizzen sail is typically a small triangular sail set on the aft mast of a boat with several masts, like the ketch rig.
Storm sail: A storm sail is a small, strong sail to be used in heavy weather conditions where the headsail is furled to the point where its shape doesn’t give you drive anymore or/and when you want a smaller mainsail than your reefing setup allows you. The storm sails provide stability in the vessel in heavy weather sailing.
Spinnaker: A Spinnaker is a symmetric light wind sail used to sail off the wind at deep angles between 120 and 180 degrees.
Gennaker: A Gennaker is a cross between the Genoa and Spinnaker. It has the same type of light fabric as the Spinnaker but is asymmetrical like a Genoa with a tack set on the bow and a sheet led back from the clew to the stern of the boat.
Code Zero: A code zero sail is a cross between a Genoa and a Gennaker. It is also designed for light wind with its lightweight fabric but has a different shape than a Gennaker. This makes it able to be used while sailing upwind, unlike the Gennaker.
Parasailor: A parasailor is similar to a spinnaker but with some differences. It has a double-layer wing that inflates as the sail gets filled with air. This wing works like a batten and keeps the leech out while generating lift on the bow, making it effective between 70 degrees and all the way down to 180 degrees dead downwind.
The different parts of a sail
Tack: The tack of the sail is the lower forward corner.
Clew: The clew of a sail is the lower aft corner.
Head: The top corner of a sail.
Foot: The foot of the sail is logically the bottom part of the sail between the clew and the tack.
Luff: The luff is the front edge of the sail between the tack and head.
Leech: The leech is the aft part of the sail between the clew and head.
Telltales: Telltales are small ropes, bands, or flags attached to the sail to give you an indication of the airflow around your sail.
Battens: Battens are slates or tubes inserted in pockets on the mainsail to help it keep its shape better and increase its lifespan.
Learn more about the different types of sails in this guide .
Terms used when we talk about wind and weather
Gust : A gust is a sudden, brief increase in wind speed, often accompanied by a change in direction.
Squall : A squall is a sudden, strong wind that typically lasts for a short period and is often associated with rapidly changing weather conditions, such as thunderstorms or cold fronts.
Barometer : A barometer is an instrument used to measure atmospheric pressure. Changes in atmospheric pressure can indicate upcoming weather changes.
High-Pressure System : A high-pressure system is an area of relatively high atmospheric pressure, characterized by sinking air and typically associated with calm, clear weather.
Low-Pressure System : A low-pressure system is an area of relatively low atmospheric pressure, characterized by rising air and typically associated with clouds, precipitation, and potentially stormy conditions. Sailors usually refer to these systems as a “low.”
Front : A front is a boundary separating two air masses of different temperatures and humidity levels. Fronts are associated with changes in weather conditions and can cause sudden wind shifts and varying wind strengths.
True Wind Speed, or TWS: The actual wind speed affecting you at a point when you are standing still.
True Wind Direction, or TWD: The direction the wind is blowing from.
True Wind Angle, or TWA: The angle between your boat’s heading and wind direction.
Apparent Wind Speed, or AWS: The wind affecting the boat while in motion.
Apparent Wind Direction, or AWD: The direction of the wind in relation to your boat underway.
AWA – Apparent Wind Angle: The angle to wind while you are underway
Beaufort Scale : The Beaufort Scale is a system used to measure wind speed, ranging from 0 (calm) to 12 (hurricane). You can learn more about it at MetOffice here .
Saffir Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale: A scale describing hurricane wind speeds in categories from 1 to 5.
Learn more about the difference between actual and apparent wind in this guide .
Terms we use when cruising at speed under sail
Port Tack: When the wind blows on the port side of your sails
Starboard Tack: When the wind blows on the starboard side of your sails
Tacking: When you steer the boat from a starboard tack to a port tack and vice versa upwind .
Gybing: When you steer the vessel from a starboard tack to a port tack and vice versa downwind .
Heeling : When the wind fills the sails and leans the boat over to the side.
NM: Nautical Miles
Kt: Knots – A measurement of speed used on boats.
Deg: Short for degrees
SOG: Speed over Ground, usually measured by GPS
SOW: Speed over Water, usually measured by the boat’s speed log transducer.
COG: Course Over Ground, the direction your boat is moving towards.
HDG: Heading, the direction your boat is pointing towards.
Boom preventer: A line or rope tied to the end of the boom and led forward of the mast to prevent it from swinging over when sailing off the wind.
Overpowered: When wind overpowers the boats’ ability to steer a straight course. This typically happens when you try to sail above your boat’s hull speed, carrying too much sail area in relation to the wind, or your sails are poorly trimmed.
Hull Speed: The speed your boat has achieved when its created wave has the same length as the hull’s water length. Many displacement sailboats (the ones that don’t plane on top of the water) get hard to steer when going faster than this. You can learn more about how to calculate your hull speed in this guide: https://sailingellidah.com/average-distance-sailed-in-a-day/
Pro Tip: Your COG and HDG will sometimes differ due to wind and current pushing you sideways.
Terms for the boats heading in relation to the wind
These sailing terms are best known as our points of sail and describe the vessel’s heading in relation to the wind:
Close Hauled: When sailing close-hauled, the vessel’s heading is as close to the wind as possible, typically between 35-50 degrees.
Close Reach: When sailing at an angle between 50 and 80 degrees, give or take.
Beam Reach: The wind comes in from the side.
Broad Reach: When bearing away from 90 degrees to around 135 degrees.
Running: When sailing downwind.
You can learn more about the 5 points of sails in this guide :
Final Words
I know there are a lot of nautical words and terms to keep track of, but luckily, no one expects you to know them all right away. You’ve probably already taken note of the most important ones, which means you’ve taken a giant leap in the right direction. Keep at it; you’ll speak like the saltiest seadog before you know it.
Did I forget to mention any terms you know of? Let me know in a comment below!
Sharing is caring!
Skipper, Electrician and ROV Pilot
Robin is the founder and owner of Sailing Ellidah and has been living on his sailboat since 2019. He is currently on a journey to sail around the world and is passionate about writing his story and helpful content to inspire others who share his interest in sailing.
bookmarkеd!!, I love your site!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Sailing Terms and Phrases: A Comprehensive Guide to Nautical Jargon
by Emma Sullivan | Jul 19, 2023 | Sailboat Racing

Short answer sailing terms and phrases:
Sailing terms and phrases refer to language specific to the sport of sailing. They include terms related to boat parts, sailing maneuvers, wind direction, and navigation. Understanding these terms is crucial for effective communication and safe sailing practices.
Understanding the Basics: A Guide to Sailing Terms and Phrases
Welcome aboard, fellow sailors and landlubbers alike, as we embark on a voyage through the mesmerizing world of sailing terms and phrases. Whether you’re an enthusiastic beginner or a seasoned seafarer looking to brush up on your nautical knowledge, this guide will have you speaking like a true sailor in no time.
As with any specialized field, sailing has its own unique language that can bewilder even the most erudite wordsmiths. But fear not! We’re here to break down the basics and shed light on those mysterious terms that have been floating around in your mind like buoys at sea.
Let’s start by hoisting the main sail and diving headfirst into some essential terminology:
1. Port and Starboard: If someone shouts “Hard to port!” during your sailing adventure, don’t panic – they simply mean turn left. In maritime lingo, “port” refers to the left side of a vessel when facing forward, while “starboard” is the right side. Thinking of them as counterparts can help avoid confusion during moments of high-seas excitement.
2. Bow and Stern: Don’t forget where your front and back are while navigating the open waters. The bow is the forward part of the vessel (a great spot for taking epic photos), while the stern is located at the rear. Trust us – being able to differentiate between these two proves invaluable when following directions or describing intriguing sights.
3. Aft vs Forward: Just as knowing which way is up is vital for surviving gravity’s pull, understanding aft (the back part of a ship) versus forward (the front part) is crucial aboard a boat too! Being able to navigate with ease relies heavily on using these terms correctly when maneuvering around onboard.
Now that we’ve set our bearings straight let’s proceed further into more advanced seamanship jargon:
4. Shiver me Timbers: Ahoy, matey! Surely, you’ve heard this catchy phrase in pirate movies or read it in adventure novels. But do you know what it means? “Shiver me timbers” originated from the old seafaring days when wooden ships were prevalent. When they were hit by fierce storms or cannonballs, the creaking and vibrations of the hull made the timber “shiver.” Nowadays, it’s an exclamation expressing surprise or disbelief.
5. Nautical Mile: Avast, ye landlubbers! A nautical mile is a unit of measurement used specifically for sea and air travel. It’s equal to one minute of latitude along any meridian – approximately 1.15 statute miles (or about 1.85 kilometers). So, whether you’re voyaging across vast oceans or navigating through treacherous straits, understanding this term will keep you on course.
6. Windward and Leeward: When sailing the high seas, understanding wind patterns becomes crucial to harnessing their power effectively. Windward refers to the direction from which the wind is blowing (usually against your face), while leeward indicates the sheltered side where the wind is blocked by your vessel or other objects nearby. Skippers who can master these concepts will navigate their vessels with grace and ease.
7. Keelhaul: Now here’s a term that harkens back to darker maritime times! To keelhaul someone often meant dragging them under a ship’s keel as a form of punishment. Luckily for us nowadays, it has mostly been relegated to seafaring folklore and modern-day sailors rarely seek to employ such discipline.
So there you have it – a comprehensive yet entertaining guide to essential sailing terms and phrases that will surely make waves amongst your fellow salts-in-arms! From knowing your port from starboard all the way down to deciphering historical jargon like “shiver me timbers,” embracing these nautical expressions will not only deepen your understanding but also add a touch of maritime flare to your conversation.
So raise your glasses – or rather, yer grog – as you confidently navigate the mighty seas armed with newfound knowledge, humor, and a dash of seafaring slang. Bon voyage!
Exploring the World of Sailing: How Sailing Terms and Phrases Enhance Your Experience
Title: All Aboard! Unveiling the Secrets of Sailing: How Nautical Jargon Enhances Your Pleasure on the High Seas
Introduction: Welcome, fellow sailors and nautical enthusiasts, as we embark on an exciting voyage through the realm of sailing. Beyond the wind in our sails and the wide expanse of water beneath us lies a colorful world steeped in traditions, camaraderie, and rich terminology. In this blog post, we delve into how mastering sailing terms and phrases can elevate your experience on the open seas from ordinary to extraordinary. So hoist your anchor and adjust your compass – let’s set sail!
1) The Lingua Franca of Seafarers: Just as each industry has its unique lexicon, sailing boasts an impressive repertoire of its own jargon. While initially overwhelming to nascent sailors, these terms are not merely maritime buzzwords; they create a sense of belonging among seafaring communities globally. From ‘starboard’ to ‘jib’ or ‘tacking,’ understanding nautical terminology not only facilitates effective communication but also unlocks doors to a world where legends and rituals intertwine.
2) Paint Your Own Nautical Canvas: Imagine being able to articulate intricate details about your surroundings with painterly precision. As you acquaint yourself with sailing lingo, you gain access to an exquisite palette that will enable you to vividly describe cloud formations (cumulonimbus clouds), waves (swell), or even the wonders beneath (bioluminescence). By employing phrases such as “the sea rose like a mighty kraken” or “whispering zephyrs guided our course,” you’ll be painting masterpieces with words.
3) Channeling History’s Echoes: The language of sailing is deeply rooted in history, connecting us to generations past who braved unforgiving waters aboard wooden vessels. Embracing these linguistic relics imbues your journey with a sense of timelessness and reverence for those who came before us. Employing phrases like “avast ye scurvy dogs” or “there she blows!” lets you channel the spirit of earlier sailors, forging an indelible bond across ages.
4) The Poetry of Seamanship: Sailing brings together the precision of a science and the lyricality of art, creating an environment where language emotively intertwines with experience. By embracing sailing terms, you’ll find yourself effortlessly conversing in poetic cadences – from referring to land as the “shores of belonging” to desiring nothing more than catching a glimpse of the “dancing dolphins’ aqueous ballet.” These evocative expressions invite you to craft narratives that rival those crafted by Homer himself!
5) A Flotilla United by Secret Code: Picture yourself amidst a fleet regatta, surrounded by fellow sailors all fluent in this secret maritime lexicon. This peculiar linguistic bond establishes instant connections beyond conventional exchanges shared in mainstream society. An initiation into sailing terminologies is akin to unlocking a secret code, granting you access to new friendships built on shared experiences and mutual appreciation for life’s most elemental forces: wind, water, and adventure.
Conclusion: As we conclude our journey through the oceanic tapestry woven by nautical terms and phrases, it becomes evident that their power extends far beyond mere communication. Sailing lingo elevates your voyage from practicality to poetry, endowing each moment on deck with historical significance and artistic resonance. By embracing these traditions and enriching your sailing vernacular with colorful expression, you become part of a timeless legacy that has inspired dreamers and adventurers throughout centuries. So let us hoist our sails high while whispering tales told countless times before – may our newfound command over nautical terminology enhance our quest for freedom on the open seas!
Sailing Terms and Phrases Step by Step: From Beginner to Pro
Title: Sailing Terms and Phrases Step by Step: From Beginner to Pro – Unleashing the Sailor in You!
Introduction: Ahoy, aspiring sailors! Embark on an exciting journey into the world of sailing, where the wind becomes your silent ally and the vast ocean your playground. Whether you’re a beginner dipping your toes into this majestic realm or a seasoned sailor looking to polish your knowledge, our comprehensive guide will equip you with essential sailing terms and phrases. So batten down the hatches, and let’s sail through this blog together!
1. Setting Sail: Grasping the Basics Before we dive deeper into nautical jargon, let’s start by understanding fundamental concepts crucial for all sailors. We’ll cover key aspects such as wind direction, points of sail (angles relative to the wind), and boat maneuvers—tacking and gybing—to harness the wind’s power efficiently.
2. Navigating Seas of Terminology Now that you’ve familiarized yourself with the essentials, it’s time to raise anchor on our expedition of sailing terminology. From bow to stern, we’ll unravel intricate vernacular such as port and starboard (left and right), keel (the underwater part keeping your vessel steady), rigging (the system supporting sails), and many more nautical gems.
3. Anchoring Your Knowledge: Knots & Ropes No sailor can be without a reliable knot repertoire! Discover step-by-step instructions for tying knots like reef knot (square knot), figure-eight knot, clove hitch, bowline, and more. Mastering these techniques ensures safety onboard while securing sails, tying lines around cleats, or attaching fenders effortlessly.
4. Weathering Any Storm: Meteorological Mastery Weather plays an indispensable role in sailing dynamics; understanding its patterns keeps both novices and experts safe at sea. Delve into concepts such as barometric pressure systems, reading weather charts, interpreting cloud formations, and utilizing meteorological apps. Equip yourself to anticipate wind shifts, gauge tides, and discern when a storm is approaching.
5. SOS – Safety on the Seven Seas Safety should always come first! Gain insights into maritime safety procedures, including personal flotation devices (PFDs), harnesses, life rafts, flares, distress signals, and emergency protocols to ensure your sailing experience remains secure and enjoyable.
6. Racing Ahead: Sail Trim & Performance Ready to up your game? Discover the art of sail trimming—the fine-tuning required to extract maximum speed from your vessel. Learn about cunningham lines, boom vangs, halyards, traveler controls—the subtle adjustments that balance power versus pointing ability during a regatta or an adventurous day sail.
7. Navigate Like a Pro: Charting Your Course Navigational skills are the backbone of any sailor’s toolbox. Dive into the world of nautical charts—those intricate maps guiding you amidst an ocean expanse—and grasp concepts such as understanding symbols and markings; plotting courses using latitude and longitude; employing GPS systems; avoiding hazards; and converting true headings into magnetic ones for compass navigation.
8. Tales from the Sea: Maritime Lore and Trivia Immerse yourself in captivating tales woven by seasoned sailors while exploring intriguing maritime traditions like baptizing ships or crossing the equator ceremoniously. Learn lesser-known facts about famous shipwrecks or legendary seafarers who etched their names in history—fueling your passion for adventures beyond imagination!
9. Starboard ahead! Sailing into Greener Horizons In this digital era of sustainable living, embark on a conversation regarding eco-friendly sailing practices aimed at preserving our breathtaking marine ecosystems. Explore tips for reducing carbon footprints while sailing—with alternatives like electric propulsion—and join the movement towards cleaner seas with recycling initiatives that minimize plastic waste onboard.
10 Ahoi, Captain! Mastering the Ropes Congratulations on reaching this stage of our sailing odyssey. Armed with an arsenal of sailing terms, navigational prowess, safety awareness, and a passion for the sea, you’re well on your way to becoming a true sailing pro. So hoist those sails high and brace yourself for limitless adventures that await you—the world is your oyster!
Epilogue: As you set sail on this journey from beginner to pro sailor, remember to embrace the wonders of the sea while respecting its power and beauty. With time, experience, and dedication, you’ll be speaking the language of seasoned sailors confidently. Bon voyage on your nautical endeavors; may fair winds forever fill your sails!
Frequently Asked Questions about Sailing Terms and Phrases Answered
Sailing is a unique and exciting experience that brings together the beauty of nature and the thrill of adventure. Whether you are an experienced sailor or a novice looking to learn more about this captivating activity, it’s important to understand the various sailing terms and phrases that are commonly used in the sailing community. To help you navigate through these sometimes confusing waters, we have put together a list of frequently asked questions answered with detailed professional explanations, sprinkled with witty and clever anecdotes. So sit back, relax, and let’s dive into the world of sailing terminology!
Q1: What exactly is a “jib”?
A1: Ah, the jib! This term refers to a triangular sail located at the front of the boat, usually attached to the forestay (the wire that holds up the mast). The jib serves as one of the primary sources of propulsion for sailing vessels. Think of it as the boat’s secret weapon – it catches wind and propels your vessel forward! Just like a jester adding an element of surprise in medieval courts.
Q2: Can you explain what “tacking” means?
A2: Tacking is perhaps one of the most fundamental maneuvers in sailing. It involves turning your boat into or across the wind so that your sails switch sides. Picture yourself maneuvering your way through rush hour traffic – except instead of cars, there are waves crashing against each other! Tacking allows sailors to make headway against windward, zigzagging their way to their destination like Shakespearean characters in a fiery debate.
Q3: I’ve heard people talk about “heeling.” What does it mean?
A3: Ahoy there! Heeling refers to when a sailboat leans over sideways due to strong winds pushing against its sails. This ‘Michael Jackson-esque’ dance move can be quite exhilarating for thrill-seekers, but it requires careful balance and control. Imagine holding a delicate ballet pose on a tilting stage while attempting to impress the judges. That’s what heeling is all about – finding the perfect equilibrium between adventure and stability.
Q4: What is meant by “mainsail”?
A4: The mainsail is the largest and most visible sail on a sailing vessel. It is typically attached to the mast and plays a crucial role in powering the boat forward when the wind hits it just right. This sail can be compared to the lead vocalist of a band – it takes center stage and commands attention, providing maximum power to propel your floating oasis across the water.
Q5: Can you explain what “port” and “starboard” mean?
A5: Ahoy, matey! Port refers to the left side of a boat when facing its bow (front), while starboard refers to its right side. Now, how do you remember which is which? Here’s a clever trick: port has four letters, just like LEFT, so it’s easy to associate them together. And starboard has more letters than port or left, so that must be RIGHT! Remember this little rhyme, and you’ll never steer your ship in the wrong direction again.
So there you have it – some frequently asked questions about sailing terms and phrases answered with detailed professional insight mixed with witty and clever comparisons. We hope this helps unravel some of the mysteries behind those nautical expressions that sailors throw around with ease. Happy sailing!
Mastering the Jargon: Unraveling the Language of Sailing
Sailing, with its long and storied history, offers enthusiasts an escape into a world rich in tradition and adventure. From battling treacherous waves to navigating the vast expanses of the open sea, sailors are no strangers to challenges. However, there is one aspect of sailing that can often leave beginners feeling adrift – the intricate and sometimes befuddling language used in this esteemed practice.
In this blog post, we aim to demystify the jargon of sailing, allowing novices to navigate conversations with seasoned sailors and ultimately feel more at home on deck.
Tacking and Jibing – Oh My!
One of the most fundamental concepts in sailing revolves around changing direction – but don’t call it turning! Sailors use specific terms like tacking and jibing to describe these maneuvers. Tacking involves turning into the wind by steering through a series of tight angles, while jibing entails turning away from the wind in a more fluid motion. So if you hear someone say “Prepare to tack!” or “Jibe ho!”, now you’ll know what they mean.
Hoist That Main Sail!
As you familiarize yourself with sailboats, you’ll swiftly encounter talk about different sails – mainsails being one of them. The mainsail is crucial for propelling your vessel forward and adjusting its position relative to the wind. When you hear someone shout “Hoist that main!” they’re simply telling their crewmates to raise or unfurl this essential sail. Remember, timing is key when hoisting your main as it affects your boat’s performance and maneuverability.
Trimming Your Sails
Ever wondered what sailors mean by “trimming” their sails? No, they’re not talking about giving them a haircut! Trimming refers to adjusting your sails’ position relative to the wind for optimal efficiency – something akin to finetuning your instrument. By playing with the sheets (lines that control sail shape), sailors can harness the wind’s power effectively, propelling themselves along smoothly and efficiently.
The Wind Angle – A Sailor’s Best Friend
Understanding wind angles is paramount for any sailor worth their salt. When sailors refer to “the point of sail,” they are describing the direction they are sailing relative to the wind. Different points of sail include close-hauled (sailing as close to the wind as possible) and running (sailing in the same direction as the wind). Knowledge of these angles determines how a skilled sailor adjusts their sails, achieving optimal speed and stability.
Raising Anchor – Setting Sail!
Embarking on a sailing adventure often begins with raising anchor or setting sail. However, it’s not just about hoisting a heavy object; there is an art to it! The crew works together seamlessly, making sure the anchor is secured safely before preparing to lift it from its watery resting place. With a well-coordinated effort, they can free themselves from shore and set out into open waters to seek out new horizons.
Navigating Lingo Land
As you delve deeper into sailing culture, you’ll soon notice a myriad of unique terms specific to this maritime world – jargon like ‘batten down the hatches,’ ‘hard-a-lee,’ or ‘full-and-by.’ Each phrase has its own charm and colorful history that adds character and camaraderie amongst sailors. Embrace this lexicon with enthusiasm, for it symbolizes connection with centuries-old traditions and ensures clear communication at sea.
So whether you decide to hoist your sails under clear blue skies or undertake epic adventures across stormy seas, mastering the jargon of sailing will undoubtedly enhance your experience. Armed with this newfound knowledge, you’ll be able to hold engaging conversations with fellow sailors while feeling like an old salty sea dog yourself. Fair winds ahead!
Exploring Yachts Sailing in Croatia: A Seafaring Paradise
If you’re dreaming of an unforgettable sailing experience amidst stunning landscapes and crystal-clear waters, look no further than Croatia. With its picturesque coastline, countless islands, and vibrant culture, Croatia offers an idyllic setting for yacht sailing adventures.
Why Choose Yachts Sailing in Croatia?
Croatia boasts over a thousand islands, each with its own unique charm waiting to be explored. From the lively ports of Split and Dubrovnik to the secluded coves of Hvar and Vis, there’s no shortage of destinations to discover. Navigate through the serene waters of the Adriatic Sea, soak up the Mediterranean sun, and immerse yourself in the rich history and culture of this coastal paradise.
The SkipperCity Experience
For the ultimate yachting adventure in Croatia, look no further than SkipperCity. With a fleet of luxurious yachts and experienced skippers at your service, SkipperCity ensures a seamless and unforgettable sailing experience. Whether you’re a seasoned sailor or a novice explorer, their expert team will tailor a bespoke itinerary to suit your preferences, ensuring every moment on board is nothing short of magical.

To embark on your own yachts sailing adventure in Croatia with SkipperCity, simply click here to visit their website and start planning your dream getaway. With their wide range of yachts and personalized service, you’ll be setting sail for adventure in no time.
Taking Your Boating Game Up a Notch with Essential Sailing Terms and Phrases
Are you ready to elevate your boating skills and impress everyone on board with your extensive knowledge of sailing terms and phrases? Look no further, as we’re here to help you take your boating game up a notch!
Sailing has its own unique language that can initially seem daunting to beginners. However, mastering these essential sailing terms and phrases not only enhances your understanding of the sport but also ensures seamless communication with fellow sailors. So let’s dive into this linguistic adventure and emerge as refined seafarers!
1. Bow: This term refers to the front part of the boat. Imagine standing at the bow, with the wind blowing through your hair, as you confidently navigate through the open waters.
2. Stern: The opposite of the bow, the stern is the back end of the vessel. Picture yourself lounging on the stern while basking in the sun, enjoying a leisurely day on your boat.
3. Port: When facing forward towards the bow, port refers to the left side of a boat or yacht. Remember it by associating “port” with “left,” both consisting of four letters.
4. Starboard: In contrast to port, starboard indicates the right side of a boat when facing forward. An easy way to remember is by imagining a bright star guiding you towards success.
5. Tacking: To change direction against or across the wind using sails is known as tacking. It involves turning or pivoting through head-to-wind coordination, allowing your boat to zigzag efficiently while harnessing variable wind angles.
6. Jib: A triangular sail positioned in front of a mast is called a jib and primarily aids in steering when sailing close-hauled or reaching conditions.
7. Mainsail: The largest sail on most boats, attached vertically along a mast toward aft (near stern) direction commands utmost respect – it’s called a mainsail! Mastering control over the mainsail is essential for maximizing speed and maneuverability.
8. Windward: The direction from which the wind is coming is referred to as windward. Sailing toward the windward side can be challenging yet exhilarating, requiring precise navigation techniques for optimal performance.
9. Leeward: The opposite of windward, leeward denotes the side away from the wind or downwind direction. When sailing on the leeward side, you’ll experience smoother conditions with less turbulence — a perfect opportunity for relaxation and enjoying your boating adventure.
10. Rudder: Acting as a ship’s steering mechanism, the rudder controls its movement by changing its course in response to the helmsperson’s commands. Mastering rudder control ensures smooth sailing and accurate navigation.
Now armed with these essential sailing terms and phrases, you can confidently navigate through any boating expedition while impressing your friends with your newfound knowledge! So hoist those sails, trim them accurately, and let these words navigate you towards becoming an impeccable sailor. Fair winds and following seas await you on this exciting journey!
Remember, practice makes perfect, so don’t hesitate to apply these terms during your next sailing adventure. Happy sailing!
Recent Posts

- Sailboat Gear and Equipment
- Sailboat Lifestyle
- Sailboat Maintenance
- Sailboat Racing
- Sailboat Tips and Tricks
- Sailboat Types
- Sailing Adventures
- Sailing Destinations
- Sailing Safety
- Sailing Techniques

- Find A School
- Certifications
- North U Sail Trim
- Inside Sailing with Peter Isler
- Docking Made Easy
- Study Quizzes
- Bite-sized Lessons
- Fun Quizzes
- Sailing Challenge

40 Sailing Terms: How to Talk Like a Sailor
By: Zeke Quezada, ASA American Sailing , Nautical Trivia
In 1983, the American Sailing Association was founded by Lenny Shabes. Over the years, hundreds of thousands of sailors have become certified in the ASA sailing curriculum. This year, we celebrate 40 years as the leading sailing education entity in the United States. So when you get out on the water, you can be sure that ASA-certified sailors are sailing safely and confidently.
Sailing has its own language, and when you go through the ASA curriculum, you’ll find yourself using terms like port and starboard if talking about directions, or referring to a zephyr or a squall when discussing the weather. Some language is meant to help clarify sailing directions, while other terms sound like novelties or just sailors loving that we are part of a special club, but actually have super interesting origins and stories tied to them.
After 40 years, we are going strong, and we continue to help students not only talk like sailors, but become sailors.
40 terms to help you start talking like a sailor
- Aft – The rear section of the boat
- Bow – The front section of the boat
- Mast – The vertical pole that supports the sails
- Boom – The horizontal pole that extends from the mast and supports the foot of the mainsail
- Winch – A device used to adjust the tension on a rope or wire, usually used to hoist sails or adjust rigging
- Helm – The steering wheel or tiller used to steer the boat
- Tiller – A lever used to steer the boat by moving the rudder
- Rudder – The hinged device at the back of the boat used for steering
- Keel – The fin-like structure beneath the boat that provides stability
- Centerboard – A retractable fin-like structure beneath the boat that provides stability and helps prevent sideways movement
- Ballast – Heavy material, such as lead, placed in the bottom of the boat to provide stability
- Beam – The width of the boat at its widest point
- Freeboard – The distance from the waterline to the deck of the boat
- Draft – The distance from the waterline to the deepest point of the keel or centerboard
- Rigging – The ropes and wires used to support the mast and sails
- Headstay – The wire or rope that runs from the top of the mast to the bow and supports the forestay
- Forestay – The wire or rope that runs from the mast to the bow and supports the jib or genoa
- Backstay – The wire or rope that runs from the top of the mast to the stern and helps support the mast
- Shroud – The wire or rope that runs from the mast to the side of the boat and helps support the mast
- Halyard – The rope used to raise a sail
- Sheet – The rope used to control the angle of a sail
- Jib – A triangular sail in front of the mast
- Genoa – A large, overlapping jib that provides additional power
- Mainsail – The large, primary sail that is attached to the mast and boom
- Spinnaker – A large, colorful, balloon-like sail used for downwind sailing
- Tack – The forward corner of a sail
- Clew – The aft corner of a sail
- Reef – To reduce the area of a sail in high winds
- Port – The left side of the boat when facing the bow
- Starboard – The right side of the boat when facing the bow
- Leeward – The side of the boat away from the wind
- Windward – The side of the boat facing the wind
- Heeling – When the boat leans to one side due to wind or weight distribution
- Running – sailing with the wind coming from behind the boat
- Hiking – The act of leaning out over the side of the boat to counteract heeling
- Capsize – When a boat overturns or turns over
- Jibe – A maneuver in which the boat turns downwind and the mainsail moves from one side of the boat to the other
- Tack – A maneuver in which the boat turns into the wind and the mainsail moves from one side of the boat to the other
- Nautical mile – A unit of measurement used to measure distance at sea, equivalent to 1.15 miles
- Knot – A unit of measurement used to measure speed, equivalent to one nautical mile per hour
If you’re ready to take your knowledge to the next level, check out these ASA 101 Study Cards — great as a resource when you take ASA 101, 103, or 104 and even more fun later as a coffee table set to quiz your friends!

Related Posts:

- Learn To Sail
- Mobile Apps
- Online Courses
- Upcoming Courses
- Sailor Resources
- ASA Log Book
- Bite Sized Lessons
- Knots Made Easy
- Catamaran Challenge
- Sailing Vacations
- Sailing Cruises
- Charter Resources
- International Proficiency Certificate
- Find A Charter
- All Articles
- Sailing Tips
- Sailing Terms
- Destinations
- Environmental
- Initiatives
- Instructor Resources
- Become An Instructor
- Become An ASA School
- Member / Instructor Login
- Affiliate Login

Sailing Terms Demystified: A Comprehensive Guide to 14 Common Sailing Terminology
- May 28, 2023

Ahoy, sailors! If you’re new to the world of sailing, you might find yourself overwhelmed by the myriad of sailing terms that seasoned sailors casually toss around. But fear not! In this comprehensive guide, we’ll unravel the mystery behind common sailing terms, providing simple explanations and examples to help you navigate the nautical jargon with ease. Let’s set sail and explore these essential sailing terms.
Table of Contents
Port and starboard.
When on a boat, “port” refers to the left side, while “starboard” refers to the right side. These terms are used to communicate directions and indicate the location of objects or maneuvers. For example, “Please pass me the fenders on the starboard side.”
Bow and Stern
The “bow” refers to the front or forward part of a boat, while the “stern” refers to the back or rear part.
Windward and Leeward
“Windward” refers to the side of the boat or the direction from which the wind is coming. On the other hand, “leeward” refers to the opposite side, sheltered from the wind. Sailors use these terms to plan their course and make tactical decisions.
Tacking and Jibing
“Tacking” is the act of turning the bow of the boat through the wind, changing the side from which the wind is coming. This allows the boat to change direction while sailing upwind. “Jibing” is the opposite maneuver, turning the stern of the boat through the wind to change direction when sailing downwind.
“Rigging” refers to the system of ropes, wires, and other components used to support and control the sails and mast. It includes various elements such as halyards (ropes used to hoist the sails), sheets (ropes used to control the angle of the sails), and shrouds (wires supporting the mast).
“Heeling” describes the leaning or tilting of a sailboat due to the force of the wind on the sails. The boat can lean to one side, causing it to tilt and creating a thrilling sensation. Sailors adjust the sails and shift their weight to maintain balance and control.
“Reefing” is the process of reducing the area of a sail to decrease its surface area and power in strong winds. This is done by partially lowering or folding a section of the sail and securing it, thus making the sail smaller and more manageable.
The “keel” is the central structural element of a sailboat, usually made of heavy material such as lead or iron. It extends beneath the boat into the water and provides stability and prevents the boat from sliding sideways.
Navigational Markers
Navigational markers, also known as buoys, are floating objects that indicate safe passages, hazards, or important locations in the water. They are color-coded and labelled according to their purpose. For instance, a red buoy with even numbers indicates the right side of a channel when entering from the sea.
Points of Sail
Sailboats have different angles at which they can sail relative to the direction of the wind, which are called “points of sail.” The main points of sail include close-hauled (sailing as close to the wind as possible), reaching (sailing at an angle between close-hauled and a broad reach), and running (sailing with the wind directly behind).
By familiarizing yourself with these essential sailing terms, you’ll be able to communicate effectively, understand instructions, and navigate the sailing world with confidence. So hoist your sails, embrace the wind, and embark on unforgettable nautical adventures armed with the knowledge of sailing terminology. Fair winds and smooth seas!
Related Posts

Sailing Navigation: Exploring Modern Techniques for Navigating the Seas in 2023
- June 10, 2023

Sailing in Different Directions: Harnessing the Wind’s Power in 2023
- June 4, 2023

The Ultimate Guide to Sail Boat Designs: Exploring Sail Shape, Masts and Keel Types in 2023
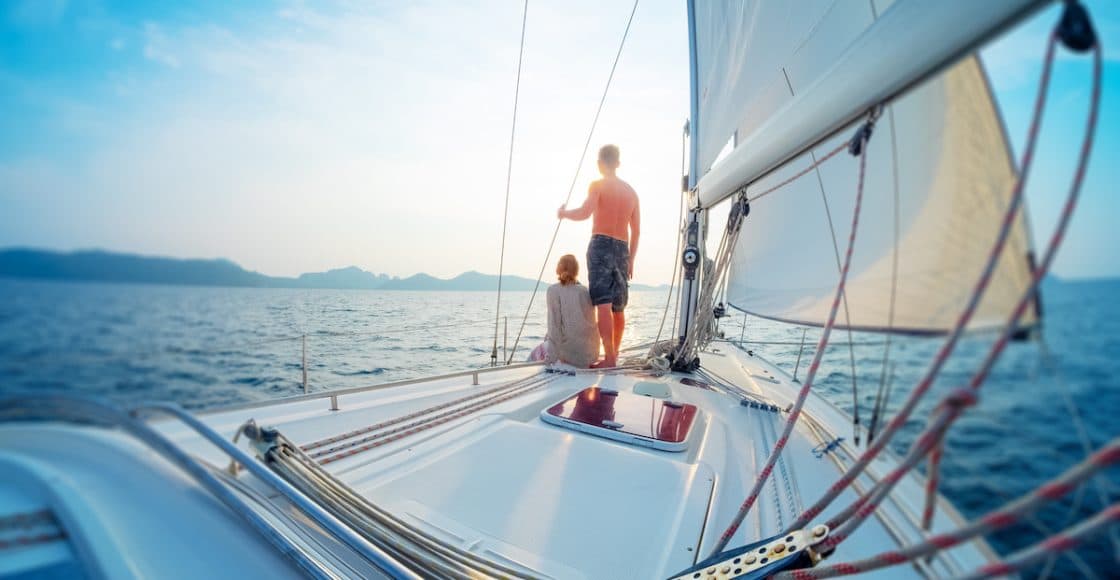

50 Nautical, Sailing & Boat Terms for Beginners

Table of Contents
Last Updated on September 29, 2023 by Boatsetter Team
Boating has its own vocabulary and if you’re going to be spending time on the water, you should understand a few basic boat terms. Knowing these will make you safer as well as more useful whether boating on your own, chartering or helping friends on their boat.
Let’s divide these words into basic nautical terms and specific sailing terms, listed in alphabetical order.
Ready to Hit the Water? Find Local Boat Rentals Near You
30 Commonly Used Nautical & Boating Terms
Here are a few expressions you’ll hear aboard both a powerboat and sailboat, or even at the dock before boarding your boat rental or charter.
- Aft – the direction toward the back or stern of a boat.
- Ashore – not on a boat but on land or a dock .
- Ballast – extra weight laid low in a boat to provide stability.
- Beam – the width of a boat at its widest point, usually the middle.
- Bow – the front of a boat. Multihulls like catamarans have more than one bow.
- Bunk – a built-in bed on a boat.
- Cabin – the sleeping accommodations on a boat .
- Cockpit – the main seating area of a boat that may also include the helm station .
- Crew – the people or staff that help drive and manage the boat.
- Deck – the top or horizontal structure that is laid over the hull of a deck.
- Dock line – the ropes used to tie a boat to a dock.
- Fender – a rubber, vinyl or foam bumper used to protect the boat at a dock; often referred to by novice boaters as “bumpers.”
- Forward – the direction toward the front or bow of a boat.
- Galley – the kitchen on a boat. It can be inside or out on deck.
- Head – the toilet or bathroom on a boat.
- Helm – the boat’s steering mechanism. It can be a tiller or a wheel.
- Helm station – the area where from which you command or drive a boat.
- Hull – the body or shell of a boat including the bow and stern.
- Keel – the longitudinal structure at the bottom of the hull and generally on the centerline. The keel helps with stability and tracking.
- Knot – either various loops tied in a line or a unit of speed which equals one nautical mile per hour.
- Line – any rope on a boat is referred to as a line – not a rope.
- Nautical mile – a unit of measurement used on the water. A nautical mile is approximately 1.2x a statue mile.
- Onboard – on a boat whether on deck, on the cockpit or below.
- Port – the left-hand side of a boat when you’re facing forward or toward the bow.
- Rudder – an appendage below the boat that is controlled by the wheel or tiller to steer the boat. A boat may have more than one rudder.
- Starboard – the right-hand side of a boat when you’re facing forward.
- Stern – the place at the back of a boat.
- Transom – the actual structure of the back edge of a boat.
- Wake – the turbulence left behind a moving boat.
- Waterline – the place where the hull of a boat meets the surface of the water.
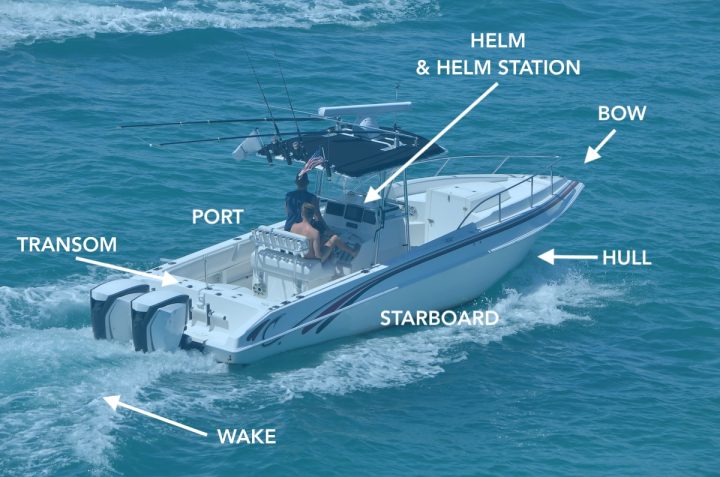

20 Sailing & Sailboat Terms
Within boating, sailing has its own specific vernacular. You’ll want to understand it before you step aboard a sailboat to help crew or when taking a lesson.
- Apparent wind – the combination of true wind and the motion of the boat at the time. It’s the wind you feel onboard.
- Boom – the horizontal pole which extends from the mast aft. It holds the bottom of the mainsail.
- Ease – to adjust sails outward or away from the centerline of a boat.
- Halyard – the line used to raise a sail whether a mainsail or a headsail.
- Headsail – a sail that is forward of the mast. It can be a genoa, a jib, a staysail or a small storm sail.
- In irons – technically a point of sail when you’re head-to-wind meaning the bow is pointing directly into the true wind and the boat is unable to maneuver.
- Jibing (also spelled gybing) – changing direction where the stern swings through the eye of the wind.
- Leeward – the direction away from where the wind is blowing.
- Mainsail – the primary sail on a boat which is usually attached in some way to the mast and boom. On most sailboats it’s the primary source of power.
- Mast – the vertical pole that supports the sails. The mast itself is supported by the rigging.
- Points of sail – the boat’s direction under sail relative to the true wind . The points of sail are: close-hauled, close reach, beam reach, broad reach and dead run.
- Reefing – shortening or reducing the area of a sail to de-power a sailboat usually used in a strong wind.
- Sheet – the line that controls the angle of a sail. There are mainsheets, jib/genoa sheets and others.
- Shroud – a part of the boat’s rigging that supports the mast from side-to-side
- Stay – a part of the boat’s rigging that supports the mast fore and aft.
- Tacking – changing direction under sail where the bow swings through the eye of the wind.
- Trim – to adjust sails inward or closer to the centerline of a boat.
- True wind – the actual wind that is blowing – both direction and speed.
- Winch – a rotating drum used to help control lines with a lot of pressure on them. A winch is cranked with a winch handle.
- Windward – the direction from where the wind is blowing.
Browse Available Sailboat Rentals Near You

Zuzana Prochazka is an award-winning freelance journalist and photographer with regular contributions to more than a dozen sailing and powerboating magazines and online publications including Southern Boating, SEA, Latitudes & Attitudes and SAIL. She is SAIL magazines Charter Editor and the Executive Director of Boating Writers International. Zuzana serves as judge for SAIL’s Best Boats awards and for Europe’s Best of Boats in Berlin.
A USCG 100 Ton Master, Zuzana founded and manages a flotilla charter organization called Zescapes that takes guests adventure sailing at destinations worldwide.
Zuzana has lived in Europe, Africa and the United States and has traveled extensively in South America, the islands of the South Pacific and Mexico.
Browse by experience

Explore articles

Affordable Boating: 7 Tips to Save Money on the Water

Best Boats for Rough Water: 6 Qualities that Make for a Smooth Cruise

Small Boats: What Type is Right for You?

The Ultimate Boat Rental Safety List

Sailing Terms: A Complete Guide 2024
Whether you dream of hoisting the mainsail, feeling the wind in your hair, or simply want to unravel the mysterious language of the sea, this blog post is your ultimate compass for popular sailing terms used today.
Sailing is an art that has been practiced for centuries, capturing the hearts and imaginations of adventurers and explorers throughout history. From the earliest voyages of discovery to modern-day regattas, the language of sailing has evolved, creating a rich tapestry of nautical terminology.
For the uninitiated, the world of sailing may seem like an intimidating labyrinth of jargon, full of puzzling phrases and unfamiliar expressions.
But fear not! In this comprehensive guide, we will embark on a voyage of understanding, demystifying the terminology that surrounds this timeless and awe-inspiring activity.
Whether you’re an enthusiastic beginner, an armchair sailor, or simply curious about the fascinating lexicon of the sea, this blog post will provide you with a sturdy anchor of knowledge.
We’ll explore the essential terms that every sailor should know, from basic equipment and boat parts to navigation techniques and crew roles.

Prepare to set sail as we delve into the meaning behind expressions like “trimming the sails,” “starboard,” “tacking,” and “point of sail.”
By the time we reach the shore, you’ll have gained a solid grasp of sailing terminology, allowing you to converse fluently with seasoned sailors, comprehend sailing literature, and perhaps even take your first steps towards mastering the art of sailing.
So, whether you’re a landlocked adventurer dreaming of the open seas or a curious soul seeking to expand your nautical lexicon, join us as we unfurl the sails and navigate the captivating world of sailing terms.
Let’s set a course for knowledge, with the wind in our sails and the horizon on the horizon!
Table Of Contents
- Important sailing terms for beginners
- Sailing terms: A complete guide
Important Sailing Terms For Beginners

We’ve all been there. In fact, sometimes I very much feel that I am still a beginner and I think any sailor that tells you they don’t have days where they feel like too is lying!
Sailing is ever-changing, and every situation is ever so slightly different. It’s one of the most wonderful things about sailing and one of the absolute worst!
But one thing is for sure, when you’re a beginner and being totally bombarded with sailing terms it’s really not helpful. You don’t need to know every single sailing term straight away. No matter what your crusty sailing instructor tells you!
There are however some really useful ones to learn straight away and these sailing terms will help you out a lot as you learn the ropes (or the lines, as us sailors like to say!) We’ve narrowed down the sailing terminology that we found essential when we started out sailing.
Focus on these for now and you’ll be amazed at how quickly the others become part of your everyday vocabulary as you learn to sail .
Aft : The back of the boat, or near the back of the boat. Aft basically means back!
Alongside: When the boat is next to a pier or another vessel.
Apparent wind : This is the wind that can be felt. It could refer to speed or direction, and is often different to the true wind. For example, if you are sailing forwards at 5 knts, the wind speed will feel stronger than if you are sitting still. The wind that can be felt is the apparent wind.
Astern : Behind the boat. Sailors often say ‘going astern’, which means going backwards or going in reverse.
Beam reach : A point of sail. When the wind is blowing perpendicular to the direction that you’re sailing.
Bearing away : Steering the boat away from the direction in which the wind is blowing.
Bilge : This is the bottom of the inside of the boat. Water collects in the bilge, and then you use a bilge pump to pump the water overboard. Many people store things in their bilge for longer passages.
Boom : This is the long pole that sticks out of the mast. It holds the bottom of the mainsail in place and can be moved from side to side depending on where the wind is coming from. Booms can be very dangerous, as they are heavy and tend to carry a lot of power when the sail is full of wind.
Bow : The front of the boat.
Broad reach : A point of sail. Sailing with the wind coming off your stern quarter, a position in between the beam and stern of the boat.
Cleats : The metal blocks to which you secure lines.
Close-hauled : A point of sail. Sailing as close to the wind as possible without the sails flapping. On a monohull, the boat will usually heel over the most on this point of sail.
Close Reach : A point of sail. When you’re sailing between a beam reach and close hauled. Again, as you are travelling towards to wind on this point of sail it is likely the boat will be heeled over.
Dead run or Running Dead Downwind : A point of sail. Sailing with the wind coming from directly behind the boat. Many people use a light wind sail to catch the wind if the conditions are right, or pole out a sail to be ‘wing on wing’ and catch as much of the wind as possible.
Draft: The depth of a boat when it’s sitting in the water.
Fender: An inflated bumper used to keep the boat from banging into the dock or another boat.
Genoa : A large forward sail that comes back past the mast when fully unfurled. It is the same as a job sail but larger.
Heave to: A sailing manouvre used mostly during storms, which lies the boat favourably to waves while making only very slight headway.
Jib : A triangular forward sail, smaller than a genoa.
Jibing : When you steer the boat downwind from one direction to the other to keep the sails full. As you move from one direction to the other the wind will come from a different side and the sails will need to be moved across the boat to keep them powered up. It is similar to tacking, but going downwind instead of up! There is more danger from the boom when jibing.
Mainsail : The main sail on the boat, attached to the mast.
Mayday : The emergency call you make over the radio to show the boat or crew are in distress and needs immediate assistance.
No-sail zone : Also called the dead zone. This is an area 45 degrees either side of directly into the wind. This is the area a boat can’t sail in, and your sails will flap and the boat will power down if you try.
Port : The left side of the boat when facing forward.
Reef : When you lower some of the sail to give less sail area to the wind, usually done as the wind speed picks up.
Sheet : A line or rope used to control the trim of a sail.
Starboard : The right side of the boat when facing forward.
Stern : The back end of the boat.
Tacking : Turning the boat into the wind to change direction. You will pass through the dead zone quickly, adjusting the sails to the other side of the boat so you can continue to sail towards the wind in a zig-zag type shape.
Topping lift : A rope running from the back end of the boom to the top of the mast. This line controls the height of the boom and prevents it from falling when the sail isn’t raised.
Winch : A mechanical device used to pull the lines that control sails.
Windlass : A winch used to raise and lower the anchor.
Most of the terms below you can muddle by without knowing and pick them up as you go.
A lot of them are just fancy terms for things you probably just use a different name for in every day life, and while they’re useful to have in your sailing vocabulary they can be communicated in other ways, or picked up as and when is necessary!
Sailing Terms: A Complete Guide

Here is a more comprehensive guide to different sailing terms. Feel free to look through them and start to get familiar with them if you’re a new sailor, but don’t let them overwhelm you! You will pick them up the more time you spend on the water and around other sailors.
Abeam : Anything to the side of your boat. If you spot a vessel beside you, you can say it is abeam, and people will know to look out at 90 degrees from the centreline of your boat.
Abaft : Towards the back of the boat. Anything abaft means towards the stern, so the life ring is abaft the mast, meaning the opposite of forward or the mast. It could also mean something behind the boat, like rocks or another vessel.
Abandon ship: A command given to leave the boat immediately. Usually given by the captain when the boat and crew are in serious danger.
Adrift: Unattached to the sea bed. It usually means a vessel that isn’t anchored and not under control, so free to float around where ever the wind blows.
Aground: Resting on or touching the ground or bottom. This usually applies to a ship that has run aground, and is now stuck on the sea floor.
Anchor: A heavy piece of specially shaped metal that keeps the boat secured to the ground.

Athwartship : The position across a vessel from side to side at right angles to the keel.
Backing (a sail) : Forcing the wind into the ‘wrong’ side of the sail by pulling it to the opposite side of the boat.
Backstay : The wire that runs from the back of the boat up to the top of the mast to stop it from falling forward. The backstay is often thicker and stronger than the other stays.
Bailer : A scoop that is used to collect water from the bottom of a vessel. It can be any container! You’ll want one in your grab bag for if you ever need to bail water from a life raft or a dinghy.
Ballast : Weight to add stability to your vessel. The weight is usually lead or iron and can often be found within the keel of the boat. Some boats add extra ballast for more stability.
Batten : A thin strip of fiberglass (usually) that slots into pockets of the mainsail to help it maintain an open shape. Battens run from the back edge of the sail, the leech, to the forward edge of the sail, the luff. Most will have more than one batten, but not all mainsails have battens.
Beam : The widest point of the boat.
Bend : A knot used to connect two ropes.
Berth : Berth has several meanings. It could be your bed onboard, or it could be your slip in a marina.
Bight : A bend in a rope or line. When a rope forms a bight, it has changed direction 180 degrees.
Bimini : The cover over the cockpit. Usually this is made from canvas and can be removed. It shades from the sun and offers a little protection from the rain.
Binnacle : The pedestal centrally located in the cockpit. It usually holds the steering wheel along with navigational equipment like your chart plotter and compass.
Bitter end: The last part of a rope or cable, usually referring to the anchor chain. Once the chain or rope has been paid out completely it has reached its bitter end.
Block : A pulley.

Boom vang : This prevents the boom and mainsail from moving upwards which sailing. It pulls the boom down to help the mainsail keep the right shape.
Boot Top or Boot Stripe : The paint between the boat’s bottom paint and it’s topside paint. It’s usually a white stripe that runs around the boat.
Bowsprit : A section of the boat that runs even further forward than the bow. It looks like a small diving board sticking out the front of the boat. Not all boats have a bowsprit and they are more common on classic boats. They allow the rigging to be attached further forward.
Broach : When a boat sailing downwind accidentally ends up sideways to the waves and heels over dangerously. This is usually caused by large waves that force the boat to travel too fast and end up in a position beam on to the waves.
Bulkhead : The walls in a boat that run across the centerline of the vessel. These are structurally important and mustn’t be messed with!
Capsize : When a vessel tips over past 90 degrees.
Catamaran : A vessel with two hulls.

Centerboard : A keel that can lift up and down depending on the point of sail. It helps the boat to point further to wind when down, or run more easily downwind when raised. When raised, the boat can sneak into shallower waters.
Centerline : An imaginary line that runs all the way from the center of the bow to the center of the stern.
Chainplate : A metal plate attached to the hull of the boat, which the rigging is attached to. Chainplates are very important to hold the mast upright, and must be well maintained. Some are visible on the exterior and others are hidden on the interior.
Chandlery : A store that sells boat supplies.
Chock : A fitting that a line passes through to change direction without chafing.
Clew : The lower back corner of a sail, where the foot and leech of the sail meet.
Coamings : A area around the cockpit or hatches that is designed to keep out water.
Cockpit : The area where the helm of the boat is. It is usually where there is seating, and the entrance to the interior of the boat. Cockpits can be at the stern of the boat or in the centre. Some sailors prefer a centre cockpit for a feeling of safety, others prefer the extra space you get with an aft cockpit.

Companionway : The entrance into the interior of the vessel.
Cotter pin : A bendable metal pin that you fit into a metal rod and then bend back to lock. You will find these most commonly on the rigging.
Daybeacons : Markers for navigation that are on posts. These are red (port) or green (starboard).
Dead reckoning : Determining a vessel’s position by knowing the direction and speed traveled.
Dinghy : The small, usually inflatable boat that you use to reach the shore when your big boat is at anchor. These are also called tenders.
Dodger : This is like the windshield of the boat. It’s a structure at the front of the cockpit to protect the helmsman from wind or spray.
Dismasting : When the mast breaks off. This usually happens because of a rigging failure, or can happen if the rig is overpowered.
Displacement : The weight of the water that would otherwise be in the place of the boat’s hull.
Drogue : A sea anchor to help slow down the boat. You might use one in big seas when the boat is sailing too fast down the waves. It can look like a small parachute on a line that you hang off the back of a boat, or even just a line or several lines hanging from the stern can help to slow the boat down.
Ebb tide : After high tide when the water is receding towards low tide.
EPIRB : Emergency Position Indicating Radio Beacon. This device transmits a distress signal to alert emergency services to the position of a vessel in trouble. Most people carry an EPRIB in their grab bag, or an easy to reach place in the boat.
Fairlead: A fitting which ensures a line runs in the right direction without snagging on anything.
Fathom : A measurement of water depth equal to 6 feet, not used very often anymore!
Fid : A tool used for splicing a line.
Fiddle : The raised edge around a table to prevent things from falling off in a seaway.
Fix : Determining a vessel’s location by using the compass bearing of two or more fixed points of reference. You will usually use this to check the boat isn’t dragging when anchored.
Fin keel : A fixed keel that hangs below the boat to provide stability.
Flogging : When a sail flaps noisily in the wind because it is not being filled properly. This usually happens when the boat is trying to sail too close to the wind.
Flood tide : The time between low tide and high tide when the water is rising.
Following sea: Waves or tidal movement going in the same direction as the boat.

Foot : The bottom edge of a sail.
Fore : At or near the bow (front) of a vessel.
Forestay : The rigging wire which goes from the bow to the top of the mast. This is where the foresail is attached, either hanked on or using a roller furling system. Most modern boats use a furling system as it is easier and quicker to use.
Full keel : A fixed, ballasted keel running the whole length of the boat.
Furling system : The system used to roll up a sail when it’s not in use and unfurl it when it is. It is most common to find furling foresails but in mast furling for the mainsail has also become more popular over recent years.
Freeboard : The distance on a vessel from the waterline to the deck.
Galley : The kitchen!
Gelcoat : The paint used on the outside of a boat. It’s a tough resin that forms a protective coating.
Gimbals : You will usually find these on your galley stove. They make your oven act a little like a rocking crib, so that it can stay level even when the boat is heeling or rocking. This is essential for keeping things on the stove while sailing or in a rolly anchorage.
Gooseneck : The point at which the boom attaches to the mast, letting the boom move freely from side to side and up and down. You then use lines to control it!
Ground tackle : The anchor, chain, and line that you use for anchoring or fixing the boat to the bottom of the sea when you want to stop and stay put.
Gunwale : The top edge of a boat’s hull.
Halyard : The line which attaches to a sail to raise it.
Hanks : The clips that attach the front edge of a sail to the forestay. It is more common these days to use a furling system for your main forestay, so you will likely only see these on a storm sail.
Hatch : A window in the ‘roof’ of the sailboat. It opens out onto the deck.
Head : The bathroom on a boat.
Headway : The amount you’re moving forward through the water. Like ‘making headway’.
Heave to : A way to keep the boat from moving through the water with minimal drift, usually used in heavy, dangerous seas. You back the foresail but lock the helm hard over towards the wind. Your boat should sit nicely creating a slick over breaking waves and you should only drift a little through the water. Not all boats will heave to nicely, so you should test this method with your vessel.
Heel : The tilt of a sailboat that usually happens when you’re sailing towards the wind.
In-Irons : When you steer the boat into the wind (by accident or on purpose) and the sails lose power. The boat will lose steerage as it slows down.
Jackline or Jackstay : Safety lines that run from the bow to the stern. You can clip yourself onto these lines so that you don’t fall overboard when doing tasks that require you to leave the cockpit.

Jib sheets : The lines you use to control the jib.
Kedge anchor : A small, lighter second anchor that you can use as a back up or a stern anchor.
Keel : The bottom of the boat.
Ketch : A sailboat with two masts, where the forward mast is the taller mast.
Knot : Usually referring to speed when sailing rather than the knots you tie in a line. One knot is equal to one nautical mile per hour.
Lazyjacks : Thin lines that run from the boom to the mast to help control the mainsail when it’s lowered.
Leech : The back edge of a sail.
Lee shore : The shore onto which the wind is blowing. This is the side of an island you want to avoid anchoring on, as it will mean the wind is blowing directly into the anchorage.
Leeward : The direction the wind is blowing towards. So if the wind is blowing from the north then the south is leeward.
Liveaboard: Someone who lives full time, or the majority of the time, on board their boat
Luff : The forward edge of the sail.
Mast: The tall pointy thing that holds up the sails!
Mizzen : The shorter mast behind the main mast on a ketch.
Monohull : A boat with a single hull.
Mooring field : An anchorage full of permanently attached buoys , to which you can moor up your boat.
Multihull : A vessel with more than one hull like a catamaran or trimaran.
On the hard : When your boat is out of the water, usually in a boat yard.
Painter : The line which attaches your dinghy to your main boat.
Pan Pan : This is a distress call that isn’t quite as urgent as a Mayday call. You will put out a pan pan on the radio if your boat needs assistance or you want to alert the emergency services of a problem that might get worse and become a mayday. For example, you have lost your engine and will drift into rocks if you can’t solve the problem or the wind doesn’t pick up in time.
Points of sail : The way your boat is travelling in relation to the wind.
Port tack : Sailing with the wind hitting the port side of the vessel.
Pulpit : The metal rails at the bow of the boat.
Pushpit : The metal rails at the back of the boat.
Quarter : The back corner area of the boat.
Reef : Reefing the sails is when you lower some of the sail to give less sail area to the wind, usually done as the wind speed picks up.

Rigging : All the wires and ropes used to hold the mast in place and adjust the sails.
Roach : The curved shape of the rearmost edge of a triangular sail.
Roller furling : The system that rolls up the sails to store them when they’re not in use.
Rudder : The thing that controls the direction of the boat. This is usually a fin at the stern of the boat under the water line and behind the propeller. It’s controlled by a steering wheel or tiller from the cockpit.
Running : Sailing downwind.
Running rigging : The lines which control the sails.
Schooner : A sailboat with two or more masts. The mainmast is at the back.
Seacock : A valve that can be opened or closed to control the flow of water in or out of the boat.
Scope : The length of chain between the anchor and the boat.
Scuppers : Deck drains to allow water to flow overboard when it rains or when crash onto the cockpit.
Securite : A call transmitted over the radio to alert sailors to potential dangers in their area.
Shackle : A metal U or D shaped link with a removable pin that can be used to attach lines to blocks and other useful things like that!
Shrouds : Wires or ropes running from the chainplates to the mast to stop the mast moving from side to side.
Skeg : An extension of the hull hanging in front of the rudder, that the rudder is attached to. It can help protect the rudder from getting hit or from debris in the sea.
Sloop : A single masted sailboat with a mainsail and one foresail.
Slugs : The things that the mainsail sits in to run it up the boom.
Spinnaker : A sail used for light, downwind sail. Spinnakers are often the biggest sail on the boat, made from a light material and they are often brightly coloured.
Splice : When you connect two lines together using their weave. You will often need a fid for this.
Spreaders : The horizontal poles that come out from the sides of the mast.
Spring line : These are used when docking the boat. They are the lines that come from the bow or the stern to a point midship on the dock. They are used to control how far the boat can move forwards and backwards while in its slip.
Stanchions : The metal posts along the outside of the deck through which the lifelines run.
Standing rigging : The wires and ropes, such as the shrouds and stays, that are permanently in place and hold up the mast.
Starboard tack : Sailing with the wind hitting the starboard side of the boat.
Stays : The wires or ropes running from the bow and stern to stop the mast moving forwards or backwards.
Storm jib : A small foresail that can be hanked on during heavy weather. It is made from tough, heavy material and often brightly coloured.
Tack : The forward lower corner of a sail.
Tender : The same as a dinghy. A small boat, usually inflatable, that you use to get to shore when the boat is anchored.

Tiller : A bar used to control the rudder from the cockpit. It is the same as a steering wheel, but some prefer using a rudder, or find it takes up less space in the cockpit.
Toe rail : The raised lip around the edge of the deck that helps stops things falling overboard.
Trim : Adjusting the shape and angle of the sails to get optimum performance.
Watermaker: A device used on board sailboats to make fresh drinkable water from the sea.
Weather helm: If the helm was centered, the boat would turn towards the wind (weather). Because of this, the tiller must be pulled to the windward side of the boat in order to make the boat sail in a straight line.
Windward : The direction from which the wind is blowing.
Wing on wing : Sailing downwind with the foresail and the mainsail out on different sides of the boat to catch as much of the wind as possible.
Conclusion: Sailing Terms

As our voyage through the captivating realm of sailing terms comes to an end, we can reflect upon the vast expanse of knowledge we have acquired.
From bow to stern, port to starboard, and every gust of wind in between, we have ventured into the depths of nautical language, emerging with a newfound understanding of this unique language.
By unraveling the mysteries of sailing terminology, we have unlocked the door to a world of adventure, heritage, and camaraderie. We now possess the tools to decipher the conversations of seasoned sailors, navigate the pages of maritime literature, and even embark on our own seafaring adventures with confidence.
But beyond the practical benefits, exploring sailing terms has allowed us to connect with a tradition that spans generations. It has illuminated the bond between humans and the vast, untamed sea, reminding us of the courage, skill, and resourcefulness required to tame its forces.
As you continue your own sailing journey, remember that understanding the language of the sea is just the beginning.
Embrace the spirit of exploration, befriend the winds, and let the gentle lapping of the waves guide you towards new horizons. Seek out opportunities to hoist the sails, adjust the rigging, and experience the thrill of harnessing the elements.
May the knowledge gained from this voyage serve as a rudder, steering you towards a deeper appreciation of sailing’s beauty and complexity.
And as you embark on your own adventures, may these sailing terms be your faithful companions, reminding you of the legacy of sailors who have come before and the timeless allure of the open water.
So, fair winds and following seas, dear readers! May you find joy, excitement, and a profound sense of connection as you explore the vast ocean of sailing terminology.
Whether you choose to cast off the lines and embark on your own voyage or simply revel in the tales and traditions of seafaring lore, let the language of sailing be your guiding star.
Until we meet again on the vast blue expanse, keep dreaming of distant shores, salty breezes, and the eternal call of the sea. Bon voyage!
And yes, this is how I talk all the time. Because I’m a sailor, and that’s how we nautical folk communicate!
Similar Posts

Anchoring For Idiots (By Two Idiots)

Sailboat Crew Interview

The 11 Most Expensive Sailboats Of 2024

Why Are Sailboat Sails White?

111+ Short And Unique Ocean Captions For Instagram 2024

22 Sailing Movies You Must Watch In 2024
- Search Search Hi! We’re Emily, Adam and Tiny Cat, liveaboard sailors travelling the world on our 38ft sailboat and writing about it as we go. We hope we can inspire you to live the life you’ve always dreamed, whether that’s exploring the world or living a more simple way of life in a tiny home. Find out more. Patreon
- Privacy Policy

Basic Sailing Terminology: Sailboat Parts Explained
Sailing is a timeless activity that has captivated the hearts of adventurous souls for centuries. But, let’s face it, for beginners, sailing can be as intimidating as trying to navigate through a dark, labyrinthine maze with a blindfold on. The vast array of sailing terminology, sailboat parts and jargon can seem like a foreign language that only the most experienced seafarers can comprehend.
Fear not, intrepid sailor, for this comprehensive guide on basic sailing terminology for beginners will help you navigate the choppy waters of sailing jargon with ease. From learning the difference between the bow and stern to mastering the intricacies of sail trim, this article will equip you with all the knowledge you need to confidently take to the seas. So hoist the mainsail, batten down the hatches, and let’s set sail on this exciting journey of discovery!
Parts of a Sailboat
Before you can begin your sailing adventure, it’s important to familiarize yourself with the different parts of a sailboat. From the sleek bow to the sturdy keel, each component plays a vital role in keeping your vessel afloat and propelling you forward through the waves.

- Hull The main body of the boat that sits in the water and provides buoyancy and stability.
- Bow The front of the boat that meets the water and helps to determine its direction.
- Stern The rear of the boat where the rudder and motor are located.
- Deck The flat surface of the boat that you stand on, which can include various features such as seating, storage compartments, and hatches.
- Cockpit The recessed area of the deck where the skipper and crew sit or stand while sailing, which allows for easy access to the sail controls and provides protection from the wind and waves.
- Keel The long, fin-shaped structure beneath the waterline that helps to keep the boat stable and upright.
- Rudder The flat, vertical surface located at the stern of the boat that is used to steer and control the direction of the boat.
- Tiller or wheel The mechanism used to steer the boat, either in the form of a tiller (a handle attached to the rudder) or a wheel (similar to the steering wheel of a car).
- Mast The tall, vertical pole that supports the sails and allows you to catch the wind and move through the water.
- Boom The horizontal pole extending off the bottom of the mast that holds the bottom edge of the mainsail.
- Mainsail The large, triangular-shaped sail attached to the mast and boom that captures the wind’s power to propel the boat forward.
- Jib The smaller, triangular-shaped sail attached to the bow that helps to steer the boat and balance the force of the mainsail.
- Rigging The network of ropes and cables that hold the mast and sails in place and help control their movement.
Sail Terminology
Understanding the terminology associated with sails is critical to becoming a successful sailor. Here are 12 of the most important sail terms you should know, along with brief explanations for each:

- Luff The forward edge of a sail that is attached to the mast, allowing you to adjust the sail’s shape and angle to catch more wind.
- Leech The aft edge of a sail that is attached to the boom, which helps to control the sail’s shape and release the wind as needed.
- Foot The lower edge of a sail that is attached to the boom, which helps to control the sail’s shape and power.
- Head The top of a sail that is attached to the mast and controls the sail’s overall shape and angle.
- Battens The long, thin strips inserted into the pockets of a sail to help maintain its shape and stiffness.
- Clew The bottom corner of a sail that is attached to the boom or sheet, which helps to control the sail’s shape and power.
- Tack The bottom forward corner of a sail that is attached to the boat or a line, which helps to control the sail’s shape and power.
- Sail Area The total area of a sail, which is measured in square feet or meters.
- Sail Draft The curve or depth of a sail, which affects its performance and power.
- Sail Shape The overall form and contour of a sail, which is critical for catching the wind effectively.
- Reefing The process of reducing the sail area by partially lowering or folding the sail, which can be necessary in strong winds or heavy seas.
- Furling The process of rolling or folding a sail to reduce its size or stow it away, which is often used when entering or leaving port or in rough conditions.
Wind Direction and Sail Positioning
Understanding wind direction and sail positioning is crucial for successful sailing. Here are the key terms you need to know:
Types of Wind

- Apparent Wind The wind that is felt on the boat, which is a combination of the true wind and the wind generated by the boat’s movement.
- True Wind The actual direction and strength of the wind.
Points of Sail
You can find a detailed explanation of the points of sail here

- Close-Hauled Sailing as close to the wind as possible, with the sail set at a sharp angle to the boat.
- Beam Reach Sailing perpendicular to the wind, with the sail set at a right angle to the boat.
- Broad Reach Sailing with the wind at a diagonal angle behind the boat, with the sail angled away from the boat.
- Running Sailing directly downwind, with the sail on one side of the boat.
Other Terms
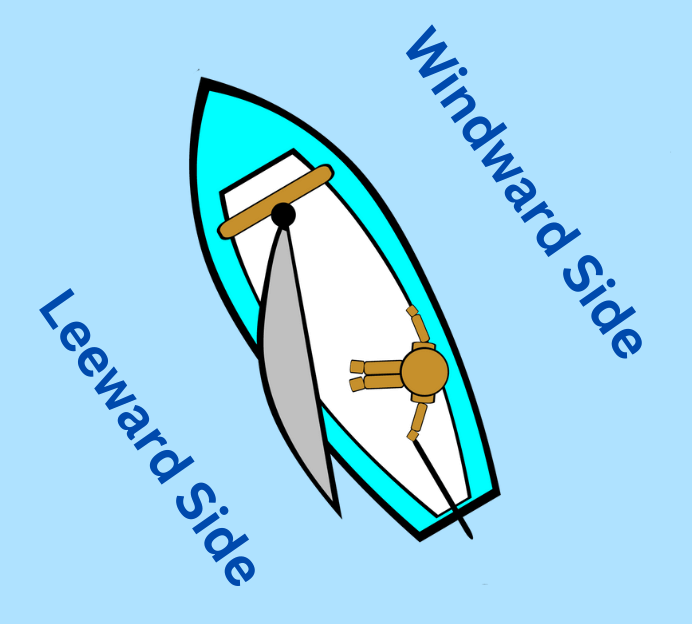
- Windward The side of the boat that is facing the wind.
- Leeward The side of the boat that is sheltered from the wind.
- Sail Trim Adjusting the sail and rigging to maximize the power and efficiency of the sailboat.
Navigation Terminology
Navigating a sailboat requires an understanding of a variety of nautical terms. Here are some of the most important terms you should know:
- Starboard Side The right side of a boat
- Port Side The left side of a boat
- Compass A device used for determining the boat’s heading or direction.
- Bearing The direction from the boat to a specific point on land or water.
- Chart A map or nautical publication that displays water depths, navigational aids, and other important information for safe navigation.
- Latitude The angular distance between the equator and a point on the earth’s surface, measured in degrees, minutes, and seconds.
- Longitude The angular distance between the prime meridian and a point on the earth’s surface, measured in degrees, minutes, and seconds.
- Course The direction in which the boat is traveling.
- Plotting The process of marking a course on a chart or map.
- Waypoint A specific point on a navigational chart or map that serves as a reference point for plotting a course.

- Tacking This maneuver involves turning the bow of the boat through the wind in order to change direction. To tack , the sailor will turn the helm towards the wind until the sails begin to luff, then quickly steer the boat in the opposite direction while adjusting the sails to catch the wind on the new tack.
- Jibing This maneuver is similar to tacking, but involves turning the stern of the boat through the wind. To jibe, the sailor will steer the boat downwind until the sails begin to luff, then quickly turn the stern of the boat in the opposite direction while adjusting the sails to catch the wind on the new tack.
- Heading up This maneuver involves turning the boat closer to the wind in order to sail upwind. To head up, the sailor will turn the helm towards the wind while simultaneously trimming the sails in to maintain speed and prevent the boat from stalling.
- Falling off This maneuver involves turning the boat away from the wind in order to sail downwind. To fall off, the sailor will steer the helm away from the wind while simultaneously easing the sails out to catch more wind and accelerate the boat.
- Docking This maneuver involves bringing the boat alongside a dock or other fixed object in order to moor or disembark. To dock, the sailor will typically approach the dock at a slow speed while using lines and fenders to control the boat’s position and prevent damage.
Knots and Lines
Learning the right knots and lines to use is essential for any sailor. Here are some of the most important knots and lines to know:
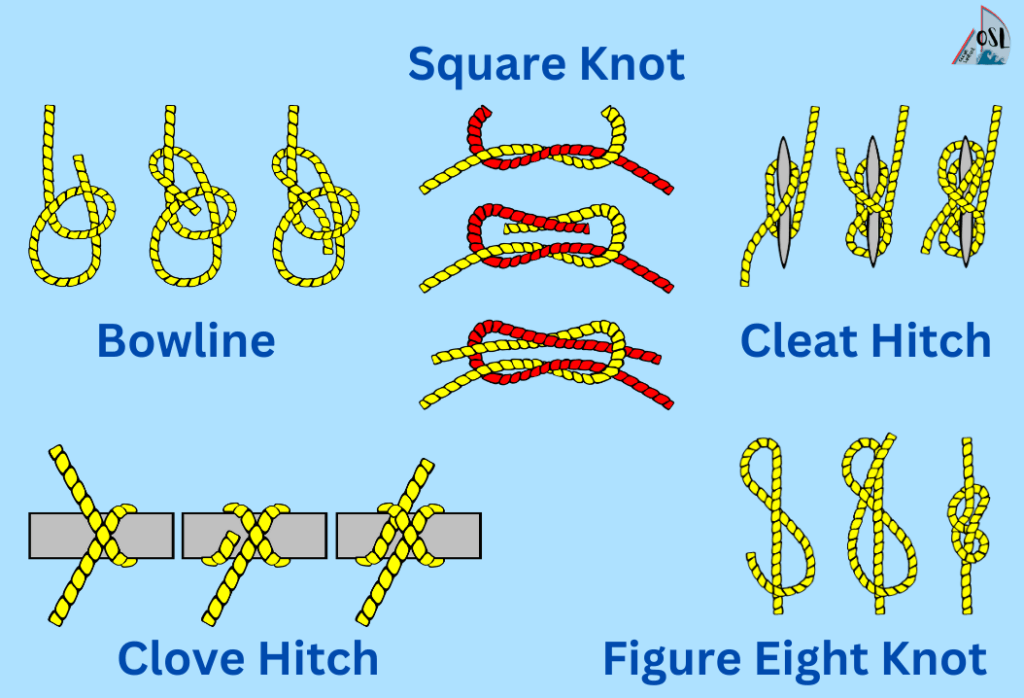
- Bowline This is a versatile knot used for many purposes, including attaching a line to a fixed object, such as a mooring or cleat.
- Square Knot A simple knot used to join two lines of the same diameter.
- Clove Hitch A quick and easy knot for attaching a line to a post or piling.
- Figure-Eight Knot A knot used to stop the end of a line from unraveling.
- Cleat Hitch A knot used to secure a line to a cleat.
- Sheet Bend A knot used to join two lines of different diameters.

- Main Halyard A line used to raise the mainsail.
- Jib Sheet A line used to control the angle of the jib.
- Mainsheet A line used to control the angle of the mainsail.
- Jib Furling Line A line used to furl the jib.
Sailing Safety
- Personal Flotation Devices (PFDs) These are the life jackets or vests that you must wear when on board to ensure your safety. Choose a PFD that fits you properly and is appropriate for your body weight.
- Tethers and Harnesses These are designed to keep you attached to the boat and prevent you from falling overboard. Make sure to clip yourself onto the boat when you’re on deck or going up to the mast.
- Man Overboard ( MOB ) Drill This is a critical safety procedure to practice with your crew. Learn how to quickly identify and recover someone who has fallen overboard.
- Emergency Position Indicating Radio Beacon (EPIRB) An EPIRB sends a distress signal and your location to rescue services in an emergency. Make sure it’s properly registered and in good working condition.
- Navigational Lights Ensure your boat has the required navigational lights and know how to use them properly. These lights help other boats see you in low-light conditions.
Remember that safety is always the top priority when sailing, and it’s essential to take it seriously.

Sailing Terminology Conclusion
As we come to the end of our sailing terminology crash course, it’s important to remember that the world of sailing is vast and varied. Learning even the basics can be a daunting task, but with practice and perseverance, you’ll be able to hoist your sails and set a course for adventure.
Whether you’re a seasoned sailor or just starting out, understanding the terminology is crucial to ensure a safe and enjoyable voyage. From the parts of the boat to the knots and lines, each aspect plays a significant role in the overall sailing experience.
So, as you prepare to embark on your next sailing adventure, keep in mind the importance of safety, navigation, and proper etiquette on the water. And remember, when all else fails, just hoist the Jolly Roger and hope for the best! (Just kidding, don’t actually do that.) Happy sailing!
What is the difference between apparent wind and true wind?
Apparent wind is the wind felt by the sailor on the boat, while true wind is the wind direction and speed relative to the ground.
What are the points of sail?
The points of sail are the directions that a sailboat can travel in relation to the wind. They include upwind, close-hauled, beam reach, broad reach, and downwind.
What does it mean to be “on a reach”?
Being “on a reach” means sailing with the wind coming from the side of the boat, at a perpendicular angle to the boat’s direction.
What is tacking?
Tacking is the maneuver used to turn the boat’s bow through the wind, allowing the boat to change direction while still sailing upwind.
What is jibing?
Jibing is the maneuver used to turn the boat’s stern through the wind, allowing the boat to change direction while sailing downwind.
What is the difference between windward and leeward?
Windward is the side of the boat that is facing into the wind, while leeward is the side of the boat that is sheltered from the wind.
What is a boom vang?
A boom vang is a line used to control the position of the boom, which helps control the shape and position of the sail.
What is a cleat?
A cleat is a device used to secure a line to the boat, allowing the sailor to adjust the tension of the line without having to hold onto it constantly.
What is a winch?
A winch is a mechanical device used to control lines and adjust sails. It typically consists of a drum and handle that can be turned to wind or unwind a line.
Similar Posts
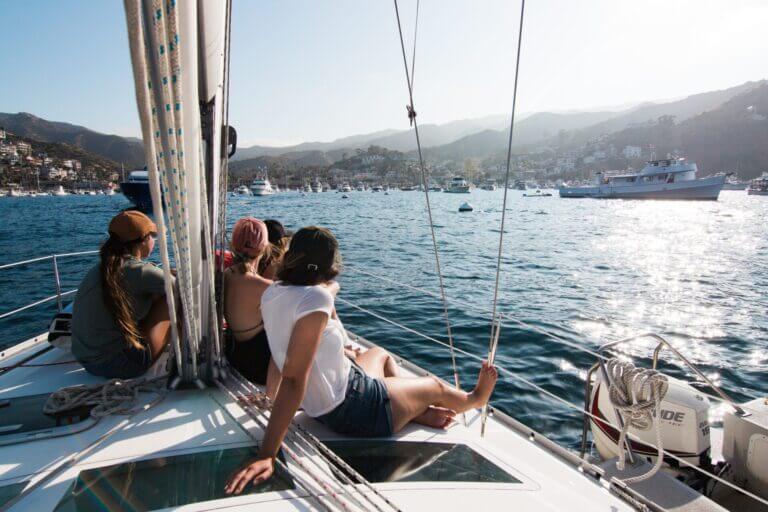

Sailing Etiquette: The Do’s and Don’ts
Sailing is a wonderful way to enjoy the beauty of nature and explore the open waters. However, it’s important to remember that sailing etiquette plays a crucial role in ensuring everyone’s safety and enjoyment on board. Whether you’re an experienced sailor or a beginner, understanding and following proper yachting etiquette is essential. Yacht clubs and…

What is a Ketch Sailboat?
Ketch boats are frequently seen in certain regions and offer various advantages in terms of handling. However, what is a ketch and how does it stand out? A ketch is a sailboat with two masts. The mainmast is shorter than the mast on a sloop, and the mizzenmast aft is shorter than the mainmast. Ketches…

10 reasons why sailing is the best way to travel
Are you feeling restless and looking for a new way to explore the world? Tired of being cooped up in airplanes, trains, or cars for hours on end? Well, why not try something different and embark on a sailing adventure? While I may not be a seasoned sailor myself, I can tell you that there’s…

What is a Sloop? Definition, Types and History
A sloop is a type of sailboat that has a single mast and a fore-and-aft rig. Sloops are a type of sailboat that has been around for centuries. They are known for their versatility and ease of handling, making them popular among sailors of all skill levels. Sloops have a single mast and a fore-and-aft…
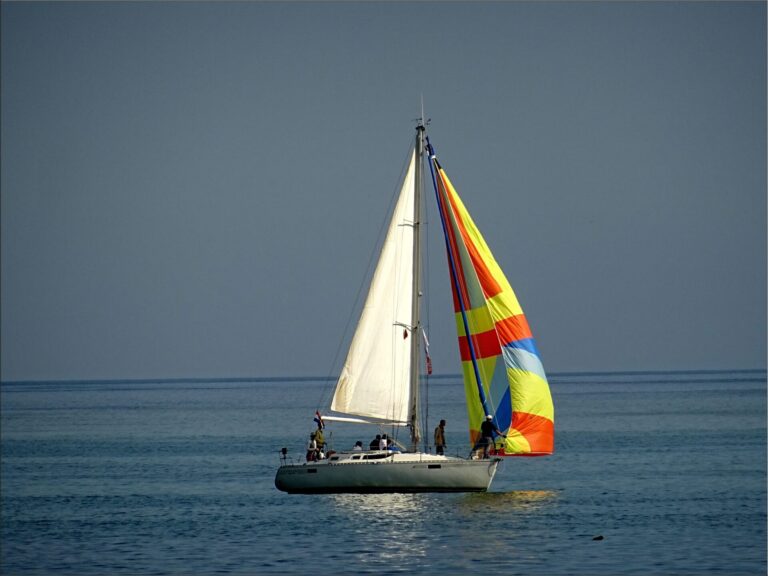

Types of Sails: A Comprehensive Guide
In the enchanting world of sailboat dynamics, where the dance between wind and water takes center stage, the significance of sails cannot be overstated. Like the wings of a bird, these meticulously crafted sails unfurl to catch the slightest whisper of breeze, converting it into a powerful forward thrust that carries us through the vast…
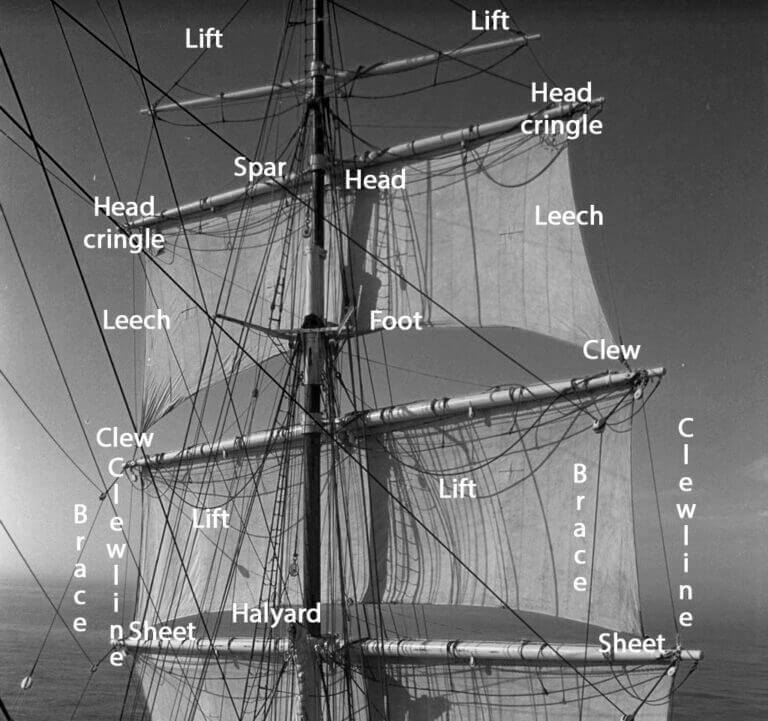

Whats the Difference between Standing Rigging and Running Rigging?
Running rigging refers to the movable lines and ropes used to control the position and shape of the sails on a sailboat. Standing rigging, on the other hand, refers to the fixed wires and cables that support the mast and keep it upright. As the sun rises on another day, we find ourselves immersed in…

Glossary of sailing and nautical terms

COVID 19: You can change your booking on most of our boats if your travel plans are affected by coronavirus. See here for more details
Let us help you plan the perfect sailing trip
Provide your travel details, receive free offer and enjoy your holiday!
In order to become a true sailor, you’ll first need to learn some essential sailing terms. Luckily, we’ve got you covered! In this A-Z of yachting terms, we’ll briefly explain yacht terms, parts, equipment, sailing commands, and even some pirate jargon.
For you to understand the ins and outs of a boat you should know where it starts and where it ends. The front of a boat is known as the bow while the back is called the stern. Also, while the left of the boat is called the port side, the right is called starboard. Now that you’re familiar with the different sides of a boat, let's get down to real sailing business.
- ABANDON SHIP! – You have probably heard this in movies and you know it doesn't bring any good. You should leave the vessel immediately as it looks like your ship is in some imminent danger.
- ABOARD – When you’re aboard, you are on a boat. The opposite of ashore.
- ABOVE DECK – Above deck means you are standing on the deck, not above it.
- ABREAST – We call vessels that are side to side - abreast.
- ADRIFT – Don't panic but if your vessel is adrift it means it has sailed off without you. Okay, you can panic a little.
- AGROUND – If the water is not deep enough, then you go aground and your vessel’s bottom touches the ground.
- AHEAD – This means something is in front of the boat, for example your destination is ahead.
- AHOY – Another way to say hello, with a little pirate tone.
- ALL HANDS HOAY – Everyone should get on the deck.
- AMIDSHIPS – The middle of a vessel, whether from her length or width.
- ANCHOR – A chain with a hook on the end that falls to the bottom of the sea and prevents your yacht from sailing off without you. Used for parking your yacht in a bay.
- ANCHORAGE – A great spot for holding, anchoring and sheltering your vessel.
- APPARENT WIND – A mixture of the true wind direction and the wind created by the sails.
- ASHORE – Being on the shore, and not on your vessel.
- ASTERN – Opposite of ahead is astern, in other words behind.
- AYE, AYE – A reply to a command to show that it will be carried out.
- BAGGYWRINKLE – A soft covering for cables that prevents friction between sails.
- BAREBOAT – Sailing a yacht on your own without a crew or skipper.
- BATTEN DOWN – If you hear “Batten down the hatches!” make sure you secure any hatchets and loose objects so you don’t lose anything important.
- BEAM – The width of your vessel.
- BEARING – Bearing is the direction in which we are headed. The reference point can be a compass or the heading direction.
- BELOW – Instead of being “above deck,” you can also be “below” it.
- BERTHS (Sleeping) – The number of people able to sleep on a specified vessel.
- BERTHS (Mooring) – The location in a harbour or port for mooring a vessel
- BEAM REACH – Is the position of a sail when the true wind hits it at a 90 degree angle.
- BILGE – The deepest part of the vessel’s hull, where water can enter.
- BOAT HOOK – A pole with a hook on the end. You can use it to grab and pick up a rope, collect something that has fallen overboard, or push the vessel off the port.
- BOOM – This is the horizontal pole that runs along the bottom of the sail. A part that often hits unsuspecting victims on the head in small vessels. Not a very pleasant experience.
- BOW –The front of the vessel also known as the ”pointy end” of the boat.
- BOW LINE – A rope that’s tied onto the front of the vessel that stops the vessel from moving sideways when moored.
- BOWLINE – To confuse you, this is a completely different from the bow line. It’s pronounced “boh-lin” and it’s a knot which creates a loop at the end of a rope.
- BRIDGE – The part of the vessel from where you steer and control the speed.
- BRIGHTWORK – Brightwork is the shining woodwork or polished metal that you can see on a vessel.
- BUOY – A buoy is a floating device that marks a position, a hazard, or shallow sea. Some are also used to moor vessels.
- BROAD REACH - Sailing downwind with the wind is hitting the sails at an angle between 91 and 170 degrees.
- CABIN – Separated living units, like a bedroom.
- CAPSIZE – When a vessel leans too far causing it to flip over. This can result in the sinking of the ship.
- CAST OFF – When you cast off you let go of a rope from where your vessel has been moored up.
- CHAFING GEAR – It sounds quite uncomfortable, but it's not for you. “Chafing gear” is a tube or some type of fabric that you wrap around a rope to stop it from rubbing on a rough surface.
- CHART – A nautical map that gets you from point A to point B.
- CLEAT – A fitting on vessels used to tie or secure ropes.
- COCKPIT – An opening from where you can control the vessel.
- COIL – When it’s time to put away ropes, you make a neat, circular coil with them.
- COMPASS – A navigational instrument that revolutionised travel.
- COURSE – The route you follow across the water.
- CURRENT – The current is actually the movement of water, usually caused by tides or wind.
- DEAD AHEAD – Dead ahead means straight ahead.
- DEAD ASTERN – Meaning behind you. The complete opposite of dead ahead.
- DECK – Not the deck of playing cards. This is a surface that covers any part of a vessel on which you can walk on.
- DINGHY – A small inflatable boat attached to the yacht. It is sometimes easier to go with the dinghy.
- DOCK – A pier, float or a wharf where you can moor your vessel.
- DRAFT/DRAUGHT – It can mean two things, the depth of a vessel underwater or the fullness of a sail.
- DUNSEL – This part has no use on a ship. Don't be a dunsel!
- EASE – To let the sails out.
- FATHOM – In sailing, a fathom is a nautical unit of length. It matches six feet or approximately two metres.
- FENDER – The colourful cushions that hang over the edge of a vessel to prevent damage to the boat or pontoon.
- FLOOD – This doesn't have to be super dramatic, it can simply be used to describe an incoming tide.
- FORE-AND-AFT – A centre-line of a vessel that runs lengthwise, parallel to the part of the hull that goes deeper into the water below it.
- FOREPEAK – An open area in the front front of the vessel.
- FOULED – A fouled piece of equipment is blocked, tangled, or tarnished.
- GALLEY – A vessel’s kitchen. Go on, we know you’re hungry.
- GANGWAY – The gangway is where you can get in and out of the vessel.
- GEAR – When you hear “Get your gear!” it means ropes, lines, blocks, and other equipment on board.
- GENOA/JENNY – Might be quite confusing if your name is Jenny. A Genoa or Jenny is a sail that overlaps the mainsail.
- GRAB RAILS – When in danger of falling off the boat, it’s a good idea to hold onto the grab rails to prevent that.
- GROUND TACKLE – The bits that touch the ground such as the anchor and its gear.
- GUNWALE – The rail that goes around the edge of the deck.
- HALYARD – All the ropes used to pull sails up.
- HATCH – An opening in the vessel’s deck that has a water-resistant cover.
- HEADING – The direction the vessel is going in.
- HEADWAY – A headway vessel is going forward, while the sternway is moving backward.
- HEADS – The heads are actually the toilets, the loo, dunny… It can also be the upper corner of a triangular sail.
- HELM – If somebody asks you to take the helm, drop everything you are doing and take the wheel. The helm is the wheel or tiller that controls the vessel.
- HELMSPERSON – The best and the worst job on board. The person steering the wheel.
- HOLD – The inside of the yacht’s hull.
- HULL – The main body of a vessel, the part that floats.
- INBOARD – Simply inside the vessel’s edges.
- IN IRONS – When the boat is difficult to manoeuvre under sail.
- IRON MIKE – A slang for auto-pilot. Not a famous boxer.
- ITINERARY – The route of travel on your holiday. Usually planned in advance but needs to remain flexible to respond to weather conditions and personal preference
- JACOB’S LADDER – The type of rope ladder that you’d use to climb up something. It can be lowered from the deck when passengers come on board.
- JETTY – A jetty is a structure made to create breakwater, shelter, erosion control, or a channel.
- JIBING/GYBING – On a vessel, jibing means turning away from the wind until the wind comes from the other side.
- KEEL – The central structural base of the hull, the “backbone” of a vessel.
- KNOT – Not just a loop you tie in a rope or string, but also a unit of speed (equals one nautical mile an hour)

- LATITUDE – Geography knowledge can be used here. The latitude is the distance north or south of the equator. It’s measured in degrees and up to 90˚ north and 90˚ south. Each degree of latitude accounts for 60 nautical miles.
- LAZARETTE – A storage space at the back of the vessel.
- LAZYJACK – Wires leading from the mast (the big central metal pole) to the boom (pole that runs along the bottom of the front partl) that helps lowering the sails.
- LEE – The down-wind side of a vessel or shore which is sheltered.
- LEE CLOTHS – To avoid falling out of bed in the middle of the night, you can use a lee-cloth to keep you safe.
- LEEWARD – This is the direction away from the wind, as opposed to windward, which means into the wind.
- LOA – The maximum length of a yacht including overhanging ends that extend beyond the main bow and main stern.
- LOG – The log measures speed and records the vessel’s course.
- LONGITUDE – This is the distance east or west of the meridian line at Greenwich, UK, which is measured in degrees. There are 180˚ west and 180˚ east of Greenwich.
- LINE – This is a general term for a rope or line on a vessel that has a control function.
- LWL – Load waterline length or the length of a yacht that is in contact with the water.
- MAINSAIL – The main sail that sits behind the main mast on a yacht.
- MAST –The big metal pole that reaches from the bottom of the yacht to the sky. The sails hang from the mast.
- MED MOORING – The art of reverse parking a yacht into a small gap, a typical mooring technique in most Mediterranean harbours.
- MIDSHIP – The middle of the vessel.
- MONOHULL – A boat with one hull. The classic sailor’s yacht
- MOORING – When you moor a vessel, you tie it to a buoy or a pier. And then hope it won’t go adrift.
- NAUTICAL MILE – A measure of distance when on water. It’s around 6,076 feet, 1,852 metres, 2,025 yards, or one minute of latitude.
- NAVIGATION – Keeping to the route of a vessel when on a voyage from point A to point B. Basically, figuring out where you are and where you are going.
- OCEAN – Don’t think this one needs explaining, but anyhow a huge blue surface, pretty wet too.
- OPERATIONAL LANGUAGE – The language that the crew use to give instructions.
- OUTBOARD – When something is outboard, it’s beyond the vessel’s sides.
- OVERBOARD – It’s probably best to avoid this one. When someone or something is overboard, it’s over the side of the boat.
- PIER – A pier is a loading platform held by posts that extends out from the shore.
- PILOTAGE – Piloting when you navigate using visible features on land or water.
- PORT – The left side of the vessel is called the port side. It is also another name for a harbour.
- PROW –A poetical alternative term for bow.
- QUAY – A stone or metal platform lying alongside or above the water. Usually used for parking, loading and unloading vessels.
- REACHING – For most sailboats, this is the fastest way to travel. A close reach is toward the wind, and a broad reach is slightly away from the wind.
- REEFING – The preferred method of reducing sail area so it is easier to control. Especially useful in higher winds and bad weather conditions.
- REGATTA – A series of boat races.
- RIGGING – The ropes and wires that control the sails and support the masts.
- RIP RAP – A pile of rocks and rubble made to form a breakwater, often surrounding an off-shore lighthouse or vulnerable harbour.
- RUDDER – When you change directions on the vessel, it moves the rudder which in turn steers the vessel. It’s usually a vertical plate or a board connected to the back.
- SAILS – The most important part for sailing. An eco-friendly engine that converts wind power into boat speed.
- SALOON – The living area, you go here to relax.
- SATELLITE NAVIGATION – You have probably used regular navigation that uses radio transmissions before. However, the equipment on a vessel is a bit more complex and sophisticated.
- SCUPPERS – Scuppers are the holes in the deck that let the water drain off.
- SEA COCK – A sea cock is a faucet in the hull that can be turned off when not in use.
- SEAMANSHIP – All the skills of boat handling can be called seamanship. It could be maintenance, repairs, piloting, sail handling, marlinespike work, and rigging.
- SEA ROOM – It’s actually used to describe a safe distance from the shore or other hazards.
- SEAWORTHY – If a vessel can safely sail in rough weather, we call it seaworthy.
- SECURE – When something is secure, it is tied safely.
- SET – When the current is flowing toward a particular direction, it is set!
- SKIPPER – The most important person on your yacht, the person in charge and responsible for the safety of all aboard
- SLACK – Something that is not fastened.
- STERN – The rear of the yacht. Also can be the skipper’s voice tone if your yacht floats away.
- SOUNDING – This has nothing to do with sounds, it is actually a measurement of water depth.
- SPRING LINE – This is a rope that stops a boat from moving forward or backward while being fastened to a dock. Also used during docking and undocking.
- SQUALL – A squall is a sudden, violent wind that often brings rain. Get your bad weather gear ready!
- STAND-ON VESSEL – A “stand-on vessel” is a vessel that has right of way and should maintain its speed and direction. A give-way vessel should take steps to avoid a stand-on vessel
- STARBOARD – Starboard is the right side of a vessel when looking towards the front/bow
- STEM – The front of the vessel.
- STERN – The back of the vessel.
- STERN LINE – This is a rope leading from the stern (back) of the vessel.
- TACKING – Zig-zagging into wind so the wind passes from one side to another.
- TILLER – A tiller is a bar or handle that you use to turn a vessel’s rudder to change directions.
- TOPSIDES – This is the bit of the vessel that’s between the waterline and the deck.
- TRIM – No, not a haircut trim. This trim means making adjustments to sails to maximise their efficiency.
- TRADE WINDS – These winds blow from the north east in the Northern Hemisphere and the south east in the Southern Hemisphere. Sailors use them because they push vessels toward the equator.
- TRANSOM – The transom is a wall at the back of a vessel.
- TRUE WIND DIRECTION – The direction from where the wind is actually coming from.
- UNDERWAY – When you are on the sea, your vessel is underway. In other words, it’s not moored, at anchor, or aground.
- VESSEL – A craft for traveling on water, usually a larger boat or a ship.
- WATER – The liquid you can drink and float on.
- WATERLINE – A painted line on the vessel that shows where the vessel ends and the sea starts.
- WAY – The path that a vessel leaves after itself when it moves across the sea.
- WATCH – When you are on a watch on board you have to work with your fellow watch members.
- WINCH – A rotating, horizontal drum, powered either by electric motor or human motion
- WINDWARD –This means to go into the wind, and it’s tough to sail windward.
- YACHT – All kinds of vessels that are either powered or have sails
Learn the Parts of a Sailboat and How to Communicate Them
Essential Words You Need to Know
Pierre-Yves Babelon/Getty Images
The following are terms related to sailboats and their equipment , including the parts of the boat and how to communicate on one. Enjoy our list of all things nautical.
- Auxiliary - A sailboat's engine, or a sailboat with an engine
- Backstay - The cable, usually made of wire, running from the stern to the masthead that helps support the mast
- Ballast - The weight in a sailboat's keel (sometimes in a centerboard) that helps keep the boat from leaning too much
- Batten - A slat, typically made of plastic, placed in a pocket in the mainsail to help it maintain good shape
- Beam - The width of the boat at its widest point
- Bitter end - The free end of a line
- Block - A pulley-like device used on a boat, with a sheave around which a line runs
- Boom - The spar, which is usually horizontal, back from the mast to which the foot of a sail is attached
- Boom vang - A device that prevents the boom from rising and, in some types, lowering
- Bow - The front section of the boat
- Cat rig - A sailboat designed for using a mainsail only, with the mast usually located more forward than in a sloop
- Centerboard - A thin, keel-like structure that can be raised (usually rotated on a hinge up into a centerboard trunk in the hull) that's present on many sailboats without a fixed keel to prevent the boat from being blown sideways
- Chock - A type of fairlead fitting through which an anchor rode or dock line passes to reduce chafing
- Cleat - A fitting around which a line is secured
- Companionway - The entrance area and steps from the cockpit into a sailboat's cabin
- Clew - The lower rear corner of a sail
- Daggerboard - Like a centerboard, but raised and lowered vertically instead of rotating on a hinge
- Daysailer - Generally a small sailboat without a cabin large enough for comfortable overnight cruising
- Dinghy - A type of small sailboat or a small row or powered craft typically taken along when cruising in a larger sailboat
- Displacement - The weight of a boat, equal to the weight of water the boat displaces
- Dodger - A spray shield often made of foldable or removable fabric at the front of the cockpit
- Draft - The distance from a boat's waterline to the lowest part of its keel
- Fender - A bumper generally made of rubber hung alongside the boat to prevent the hull from rubbing against a dock or other structure
- Foot - The bottom edge of a sail (compare to leach and luff, below)
- Forestay - A cable usually made of wire running from the bow to the masthead that helps support the mast
- Forward - Toward the bow
- Freeboard - The height of the deck above the water (the topsides section of the hull)
- Gate - An opening in the lifelines for boarding the boat, also called gangway
- Genoa - A large jib sail (the clew extends aft of the mast)
- Gooseneck - The fitting that attaches the boom to the mast
- Ground tackle - The collective term for a boat's anchor and anchor rode
- Gunwale (sometimes gunnel) - The outer edge of the boat's deck and cockpit, also called the rail
- Halyard - Line or wire used to hoist a sail
- Hank on - To attach a jib sail to the forestay with small snap hooks called hanks
- Head - The bathroom of a boat and also the top corner of a sail
- Helm - The means by which the sailboat is steered: the tiller or wheel
- Jackline - A line, strap, or wire secured over the deck as an attachment point for the tether of a safety harness
- Jib - The triangular sail attached to the forestay
- Keel - The lower section of a sailboat's hull that's usually permanent and counteracts sideways movement and typically contains ballast
- Ketch - A type of sailboat with two masts
- Lanyard - A short cord or line, often used to secure a piece of gear (knife, whistle, etc.) that might be dropped
- Leech - The back edge of a jib or mainsail (compare to foot and luff, above and below)
- Lifeline - A line or wire (often vinyl coated) all around the boat that's held up with stanchions to prevent falling overboard
- Line - Any piece of rope used on a boat
- Luff - The leading edge of a jib or mainsail (compare to foot and leech, above)
- Mainmast - The mast, or the tallest mast of a sailboat with multiple masts
- Mainsail - The sail affixed to and behind the mainmast
- Mast - A tall vertical pole on a sailboat to support sails and rigging
- Mast step - The support structure for the bottom of the mast
- Mizzen - The smaller aft mast on a ketch or yawl; the mizzensail is affixed to and behind the mizzenmast
- Multihull - A catamaran (two hulls) or trimaran (three hulls)
- Outhaul - A fitting to adjust the tension of the foot of the mainsail on the boom
- Padeye - A fitting usually made of metal with a loop or hoop to which other gear is attached
- Pendant (sometimes pennant) - A short line attaching the bow of a boat to a mooring, or a short wire attached to a sail or halyard as an extension
- PFD - A personal flotation device such as a lifejacket or an inflatable PFD
- Port - The left side of the boat when facing forward; the opposite of starboard
- Preventer - A-Line or other device used to prevent the boom from accidentally swinging from one side to the other
- Pulpit - A rail generally made of stainless steel around the bow or stern typically at the height of the lifelines
- Rail - the outer edge of the boat's deck and cockpit; also called the gunwale
- Rig (or rigging) - The mast, boom, and associated equipment including stays, shrouds, sheets, and halyards
- Rode - The line or chain between an anchor and the boat
- Roller furler - A device by which a sail is rolled up, such as the jib rolling around a rotating forestay fitting
- Rudder - An appendage below or on the boat's stern that is rotated by moving the tiller or wheel to steer the boat
- Safety harness - Personal gear, either a separate harness or one built into a PFD, that attaches to a tether to keep the person on board
- Sail ties - Short straps or pieces of line used to tie a lowered mainsail to the boom or secure a sail on deck
- Schooner - A type of sailboat with two or more masts, the forward one being shorter than the main mast
- Seacock - A valve fitting for closing an opening through the boat's hull (drains, water pipes, etc.)
- Shackle - A fitting typically made of metal that secures two things together, such as a halyard shackle connecting to a sail
- Sheet - The line used to let out or trim in a sail; on a sloop, a mainsheet and two jib sheets
- Shroud - Wire or line stay from the deck or hull supporting the mast on each side
- Sloop - A type of sailboat with one mast and two triangular sails (main and jib)
- Sole - The floor of the cockpit or cabin
- Spinnaker - A lightweight sail used downwind, often ballooning in front of the boat
- Spreaders - Metal struts on the mast that hold the shrouds out from the mast for a better support angle
- Stanchions - Short metal poles around the boat's perimeter that support the lifelines
- Starboard - The right side of the boat (when facing forward); opposite of port
- Stay - Wire or line from the deck or hull to support the mast; stays include the forestay, backstay, and shrouds (on the sides)
- Tack - The bottom front corner of a sail
- Telltales - Pieces of yarn or ribbons on the luff of a sail to help with trimming, or fastened to shrouds to show the wind direction
- Tether - A short line or strap that runs between a safety harness and a point of attachment on the boat to prevent going overboard
- Tiller - A long handle connected to the rudder or rudder post on many sailboats for steering
- Topping lift - A wire or line from the masthead that holds up the boom when the sail is lowered
- Topsides - The area of outer hull above the waterline
- Traveler - A fitting allowing the mainsheet attachment to the boat to be adjusted side to side
- Vang - See Boom vang
- Whisker pole - A pole used to hold out the jib when sailing off the wind
- Winch - A drum-like device used to pull in lines under strain (halyards, sheets)
- Windless - A heavy winch used with the anchor rode
- Yawl - A type of sailboat with two masts, the aft one (mizzen) being behind the rudder post
How to Rig Your Small Sailboat and Prepare to Sail
West Wight Potter 19 Sailboat Review
The Various Types of Sailboats and Rigs
Heavy Weather Sailing
Learn How to Sail a Small Sailboat
Owner's Review of the MacGregor 26 Sailboat Models
Buying a Sailboat: Sloop vs. Ketch
The 9 Best Kayak Roof Racks of 2024
The 7 Best Travel Car Seats of 2024
The 10 Best Beach Canopies of 2024, Tested and Reviewed
The 8 Best Camping Tarps of 2024
The 11 Best Two-Person Tents of 2024, Tested and Reviewed
Review of the O'Day Mariner 19 Sailboat
The 12 Best Inflatable Stand-Up Paddleboards of 2024, Tested and Reviewed
The 10 Best Towable Tubes of 2024
The Otentik Original Beach Sunshade is Highly Portable
- Meet Our Sailing Instructors
- Sailing Captains
- Testimonials
- Become an ASA Instructor
- Earn Your Captain’s License

Email (required) *
- International edition
- Australia edition
- Europe edition

Yacht sinks after latest incident involving orcas in strait of Gibraltar
Vessel measuring 15 metres in length sank after encounter with the animals, Spain’s maritime rescue service reports
An unknown number of orcas have sunk a yacht after ramming it in Moroccan waters in the strait of Gibraltar, Spain’s maritime rescue service has said, in the latest in a series of similar incidents involving the animals.
The vessel, Alboran Cognac, which measured 15 metres (49ft) in length and carried two people, encountered the highly social apex predators, also known as killer whales, at 9am local time on Sunday.
The passengers reported feeling sudden blows to the hull and rudder before the boat started taking on water. After alerting the rescue services, a nearby oil tanker took them onboard and transported them to Gibraltar. The yacht was left adrift and eventually sank.
The incident is the latest example of recurring orca rammings around the Gibraltar strait that separates Europe from Africa and off the Atlantic coast of Portugal and north-western Spain. Experts believe them to involve a subpopulation of about 15 individuals given the designation “Gladis”.
According to the research group GT Atlantic Orca, which tracks populations of the Iberian orca sub-species, there have been nearly 700 interactions since orca attacks on ships in the region were first reported in May 2020.
Researchers are unsure about the causes for the behaviour, but theories include that it is a playful manifestation of the mammals’ curiosity, a social fad or the intentional targeting of what they perceive as competitors for their favourite prey, the local bluefin tuna.
Although known as killer whales, endangered orcas are part of the dolphin family. They can measure up to 8 metres in length and weigh up to 6 tonnes as adults.
- Marine life
- Water transport
Most viewed

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Starboard, tack, jib…. Well, no worries. In this article, I'll go over the most important sailing terms for beginners. This is a great resource for beginning sailors that need an overview of the most important sailing terms without drowning in it. For a comprehensive list, check out this Wikipedia glossary of nautical terms.
Dead downwind - Sailing in a direction straight downwind. Deck - The mostly flat area on top of the boat. De-power - Reducing the power in the sails by luffing, easing the sheets, or stalling. Dinghy - A small sailboat or rowboat. Displacement - The weight of the boat; therefore the amount of water that it displaces.
Learn common sailing terms for boaters, such as aft, bow, leeward, and jibing, as well as some funny terms, such as brass monkey, cat head, and monkey fist. Find out the meanings and usage of these terms in nautical language and how to become a better sailor.
Learn the correct names of all parts of your sailboat, rigging, and sails with this comprehensive list of sailing terms. From abeam to zephyr, from apparent wind to zigzag, find out the meanings and usage of hundreds of nautical terms with pictures and examples.
Winch. A mechanical device featuring a cable or line attached to a motor. The winch pulls the boat aboard the trailer and helps with the vessel's launch from the trailer. The winch also gives more pulling power to withdrawing nets or other apparatus from the water.
The sailing terms beginning with the letter W are: Wake: The trail of water left behind a sailboat as it moves. Waterline: The line where the water meets the side of a boat or ship. Windward: The direction from which the wind is blowing. Watertight: Describes a boat that is designed to prevent water from entering.
Learn the key sailing terms to use on board a boat, from port and starboard to tack and jibe, and how they relate to the wind, the direction, and the stability of the boat. This article explains the meaning and usage of these terms with examples and quizzes for you to test your knowledge.
The term "sailboat" includes many different sizes, shapes, and hull types. Here's how to identify most of the common ones. By Carol Cronin. May 10, 2021. Sailboats are powered by sails using the force of the wind. They are also referred to as sailing dinghies, boats, and yachts, depending on their size. Sailboats range in size, from lightweight ...
Adrift - a boat that is floating without any propulsion or anchor holding it in place. Aft - toward the back of the ship (stern). Aground - a boat that has run aground or is stuck on a reef or sandbar. Ahead - forward of the ship, in forward direction. Ahoy - a nautical greeting used to call or draw attention.
One reason why sailing terms are so different is that sailing has a long history dating back thousands of years, and the terminology that is used has developed over time to reflect the unique aspects of this activity. Another reason is that sailing involves a variety of different types of boats, each with its own set of equipment and terminology.
Terms for the boats heading in relation to the wind. These sailing terms are best known as our points of sail and describe the vessel's heading in relation to the wind: Close Hauled: When sailing close-hauled, the vessel's heading is as close to the wind as possible, typically between 35-50 degrees.
Short answer sailing terms and phrases: Sailing terms and phrases refer to language specific to the sport of sailing. They include terms related to boat parts, sailing maneuvers, wind direction, and navigation. Understanding these terms is crucial for effective communication and safe sailing practices. Understanding the Basics: A Guide to Sailing Terms and Phrases Welcome
40 terms to help you start talking like a sailor. Aft - The rear section of the boat. Bow - The front section of the boat. Mast - The vertical pole that supports the sails. Boom - The horizontal pole that extends from the mast and supports the foot of the mainsail. Winch - A device used to adjust the tension on a rope or wire, usually ...
Heeling. "Heeling" describes the leaning or tilting of a sailboat due to the force of the wind on the sails. The boat can lean to one side, causing it to tilt and creating a thrilling sensation. Sailors adjust the sails and shift their weight to maintain balance and control.
A boat's displacement is equal to its weight at any given time, with any given load. Draft: The total distance a boat penetrates the water, from waterline to keel or appendage bottom. "The Schenectady 54 has a draft of four feet, six inches.". Dry Weight: The weight of a boat without fuel or water onboard.
20 Sailing & Sailboat Terms. Within boating, sailing has its own specific vernacular. You'll want to understand it before you step aboard a sailboat to help crew or when taking a lesson. Apparent wind - the combination of true wind and the motion of the boat at the time. It's the wind you feel onboard.
Aft: The back of the boat, or near the back of the boat.Aft basically means back! Alongside: When the boat is next to a pier or another vessel. Apparent wind: This is the wind that can be felt.It could refer to speed or direction, and is often different to the true wind. For example, if you are sailing forwards at 5 knts, the wind speed will feel stronger than if you are sitting still.
Close-Hauled. Sailing as close to the wind as possible, with the sail set at a sharp angle to the boat. Beam Reach. Sailing perpendicular to the wind, with the sail set at a right angle to the boat. Broad Reach. Sailing with the wind at a diagonal angle behind the boat, with the sail angled away from the boat. Running.
AHOY - Another way to say hello, with a little pirate tone. ALL HANDS HOAY - Everyone should get on the deck. AMIDSHIPS - The middle of a vessel, whether from her length or width. ANCHOR - A chain with a hook on the end that falls to the bottom of the sea and prevents your yacht from sailing off without you.
Genoa - A large jib sail (the clew extends aft of the mast) Gooseneck - The fitting that attaches the boom to the mast. Ground tackle - The collective term for a boat's anchor and anchor rode. Gunwale (sometimes gunnel) - The outer edge of the boat's deck and cockpit, also called the rail.
11. Three Sheets to the Wind. Meaning: Very, very drunk. 12. Left High and Dry. Meaning: Abandoned (by an individual or group) in a difficult situation. 13. Sailing Close to the Wind. Meaning: Taking risks that may be unreasonable, being close to breaking the law.
The side of the boat aft of the beam. There are 2 quarters in a boat - port quarter and starboard quarter. Mast. The highest spar (Vertical pole) in the center of the boat. Boom. The horizontal spar that is attached to the mast to support the bottom part of the main sail. 4 parts of the hull. 1. Deck 2.
Both terms mean the largest enclosed, common area of a yacht (essentially the "living room" in the terms of a land-based home). Most modern boaters use the term salon to avoid confusing it with a bar found in the old west. Old salts and those who sail with the wind prefer the old-school term, saloon. Common Boat Hardware
Last modified on Mon 13 May 2024 14.33 EDT. An unknown number of orcas have sunk a yacht after ramming it in Moroccan waters in the Strait of Gibraltar, Spain's maritime rescue service has said ...
Someone found a 16-foot boat that had run into the bank of Colyell Bay in Livingston Parish, its engine running and the throttle forward — and nobody inside. Then, about 15 minutes later, they ...