

Search form
- As Is Specials
Buying a Boat
LEOPARD 43 POWERCAT
Rodney bay, saint lucia.

Road Town, Virgin Islands (British)

Tortola, Virgin Islands (British)

POPULAR SEARCHES

New pre-owned boats added daily. Over 100 used boats in stock.
Welcome to the Moorings Yacht Brokerage
Our brokerage offices specialize in pre-owned cruising boats, including sailing catamarans and monohulls as well as power yachts. These used yachts come not only from our worldwide Moorings sailboat charter fleet, but also the worldwide fleets of Moorings Power, Sunsail and Footloose. We also offer a select few used boats maintained by meticulous private owners.

Featured Boats

Jeanneau Sun Odyssey 419

Leopard 53 Powercat

Leopard 43 Powercat

View more boats
Looking for a new boat or a private, never-chartered boat? View charter yachts and private yachts available for purchase through our sister companies: The Moorings Yacht Ownership, Leopard Catamarans, and Leopard Brokerage.
Sign up for our newsletter
Our monthly e-List advertises the best deals on the brokerage market each month. Sign up for our eList so you never miss an opportunity for a deal!
Used Boat Buying Guide
Read our expert tips for the entire process of finding a boat, drawing up a contract, making a deposit, undertaking a marine survey and sea trial, documenting the boat and closing the transaction.
The Moorings Yacht Brokerage
850 NE 3rd St #201, Dania Beach, FL 33004
800-850-4081 / 954-925-4150
[email protected]
Cookie Policy
Privacy Policy
eList Newsletter Signup
Current Inventory
Selling Your Boat
Jeanneau Yachts for Sale
Beneteau Yachts for Sale
Leopard Catamarans for Sale
Sailing Monohulls for Sale
Sailing Catamarans for Sale
Yachts for Sale in Tortola
LIKE / FOLLOW

- Search Used Yachts For Sale
- Search Boats By Brand
- Search Boats By Type
- Search By Location
- Search By Price
- What's My Boat Worth?
- Search Boats Just Listed
- Small Yachts
- Custom Sport Fishing Boats
- Finance A Boat
- Amer Yachts
- Aquitalia Yachts
- Cabo Yachts
- French Yachts
- Gulfstream Yachts
- Hatteras Yachts
- Shelter Island Yachts
- Solaris Yachts
- Sunpower Yachts
- Sunreef Yachts
- Vela Boatworks
- Virtus Yachts
- Why List With United?
- Why Own A Boat Or Yacht?
- Custom Website For Your Yacht
- United Sold Boats
- Buy A Yacht With Crypto
- Find a Yacht Broker Near Me
- Search For Broker By Name
- Meet The United Support Team
- Our History
- Fort Lauderdale Boat Show
- Stuart Boat Show
- Miami Boat Show
- Palm Beach Boat Show
- Other Boat Shows
- Yachting News
- Yacht Closing Services
- River Forest Yachting Centers

Search All Yachts
Used Sailing Catamaran Boats For Sale
Narrow your search.
Manufacturer
Catamarans have seen a steady increase in popularity over the last several years as more people charter them in exotic destinations and realize the value of having that much extra space on board. Sailing catamarans have exceptionally wide beams which make for a sturdy platform while enjoying the boat, but this design feature also gives owners a lot of livable space. The salon, galley, and entertainment spaces on a catamaran can be exceptional thanks to the additional volume.
The stability of catamarans are one of the main selling points and why so many more are selling in recent years. It is a much different experience being anchored at night in a catamaran than in your more traditional monohull boats. Sailing cats also don't need much water to run so your draft is generally a lot lower than monohulls. This makes owning a catamaran ideal for Florida, Bahamas, and the Caribbean. Power catamarans have also become increasingly popular for boaters that desire the benefits of a cat hull, but don't want to worry about a sail.
PRE-OWNED Sailing Catamaran Boats

BBC130 PROJECT GARFIELD
124' Dynamic Custom 38M 2025
Ft. Lauderdale, Florida, United States

115' New Zealand Yachts Wave Piercer 2005
Dania Beach, Florida, United States

110' JFA 2012
West Palm Beach, Florida, United States

CUSTOM 107 CATAMARAN
107' Custom Cruiser Catamaran 2023
Mannheim, Germany

100' Extra Yachts X30 VILLA 2025
Ancona, Italy

LITTLE GIANT
88' Sunreef Sunreef 88 DD 2017

WHITE LIGHTNING
85' Mares Power Cat 85 1997
Seattle, Washington, United States

85' JFA World Cruiser Catamaran 2018
Genoa, Italy

PERFORMANCE CATAMARAN
82' McConaghy Boats 82P 2024
Fort Lauderdale, Florida, United States

80' Mystique Yachts Silhouette 800 2023

80' CUSTOM US BUILT Morelli/Miller 1991
Phillipsburg,

78' Naval Yachts 2024

78' Lagoon Lagoon Seventy-8MY 2019
Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam

HELICAT RED
77' Fountaine Pajot Catamaran 2010
Saint George's, Grenada

78' Custom 78 TransOcean Powercat 2012
- Page 1 of 19
SEARCH ALL YACHTS
There are many sailing cat manufacturers today whose boats are used in both charter and private ownership. Sometimes the charter companies even put their charter boats on the market at a reduced price when they sell them. Sailing Catamaran manufacturers like Lagoon, Leopard , Privilege, and Gunboat, among others, have continued to advance their products by using new construction methods, higher quality, materials, and design layouts that promote private ownership and not just charter. Let the team at United Yacht Sales help you find the right used sailing catamaran for sale that fits your budget and needs.

Here Are Some Commonly Asked Questions About Sailing Catamarans
What is the difference between a catamaran and monohull sailboat?
A catamaran sailboat is basically two parallel set wide apart hulls with mast and sails in between, while a monohull sailboat is a single hull centered around a heavy ballasted keel to counterbalance the mast and sails. The catamaran footprint tends to be square or rectangular instead of a long and narrow single hull. These basic differences impact the entire sailing experience. Because catamarans’ stability is based on its beam and multihull configuration (called form stability), they do not heel (tilt) like a monohull, nor do they require a ballast and large keel. Traditional sailors tend to prefer the exhilaration of heeling under sail, but it does require physical strength and skill. Since catamarans don’t heel, the boat’s motion is different, and sails need to be trimmed differently. Catamarans don’t really tack or handle that well in increased winds; they don’t “feel” the wind immediately as a traditional sailboat. But the advantages of a catamaran far outweigh the detractions and include stability, safety, speed, spaciousness, efficiency, comfort, and greater privacy in the accommodations.
The two hulls offer inherent stability and a deck platform that tends to stay level—no rolling or heelingwhich greatly helps with seasickness! The large open and enclosed main deck areas, along with accommodations in separate hulls, are great for entertaining, families, and charter groups. With less drag (less wetted hull surface and weight), the speedy catamarans can outrun weather and travel farther. They are less likely to capsize, since they don’t heel or rock and are less dependent on weight distribution; but if they do, catamarans do not right themselves like a monohull is designed to do…but neither will a catamaran sink, there is enough buoyancy in the hulls to keep them afloat.
Catamarans can have a flybridge or raised bridge decks with 360-degree visibility, a distinct advantage over traditional sailboats that cannot have a flybridge. Being lighter weight and without a keel, catamarans can sail in shallower waters making them ideal for cruising around islands, anchoring closer to shore, and a great platform for diving. Some catamarans can be beached, resting on their hulls, allowing quick repairs or a shore picnic!

Lighter weight also translates into fuel efficiencies and having two engines set wide apart allows a catamaran to track very straight or rotate in place, and even ‘crab’ sideways making bow thrusters unnecessary. With so many benefits, it’s no wonder sailing (and power) catamarans are one of the fastest growing recreational boat categories.
Is a monohull or catamaran sailing yacht better for long range cruising?
While much of the choice is based on personal preference, some sailors who have experienced worldwide cruising in both types of sailing yachts, prefer the modern catamaran for undeniable advantages in safety. This includes no heeling, level sailing for less crew fatigue and seasickness, speed to outrun weather, hard to capsize, will float if they do capsize, and have redundancy of engines, props, charging and other systems.
Monohull sailboats are designed to work with the elements and have a sailing advantage—tacking and quicker maneuvering under sail especially upwind, better performing in heavy weather, and the keel/ballast enables monohulls to right themselves from a capsize but will not float if holed. Monohull sailboats are less costly to purchase and maintain.
Are there any superyacht sailing catamarans?
Currently the largest sailing catamaran is “Hemisphere”, built in 2011 by Pendennis Shipyard, UK and designed by renowned naval architect VPLP Design (Van Peteghem Lauriot Prévost). The 145ft sloop-rigged yacht sails at 13 knots and was designed for the luxury charter market. It can accommodate 12 guests and 8 crew for world-class cruises in sumptuous comfort. Enjoy dive trips all around French Polynesia. Also designed by VPLP, the all-aluminum schooner catamaran built in 1998 by French builder, Alu-Marine, and is capable of sailing at up to 15 knots and cruising at 12 knots. “Douce France” is 126.6 ft in length and can accommodate 12 guests plus 7 crew. Though catamarans make up less than 10% of the global superyacht fleet, more superyacht concept catamaran sailing yachts are on the drawing boards of top design firms for the many advantages catamarans offer.
Seen below: An image of HEMISPHERE, the largest catamaran built to date.

When were the first sailing catamarans built?
The first Western example of a double-hulled sailing vessel was designed in Europe by William Petty in 1662 for the same advantages catamarans offer today—to sail faster, in shallower waters, in lighter wind, and with fewer crew than other vessels of that era. It was not accepted commercially, due to people’s skepticism of the unfamiliar and the design was generally unused until 160 years later when an Englishman built a double-hulled merchant ship described as “a fast-sailing fine sea boat” for trading during the monsoon season in Burma (Myanmar). Later in the 19th century, American Nathanael Herreshoff designed and patented his double hulled sailing boat named Amaryllis, and raced her in a June 1876 regatta, in which she performed extremely well, demonstrating the catamaran’s distinct performance advantages over standard monohulls.
Then in 1936, Eric de Bisschop built a Polynesian style “double canoe” that he sailed from Hawaii to France and was given a hero’s welcome, like Lindberg’s transatlantic flight! Considered the “grandfathers of the cruising catamaran industry,” brothers Roland and Francis Prout worked on their own catamaran design in 1949 and then converted their boat factory in England to catamaran production in 1954. Their Shearwater catamarans handily beat monohulls in races. Their sail plan of enlarged jib (over 2x area of mainsail) set aft of midships, and reduced size of mainsail kept the bows from digging in! A winning model sailed by Francis Prout is in the collection of the National Maritime Museum Cornwall. The speed and seaworthiness of the Prout catamarans attracted attention and orders; the 1970s were the most productive. Though production ended in 2002, Prout catamaran sailboats are still in the boat brokerage market today.
When were the first catamaran sailboats raced?
American Nathanael Herreshoff designed and patented his double hulled sailing boat named Amaryllis in 1876, and raced her in a June 1876 regatta, in which she performed amazingly well, proving the catamaran’s performance advantages over traditional monohulls. As a result of Amaryllis’ easy win at the Centennial Regatta of the New York Yacht Club, catamarans were barred from the regular sailing classes for nearly 100 years, until the 1970s. In Europe, the Prout brothers sailing catamarans went into production in 1954, after they easily won races against monohulls, creating demand for the Prout brothers’ Shearwater catamaran and subsequent models that became very popular during the 1970s.
The “America’s Cup” is the oldest and longest running yachting race in the world and has been dubbed “The Formula One” of yacht racing. Begun in 1851 with a race around the Isle of Wight in England that was won by the yacht, “America” of The New York Yacht Club (NYYC) which was awarded custody of the trophy cup, renamed “America’s Cup” in honor of the winning team. The rules were changed in 2010 to include 90ft multihull racing yachts and that led to the 2013 Americas Cup Race between Oracle USA Team’s AC72 with its towering wingsail and Emirates New Zealand’s AC72 introduction of foiling. Modern racing catamarans have come a long way, utilizing hydrofoils and rigid sails to achieve speeds of 50+ knots, faster than the winds propelling them by combining the laws of hydrodynamics with aerodynamics to achieve these astonishing speeds.

Hydrofoils reduce wetted surface to a minimum, effectively reducing friction and wave drag to lift the hulls above the surface; rigid sails are shaped like aircraft wings, effectively producing a greater apparent wind when combined with true wind to power the craft beyond true wind speed. The racing catamarans literally fly out of the water like flying fish! Today racing yacht design is moving away from catamarans to monohulls with huge hydrofoils and soft wing mainsail, as new design rules are set. The America’s Cup has challenged competing teams to push the limits of sailing skill and boat/sail design producing the innovations seen over the years of this most prestigious race.
What are beachable sailing catamarans?
Simply put, shallow draft catamaran sailboats that can be pulled up on a beach to sit on its keels. Most 40-50 foot catamarans only draw between 3' - 4.5' of draft. Some hulls are reinforced with Kevlar for extra protection and strength. Most catamarans are lighter and those with daggerboards and/or rudders can lift to allow beaching. Monohull sailboats cannot be beached because of the large keel and ballast. Iconic California surfboard manufacturer Hobie built the first beach launchable, daysailing 14ft HobieCat in 1967 based on the Polynesian catamaran. They are ideal for youth sailing schools. HobieCats in a range of models are still being manufactured today and marketed around the world!
What are some of the current popular brands of catamaran sailboats?
- Lagoon – customer centric brand by French boatbuilder since 1984. Fountaine Pajot – founded by French maritime catamaran builder in 1976.
- Leopard Catamarans established partnership with South African builder, Robertson & Caine in 2000. Catana Catamarans built by Catana Group/France, formerly Poncin Yachts, building catamarans since 2001.
- Nautitech – French catamaran brand founded in 1990 in Rochefort Sur Mer shipbuilding center. Privilège Catamarans – founded in 1985 in France.
- Gemini –subsidiary of Performance Cruising Inc. in USA has been building catamarans since 1981.
- Seawind – catamaran designer/builder in Australia (now built in Vietnam) founded by Aussie surfer/sailor Richard Ward.
- Sunreef Yachts – world’s leading manufacturer of luxury sailing and power multihulls—all custom; established in 2002 in Gdansk, Poland. Bali Catamarans – brand established in 2014 also produced by renowned Catana shipyard.
- Manta Sailing Catamarans are a USA built classic originally designed by noted multihull French naval architect Erik Lerouge and are still prized by catamaran sailors who have established a Manta owners group. Gemini and MaineCat are the only sailing catamarans produced in the USA today.
What is the cost of a 40-to-42 foot sailing catamaran?
The median cost of preowned cruising catamaran sailboats model year range 2000 to 2009 and 40-42ft length, currently available in the USA, is $219,900. Worldwide median cost is about $35K higher. For preowned model year range 2010 to 2019, 40-42ft length currently available in USA, median cost is $487,500. Worldwide median is about $10K lower, as there are more available abroad.
Worldwide Yacht Sales
- Virginia Yacht Brokers
- Boats For Sale Canada
- 20 Million Dollar Yacht
- Sailboats For Sale NC
- Yachts For Sale California
- 5 Million Dollar Yacht
- Boats For Sale Kemah TX
- Oregon Yacht Sales
- Yacht For Sale NY
- 10 Million Dollar Yacht
- 100 Foot Yacht
- Yachts For Sale Seattle
Luxury Boats & Yachts
- $200000 Yacht
- 30 To 40 Foot Boats For Sale
- Used Center Console
- Fishing Boats For Sale in Texas
- Yacht Dealer
- Yachts For Sale by Price
- What Is The Cost To Buy A Yacht?
- 48 Ocean Super Sport For Sale
- Sabre Yachts For Sale in Maine
- Cabo Yachts For Sale
Popular Builders & Models
- Hatteras 54 For Sale
- Edgewater Boats
- Albemarle Boats
- 40 Foot Sea Ray
- Back Cove Yachts
- Tug Boats For Sale
- Sea Ray Sedan Bridge
Trending Brands & Types
- Yellowfin Bay Boat
- Riviera Yachts For Sale
- Marquis Yachts For Sale
- Liveaboard Boats
- Ocean Alexander Yachts For Sale
- Ranger Tug Boats
- Used Intrepid Boats For Sale
- Carver Yachts For Sale
SPEAK TO AN SPECIALIST
Speak to a sales professional.
Did You Know That We Offer Contract to Closing Services? Click Here to Find Out More.
Need Marine Financing? Apply Here With Our Partner, First Approval Source
- Bahamas (3)
- Chesapeake Bay (0)
- Florida (27)
- New England (0)
- North Carolina (0)
- South Carolina (2)
- Atlantic South (0)
- Caribbean (28)
- Indian Ocean (1)
- Pacific (9)
- Mexico Pacific (4)
- South Pacific (2)

Large Multihulls
Lagoon 410 s2 (caribbean), custom roake 50 (guatemala), stealth 11.8 (california), leopard 44 (atlantic), leopard 40 (puerto rico), lagoon 440 (puerto rico), dean 440 (georgia), lagoon 42 (florida), bali 4.0 open space (caribbean), fountaine pajot 48 custom (florida), leopard 45/47 (caribbean), lagoon 450 f (florida), lagoon 42 (mexico pacific), lagoon 40 (caribbean), aquila 44 (caribbean), catana bali 4.3 (guatemala), dean 440 espace (caribbean), looping 50 (caribbean), fountaine pajot lucia 40 (south carolina), fountaine pajot belize 43 (caribbean), lagoon 410 (atlantic), voyage 380 maxim (indian ocean), outremer 50 standard (florida), knysna 440 (caribbean), fountaine pajot lucia 40 (caribbean).
- Endeavour 44 TrawlerCat (Florida)
- Fountaine Pajot Helia 44 Evolution (South Pacific)
- Bali 4.1 (Italy)
- Leopard 46 (Caribbean)
- Lagoon 450S (Caribbean)
- Leopard 46 (Bahamas)
- Royal Cape 45 (Florida)
- Lagoon 42 (Caribbean)
- Endeavour 44 SailCat (Florida)
- St. Francis 44 Mk II (Florida)
- Fountaine Pajot Athena 38 (Mexico Pacific)
- Crowther-Alwoplast 47 (Caribbean)
Pocket Catamarans
Endeavour 36 endeavourcat (florida), fountaine pajot 35 tobago (bahamas), fountaine pajot tobago 35 (florida).
- Catalac 9m (Europe)
- Gemini 105MC (Greece)
- Lagoon 37 TPI (Florida)
- Corsair F28R (Texas)
- Endeavour Victory 35 (Mexico Pacific)
- Catalac 8M (Turkey)
- Gemini 105M (Florida)
Power Catamarans
- Leopard 39 PowerCat (Florida)
- Endeavour Trawlercat 44 (Florida)
Sale Pending
- Prout 37 Snowgoose Elite (USVI)
- Lagoon 450F (Florida)
- Fountaine Pajot Helia 44 (Caribbean)
- Catana 471 (Bahamas)
- Privilege 42 (Florida)
- Lagoon 52F (Caribbean)
- Admiral (0)
- Americat (0)
- Antares (0)
- Beneteau (0)
- Broadblue (0)
- Catalac (2)
- Chris White (0)
- Contour (0)
- Corsair (1)
- Crowther (1)
- De Villiers (0)
- Dolphin (0)
- Endeavour (6)
- Farrier (0)
- Fortuna (0)
- Fountaine Pajot (11)
- General (0)
- Grainger (0)
- Hirondelle (0)
- Kelsall (0)
- Lagoon (26)
- Leeuwin (0)
- Leopard (12)
- Looping (1)
- Maine Cat (0)
- Maverick (0)
- Nautitech (0)
- Outremer (1)
- Privilege (1)
- Royal Cape (1)
- Sailcraft (0)
- Schionning (0)
- Seawind (0)
- Simpson (0)
- Solaris (0)
- St Francis (1)
- Stealth (1)
- Wauquiez (0)
- Wharram (0)
- Whitehaven (0)
- Xquisite (0)
All Catamarans For Sale

S/V Breezy is a 2004 Lagoon 410 S2 catamaran, for sale by owner. We are selling our 2004 Lagoon 410 S2. A current survey from August 2023, with a job list completed.
We spent the last couple of months fixing everything on the boat that was deemed an issue in the recent survey including brand new anti-slip and top paint. The hulls are also freshly painted with Seahawk and the hulls have been polished to bring the exterior of the boat to a sparkling new finish.
With the water maker, solar, lithium, and washing machine this boat is completely self-sufficient. This boat is in Excellent condition, ready to take your family around the world.

S/V Discovery is a 1999 Endeavour 36 Endeavourcat catamaran, for sale by owner. Cruiser Ready complete with Ice Maker and Blender!! Completely redone within 2 years, with all new sails, running and standing rigging, roller furling’s on jib and main. New canvas and Eisen glass windows, with No-See Screens for full cockpit enclosure.
2 Volvo Penta MD2030 inboard engines 29 hp w/ approx. 1500 hrs on each. Volvo-Penta sail drives. 90 gal water,60 gal fuel. All new Marine Grade electric wiring throughout. Solar power system includes-4 100w solar panels, 4 175w flexible solar panels mounted and installed. Victron Smart Solar Controller MPPT 150/70-tr Victron MultiPlus 12/3000/120-50 120v VE Bus Smart Charger/Invertor, Victron BAM0307 1200 R Battery Monitor with Bluetooth.
Batteries- 2 new 300 AMP lithium’s runs microwave, coffee Maker and more for weeks. Next Generation Power Engineering Generator. Dometic AC 16,000 BU AC throughout boat. New TV, Cd player and surround sound. New cushions inside and out and all matching linens-includes much more extras. The 15′ beam and only 36″ draft allows you into areas other Sailboat and Cats cannot go!! Includes Highfield Dinghy.

S/V Panta Rhei is a 2012 Custom Custom Roake Guenter 50 catamaran, for sale by owner. The design concept for Panta Rhei was formulated in 1981. We wanted a fast sailing catamaran with comfortable but minimal accommodation capable of cruising the oceans of the world and at the time couldn’t find anything that suited our needs. The design and construction of Panta Rhei was an evolution that occurred over a number of years and involved a cast of naval architects, a variety of construction methods, what at the time were cutting edge technologies and the development of novel approaches to implementing the smooth working of all components.
Panta Rhei has been our only home since 2014 and part time prior to that. While we never did sail the oceans of the world as hoped, we cruised extensively from Nova Scotia to the Bahamas and throughout the Caribbean. During that time, Panta Rhei proved her sea keeping abilities, potential for speed and ease of handling. She is a capable world cruiser and all that has prevented us from venturing further afield is our advancing maturity.
While Panta Rhei will not appeal to those who desire a spacious catamaran suitable for families or entertaining, she is perfect for an individual or couple who is minimalist in accommodation needs, wants the option for speed and who appreciates safe and easy sailing.

S/V Hurricane is a 2012 Stealth 11.8 catamaran, for sale by owner. Please note that we are also listed with the broker Nils Erickson. Hurricane is a rare West Coast lightweight racer-cruiser in excellent condition and well sorted and optimized. Ready to race or cruise immediately.
Designer Alan Carwardine, of Asia Catamaran, has always focused his designs on fast but comfortable boats. His current range of sailing catamarans, the STEALTH series, is no exception with stylish lines, large open living areas and easy access to side decks and foredeck. The undercover cockpit with minimal areas open to direct sunlight cleverly maximizes air flow like no other design of its kind. With the added advantage of excellent vision from the twin steering stations, it has functional sailing systems set up for short handed sailing making it a pure pleasure to sail.
The STEALTH catamarans are truly refined design for tropical and sub-tropical boating. An established race winner and comfortable to cruise, Hurricane has many recent upgrades, including new bottom paint in 2023. Recent Victron 400AH (2021) battery bank, with two new 180W flexible solar panels and controllers, new motors in 2021 and new sail cover 2024.

S/V Nomad is a 2015 Leopard 44 catamaran, for sale by owner. She is a 4-Cabin with the light interior. This was a Belize charter, so this is not a hurricane damaged boat. She is on the hard at Zimmerman Marine in Matthew, VA. She has brand new Yanmar 39 HP engines with zero hours.
Nomad features upgraded electronics, as well as an upgraded dinghy winch and Mantus anchor. In 2023, she also got new Insinglass in the cockpit, as well new running rigging.
The Leopard 44 features two cockpits, one fore and one aft with outside dining area protected by a functional hard-top bimini. Sailing the Leopard 44 is easy: both main and jib sheets lead to stoppers and self-tailing (electric) winches directly adjacent to the helm. The galley-up has ample storage and a huge drawer type fridge and freezer. No steps up or down anywhere on the salon level.

S/V Ooga Chaka is a 2005 Leopard 40 Catamaran, for sale by owner. IT’S ELECTRIC! We are excited to present Ooga Chaka! An all electric catamaran!
We are currently living on Ooga Chaka in the Caribbean and will continue to do so until the day she sells. During Ooga Chaka’s electric conversion we re-wired the entire boat (2021) and upgraded ALL electrical systems (2021)….nav, fridge, pumps, induction stove…everything!
Ooga Chaka is an older boat and has some cosmetic considerations but her foundation is strong with new standing rigging (2021) and new sails (2023)…she is ready for adventure and to provide a comfortable home for your life on the water. She is a 4 cabin 2 head layout with brand new macerating toilets, holding tanks and pipes (2024). We love the 4 cabin layout allowing space for the entire family.

S/V Nani is a highly sought-after and wonderfully maintained 3-cabin Owners Version, 2007 Lagoon 440 catamaran and has never been in charter, for sale by owner. No hurricane damage or bulkhead issues. Are you looking for a turnkey, bluewater catamaran that is ready for sailing?
SV Nani has an enclosed flybridge that made sailing the Eastern Caribbean comfortable with spectacular views of the great open ocean. In addition, she features two upgraded low-hour Volvo Penta 55HP engines, a generous sail inventory, a four 48,000 BTU A/C throughout, and 800 amp-Lithium batteries with 1000 Watt solar, Spectra water maker, SOBA Laundry Wash machine, 7000 watt Onan Generator (2019) that leave you totally self-sufficient for off the grid living.
These are just a sampling of the upgrades she holds. The standing riggings ( Lower and Upper Diamond and outer Shrouds) were replaced 2024, new sailbag and dynema Halyard (Nov 23). In April 2024, new bottom paint completed, both saildrives were serviced (new seals/orings/gaskets), thru hulls checked and lumitc underwater lights added. The Port and Stbd folding blade propellers were serviced. A recent SAM survey is available for review.

S/V Traveller is a 2014 Leopard 44 owners version sailing catamaran, for sale by owner. Privately owned, never chartered. She is lightly used as we bought her in 2019 in pristine condition and continue to maintain her in excellent condition.
Much of the work during our stewardship was preventive maintenance. We live on her for six months each year and she lays up each summer in Georgia and/or South Carolina. We have sailed most of Florida and the Bahamas, and yet she has still been a dock-princess for well over 90% of our ownership.
While docked for the summers, owner was onboard every 6-8 weeks to consistently exercise all systems to keep everything in top notch operating condition. She looks and operates like a boat half her age. Lots of recent upgrades to prepare her sale.

S/V IMPROBABILITY is a 1998 DEAN 440 catamaran, for sale by broker. If you were to walk down a dock full of large catamarans, the Dean would stand out with its overly raked mast and unique aerodynamic styling hull shape. Beautifully fitted out in high gloss cherry throughout she oozes comfort and warmth. 4 cabins with in-suites and bathrooms a plenty ensure comfort at sea is a given. With a very well thought out large aft deck she is comfortable for entertaining or on the high seas.
A well-loved and expertly maintained Dean. She has completed several voyages across the Atlantic and cruised the Caribbean down to South America. Over the years she has completed at least 14 round trip ICW voyages from Southern New England to the Florida Keys including offshore passages with Bahamas cruising. Being full time liveaboards space is a must and this Dean answers the bill with hanging lockers and cabinets at every turn.

This is a 2019 Lagoon 42 catamaran, for sale by owner.
This new member of the Lagoon family is a sleek, modern design. While retaining the main features of the latest generation of Lagoons, it shows us a new path. The elegant silhouette with new coach roof design emphasizes the powerful and dynamic nature of this new model… A VPLP design , performance under sail.
This Lagoon 42 was never chartered and has many upgrades and options as part of a complete overhaul in November 2023. These include engines and generator (all serviced in 2023) as well as propellers, Starlink, and bottom paint new in 2023.

S/V Maeva is a 2019 Bali 4.0 catamaran, for sale by owner. We ordered and bought this catamaran new in March 2019, it was built at the Marans factory in La Rochelle. We spent our first year in the Canaries and Cape Verde, then crossed the Atlantic in 2020 and spent the last 4 years exploring the Caribbean.
It’s fully equipped (all the original options plus the excellence pack, AC watermaker, solar panels, etc.). She’s been maintained to an exemplary standard. She’s ready for your round-the-world trip or simply to live full-time in the Caribbean.
The Bali 4.0 offers a particularly innovative layout. A large saloon-cockpit area with a huge opening. Flying bridge and forward cockpit. A Owner’s version + 2 guest cabins and a large head in the starboard hull.

S/V Catalyst is a 1988 Fountaine Pajot 48 Custom, for sale by owner. She is a classic, fast cruiser with long, narrow hulls and high bridge-deck clearance for efficient and comfortable (no slamming) open-ocean sailing. She is a custom sleek 48’ long (14.7 meter), 23’ beam sailing catamaran in excellent condition. Strong, light construction of isophthalic resin and S-glass. Stellar sailing machine with excellent sea-keeping qualities. All systems serviced/upgraded, ready to cruise.
Roomy, airy, comfortable accommodations with 4 staterooms, plus two single berths in bows, two heads, galley-up, comfortable salon with teak dining table and comfortable seating for 6 with ample storage. Easy handling with protected helm station; all sail and furling lines leading to the cockpit.
Cockpit has teak surround seating with custom-made cushions and plentiful storage. Dedicated engine rooms, large anchor locker, sizeable front trampoline for lounging and rear trampoline for dinghy storage. The boat is long enough to have good accommodations without sacrificing sailing performance and ability. The boat is a U.S. documented vessel.

S/V Althea is a newly redone 2000 Leopard 45/47 catamaran, for sale by owner. Althea has had her sugar scoops extended by 2 feet to a total of 47 feet to enhance her performance in 2023.
The classic Leopard 45, also known as the Moorings 4500, was designed by Simonis Voogd and built by Robertson & Caine in South Africa. When it was introduced in 1997, the Leopard 45 was selected by Cruising World Magazine as “Charter Boat of the Year” and quickly built an outstanding reputation in the Moorings and Sunsail charter fleets. These catamarans set the standard for comfort, ease of sailing and performance when they were introduced.
The layout allows easy movement about the boat from the spacious aft deck, a step down to the swimming platform, or relaxing on the foredeck trampoline. The innovative deck layout brings a host of features to make life and sailing simplicity itself. From the aft deck arch that puts the mainsail sheeting system out of harm’s way, to the ingenious anchoring system, sailing the Leopard 45 is a breeze. The Leopard 45 has robust shaft drives and skeg protected rudders making it well suited to cruising in remote areas.

S/V Marlove is a 2011 Lagoon 450 F Owner version catamaran, for sale by owner. EU VAT PAID, NEVER chartered, she is viewable in Bahamas from Jan 10th, in perfect shape. Small trades such as for cars and monohulls can be considered.
The Lagoon 450 has taken several items ideas from its predecessor, enhanced them through owner feedback, and created a larger sail area for favorable cruising speeds. The 450 flybridge version gives optimal visibility and access to sailing controls while providing easy access to the main cockpit and seating areas via twin stair wells. Cushions and lounging areas abound for the family and crew to relax under way or in port. As with all Lagoon catamarans the vertical windows provide superb visibility while maximizing interior space and keeping the interior cool under those overhanging eyebrows.
The engines are 2200 hours, fully accessories included watermark, washing machines and dryer, ice maker, Fully AC, dishwasher, generator 11Kw, new sail 2022, new electronic 2022, Teak ,full of spare parts, new life raft (2022). All safety equipment are in and new (2022) and so much more.

S/V Korra is a 2018 Lagoon 42 catamaran, for sale by owner. Korra has been owned and actively maintained by a full-time cruising couple since 2020. She is a 3-cabin owner’s version and is extremely well outfitted for blue-water cruising.
Starting in Spain, the owners sailed across the Atlantic, through the Panama Canal and up the west coast of Mexico to her current destination in Puerto Vallarta, Mexico. The boat has never been chartered and has been lovingly cared for and maintained. Korra comes with significant upgrades, spares, creature comforts and toys for an easy start to your new adventure. Most of the upgrades were installed between 2021 and 2023.The boat has everything necessary for coastal or long-distance cruising – bring your bathing suit and sail away!
An out-of-water survey from September 2023 is available at request.

S/V Blue Iris is a 2019 Lagoon 40 catamaran, for sale by owner. She has been in charter in BVI for past 5 years minus 2 years during the pandemic. Regular maintenance with yearly hauling out checked over and bottom paint. Priced to sell in BVI. Once we bring her to the US, the price will be much higher.
The 40 is endowed with enhanced performance. The larger sail plan than other Lagoon models ensures a better sail surface/displacement ratio, making the 40 a fast and seaworthy boat. The decision to move the mast further aft, arising directly from VPLPs experience in racing, has many advantages. For ease of handling, the 40 has a self-tacking jib and a shorter boom. For more performance, the 40 has a large foretriangle offering a greater choice of foresails and a high-aspect mainsail, enabling use of less disturbed air higher up.
On deck, space and comfort are combined with a new aft cockpit layout like that of the 42. This space is open to the sea, with a dining table to port that can accommodate up to twelve guests, a relaxation area on the same side, and a seat on the aft crossbeam. The ergonomic helm station can be accessed from the cockpit or the deck, affording continuous communication between the helmsman and the rest of the crew. The skirts are wide, with a large platform, to enjoy the sea with feet in the water as well as to facilitate access to the dinghy and enable an easy and safe climb aboard.

M/Y Vieux Carré is a 2022 Aquila 44 Yacht catamaran, for sale by broker. The most Attractive Market Price for this boat. Replacement Value 1,650,000 USD. Owner version, Owner boat, never chartered for sale in the Caribbean. The boat is fully loaded and has little use and low engine hours.
She is loaded with Twin 320HP Volvo engines, a Generator, a Watermaker, an Air Conditioning Interior, and at Flybridge. Engines were observed running during sea trials. Started easily and ran adequately, topping out around 3560 rpm on port and 3510 on starboard (engines are rated for 3500). Speed was 19.5 knots; the fuel burn rate was 32 gallons per hour. At 3000 rpm cruise, speed was approximately 16 knots with a fuel burn rate of 21 gallons per hour.
Bow Thruster, Generator, Air Conditioning, Watermaker, Inverter, Full Enclosure, Underwater Lights, Washer/Dryer all included and installed from Factory.

S/V “Pearl Bali” is a 2016 Bali 4.3 catamaran for sale by owner. Built in France by a division of Catana Catamarans, the Bali 4.3 is a revolution. Its central platform entirely free of bulkheads and accessed via a huge glass door which is completely retractable, gives a living space of over 30m², with exceptional panoramic views.
Resolutely modern lines, combined with a choice of carefully selected, fine materials, give the BALI 4.3 a strong, elegant and prestigious with all the innovations that make BALI so successful and an unrivalled living space in her class.
Immense interior and exterior living spaces with a sleek design, incredibly bright, panoramic views, fully opening forward window, forward and cockpit sunbathing areas, fully equipped and a level of self-sufficiency unique in its class.

S/V Akua Aminata is a 2003 Dean 440 Espace catamaran, that has undergone an extensive refit in 2023/2024. Due to a change of plans, now for sale by owner.
The Dean is well noted for the distinctive raked mast to increase lift. She is an strong and well-built boat with asymmetrical hulls and a high bridgedeck clearance to minimize pounding. She has a high freeboard and ultra modern curved lines. Fitted with new standing and running rigging in November ’23 and new dark grey laminate sails.
The decks are wide and spacious and her cockpit is vast and easily accommodates 8 to 10 guests. The helm is located within the cockpit so even the skipper is always part of the social action while sailing, instead of being stuck out of the way on a fly bridge as on most cats. If you are looking for a nice, affordable blue water cruising catamaran this might be the one! She is a good sailor (double digits), also goes up wind pretty decent, Sturdy, spacious (galley down!) catamaran. Ready to sail you anywhere!

S/V Hands and Feet is a 1995 Fountaine Pajot 35 Tobago catamaran, for sale by owner.
Naturally seaworthy, the Tobago 35 is an innovative-looking sailing vessel. Take the helm and appreciate the power. With the autopilot and the raised platform, you can have a drink away from the motion of the waves. Every Fountaine Pajot is built to the highest ISO 9002 European standard for offshore yachts, incorporating vacuum-bagging construction and careful hand lay-up with sophisticated high-strength resins which results in an extremely high strength-to-weight ratio.
The keels are fixed and filled with foam, protecting the rudders and shafts. Should they strike a reef or submerged object they harmlessly break away without allowing water intrusion. Fountaine Pajot catamarans use nets forward and eliminate weight in the forward hulls to prevent pitching and aid bow recovery in heavy seas. Flat deck spaces, and especially the relatively flat coach roof, make it comfortable and easy to move around and handle sails. A unique, patented feature is the eyebrow overhang of the coach roof over the window areas. This prevents the high sun from creating a greenhouse effect inside the boat.

S/V Lizzie a 2018 LOOPING 50 – OWNERS VERSION, CUSTOM BUILT FAST CATAMARAN, for sale by owner. This is a Looping 50 catamaran designed by French naval architect Patrick Luscher. His designs are famous for their simplicity, lightness and speed, while being functional and easy to use. About 25 such catamarans sail around the world, this stunning vessel has sailed extensively in the US, Northern Europe and the Mediterranean.
Lizzie features an array of exceptional upgrades completed in 2023 all aimed at making her a true bluewater cruiser. The new electric system boasts a custom-made 2.3kw solar arch and new flexible solar panels on the bimini to make a total 3.1Kw, ensuring you’ll harness the power of the sun wherever your travels take you.
Starlink and IridiumGo as backup are both installed for safety and fast internet coverage wherever you are on the ocean. She is a fast, dry and a pleasurable boat to sail short-handed. With her large volume and comfortable accommodation, she offers impressive home-from-home comfort. The Looping is fully equipped with all creature comforts one would expect from this fast family-cruiser, the owner has spared no expense in maintaining the boat at all times. Turn key! Ready to Go!

S/V Escape Plan is a 2017 Fountaine Pajot Lucia 40 catamaran, for sale by owner. Escape Plan has been lovingly maintained and enjoyed by our family while cruising from the Abacos up the East Coast to Annapolis for the past seven years. Due to personal family matters which restrict our ability to cruise, we are regrettably having to offer her up for sale before we could sail away in retirement.
She is a low time, well maintained Maestro (owners) version with 3 cabins and 3 heads, offering your guests their own cabin suite. Many extras make this boat a safe and enjoyable cruising option for a couple (or single hander) that likes to entertain or enjoy quality time together!
The 38 ft length makes this boat a snap for a couple to get in and out of tight marina slips, and the oversized Rocna 33kg anchor gives you peace of mind while on the hook in anchorages. She has a fresh (September 2023) survey with a clean bill of health.

S/V Gaia is a 2006 Fountaine Pajot Belize 43 catamaran, for sale by owner. We are offering our 2006 Belize 43. This model of Fountaine Pajot sailing catamaran is one of the most popular cruising catamarans of all time. Its the perfect boat as she is fast, safe, comfortable and robust. It is well known for its superior sailing capabilities in all weather, ease of handling and unparalleled cruising comfort.
It has always been kept in perfect condition. Fully self-sufficient in water and electricity with a watermaker (120l/h), the last generation solar panel 760W and new set of batteries from 2024 (5x150Ah). The 4 double cabins give the opportunity to invite your friends or take some paying guests with you on your trips. Each cabin has its own bathroom fitted with shower, sink and toilet. LED lights and USB ports run throughout the boat.
Sail away with peace of mind with new standing riggings 2023, new dinghy, new outboard engine 15hp, inboard engines at 1500hours, solar panel 760 W, new trampoline, new Victron convertor, new generator, new electronic navigation instruments 2023, etc. All safety equipment is up-to-date and includes 2 automatic life vests, and 8 150N life vests, 2kg fire extinguishers new 2023 and10-person life raft new from November 2023.

S/V Permanently Temporary is a 2002 410 Lagoon OWNER’S VERSION catamaran, for sale by owner. She comes with 3 staterooms and 2 heads.
PORT HULL – V-Berth, Spectra Watermarker (under v-berth), storage, hanging locker. Electrical Control Panel, access to wiring and storage. Head with Jabseco manual head, sink and separate shower. Queen Stateroom with a hanging locker is aft. STARBOARD HULL – Full shower, sink, storage, large hanging locker, poo-poo tank, Raitian electric head, storage and space for washer. Hallway-large hanging locker, storage desk with bookshelves. Queen Berth, hanging locker, escape hatch.
SALON – SB-Double Sink, Force Ten gas stove, countertop storage, under sink and stove storage. IsoTherm AC/DC refrigerator and freezer. Salon table, circular bench seating with storage under cushions and seating on credenza with cabinet and under cushion storage. To Salon Port – Nav Station with VHF radio, Icom SSB, Weather Fax and Snailmail modem, Heart 2500 inverter controls, AIS. Air conditioning controls located on nav station and on SB stairs.

S/V OCEAN TRADER is a 2000 Voyage 380 Maxim catamaran, for sale by owner. She is an easy-handling cruising catamaran in a good condition with 3 cabin’s, master cabin has a luxury shower. She is registered (tax paid) in Kenya and has the right documentation.
This model can be called a Voyage 38 or a Maxim 38 because Maxim Yachts, from Durban South Africa, provided Voyage Yachts with the Voyage 38. These performance cruisers were built in South Africa by Maxim and distributed through Voyage Yachts. The Maxim 380 was the winner of the 2005 Cruising World Best New Catamaran under 40 Ft . The 380 got the judges’ attention with its four-burner stove, and added headroom in the galley.
There are 6 solar panels with a total of 1100 wats on top of the afterdeck. They give the perfect shade and are very functional. There is no noisy generator on board. Ray marine equipment includes a good autopilot and radar.

S/V Cheval is a 1995 Outremer 50 Standard catamaran, for sale by owner. We purchased Cheval in January 2013. As the second owners we have continuously upgraded her including her most recent upgrade late 2023 through 2024 in preparation for a pacific passage. A change of plans creates a rare opportunity to acquire this Outremer 50 standard ready to cross an ocean.
As of this writing to the best of my knowledge she is the only Outremer 50 standard currently for sale in the world. Sometimes referred to as the Porsche of catamarans this boat has the speed you would expect while being large enough to provide comfortable accommodations.
As she is only cored in the decks with solid hulls the common occurrence of water found in the cored hull at survey will not be a problem.

SV Quazami is a recently surveyed 2004 Knysna 440 Catamaran in sail away condition, equipped for the cruising lifestyle and ready for blue water crossing, for sale by owner. She was extensively upgraded in 2021 and then sailed from South Africa to Brazil and then onto the Caribbean in 2022 by the current owner and his family of 5, who comfortably live aboard.
With 1190w of solar, Quazami is energy self-sufficient and can be taken to remote locations, without the need to ever go into marinas. She can comfortably sleep up to 7 people. Quazami has only ever had two owners and has never been in charter. Currently in the Dominican Republic, and soon to be sailed to the British Virgin Islands and then onto St Martin. Recent survey available on request.
Designed by renowned naval architect Angelo Lavranos, one of the pioneers of the light construction technique for racing yachts, the Knysna 440 is an improved version of the legendary St Francis 44. She has been built to a high standard by the Knysna Yachting Company, who prides itself on its reputation within the industry for producing high quality, fast yachts that are able to safely and comfortably cross oceans.

S/V Bonaventure 1 a Florida based 1994 Fountaine Pajot Tobago 35 catamaran for sale by owner.
It is a 3 cabin and 1 head. The saloon is bright with a 360 panoramic view. The galley, navigation table and dining table are all located in the spacious saloon. The Tobago 35 is light and well canvassed. With 20 knots of wind on the beam the polars promise 9 knots of boat speed particularly with it JProp folding propellers, it make this model and exciting machine to sail. Despite his age it remain a solid choice for those seeking adventure on the water.
The Tobago 35 is a compact catamaran that offers a good opportunity with a smaller budget. Naturally seaworthy, the Tobago 35 is an innovative-looking sailing vessel.

S/V Drunken Cat is a 2018 Lagoon 42 Owner’s Version catamaran, for sale by owner. Are you tired of boats just not measuring up to your expectations? Well look no further than this 42 Lagoon sailing catamaran. This 2018 Owners Version has it all and it all works! From bow to stern this vessel is turn key and blue water ready.
She’s currently in the Virgin Islands experiencing the joys of cruising while offering the comforts of home. We are the second owners and have lived aboard Drunken Cat for 2 years. We’ve outfitted her with a new lithium battery system, new water maker, new inverter, new Code 0, new electronics and many other upgrades to make sailing the Caribbean an enjoyable experience.
If you’re looking to enter the live aboard /cruising world, this catamaran will not disappoint. Come check it out in St. Thomas USVI. You will not be disappointed. Complete videos available upon request along with a drone fly over.

S/V Dare Greatly is a 2020 Fountaine Pajot Lucia 40 catamaran, for sale by value broker YachtX.
This yacht is the 4 stateroom/2 head layout and has been maintained to the highest levels. US flagged & documented (duty not paid), she is a blue water cruiser that presents as new from top to bottom with just 800 hours on her engines.
Priced $250K below a new one and without the 1.5 year wait, she is as close to a new, off-grid equipped boat as you’ll find with bottom paint Oct 2023, 7.5KW generator AND 850W solar with 400AH lithium ion batteries, A/C climate control, water maker, SCUBA compressor and numerous other cruising features.

(215) 508-2704
- Tao Catamarans
- Dolphin Catamarans
- Voyage Catamarans
- All Pre-Owned Catamarans
- Exclusive TMC Catamarans
- Sold Catamarans
- Buying A Multihull
- Selling A Multihull
- Sailing Schools
- Yacht Charters
- TMC Newsletter
- Employment Opportunities
- Mission Statement
- Affiliations
Spray Cat | 2004 Island Spirit 400
Rock hall, md, us.
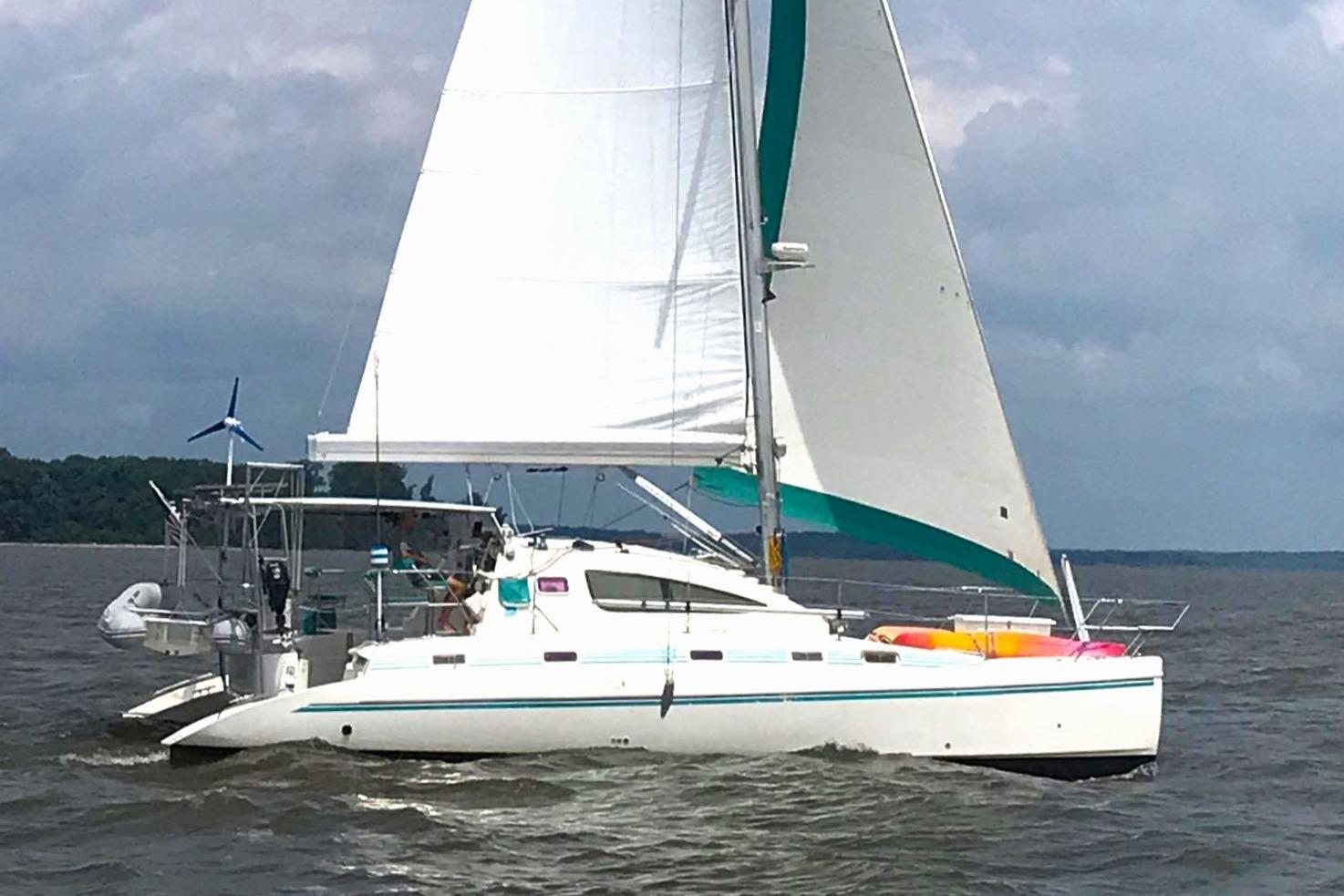

Spray Cat | Island Spirit 400 40ft
Us $169,000.
Owners health situation necessitate a major price reduction . This Island Spirit 400 was designed by Phil Southwell, built by Fortuna Catamarans in South Africa and sailed over to the US on her own bottom(s). Island Spirit Catamarans are known to be very well built and highly capable.
This three cabin version has never been chartered and her second owners have enjoyed cruising her and now must move on. Set up to be easily handled she features in boom furling!
Exceptionally well maintained and upgraded. "Spray Cat" is ready for your adventure.
Preliminary Listing Interior Photos to Follow
Reach out to Salt for details
Specifications
- Length: 40ft
- Beam: 23' 0"
- Draft: 3' 8"
- Hull: Fiberglass
- Status: Sale Pending
View More Specs
MEASUREMENTS
- Length Overall: 39 ft
- Max Draft: 3' 8"
- Beam Measure: 23' 0"
Accommodations
- Number of heads: 2
Welcome Aboard Spray Cat…
ON DECK…
Stepping aboard you are immediately struck by how easy this cat is to move around on. Her extended transoms allow for easy boarding regardless of the pier height. Large protected seating areas aft with a hardtop and easy access forward make for a wonderful playground! With new tramps forward for lounging or work there is plenty of space to spread out!
- Raised Helm bench seat
- Fiberglass Hardtop
- Dinghy Davits
- Outboard Motor Crane and Mount
- Wind Generator (2021 rebuild)
- Propane Grill
- Electric Windlass
- Proper Ground Tackle
- 150′ 3/8″BBB Chain with Snubber
- Bow Bridles
- 60 lbs. Manson Supreme Anchor
- Windlass Control at Helm
- New Lifelines ’19
Below …. Spacious, bright, airy and clean!
- 3 Staterooms
- Large U shaped Galley
- Propane 3 burner Cooktop
- Two Refrigerators
- Separate Top load Freezer
- Large L shaped seating area with Dining table
- Stand up Navigation Table Top
Sails and Rigging
- Leisure Furl Boom (’18)
- Mainsail (’18)
- Jib (’18)
- Standing Rigging (’18)
- All sail controls at helm station
- Both Trampolines replaced ’19
- 2 Strong and Clean Running Yanmar 3YM-30 Diesels (5853 hours)
- SD20 Sail Drives
- 3 Blade MaxProp Feathering Propellers
- Northern Lights Diesel Genset (2500 Hours)
- 4-100 Watt Renogy Solar Panels w/controller.
- Wind Generator (rebuilt 2021 with blue blades)
- 8ea. Batteries (800 Amp total hours)
- Charger / Inverter
- Smartplug Shore Power Cord and Plug
- Blue Seas Multimeter
- Victron Energy Phoenix Multi Controller
- Reverse Cycle AC 10000BTU (’20)
Electronics
- Raymarine ST6001 Autopilot
- Raymarine ST 60 Wind
- Raymarine ST 60 Tridata
- Raymarine Radar on mast
- Raymarine C80 Chartplotter
- VHF Ram Mike at helm
- Second Depth Sounder
- Fuel – Two 66 Gallon (132 Gallon total)
- Water- Two tanks 132 Gallons Total
- Holding -Two Tanks 40 Gallons Ea. (80 Gallon Total)
- LPG – 20 Gallons
Additional
- Bottom soda blasted ’17
- 9’s Highlander Inflatable ’22
- Torquedo Electric Outboard
- Tohatsu 9.2hp Outboard
Brokers Comment: Many spares and safety gear convey…
Spray Cat is a really nice sailing platform that has had thoughtful upgrades and thorough maintenance by knowledgeable owners. -Tom
Disclaimer The Company offers the details of this vessel in good faith but cannot guarantee or warrant the accuracy of this information nor warrant the condition of the vessel. A buyer should instruct his agents, or his surveyors, to investigate such details as the buyer desires validated. This vessel is offered subject to prior sale, price change, or withdrawal without notice.

Request More Information
Island spirit 400, loan calculator, shelley joyce, share this boat, log in or create an account to save searches, connect directly with your broker and get regular updates on desired boats and services..
Username or Email *
Remember Me
Lost your password?
Not a member yet? Register now.
- Login with google
More Information
Recent News
The multihull company announces the sale of the first pre-owned balance 482.
The Multihull Company is pleased to announce the closing on the Balance 482 "SeaLife" We wanted to take a moment and thank her new owners on their amazing new catamaran, and to also congratulate our team handling the sale. TMC agent Andrew Hodgdon successfully represented the buyers on the sale of the vessel, while TMC CEO Will Miller represented the...
THE MULTIHULL COMPANY ANNOUNCED AS DEALER FOR THE VOYAGE 590
The Multihull Company is pleased to announce their appointment as a dealer for Voyage Yachts and their new model – the Voyage 590! The Voyage 590 is being celebrated as the ultimate, luxury sailing catamaran with all the comforts of home surrounded by panoramic views of paradise. She maximizes luxury accommodation and comfort, with the performance and blue-water capability characteristic...
6 Great Starter Catamarans
In early 2023, Cruising World approached us to seek our opinion on recommending a couple of brokerage catamaran options for first time catamaran buyers to consider when they first stepping into the catamaran market. Here are six boats hand-picked by The Multihull Company’s president and CEO, Capt. Will Miller, as excellent choices for brokerage-catamaran seekers. These are all worth a...
The Multihull Company Named Exclusive Dealer for Dolphin Catamarans and their New Model, the Dolphin 380
The Multihull Company, the world’s leader in multihull sales and service is excited to announce that it has been named the exclusive dealer for Dolphin Catamarans, a premier builder of high-quality catamarans, and their newest model, the Dolphin 380, designed by Philippe Pouvreau. "We are thrilled to be working with Dolphin Catamarans again and to be able to offer their...
Visit Us at the 2023 Miami Boat Show
The Multihull Company is thrilled to announce our participation in the Miami Boat Show, taking place on February 15-19, 2023. As one of the premier boat shows in the world, this event is the perfect platform for us to showcase our wide range of high-quality multihulls for sale. We are committed to providing our customers with the best experience possible,...
Introducing the Tao 452: On Display At The Annapolis Boat Show October 12 – 15, 2023
The Multihull Company is thrilled to unveil the new Tao 452, an exciting addition to the world of blue-water performance cruising catamarans. Meticulously engineered and crafted to perfection, the Tao 452 is set to redefine the catamaran experience for sailors worldwide. If you've ever felt the need for more sailing performance from your current production charter catamaran or been disappointed...
Join Us At The Annapolis Boat Show Aboard the Voyage 590
The Multihull Company is excited to announce its participation in this year's Annapolis Sailboat Show. The event will be held from October 12 - 15, 2023 in downtown Annapolis, and The Multihull Company will be showcasing the exquisite Voyage 590 catamaran from Voyage Yachts. The Annapolis Boat Show is a highly anticipated annual event that brings together boating enthusiasts, industry...
Ian Edmonson Joins TMC As Yacht Broker in Fort Pierce, FL.
The Multihull Company is thrilled to announce the appointment of Ian Edmonson as a yacht broker at its newly opened Fort Pierce location. Ian brings a unique blend of boating passion, brokerage experience, real estate expertise, and customer-focused mentality to the team. Ian's love for boating began at an early age and has only continued to grow, leading him to...
The Multihull Company Opens New Office in Virginia
We are thrilled to announce that Alan Prater has joined The Multihull Company team as a Yacht Broker in Virginia covering the Hampton Roads area of Virginia. With a lifelong passion for the water and a career spent in the US Navy and as a maritime training professional, Alan brings a wealth of experience and expertise to our team. Alan...
- Read All Articles
We take pride in our happy customers
Your team delivered on every mark. You’ve got an amazing broker in Mark Wattrus and I’m confident you will have continued success moving forward together. He was available 24/7 whenever I had questions. We had a great initial visit on the boat and his marketing plan and photos were superb
I bought a yacht that I had never seen. I did this because I trusted my broker Andrew Holland. It was not an easy job for Andrew, as I am an experienced boat builder and owner of previous yachts, but work in West Africa. Imagine how hard it was to communicate what I was looking for. Andrew came up with exactly what I wanted. He dealt with time delays, all my questions at odd hours, and was there for the survey. He reported honestly and professionally. After buying the yacht, I arrived at the boat on a Sunday night, after dark, after travelling from West Africa to the Caribbean, and found it was better than expected. He never pulled punches and made me aware of shortfalls. I expected to spend my one month leave working on the boat, but actually spent less than one week, and was able to spend 3 weeks sailing – wonderful bonus.
Thank you Andrew for putting up with all my questions, all my worries and all my crazy out of the time zone concerns – you were totally professional, but also I know that if and when we meet up, it will be like a friend finally meeting. You are always welcome on Aseka.
— Beverly Cory
Outstanding company with professional subject matter experts. If I were to buy or sell cruising sailboat, particularly a catamaran, Andrew would be my go to broker.
I have been sailing since I was a child and attended Massachusetts Maritime Academy. But when my wife and I began the process of purchasing an ocean cruising/racing catamaran, I realized that this is a world unto itself. Obviously, we needed to find someone knowledgeable to help us make an informed decision. More importantly, we needed someone honest and willing to put our interests before his or her own. I was lucky to work with Phil Berman at The Multihull Company. He repeatedly shunned the fast buck, choosing instead to work the long road to connect us with the “perfect boat”. I would be glad to recommend Phil and his company to anyone planning to purchase or sell a performance sailing machine.
— Eric Boutiette
Andrew Hodgdon was our broker when we bought our 2018 Lagoon 450F in Antigua in April 2922. He provided great service and was very attentive to our needs. We would highly recommend Andrew and the Multihull Company.
Trust & Expertise About Us
Successful relationships cannot exist without it. At The Multihull Company we base every relationship on a firm commitment to earning and retaining our client’s trust.
Advice of any kind is valuable only when grounded in hard-won expertise. It too, must be trustworthy. Trust and expertise define the heart and soul of The Multihull Company. We are a team of skilled professionals who thrive on providing expert, trustworthy advice and service to catamaran and trimaran sailors around the globe.
Follow us @themultihullcompany
- Pre-Owned Sales
Global Locations
New England +1-267-324-9067
Philadelphia +1-215-508-2704
Virginia +1-757-407-2526
Annapolis +1-703-350-8160
Charleston +1-843-364-4123
Brunswick +1-937-243-2213
Saint Augustine +1-910-477-2508
Fort Pierce +1-340-473-7469
West Palm Beach +1-561-312-0010
Ft. Lauderdale +1-484-744-2740
Miami +1-513-677-5338
San Francisco +1-215-508-2704
Seattle-Tacoma +1-206-297-1151
St. Martin +590 690 58 66 06
Grenada +1-473-457-3245
Puerto Rico +1-787-379-7348
Panama +1-305-735-1661
Trinidad +1-868-680-8909
Croatia +385 95 849 8009
France +33 (0) 6 73 97 17 30
Mauritius +1-215-508-2704
Australia +61 (0)7 5444 4822
Cape Town +1-843-614-2028
© Copyright 2024 The Multihull Company. All rights reserved.


Sail Catamarans 40ft > 50ft | Used Yachts For Sale

amadeus sailing yacht
New on boatsatsea.
- Mischievous
- The Blue Dream

NEWEST SPECIAL OFFERS
- Adeona ( Lastminute 30% off )
- Royal Flush ( Jun 20% off )
- Aquarella ( 10% off)
- Aquila ( 5% off)
- Ulisse ( 10% off)
- Boom ( 10% off)
- See All Special Offers
TOP CHARTER YACHTS
- Crystal Dreams ( 15% off)
- Bella ( $1,000 off)
- See All Yachts
Most Searched Yacht
Ad astra 5.4.
From $28,500 per week
TOP DESTINATIONS
- Virgin Islands (BVI & USVI)
- Leeward Islands / St. Martin
- Windward Islands / Grenadines
EUROPE / MEDITERRANEAN
- Amalfi Coast & Sicily
- Riviera & Corsica & Sardinia
- Spain / Balearics
- New England
- South America
MY FAVORITE YACHTS
- See Favorite Yachts
- Send & Share Favorite Yachts
- Empty Favorite Yacht List
- Yacht Charter FAQ
- Rates Explanations
- Concierge Service
- Customer Satisfaction
- BoatsAtSea Reviews
- Dedicated Support
Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
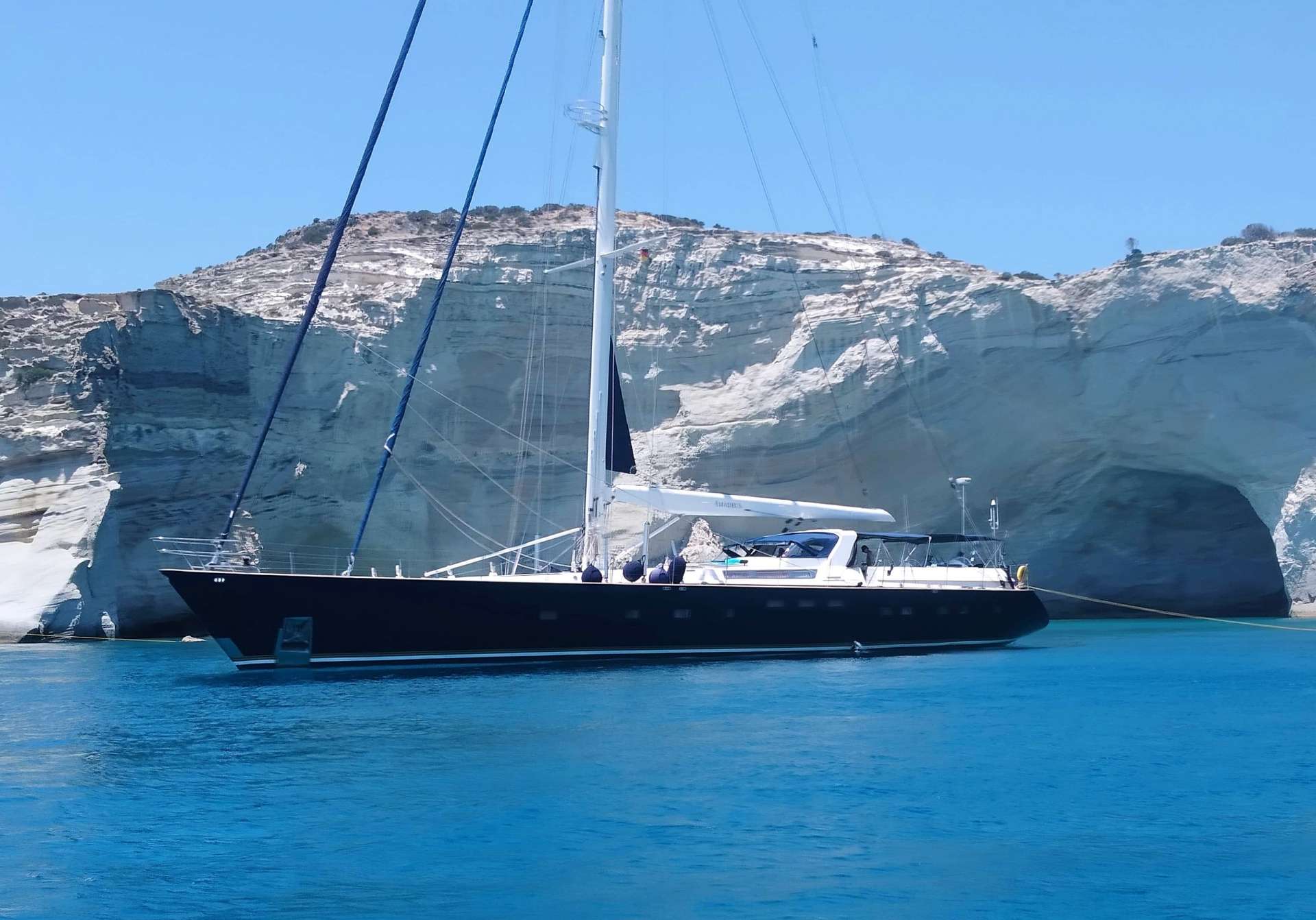
Amadeus - Crewed Sailing Yacht Charter
Amadeus €35,000.

Amadeus Image 1/22
Layout of Amadeus
Amadeus Image 3/22
Amadeus Image 4/22
SUNBATHING FORWARD
SUNBATHING FORWARD ANOTHER VIEW
- Splash Pool
Splash Pool another view
Amadeus Image 9/22
Amadeus Image 12/22
Amadeus Image 13/22
Amadeus Image 14/22
Amadeus Image 15/22
Amadeus Image 19/22
Amadeus Image 20/22
Anastasia Yurash (Asst. Stewardess)
Stelios Mandos (Engineer)
- From €35,000 / week
- Sailing Monohull + 6 crew
- Summer Port: Cruising Areas Summer: Greece, Turkey Summer Port: Marina Zea, Piraeus, Greece Winter: Greece Winter Port: Marina Zeas, Pireaus, Greece ">Marina Zea, Piraeus, Greece
- Winter Port: Cruising Areas Summer: Greece, Turkey Summer Port: Marina Zea, Piraeus, Greece Winter: Greece Winter Port: Marina Zeas, Pireaus, Greece ">Marina Zeas, Pireaus, Greece
- Length: 110 ft / 33.5 meters 110 feet 33.5 meters
- Guests: 12 in 5 cabins
- Builder: Dynamique Ya
- Built: 1996 / Refit: 2014/2020
- Offers Rendezvous Scuba Diving only
Plus Expenses
- Reviews (1)
Amadeus Description
Built by the famous Dynamique Yachts shipyard, and having undergone a total refit in 2018, S/Y Amadeus was designed to please the most demanding of yachtsmen. Built for smooth sailing, this elegant cutter rigged sloop has a sleek hull design, comfortably reaching top speeds of 12 knots and ensuring excellent sailing performance. S/Y Amadeus has just undergone this past winter (2018) a major refit such as total repaint top to bottom, new rigging (BSI Denmark), Novourania with new Evinrude 75hp outboard, Splash pool, new Bimini/Sprayhood/Awnings, new exterior fabrics and many other enhancements. In 2016 new “North Sails” were placed onboard. The yacht is maintained in excellent condition with a five-star crew year round. Her generous uncluttered teak deck offers plenty of space for sunbathing. The spacious and unique outdoor saloon has two tables seating upto 12 guests and is a perfect setting for outdoor dining and entertainment. Thanks to a special canopy and roll-up windows, the deck saloon has the added attraction that it can be fully enclosed, making it ideal for all weather conditions. Her forward area includes a splash pool and sun bathing area which can also be shaded with a removable awning. From the cockpit, a stairway leads to the light-filled spacious saloon offering ample seating, ideal for relaxing or enjoying a drink from the bar, and offers a formal dining area. This area also includes a LCD TV, entertainment center, ipod dock station, playstation, and is ideal for indoor activities. She can accommodate 10-12 guests in one full width master stateroom, two double bedded cabins each having one extra single bed and two twin bedded cabins which can be easily converted to double beds (upon request), thus, making her the only 5 double bedded sailboat in the Greek market. She also has a nice selection of toys which include water ski (adult and children), tubes, inflatable canoes, wakeboard, fishing rod and snorkeling gear.
Cruising Area of Amadeus
Accommodations, specification, water sports, scuba diving, entertainment, amadeus crew profile, chief stewardess.
CAPTAIN - Harry Fotopoulos Captain Harry is a graduate of the Merchant Marine Academy and holds a Captain Class A’ Diploma. He also holds a Canadian Commercial Pilot license class B, sailing and speedboat license. He has over 15 years of experience onboard many types of Charter Yachts. He holds Certificates in GMDSS, Fire Fighting & First Aid, Personal Safety, Life Saving, and Ship Security. He has a great knowledge of the Greek islands and will navigate guests to remarkable destinations. During his one season on board he showed great leadership skills and received positive feedback from all guests. He is calm yet very outgoing and speaks very good English. DECKHAND - Konstantinos Santas CHIEF STEWARDESS - Mirella Davint Mirella has 8+ years of experience as a stewardess onboard charter and private yachts. She has a very pleasant personality and she aims to accommodate her guests to the fullest. Comments received from previous guests are memorable. This will be Mirella’s eighth season onboard. Mirella speaks English and she is 38 years old. ENGINEER - Stelios Mandos Stelios holds an Engineer Class B’ Diploma from the Greek Merchant Marine Academy as well as a Sailor’s License. He has over 15 years of experience onboard Ocean-Going Vessels and Charter Yachts. His hobbies include spearfishing and sailing. He speaks good English. Stelios is 45 years old, married with two children. CHEF - Thanasis Kiritsis Thanasis is 39 years old and has worked as a chef for more than 20 years in numerous hotels restaurants, yachts and resorts including owning his own pastry shop / bakery for 5 years. Thanasis looks forward to welcoming his guests on board and introducing them to his culinary world. He speaks good English and Greek. He is a young chef full of energy, skills and passion towards his job. We are confident that he will serve his guests unforgettable flavors. ASSISTANT STEWARDESS - Anastasia Yurash Anastasia is 31 years old and has been in the yachting industry since 2021. Her working experience includes 7 years as a housekeeper and assistant stewardess. Anastasia speaks very good English. One of Anastasia’s strongest attributes is her appetite for work. She is also very sociable, welcoming and looks forward to having guests on board S/Y Amadeus. Her hobbies include Latin dancing, snowboard and yoga.
Amadeus Calendar
Amadeus reservations & port locations, amadeus rates / week, low price: €35,000, high price: €42,500, additional rate details, amadeus guest reviews, amadeus / charter july 20-27, 2019.
Sent: Wednesday, July 31, 2019 9:02 PM Hi George, client just informed me, that he and his friends were very happy. Good atmosphere on board, excellent crew, good chef and professional service. Yacht in good condition, nice cabins. The proposed itinerary was good. Clients intend to book AMADEUS next summer again. Please send my big thank you to the Captain. Best regards,
Amadeus Sample Menu
Breakfast selections.
Freshly Squeezed Orange And/Or Grapefruit Juice
Selection Of Other Juices Such As Peach, Pineapple, Tomato.
Fresh Milk Cold And/Or Hot.
Freshly Brewed Coffee And/Or Decaf Coffee, Cappuccino, Espresso (Nespresso)
Hot Or Cold Chocolate, Selection Of Teas Served With Lemon, Honey And/Or Milk.
Breads: Plain Croissant, Chocolate Croissant, Brioche, Muffins, Traditional Greek Bread,
Rolls, Pastries, Toast White/Wheat/Rye.
Selection Of Jams And Marmalades Such As Apricot, Strawberry, Rasberry, Orange And Honey.
Selection Of Cheese Such As Emmental, Edam, Gruyere, Kefalotiri, Graviera,
Cream Cheese, Cottage Cheese, Cheese Spread.
Ham, Bacon, Salami, Smoked Turkey, Prosciutto.
Choice Of: Scrambled Eggs, Boiled Eggs, Fried Eggs, Poached Eggs, Omelets.
Eggs And Omelets Are Prepared To Order And Accompanied According To The Guest’s Requests.
Pancakes, Served With Jam, Honey, Maple Syrup, Fruits And/Or Whipped Cream.
Home-Made Carrot Cake.
Selection Of Cereals Such As Corn Flakes, Bran,Rice Crispies , Muesli.
Greek Plain Yoghurt And Fruit Yoghurt.
Fruit Salad, Half Grapefruit, Mixed Berries, Stewed Prunes, Dried Fruits And Nuts.
LUNCH SELECTIONS
Greek Salad With Marinated Anchovy And Extra Virgin Olive Oil
Fresh Talliatele With Mushrooms And Parmesan Chips
Seawolf Fiilet With Vegetables Briam, Fried Caper And Fresh Thyme Panacotta With Ginger
Salad With Radish, Dill, Parsley, Arabic Pita Bread And Soumak
Egg-Plant Napoleon With Feta Cheese And Tomato Couli
Chicken Roll, Cous-Cous With Raisins, Pine Nut And Orange Sauce Walnut Cake With Vanilla Ice-Cream
Salad With Grilled Peach And Apricot And Watermelon Vinaigrette Sauce
Risotto With Red Mullet, Pine Nuts And Sun Dried Tomato
Pork Loin Filled With Naxos Graviere
Halvas (Semolina) With Korinthous Raisins Kai Cinnamon
Salad With Fennel Root, Olives And Orange
Tarte With Goat Cheese And Green Apple
Gurnet Fillet With Lemon Sauce Baby Potatoes And Parsley
Yogurt Mousse With Fresh Vanilla
Watermelon Salad,Feta Onion And Lemon Sauce, Balsamic Vinegar And Extra Virgin Olive Oil
Stuffed Squid With Chocolate Sauce
Tuna Fillet With Orange Confite And Red Wine Sauce
Peach Cheesecake
Green Salad With Smoked Salmon And Salmon Eggs
Mussels With Fresh White Cheese (Anthotiro) And Peppers
Sole Fillet Saute With Spring Onion And Fava (Yellow Split Peas) Fron Santorini Island
Galaktompoureko (Pastry Fillo Filled With Cream) And Orange Couli
Salad With Rocket, Parmezan Flakes, Sun Dried Tomato And Caramel Balsamic Sauce
Grilled Octapus With Chick Peas And Lemon
Anglerfish Stew With Green Talliatele
Tiramisu With Aigina Pistachios
DINNER SELECTIONS
Salad With Cretan Hard Bread , Tomato And Fresh White Cheese (Anthotiro) Grilled Vegetables Napoleon With Mastello (Chios Cheese) Bream Fillet With Crust From Cuttlefish Ink, Artichoke Mousse And Marinated Fennel Root Chocolate Souffle With Ice-Cream
Green Salad With Cottage Cheese, Walnuts And Extra Virgin Olive Oil With Herbs Cabbage Leafs Filled With Shrimps, Cracked Wheat And Egg-Lemon Sauce And Ginger T-Bone Steak With Mushrooms Sauce,Dofinouaze Potato Trifle With Coffee
Caesars Salad With Poached Egg, Parmesan Tuille And Mustard Crackers Fousili With Pesto Sauce And King Prawns Cod Fish Cooked With Safron, Green Olives And Potato Kantaifi With Pistachio And Ice Cream
Mozzarella Buffal0 With Black Eyed Beans And Fennel Rizotto Venere With Chicken Breast And Crawfish Rib-Eye With Fresh Potato Chips And Vegetable Sauce Almond Pie With Chocolate
Baby Spinach Salad, Pears With Pepper And Walnut Vinegar From Blackberry Beef Carpaccio With Caper, Parmesan And Rocket Gilthead Fillet, Vegetable Chips And Hot Balsamic Sauce Greek Loukoumades, Thyme Honey And Walnuts
Cracked Wheat Salad, Parsley,Cucumber,Tomato And Pomegrenade Sauce Goat And Feta Cheese Croquete, Orange And Cumin Sauce Pork Souvlaki, Greek Pita Bread, Tzatziki Sauce And French Fries Caltsounia (Pastry) With Manouri Cheese, Mint, Honey-Orange Sauce
Grilled Vegetables Salad And Chaloumi (Cyprus Cheese) Eggplant “Papoutsakia”, Mince Meat With Fresh Tomato Sauce Spagetti Flavored With Cutlefish Ink, Shrimps Hazelnut Cream Profiterolle
SIMILAR YACHTS
Check out similar yachts to amadeus.
Estrella De Mar
€23,450 / week
Guests in Cabins: 12 / 5
Length: 111.5 ft (34 m)
Summer Port: Bodrum, Turkey
Prices from: €23,450 / week
€50,000 / week
Guests in Cabins: 9 / 4
Length: 100.6 ft (30.65 m)
Summer Port: Athens, Greece
Winter Port: Athens, Greece
Prices from: €50,000 / week
Wind of Change
€24,000 / week
Guests in Cabins: 6 / 3
Length: 95.1 ft (29 m)
Prices from: €24,000 / week
€29,000 / week
Guests in Cabins: 8 / 4
Length: 99 ft (30.2 m)
Winter: Greece
Prices from: €29,000 / week
€43,500 / week
Length: 108.3 ft (33 m)
Summer Port: Lavrio, Greece
Prices from: €43,500 / week
€21,000 / week
Guests in Cabins: 14 / 7
Length: 115.5 ft (35.20 m)
Summer Port: Gocek, Turkey
Winter Port: Gocek, Turkey
Prices from: €21,000 / week

AMADEUS is a fast cruising sailing yacht built by the famous Dynamique Yachts shipyard and totally refit in 2004, she was designed to please the most demanding of yachtsmen. Built for smooth sailing, this elegant cutter rigged sloop has a sleek hull design that enables her to comfortably reach top speeds of 12 knots and ensures excellent sailing performance.
This sailing yacht's generous uncluttered teak deck with a foredeck pool, offers plenty of space for sunbathing. The spacious and unique outdoor saloon has two tables, a bar and barbeque, a perfect setting for outdoor dining and entertainment. Thanks to a special canopy and roll-up windows, the deck saloon has the added attraction that it can be fully enclosed, making it ideal for all weather conditions. From the cockpit, a stairway leads to the light-filled spacious saloon offering ample seating, ideal for relaxing or enjoying a drink from the bar, and a formal dining area with seating for up to 12 guests.
Accomodation is offered for up to 12 guests in 5 spacious cabins: the bow master cabin on AMADEUS features a double bed, vanity unit and generous storage facilities, as well as audio/visual entertainment. The en-suite bath includes a shower and separate large bath. Two double cabins with additional single bunks situated forward. Two twin cabins situated aft. All cabins with en suite facilities and audio/visual entertainment. Crew of 5 in separate quarters.
Special Features :
- Fast cruising sailing yacht - Spacious teck deck, sunbathing areas - Outdoor saloon with a bar and barbecue
Tender: Novourania tender 4.20m with YAMAHA X 70hp plus MERCURY x 10hp
Activities : Wakeboard , Kayak , Snorkeling equipment , Waterskis , Fishing equipment , Monoski , Tender , Tubes .
Summer : East Mediterranean Greece - The Cyclades Islands | Turkey | Greece – The Ionian Islands
Winter : East Mediterranean Greece - The Cyclades Islands | Turkey | Greece – The Ionian Islands
News & publications

SHINE: New yacht for sale!
A simply stunning Swan 58 as only Swan can. The big sister to the 48 she sails phenomenally well and was designed to allow for fast, safe and comfortable Bluewater passage making. This original owner has used her to cruise the Baltic and she has certainly proven herself. She is ready...

JACK: New Central Agency Yacht
Built in 2023, JACK is a sophisticated and comfortable catamaran that embodies a blend of lightweight construction, eco-friendliness, and remarkable performance. Indeed, she is able to achieve remarkable speeds of up to 21 knots in just 20 knots of wind. Her exterior includes a sprawling...

ONYX 2: New sailing yacht for sale!
ONYX 2 offers amazing space and comfort for those onboard to cruise anywhere in the world. She is seaworthy, solidly-built and well-equipped. She accommodates up to 12 guests in 6 cabins and 7 crew in 3 cabins. There is also a fantastic deck house which offers an incomparable interior...
Similar boats for charter

Length : 31.95 m / Passengers : 6
Special features : - Elegant and sophisticated, with classy mahogany interiors- Wide beam and high volume with a vast centre cockpit, large deckhouse and voluminous main...

Length : 30.3 m / Passengers : 8
Special features : - Deck plan designed for easy sailing and comfort both for crew and guests- Maximum flexibility for shading the guest cockpit and the sunbathing area,...

Length : 34.8 m / Passengers : 8
Special features : Tenders:- "Lina": 7.10 m Scanner with 300 HP inboard engine, specially equipped wih bimini and sprayhood, new in 2018- "Mieke": 4.70 m ZAR with 100 HP...

Length : 37 m / Passengers : 8

Length : 35.2 m / Passengers : 6
Special features : - High tech performance sailing yacht- Plumb bow and wide stern for improved performance and stability- Twin rudders for increased responsiveness- Aerodynamic...

Length : 33.7 m / Passengers : 8
Special features : - Five Stars Crew with an outstanding Chef led by Captain Eddy- Best combination of Elegance and High Performance Sailing yacht- New sails ( DFI aramide...

Length : 30.48 m / Passengers : 12
Special features : - Gold medal winner for the RORC Transatlantic 2015, setting a new record. This performance yacht with the sensation of speed and power is equipped with...
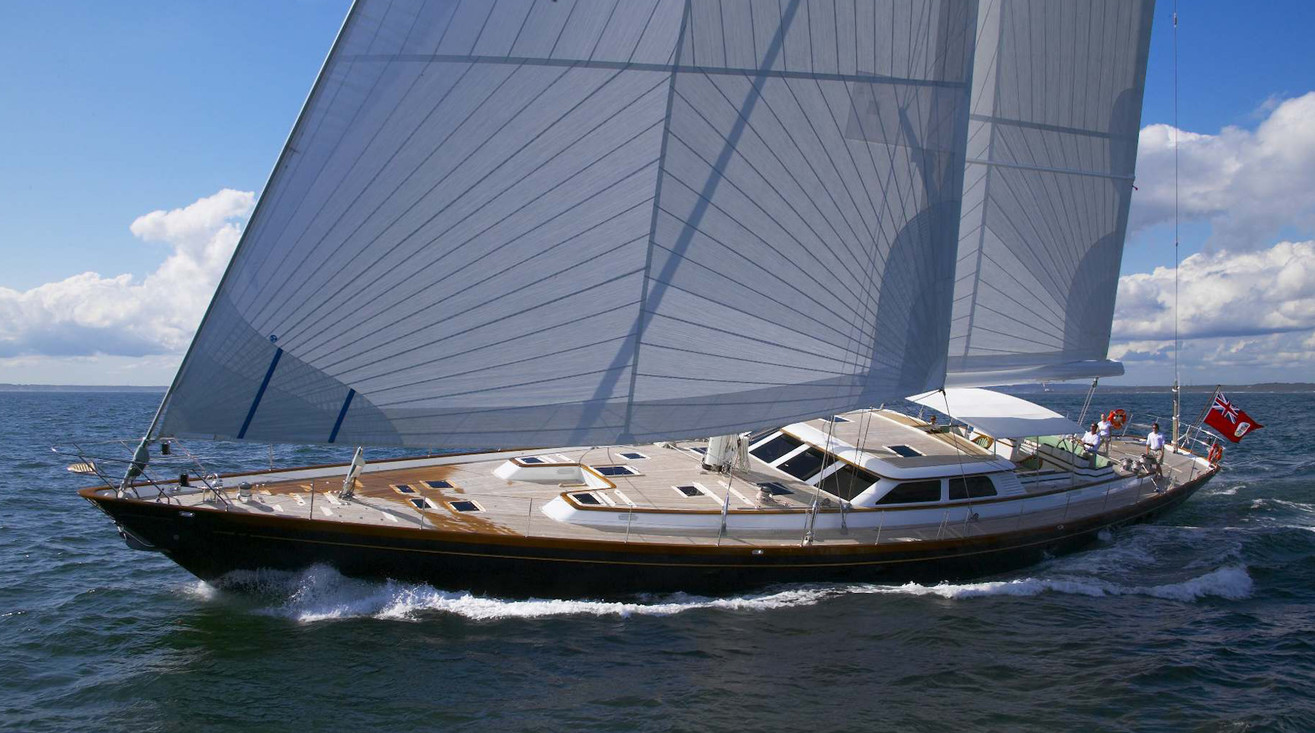

Length : 35.36 m / Passengers : 6
Special features : Tender: 115 Hp Yamaha on 15' Rendova
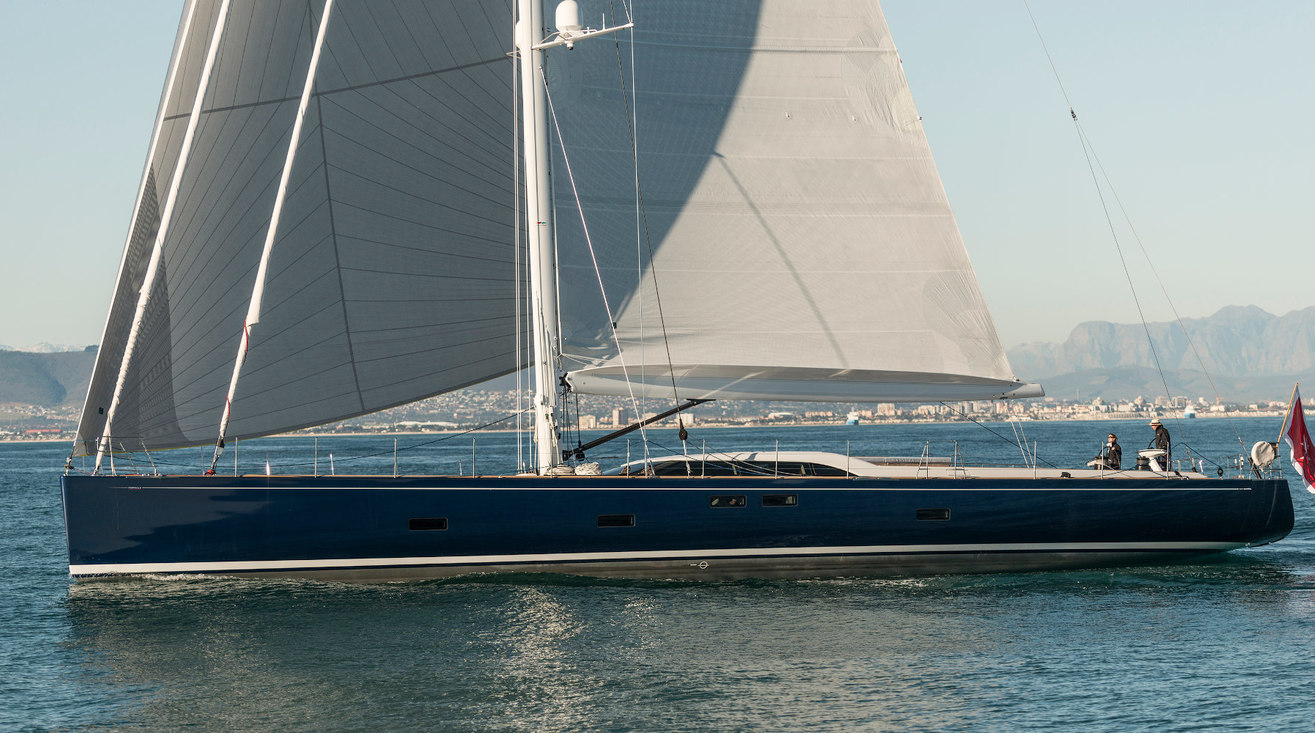

Length : 31.78 m / Passengers : 8
Special features : KEY FEATURES- Awarded the prestigious Quality and Value award at the 2015 World Superyacht Awards- Offers high performance sailing with first class...
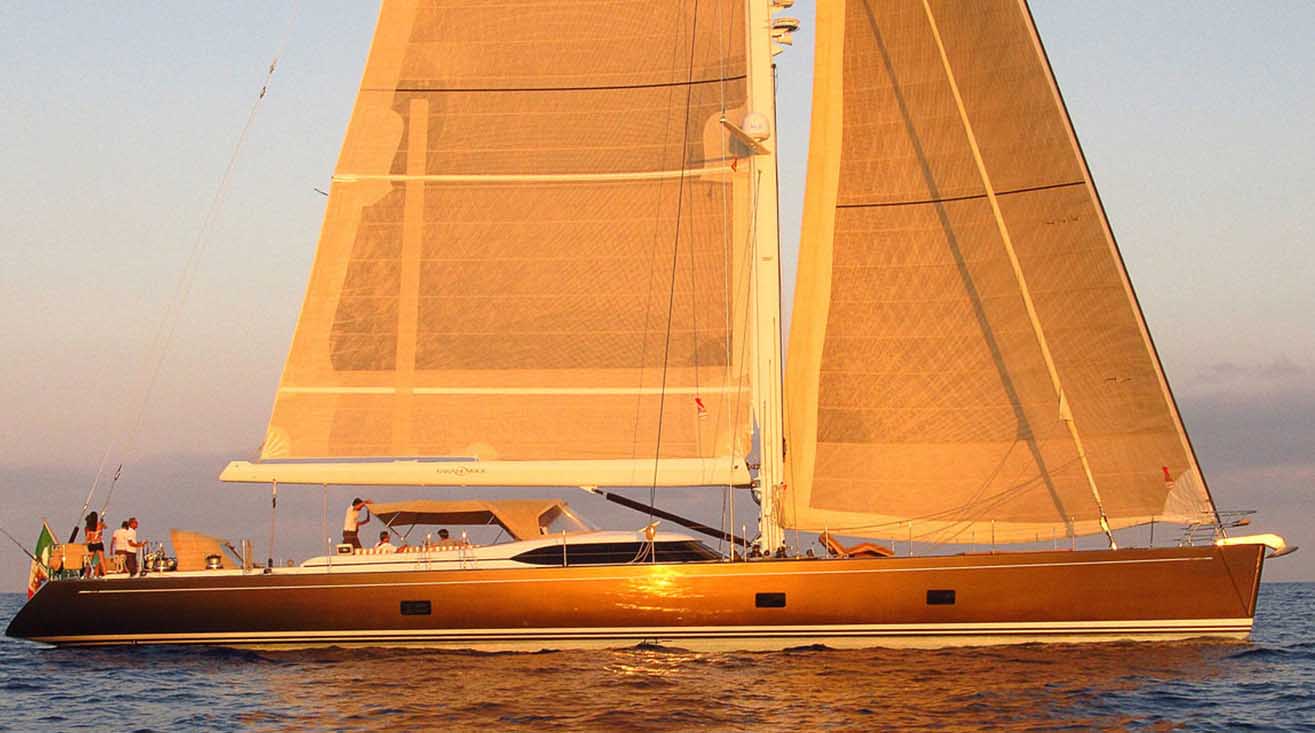

Length : 30.2 m / Passengers : 8
Special features : - One of the most elegant SW100- Excellent and experienced crew- Very elegant interiors- Available in West and East Med- Large outdoor spaceTender: 4.30...
- Receive the brochure of this yacht
- FR +33 AC +247 AD +376 AE +971 AF +93 AG +1 AI +1 AL +355 AM +374 AO +244 AR +54 AS +1 AT +43 AU +61 AW +297 AX +358 AZ +994 BA +387 BB +1 BD +880 BE +32 BF +226 BG +359 BH +973 BI +257 BJ +229 BL +590 BM +1 BN +673 BO +591 BQ +599 BR +55 BS +1 BT +975 BW +267 BY +375 BZ +501 CA +1 CC +61 CD +243 CF +236 CG +242 CH +41 CI +225 CK +682 CL +56 CM +237 CN +86 CO +57 CR +506 CU +53 CV +238 CW +599 CX +61 CY +357 CZ +420 DE +49 DJ +253 DK +45 DM +1 DO +1 DZ +213 EC +593 EE +372 EG +20 EH +212 ER +291 ES +34 ET +251 FI +358 FJ +679 FK +500 FM +691 FO +298 FR +33 GA +241 GB +44 GD +1 GE +995 GF +594 GG +44 GH +233 GI +350 GL +299 GM +220 GN +224 GP +590 GR +30 GT +502 GU +1 GW +245 GY +592 HK +852 HN +504 HR +385 HT +509 HU +36 ID +62 IE +353 IL +972 IM +44 IN +91 IQ +964 IR +98 IS +354 IT +39 JE +44 JM +1 JO +962 JP +81 KE +254 KG +996 KH +855 KI +686 KM +269 KN +1 KP +850 KR +82 KW +965 KY +1 KZ +7 LA +856 LB +961 LC +1 LI +423 LK +94 LR +231 LS +266 LT +370 LU +352 LV +371 LY +218 MA +212 MC +377 MD +373 ME +382 MF +590 MG +261 MH +692 MK +389 ML +223 MM +95 MN +976 MO +853 MP +1 MQ +596 MR +222 MS +1 MT +356 MU +230 MV +960 MW +265 MX +52 MY +60 MZ +258 NA +264 NC +687 NE +227 NF +672 NG +234 NI +505 NL +31 NO +47 NP +977 NR +674 NU +683 NZ +64 OM +968 PA +507 PE +51 PF +689 PG +675 PH +63 PK +92 PL +48 PM +508 PR +1 PS +970 PT +351 PW +680 PY +595 QA +974 RE +262 RO +40 RS +381 RU +7 RW +250 SA +966 SB +677 SC +248 SD +249 SE +46 SG +65 SH +290 SI +386 SJ +47 SK +421 SL +232 SM +378 SN +221 SO +252 SR +597 SS +211 ST +239 SV +503 SX +1 SY +963 SZ +268 TC +1 TD +235 TG +228 TH +66 TJ +992 TL +670 TM +993 TN +216 TO +676 TR +90 TT +1 TV +688 TW +886 TZ +255 UA +380 UG +256 US +1 UY +598 UZ +998 VA +39 VC +1 VE +58 VG +1 VI +1 VN +84 VU +678 WF +681 WS +685 XK +383 YE +967 YT +262 ZA +27 ZM +260 ZW +263
Thanks for contacting us. We will get back to you shortly.
Une erreur s'est produite. Merci de rééssayer.
Contact us
Send message

About Amadeus
Charter rates.
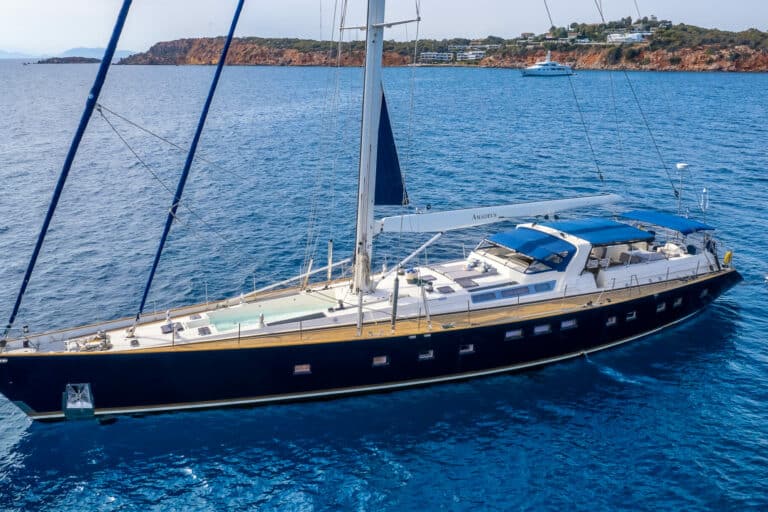

specifications
- Length 33.52M (110′)
- Beam 7.53M (25′-4″)
Builder Dynamique Yachts
- Year of build 1996
Tenders & Toys
- Fishing equipment
- inflatable canoes
- On deck pool
- Snorkeling gear
Talk to our experts
Looking for a yacht charter? We’re happy to help! Please call the number below, send an email or contact us via WhatsApp.

Maxim Beckers

Carl-Antoine Saverys
Share this yacht, related yachts for charter.
© EXMAR YACHTING | All rights reserved
Subscribe to receive the latest news
Contact our team.

Sales Department

Crewed Department

Bareboat Department
- Sailing Yachts
- Motor Sailers
- Motor Yachts
- Our bareboat bases in Greece
- Yacht Management
- Technical Support / After-sales services
- Concierge services
Vernicos Yachts
Get in Touch
Sales Department: [email protected]
Crewed Department: [email protected]
Bareboat Department: [email protected]
Other: [email protected]
T : +30 210 9896 000
Ideas for you

BALI Catsmart

BAVARIA Cruiser 51

Private: FERRETTI 760

Lagoon 450F “ZACAPA”

LAGOON 42 “ALEXANDROS”

LAGOON 50 “VICTORIA”

BARACUDA VALLETTA

Bareboat yacht charter in Greece

Best beaches for Mykonos boat trips

Boats for sale in Greece

Bareboat Yachts

Bareboat Bases
or chat with an expert
Contact our charter team
Crewed Team

Send me a message
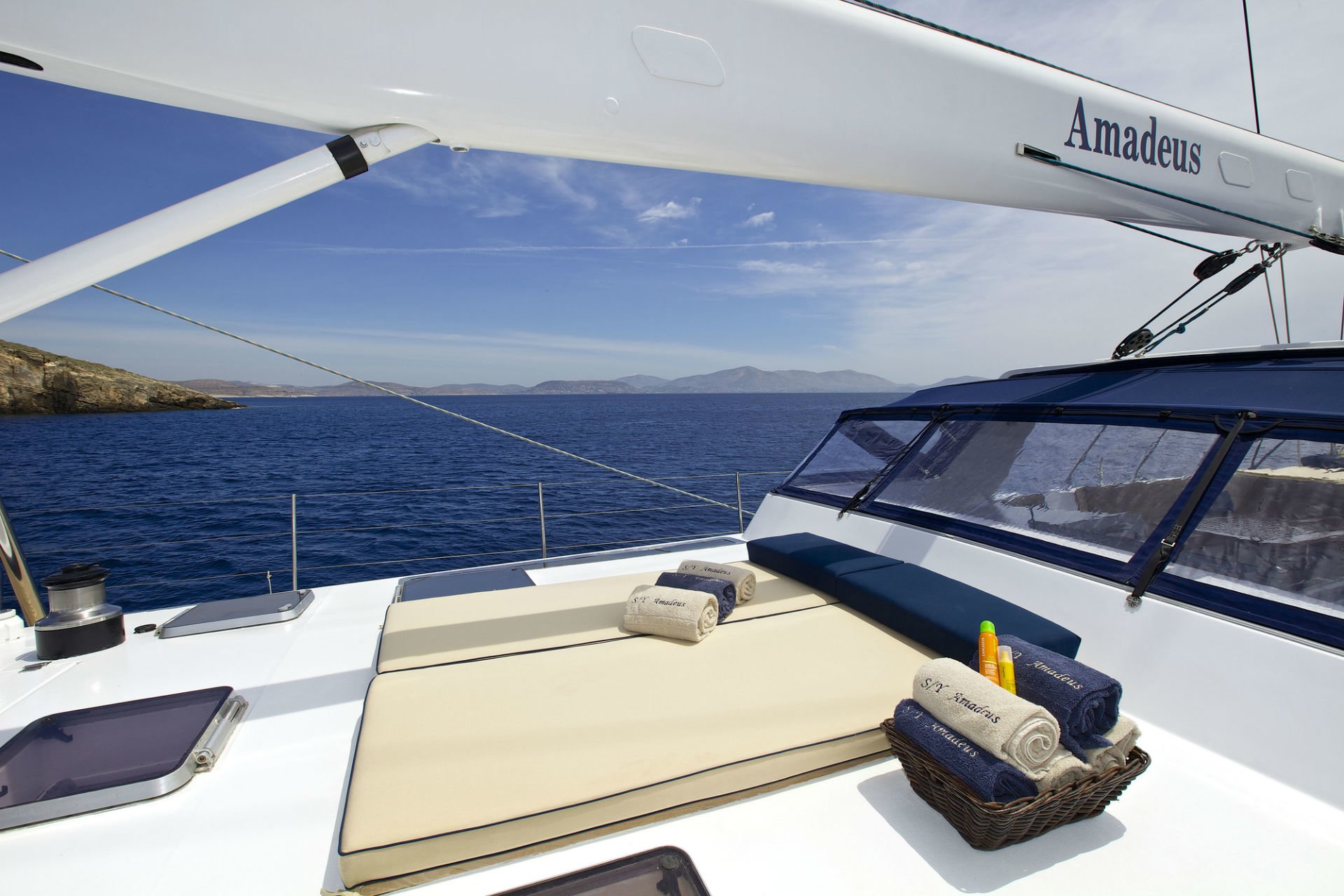

Built by the famous Dynamique Yachts shipyard, and having undergone a total refit in 2014, S/Y Amadeus was designed to please the most demanding of yachtsmen.
Built for smooth sailing, this elegant cutter rigged sloop has a sleek hull design, comfortably reaching top speeds of 12 knots and ensuring excellent sailing performance. Accommodation is offered for up to 12 guests in 5 spacious cabins (one master cabin, two identical double cabins with additional single bunks, two identical twin cabins) all with en suite facilities and audio/visual entertainment.

General Description
Carian Coast, Ionian Islands
Dynamique Yachts
1996 / 2018
Rates (MYBA Terms: + ALL)
45,500 € per week
35,000 € per week
2018 Nuvorania tender 4.60m Outboard EVINRUDE 75hp Splash pool Water Skis (adult and kids) Mono Ski Wakeboard
2 Tubes Inflatable Kayak Fishing Gear Snorkeling Equipment 4 Yoga mats
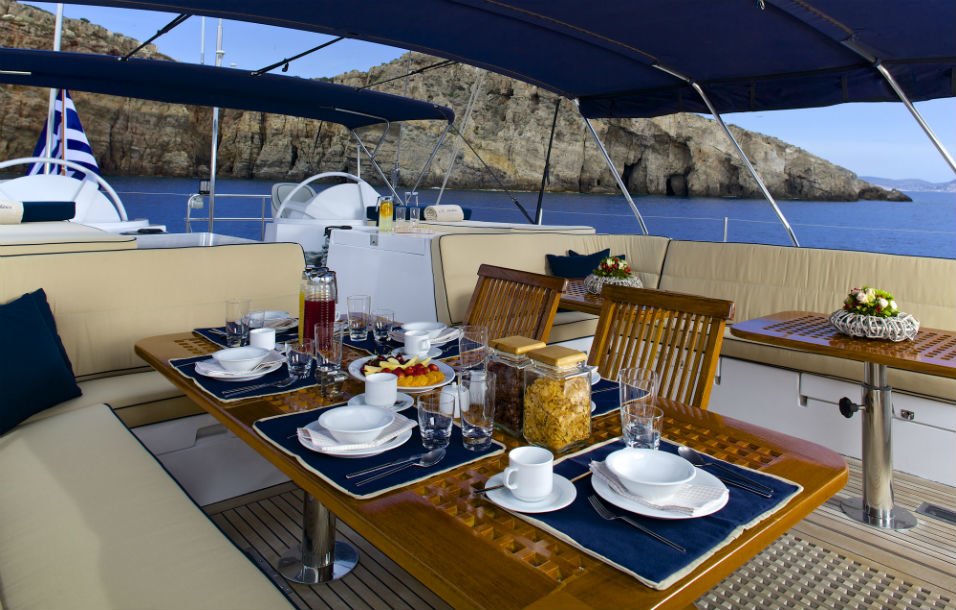

Destinations

Carian Coast
Superb historical sites set in magnificent scenery

Ionian Islands
Unforgettable Sailing Holidays
Request Availability
Get in touch for the yacht: AMADEUS
Download Brochure
Download brochure for the yacht
Add to Favourites
Keep track of your preferred yachts and access them quickly whenever you revisit our website.
AMADEUS Dynamique Yachts SA
- Inspiration
AMADEUS has 2 Photos

Amadeus News

Reduced charter rate offered by 44m ...
Similar yachts.

SHAMOUN | From US$ 65,100/wk
- Yachts >
- All Yachts >
- All Sail Boats Over 100ft/30m >
If you have any questions about the AMADEUS information page below please contact us .
A General Description of Sailing Yacht AMADEUS
AMADEUS was previously registered as project/yacht name Amadeus 1er. This 33 metre (109 ft) luxury yacht was built by Dynamique Yachts in 1991. Sailing Yacht AMADEUS is a well proportioned superyacht. The yacht is a modern sloop with a cutter rig. The naval architecture office whom authored the design work on this ship was Philippe Briand. Luxury yacht AMADEUS is a quality yacht that is able to accommodate as many as 12 guests on board and has a total of 5 crew members.
Sailing yacht AMADEUS was built by the famous Dynamique Yachts shipyard .The yacht features superb sailing characteristics which are complimented by her spacious interior and abundant deck space. Sailing sloop AMADEUS can accommodate 10 passengers in five cabins. With one large master stateroom and four additional cabins which are all air conditioned and have en suite bathrooms. She also has two separate salons and a full dining room. The aft deck is fully covered with seating. The fore deck has an unique pool on deck and swimming in the sea is made accessible by a large swim aft platform.
The Construction & Naval Architecture relating to Luxury Yacht AMADEUS
Philippe Briand was the naval architect firm involved in the formal nautical design work for AMADEUS. Also the company Philippe Briand skillfully collaborated on this undertaking. In 1991 she was actually launched to triumph in Marans and following sea trials and final completion was afterwards passed on to the yacht owner. Dynamique Yachts completed their new build sailing yacht in France. A reasonable proportion is brought about with a maximum beam (width) of 7.5 metres / 24.6 feet. With a 3.6m (11.8ft) draught (maximum depth) she is reasonably deep. The material composite was used in the building of the hull of the sailing yacht. Her superstructure above deck is built with the use of composite. Over the deck of AMADEUS she is 32.7 (107.3 ft) in length. In 2004 extra refitting and modernisation was also finished.
Engines & Speed For S/Y AMADEUS:
She is driven by twin screw propellers. The main engine of the ship gives 375 horse power (or 276 kilowatts). She is equiped with 2 engines. The combined thrust for the boat is therefore 750 HP / 552 KW.
On board Superyacht AMADEUS She has The Following Guest Accommodation Format:
Bestowing bedding for a maximum of 12 yacht guests sleeping aboard, the AMADEUS accommodates them in style. Normally the vessel requires approximately 5 professional crewmembers to run.
A List of the Specifications of the AMADEUS:
Further information on the yacht.
Condaria is the company that installed the A/C on the yacht. AMADEUS features a teak deck.
AMADEUS Disclaimer:
The luxury yacht AMADEUS displayed on this page is merely informational and she is not necessarily available for yacht charter or for sale, nor is she represented or marketed in anyway by CharterWorld. This web page and the superyacht information contained herein is not contractual. All yacht specifications and informations are displayed in good faith but CharterWorld does not warrant or assume any legal liability or responsibility for the current accuracy, completeness, validity, or usefulness of any superyacht information and/or images displayed. All boat information is subject to change without prior notice and may not be current.
Quick Enquiry
"Indeed we believe that the first function of a sailing yacht is the aesthetics and we spent a lot of time in refining the lines during the project." - "I understood very young that to win a race you have to have the best boat, and so I started to be interested about the technology and the design of the boat." - Philippe Briand

Yan Yelken | From EUR€ 28,980/wk
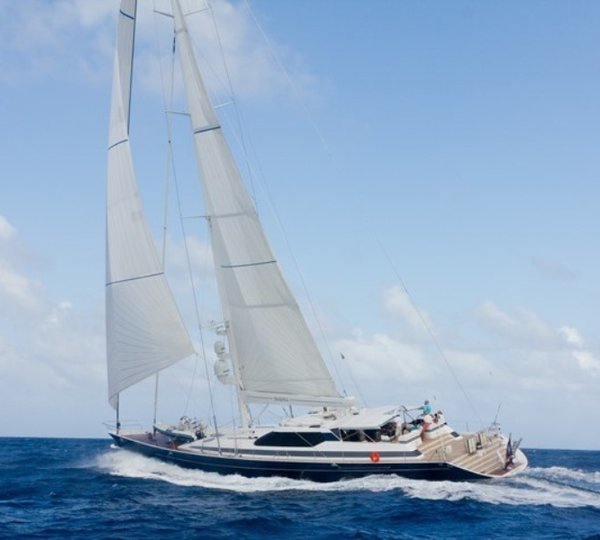

Seaquell | From US$ 40,000/wk

Shanti | From EUR€ 28,000/wk
- Yachts for sale
- Yachts for charter
- Brokerage News

- Yacht Harbour
- Yacht Amadeus
Contact agent, specifications, similar yachts.

New listings

- USA:-1.866.492.4768
- UK:-0800.011.2492
- How We Help Clients
- How to book a charter?
- Why Use Our Company
- Where our Charters Go
- Why Charter a Yacht
- Decades of Experience
- Meet our staff
- Contact us now
- Search charter yachts online
- What type of yacht should I charter?
- About Luxury Yacht Charter
- Charter a Mega Yacht
- Charter a Motor Yacht
- Charter a Crewed Catamaran
- Charter a Sailboat
- Yacht charter Blog
- About Caribbean Yacht Charters
- Virgin Islands
- Leeward Islands
- Windward Islands
- Yachts in the Caribbean
- About Bahamas Yacht Charters
- Bahamas weather
- Yachts in the Bahamas
- Western Mediterranean Yacht Charters
- Eastern Mediterranean Charters
- Browse Yachts in the Mediterranean
- South of France
- Spain, Mallorca, Ibiza
- Italy, Sicily, Naples & Amalfi
- Corsica and Sardinia
- Pacific Islands
- Sample Charter Itineraries
- Destinations Blog
- How to choose a yacht charter broker?
- How to book a yacht charter?
- What is special about yacht charter?
- What yacht charter costs are there ?
- Are there all inclusive charters?
- Why charter a yacht?
- What kinds of yacht can I charter?
- Where do yacht charters go?
- What defines luxury yacht charter?
- How to rent a yacht?
- How We Help
- 5 Common Yacht Charter Questions
- How to choose the right yacht?
- When is the best time to charter?
- All Yacht Charter Destinations
- What can you do on a yachting vacation?
- What to expect on a luxury charter?
- What contracts are used to book?
- Even more questions about chartering a yacht
- Crewed charter reviews
- Caribbean Reviews
- BVI Reviews
- Bahamas Reviews
- Mediterranean Reviews
- Email or Call Us

AMADEUS 110' Fully Crewed Sailing Yacht
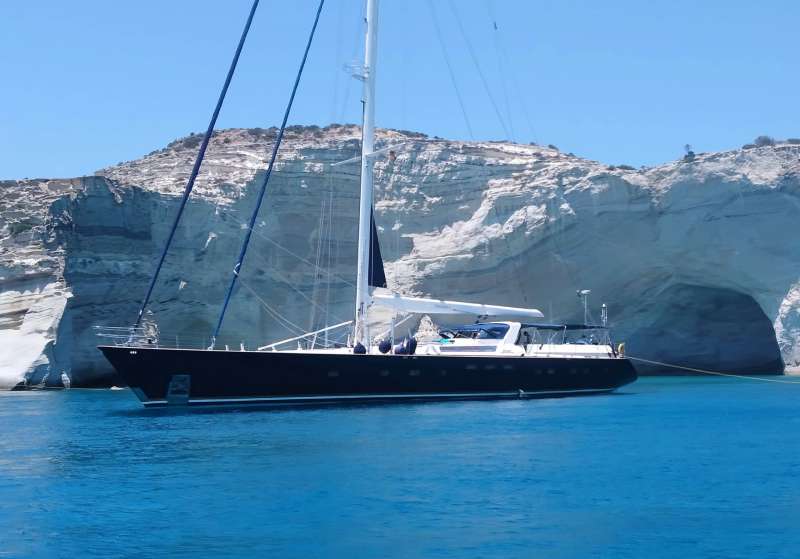

- Summer Locations: Greece , Turkey Winter Locations: Greece
- Max Guests : 12 Cabins : 5 Crew : 6
- Starting at : EUR €39,500 (approx. $45,820 USD )
Charter rates do not include expenses or taxes
Her master cabin features a walk around king bed, desk/vanity, and en-suite bathroom. Additionally, there are two guest cabins each with a queen bed convertible to two twins, and two guest cabins each with a queen bed and twin bed. Each guest cabin has an en-suite.
Her main salon has a spacious, contoured conversational area, along with a large, flatscreen T.V. The aft deck features al fresco dining with Bimini top. Up on deck there are sun pads and a splash pool for you and your guests to enjoy.
Watersports offered include a 15 foot tender with 75hp engine, water skis for adults and children, tube, wakeboard, kayak, fishing gear, snorkeling gear, and rendezvous diving.
Additional Images
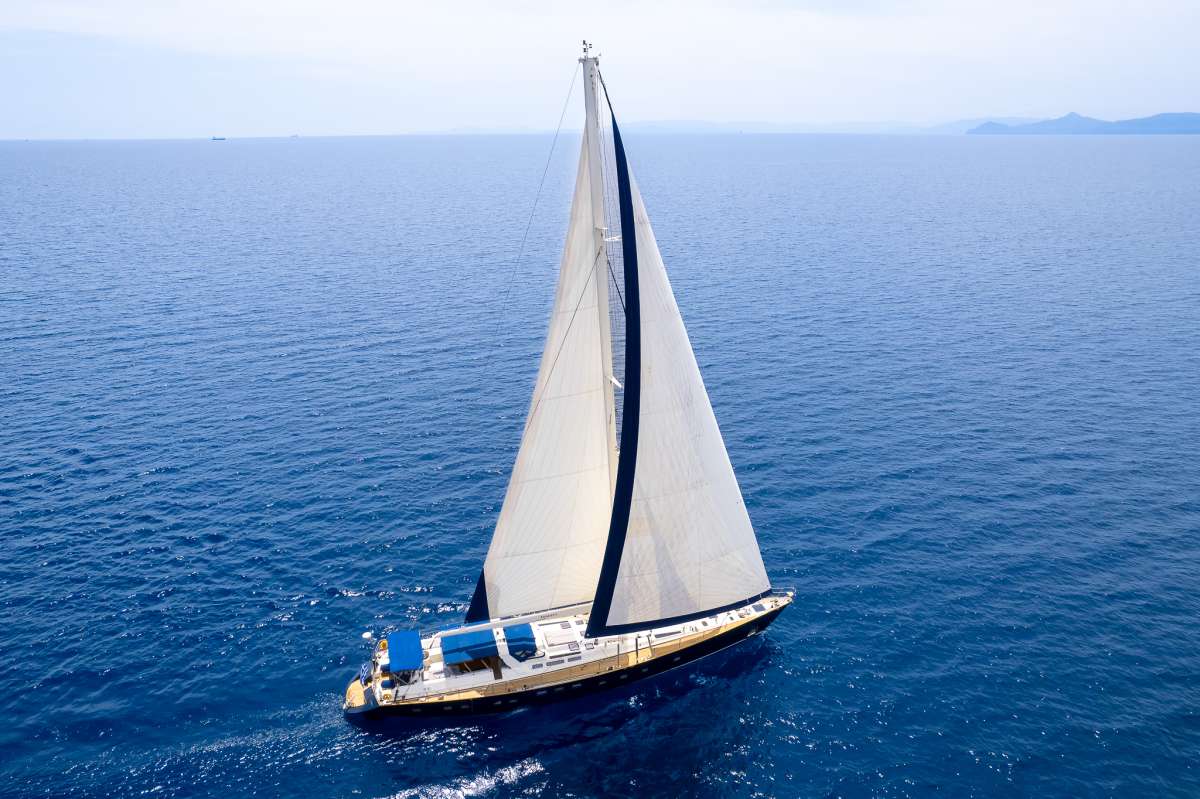

Does this yacht interest you?
Let us know a few details below, we'll check availability and answer all your questions:.
Even faster answer? Call Toll Free from USA/Canada: 1 866.492.4768 , Direct 1.954.448.5053
Send Message
Additional Sailing Yachts with 5 cabins:

LONG ISLAND 127' sailing yacht
Can sleep up to 10 guests in 5 staterooms Weekly rate starts at: EUR €45,500 (approx. $52,780 USD)
Summer Locations: Turkey
See additional pictures and info about LONG ISLAND » Contact us about LONG ISLAND »

TIGRA 124' sailing yacht
Can sleep up to 10 guests in 5 staterooms Weekly rate starts at: EUR €32,000 (approx. $37,120 USD)
Winter Locations: Greece , Turkey
Summer Locations: Greece , Turkey
See additional pictures and info about TIGRA » Contact us about TIGRA »

ALTHEA 122' sailing yacht
Can sleep up to 10 guests in 5 staterooms Weekly rate starts at: EUR €39,500 (approx. $45,820 USD)
Winter Locations: Greece
Summer Locations: Greece
See additional pictures and info about ALTHEA » Contact us about ALTHEA »

AMADEUS 110' sailing yacht
Can sleep up to 12 guests in 5 staterooms Weekly rate starts at: EUR €39,500 (approx. $45,820 USD)
See additional pictures and info about AMADEUS » Contact us about AMADEUS »
Yacht Name Search
Do you have a particular yacht in mind? We likely have it online and if not, email or call us for details. Search for it online by name here:
See Charter Yachts by region:
- Yachts in the Mediterranean
- Why you should choose us
Read more about charter yacht types:
- Mega Yachts
- Sailing yachts
International Yacht Charter Group Inc. does not guarantee the accuracy of any information or images displayed. Both are subject to change and may not be current. All information contained herein is not contractual. Continue reading for more details: 2003 - 2023 © All Rights Reserved. Privacy Policy Site map

Sailing Yacht | Amadeus

Fuel Capacity
Water capacity, sailing yacht amadeus | luxury crewed monohull.
Sailing yacht AMADEUS is a stunning 110 ft yacht available for charter in Greece. With a clean, spacious teak deck and a unique outdoor saloon that can seat up to 12 guests across two tables, it’s the perfect place for outdoor dining and entertainment. The deck saloon can also be enclosed with a special canopy and roll-up windows, making it suitable for use in all weather conditions. At the front of the boat, there’s a splash pool and sunbathing area with a removable awning for shade.
Inside the boat, a staircase from the cockpit leads to a well-lit and roomy saloon area with plenty of seating, including a formal dining area, bar, LCD TV, entertainment center, iPod dock station, and Playstation. Sailing Yacht AMADEUS can accommodate 10-12 guests in five large cabins, including a full-width master stateroom and two double cabins, each with an extra single bed. The two twin cabins can also be converted to doubles upon request, making her the only sailboat on the Greek market with five double beds.
To add to the fun, sailing yacht AMADEUS also comes with a range of water toys, including adult and children’s water skis, tubes, inflatable canoes, wakeboard, fishing rod, and snorkeling gear. She was built by Dynamique Yachts in 1996 and underwent a refit in 2014/2018.
ACCOMMODATION
- 1 Master cabin
- 2 VIP cabins
- 2 Twin cabins
Accomodation is offered for 10 -12 guests in 5 spacious cabins: Master cabin forward features a double bed, vanity unit and generous storage facilities, as well as audio/visual entertainment. The en-suite includess a large bath tub, shower and separate WC. Two identical double cabins with additional single bunks situated forward. Two identical double cabins situated aft which can be convertible to twins. (Total 5 double beds) All cabins with en suite facilities and audio/visual entertainment.
A professional crew of 5-6 members are accommodated in separate quarters.
Note that these specifications may vary slightly depending on the specific yacht’s configuration and modifications made by the owner.
New rigging BSI Denmark (2018) New North Sails (2016) Nuvorania tender 4.60m with a New Outboard EVINRUDE E tec 75hp Engines: 2 x 320HP Perkins Rolls Royce Generators: 1 Northern Lights x 25KW, 1 ONAN x 60KW Cruising speed: 10 Fuel consumption: 120 Litres/Hr Generators: 250 Liters/Day
Navigation and safety
- Outside GPS plotter
- Bow thruster
- Electric winches
- Classic mainsail
Saloon and cabins
- Air conditioning
- Coffee machine
- Kitchen utensils
- Pillows and blankets
Entertainment
- LCD 27″ TV, VCR, & CD entertainment systems in Saloon
- X-Box ONE X & Playstation 3 in Saloon
- Master cabin: TV, CD, & DVD entertainment systems
- Double cabins: TV, CD, & DVD entertainment systems
- Twin cabins (convertible to Doubles):TV, CD, & DVD entertainment systems
Water Sports
- Tender & Toys:
- 2018 Nuvorania tender 4.60m with a New Outboard EVINRUDE E tec75hp
- Water Skis (adult and kids)
- Inflatable Kayak
- Fishing Gear
- Snorkelling Equipment
- 4 Yoga mats
- Bathing platform
- Stand Up Paddle
Weekly price: €35,000 – €42,500
Low Season | High Season
Charter Type: Crewed
Berths: 10-12 guests, sailing area: argo-saronic, departure ports: alimos, athens, send us your request, personal information, booking information.
Odyssey Sailing is registered and bonded with the Greek National Tourist Organisation (GNTO – EOT) and is a member of the Hellenic Yacht Brokers Association (HYBA).
SOCIAL MEDIA
Useful links.
Antonopoulou 158D Volos, 38221, Greece
JOIN OUR NEWSLETTER
By subscribing to the Odyssey Sailing newsletter you agree to allow us collecting information about your open and click rates in order for us to develop further newsletter campaigns for our subscribers.

Length 33,5m / 109′ ft.
Built/Last Refit 2009/2021
Weekly rate Low € 35.000
Weekly rate High € 45.500
Accommodation
Luxury yacht AMADEUS can accommodate up to 12 guests in 5 cabins. One Master cabin with small desk and en suite facilities (wc separate from bath and shower). Two double cabins with additional single bed and two twin cabins. All cabins with en suite facilities.
Charter Amenities and Extras
S/Y AMADEUS has the following extras onboard: Tenders & Toys include Novourania tender 4.20m with YAMAHA X 70hp plus, MERCURY x 10hp, Water Skis, Mono Ski, Wakeboard, 2 Tubes, Fishing Gear, Snorkelling Equipment, Communications include VHF-GMDSS, Cellular phone, Radar, E-Mail/internet access, Audio Visual Equipment and Deck Facilities include Master cabin: TV, CD, & DVD entertainment system, Double cabins: TV, CD, & DVD entertainment system, Twin cabins: TV, CD, & DVD entertainment system, Saloon: LCD 27’ TV, VCR, & CD entertainment system.

Leave a comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
By using this form you agree with the storage and handling of your data by this website. *
This site uses functional cookies and external scripts to improve your experience.
Privacy settings
Privacy Settings
This site uses functional cookies and external scripts to improve your experience. Which cookies and scripts are used and how they impact your visit is specified on the left. You may change your settings at any time. Your choices will not impact your visit.
NOTE: These settings will only apply to the browser and device you are currently using.
Cookie Consent
This site uses cookies to offer you a better browsing experience. By using Hellas Yachting, you agree to our Privacy Policy, including cookie policy.

Discover more!
Sign up to receive inspiration on Yachting, the Mediterranean Lifestyle & Special Offers, the Valef way
*By completing this form you are signing up to receive our emails and can unsubscribe at any time

Charter the AMADEUS
AMADEUS is a 110-foot sailing yacht that can accommodate ten to twelve passengers in five staterooms as follows: a spacious Owner’s stateroom with a double bed, a vanity and an entertainment unit including TV, DVD and music system; two cabins with a double bed and an additional single bed; two cabins with two twin beds each. All staterooms have en suite bathrooms, a TV, DVD and CD player. There are two separate salons onboard as well as a full dining room. The aft deck is fully covered and has seating for all guests to dine in the open air. Forward of the cockpit is a lovely cushioned area for sunning and an unusual pool is found in the fore of the yacht. Swimming in the sea is made accessible by the large swim aft platform.
Image Gallery

Yacht Specifications:
Length: (33.26m/109.11ft), yacht type: sailing yachts, beam: 24.7 ft, built: 1996 | 2018, draft: 12.10 ft, builder: dynamic, guests: 10-12, engines: 2 x 320hp perkins rolls royce, generators: 1 northern lights x 25kw, 1 onan x 60kw, fuel: 120 ltrs/hr, configuration: 1 master cabin, 2 doubles cabins with a single bed each, 2 twin cabins, cruising speed: 10 knots/hr.
(*All specifications are given in good faith and offered for informational purposes only. Yacht inventory, specifications and charter rates are subject to change without prior notice.*)
Recreational Equipment
• NEW Novorania tender 4.60m with NEW EVINRUDE 75hp plus MERCURY x 10hp • Wakeboard • Water Skis (adult and kids), Mono Ski • 2 Tubes • Kayak • 4 Yoga mats • Fishing Gear Snorkelling Equipment
Weekly Rates
High season: €42,500/week, med season: €37,500/week, low season: €35,000/week.
(*Rates are given based on a week charter / Rates are subject to change without notice*)
Customer Reviews
I could no joke die tomorrow and be a happy man. ~ Matthew F.
Although we have traveled just about all over the world, this was probably our best vacation ever. We will be back! ~ Louise Z.
Our trip was FABULOUS! More than exceeded expectations. ~ Anne G.
We have just completed a vacation that I have thought about for a lot of years. Thank you all for making a dream come true!!!! ~ Mae & Bill M.
Everyone is still talking about the trip and I cannot imagine it going any better. ~ Jack D.
Interested in this yacht?
Let us create a custom tailored experience for you..
Country you Live In United States Canada Mexico United Kingdom Afghanistan Albania Algeria American Samoa Andorra Angola Anguilla Antigua and Barbuda Argentina Armenia Armenia Aruba Australia Austria Azerbaijan Azerbaijan Bahamas Bahrain Bangladesh Barbados Belarus Belgium Belize Benin Bermuda Bhutan Bolivia Bonaire Bosnia and Herzegovina Botswana Bouvet Island (Bouvetoya) Brazil British Indian Ocean Territory (Chagos Archipelago) British Virgin Islands Brunei Darussalam Bulgaria Burkina Faso Burundi Cambodia Cameroon Cape Verde Cayman Islands Central African Republic Chad Chile China Christmas Island Cocos (Keeling) Islands Colombia Comoros Congo Congo Cook Islands Costa Rica Cote d'Ivoire Croatia Cuba Curaçao Cyprus Cyprus Czech Republic Denmark Djibouti Dominica Dominican Republic Ecuador Egypt El Salvador Equatorial Guinea Eritrea Estonia Ethiopia Falkland Islands (Malvinas) Faroe Islands Fiji Finland France French Guiana French Polynesia French Southern Territories Gabon Gambia Georgia Georgia Germany Ghana Gibraltar Greece Greenland Grenada Guadeloupe Guam Guatemala Guernsey Guinea Guinea-Bissau Guyana Haiti Heard Island and McDonald Islands Holy See (Vatican City State) Honduras Hong Kong Hungary Iceland India Indonesia Iran Iraq Ireland Isle of Man Israel Italy Jamaica Japan Jersey Jordan Kazakhstan Kazakhstan Kenya Kiribati Korea Korea Kuwait Kyrgyz Republic Lao People's Democratic Republic Latvia Lebanon Lesotho Liberia Libyan Arab Jamahiriya Liechtenstein Lithuania Luxembourg Macao Macedonia Madagascar Malawi Malaysia Maldives Mali Malta Marshall Islands Martinique Mauritania Mauritius Mayotte Micronesia Moldova Monaco Mongolia Montenegro Montserrat Morocco Mozambique Myanmar Namibia Nauru Nepal Netherlands Netherlands Antilles New Caledonia New Zealand Nicaragua Niger Nigeria Niue Norfolk Island Northern Mariana Islands Norway Oman Pakistan Palau Palestinian Territory Panama Papua New Guinea Paraguay Peru Philippines Pitcairn Islands Poland Portugal Puerto Rico Qatar Reunion Romania Russian Federation Rwanda Saint Barthelemy Saint Helena Saint Kitts and Nevis Saint Lucia Saint Martin Saint Pierre and Miquelon Saint Vincent and the Grenadines Samoa San Marino Sao Tome and Principe Saudi Arabia Senegal Serbia Seychelles Sierra Leone Singapore Sint Maarten (Netherlands) Slovakia (Slovak Republic) Slovenia Solomon Islands Somalia South Africa South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands Spain Sri Lanka Sudan Suriname Svalbard & Jan Mayen Islands Swaziland Sweden Switzerland Syrian Arab Republic Taiwan Tajikistan Tanzania Thailand Timor-Leste Togo Tokelau Tonga Trinidad and Tobago Tunisia Turkey Turkey Turkmenistan Turks and Caicos Islands Tuvalu U.S. Virgin Islands U.S. Minor Outlying Islands Uganda Ukraine United Arab Emirates Uruguay Uzbekistan Vanuatu Venezuela Vietnam Wallis and Futuna Western Sahara Yemen Zambia Zimbabwe
Destination Greece Turkey Montenegro and Croatia West Mediterranean
Number of Guests 1 2 - 4 4 - 6 6 - 8 8 - 10 10 - 12 12+
Number of Cabins 3 Cabin 4 Cabins 5 Cabins 6 Cabins 7 Cabins 8+ Cabins
Yacht Length 45ft - 70ft 70ft - 110ft 110ft - 130ft 130ft - 160ft 160ft +
Weekly Rate < €14,000 €14,000 - 35,000€ 35,000€ - 49,000€ 49,000€ - 70,000€ 70,000€ - 105,000€ 105,000€ - 175,000€ 175,000€ +
Write your Message
I want to receive news about Valef Yachts, yachts & charters and Mediterranean travel inspiration

Rent the Yacht, Own the feeling.

Call Us or fill the form
+90 216 900 28 62.
Don't hesitate to contact us!
Working time
Mon - Fri: 9:00 - 18:00 / Closed on Weekends
Company Headquarters
DEGIRMENDERE MAH. SANAYI CAD. 8 SK.7
KUSADASI 09400 AYDIN TURKIYE
Only for Carriers in the US , For loads, Please enter the required information.
Our offices.
Değirmendere Mah. Sanayi Cad.8
Sk. No:7 Kuşadası 09400 Aydın
+ (90) 256 340 03 40
[email protected]
Mon - Fri: 9:00 - 18:00 Closed on Weekends
Drive to us Now
Küçükbakkalköy Mah. Fevzipaşa Cad.
Bozkır Sok. No:1 ,K:3 D:15 Ataşehir 34750 Istanbul
+ (90) 216 900 28 62
+(90) 216 576 47 90
2, Stroitelny Lane, Elektrostal , Moscow
+7 (499) 390 35 04
Drive to our office
128 City Road , London EC1V 2NX
+44 20 4577 1271
Mon - Fri: 9:30 - 17:00 Closed on Weekends
26 Seaman Ave Hempstead 11550 New York
+1 646 980 28 04
Humberto 1 985,Piso 2,Ofic 222
Constitucion Capital Federal CP 1103
Buenos Aires
+54 11 52 371 371
Mon - Fri: 9:00 - 17:30 Closed on Weekends

Please use a modern browser to view this website. Some elements might not work as expected when using Internet Explorer.
- Landing Page
- Luxury Yacht Vacation Types
- Corporate Yacht Charter
- Tailor Made Vacations
- Luxury Exploration Vacations
- View All 3565
- Classic Yachts
- Catamaran Yachts
- Filter By Destination
- More Filters
- Latest Reviews
- Charter Special Offers
- Destination Guides
- Inspiration & Features
- Mediterranean Charter Yachts
- France Charter Yachts
- Italy Charter Yachts
- Croatia Charter Yachts
- Greece Charter Yachts
- Turkey Charter Yachts
- Bahamas Charter Yachts
- Caribbean Charter Yachts
- Australia Charter Yachts
- Thailand Charter Yachts
- Dubai Charter Yachts
- Destination News
- New To Fleet
- Charter Fleet Updates
- Special Offers
- Industry News
- Yacht Shows
- Corporate Charter
- Finding a Yacht Broker
- Charter Preferences
- Questions & Answers
- Add my yacht

View More Photos
- Luxury Charter Yachts
- Motor Yachts for Charter
- Amenities & Toys
- Rates & Regions
- + Shortlist
AMADEUS YACHT CHARTER
21.95m / 72' sunseeker 2008.
- Previous Yacht
Cabin Configuration
Special Features:
- Cruising speed of 22 knots
- Sleeps 6 guests
- Williams Jet RIB
Luxury yacht Amadeus is the perfect charter platform for yachting vacations spent entertaining in style
The 21.95m/72' motor yacht 'Amadeus' by the British shipyard Sunseeker offers flexible accommodation for up to 6 guests in 3 cabins.
If you're looking for a family-friendly yacht with plenty of onboard amenities, Amadeus is the perfect choice, promising superb charter vacations whatever the destination.
Guest Accommodation
Built in 2008, Amadeus offers guest accommodation for up to 6 guests in 3 suites comprising a master suite, one VIP cabin and one twin cabin. There are 4 beds in total, including 1 queen, 1 double and 2 singles. She is also capable of carrying up to 2 crew onboard to ensure a relaxed luxury yacht charter experience.
Onboard Comfort & Entertainment
Whatever your activities on your charter, you'll find some impressive features are seamlessly integrated to help you, notably Wi-Fi connectivity, allowing you to stay connected at all times, should you wish. Guests will experience complete comfort while chartering thanks to air conditioning.
Performance & Range
Powered by twin MAN engines, she comfortably cruises at 22 knots, reaches a maximum speed of 35 knots with a range of up to 250 nautical miles.
Onboard Amadeus has a range of toys and accessories to keep you and your guests entertained on the water throughout your stay. Principle among these are Super wid waterskis that are hugely entertaining whether you are a beginner or a seasoned pro. Another excellent feature are O' Brien Ace wakeboards so guests can show off at speed. When it's time to travel from land to see, it couldn't be easier with a Williams Jet RIB.
Motor yacht Amadeus boasts an impressive array of outstanding amenities for truly out-of-this-world charter vacations that you’ll never forget.
TESTIMONIALS
There are currently no testimonials for Amadeus, please provide .
Amadeus Photos

Amenities & Entertainment
For your relaxation and entertainment Amadeus has the following facilities, for more details please speak to your yacht charter broker.
Amadeus is reported to be available to Charter with the following recreation facilities:
- 1 x Williams 325 Jet RIB 100 HP engine
For a full list of all available amenities & entertainment facilities, or price to hire additional equipment please contact your broker.
- + shortlist
For a full list of all available amenities & entertainment facilities, or price to hire additional equipment please contact your broker.
'Amadeus' Charter Rates & Destinations
Please contact your charter broker for a quote or check availability .
Charter Amadeus
To charter this luxury yacht contact your charter broker , or we can help you.
To charter this luxury yacht contact your charter broker or
Update your yacht
Yacht Owner, Captain or Central Agents - Send us latest Photos, Charter Rates or Corrections Contact Us
SIMILAR YACHTS FOR CHARTER

d'Artagnan
20m | Ferretti Yachts
from $25,000 p/week ♦︎

21m | Azimut
from $27,000 p/week

21m | Ferretti Yachts
from $23,000 p/week ♦︎

21m | Aicon
from $17,000 p/week ♦︎

22m | Sunseeker
from $28,000 p/week ♦︎

20m | Galeon
from $13,000 p/week ♦︎

22m | Baia Yachts
from $29,000 p/week ♦︎

P'tite Bouille
21m | Princess
from $32,000 p/week ♦︎

Saint George
20m | Sunseeker
POA ♦︎

21m | President
from $24,000 p/week ♦︎
NOTE to U.S. Customs & Border Protection
Specification
- Share on Facebook
- Share Yacht
SIMILAR LUXURY CHARTER YACHTS
Here are a selection of yachts which are similar to the current charter yacht. To view all similar luxury charter yachts click on the button below.

As Featured In
The YachtCharterFleet Difference
YachtCharterFleet makes it easy to find the yacht charter vacation that is right for you. We combine thousands of yacht listings with local destination information, sample itineraries and experiences to deliver the world's most comprehensive yacht charter website.

San Francisco
- Like us on Facebook
- Follow us on Twitter
- Follow us on Instagram
- Find us on LinkedIn
- Add My Yacht
- Affiliates & Partners
Popular Destinations & Events
- St Tropez Yacht Charter
- Monaco Yacht Charter
- St Barts Yacht Charter
- Greece Yacht Charter
- Mykonos Yacht Charter
- Caribbean Yacht Charter
Featured Charter Yachts
- Maltese Falcon Yacht Charter
- Wheels Yacht Charter
- Victorious Yacht Charter
- Andrea Yacht Charter
- Titania Yacht Charter
- Ahpo Yacht Charter
Receive our latest offers, trends and stories direct to your inbox.
Please enter a valid e-mail.
Thanks for subscribing.
Search for Yachts, Destinations, Events, News... everything related to Luxury Yachts for Charter.
Yachts in your shortlist

Turn Your Curiosity Into Discovery
Latest facts.

3 TopRated Sites To Boost Your TikTok and Instagram Following

5 Detailed Facts About Medical Cannabis
40 facts about elektrostal.
Written by Lanette Mayes
Modified & Updated: 02 Mar 2024
Reviewed by Jessica Corbett

Elektrostal is a vibrant city located in the Moscow Oblast region of Russia. With a rich history, stunning architecture, and a thriving community, Elektrostal is a city that has much to offer. Whether you are a history buff, nature enthusiast, or simply curious about different cultures, Elektrostal is sure to captivate you.
This article will provide you with 40 fascinating facts about Elektrostal, giving you a better understanding of why this city is worth exploring. From its origins as an industrial hub to its modern-day charm, we will delve into the various aspects that make Elektrostal a unique and must-visit destination.
So, join us as we uncover the hidden treasures of Elektrostal and discover what makes this city a true gem in the heart of Russia.
Key Takeaways:
- Elektrostal, known as the “Motor City of Russia,” is a vibrant and growing city with a rich industrial history, offering diverse cultural experiences and a strong commitment to environmental sustainability.
- With its convenient location near Moscow, Elektrostal provides a picturesque landscape, vibrant nightlife, and a range of recreational activities, making it an ideal destination for residents and visitors alike.
Known as the “Motor City of Russia.”
Elektrostal, a city located in the Moscow Oblast region of Russia, earned the nickname “Motor City” due to its significant involvement in the automotive industry.
Home to the Elektrostal Metallurgical Plant.
Elektrostal is renowned for its metallurgical plant, which has been producing high-quality steel and alloys since its establishment in 1916.
Boasts a rich industrial heritage.
Elektrostal has a long history of industrial development, contributing to the growth and progress of the region.
Founded in 1916.
The city of Elektrostal was founded in 1916 as a result of the construction of the Elektrostal Metallurgical Plant.
Located approximately 50 kilometers east of Moscow.
Elektrostal is situated in close proximity to the Russian capital, making it easily accessible for both residents and visitors.
Known for its vibrant cultural scene.
Elektrostal is home to several cultural institutions, including museums, theaters, and art galleries that showcase the city’s rich artistic heritage.
A popular destination for nature lovers.
Surrounded by picturesque landscapes and forests, Elektrostal offers ample opportunities for outdoor activities such as hiking, camping, and birdwatching.
Hosts the annual Elektrostal City Day celebrations.
Every year, Elektrostal organizes festive events and activities to celebrate its founding, bringing together residents and visitors in a spirit of unity and joy.
Has a population of approximately 160,000 people.
Elektrostal is home to a diverse and vibrant community of around 160,000 residents, contributing to its dynamic atmosphere.
Boasts excellent education facilities.
The city is known for its well-established educational institutions, providing quality education to students of all ages.
A center for scientific research and innovation.
Elektrostal serves as an important hub for scientific research, particularly in the fields of metallurgy, materials science, and engineering.
Surrounded by picturesque lakes.
The city is blessed with numerous beautiful lakes, offering scenic views and recreational opportunities for locals and visitors alike.
Well-connected transportation system.
Elektrostal benefits from an efficient transportation network, including highways, railways, and public transportation options, ensuring convenient travel within and beyond the city.
Famous for its traditional Russian cuisine.
Food enthusiasts can indulge in authentic Russian dishes at numerous restaurants and cafes scattered throughout Elektrostal.
Home to notable architectural landmarks.
Elektrostal boasts impressive architecture, including the Church of the Transfiguration of the Lord and the Elektrostal Palace of Culture.
Offers a wide range of recreational facilities.
Residents and visitors can enjoy various recreational activities, such as sports complexes, swimming pools, and fitness centers, enhancing the overall quality of life.
Provides a high standard of healthcare.
Elektrostal is equipped with modern medical facilities, ensuring residents have access to quality healthcare services.
Home to the Elektrostal History Museum.
The Elektrostal History Museum showcases the city’s fascinating past through exhibitions and displays.
A hub for sports enthusiasts.
Elektrostal is passionate about sports, with numerous stadiums, arenas, and sports clubs offering opportunities for athletes and spectators.
Celebrates diverse cultural festivals.
Throughout the year, Elektrostal hosts a variety of cultural festivals, celebrating different ethnicities, traditions, and art forms.
Electric power played a significant role in its early development.
Elektrostal owes its name and initial growth to the establishment of electric power stations and the utilization of electricity in the industrial sector.
Boasts a thriving economy.
The city’s strong industrial base, coupled with its strategic location near Moscow, has contributed to Elektrostal’s prosperous economic status.
Houses the Elektrostal Drama Theater.
The Elektrostal Drama Theater is a cultural centerpiece, attracting theater enthusiasts from far and wide.
Popular destination for winter sports.
Elektrostal’s proximity to ski resorts and winter sport facilities makes it a favorite destination for skiing, snowboarding, and other winter activities.
Promotes environmental sustainability.
Elektrostal prioritizes environmental protection and sustainability, implementing initiatives to reduce pollution and preserve natural resources.
Home to renowned educational institutions.
Elektrostal is known for its prestigious schools and universities, offering a wide range of academic programs to students.
Committed to cultural preservation.
The city values its cultural heritage and takes active steps to preserve and promote traditional customs, crafts, and arts.
Hosts an annual International Film Festival.
The Elektrostal International Film Festival attracts filmmakers and cinema enthusiasts from around the world, showcasing a diverse range of films.
Encourages entrepreneurship and innovation.
Elektrostal supports aspiring entrepreneurs and fosters a culture of innovation, providing opportunities for startups and business development.
Offers a range of housing options.
Elektrostal provides diverse housing options, including apartments, houses, and residential complexes, catering to different lifestyles and budgets.
Home to notable sports teams.
Elektrostal is proud of its sports legacy, with several successful sports teams competing at regional and national levels.
Boasts a vibrant nightlife scene.
Residents and visitors can enjoy a lively nightlife in Elektrostal, with numerous bars, clubs, and entertainment venues.
Promotes cultural exchange and international relations.
Elektrostal actively engages in international partnerships, cultural exchanges, and diplomatic collaborations to foster global connections.
Surrounded by beautiful nature reserves.
Nearby nature reserves, such as the Barybino Forest and Luchinskoye Lake, offer opportunities for nature enthusiasts to explore and appreciate the region’s biodiversity.
Commemorates historical events.
The city pays tribute to significant historical events through memorials, monuments, and exhibitions, ensuring the preservation of collective memory.
Promotes sports and youth development.
Elektrostal invests in sports infrastructure and programs to encourage youth participation, health, and physical fitness.
Hosts annual cultural and artistic festivals.
Throughout the year, Elektrostal celebrates its cultural diversity through festivals dedicated to music, dance, art, and theater.
Provides a picturesque landscape for photography enthusiasts.
The city’s scenic beauty, architectural landmarks, and natural surroundings make it a paradise for photographers.
Connects to Moscow via a direct train line.
The convenient train connection between Elektrostal and Moscow makes commuting between the two cities effortless.
A city with a bright future.
Elektrostal continues to grow and develop, aiming to become a model city in terms of infrastructure, sustainability, and quality of life for its residents.
In conclusion, Elektrostal is a fascinating city with a rich history and a vibrant present. From its origins as a center of steel production to its modern-day status as a hub for education and industry, Elektrostal has plenty to offer both residents and visitors. With its beautiful parks, cultural attractions, and proximity to Moscow, there is no shortage of things to see and do in this dynamic city. Whether you’re interested in exploring its historical landmarks, enjoying outdoor activities, or immersing yourself in the local culture, Elektrostal has something for everyone. So, next time you find yourself in the Moscow region, don’t miss the opportunity to discover the hidden gems of Elektrostal.
Q: What is the population of Elektrostal?
A: As of the latest data, the population of Elektrostal is approximately XXXX.
Q: How far is Elektrostal from Moscow?
A: Elektrostal is located approximately XX kilometers away from Moscow.
Q: Are there any famous landmarks in Elektrostal?
A: Yes, Elektrostal is home to several notable landmarks, including XXXX and XXXX.
Q: What industries are prominent in Elektrostal?
A: Elektrostal is known for its steel production industry and is also a center for engineering and manufacturing.
Q: Are there any universities or educational institutions in Elektrostal?
A: Yes, Elektrostal is home to XXXX University and several other educational institutions.
Q: What are some popular outdoor activities in Elektrostal?
A: Elektrostal offers several outdoor activities, such as hiking, cycling, and picnicking in its beautiful parks.
Q: Is Elektrostal well-connected in terms of transportation?
A: Yes, Elektrostal has good transportation links, including trains and buses, making it easily accessible from nearby cities.
Q: Are there any annual events or festivals in Elektrostal?
A: Yes, Elektrostal hosts various events and festivals throughout the year, including XXXX and XXXX.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
Share this Fact:

Built by the famous Dynamique Yachts shipyard and having undergone a refit in 2018, sailing Yacht Amadeus was designed to please the most demanding of yachtsmen. Built for smooth sailing, this elegant cutter rigged sloop has a sleek hull design, comfortably reaching top speeds of 12 knots and ensuring excellent sailing performance. ...
The 33.5m/109'11" 'Amadeus' sail yacht built by the French shipyard Dynamiq is available for charter for up to 10 guests in 5 cabins. This yacht features interior styling by French designer Philippe Briand. Whether you are after the thrill of sailing or prefer to kick back, Amadeus is custom-built for adventure, offering a ring-side seat at the heart of the action once her sails have unfurled ...
Sailing yacht AMADEUS is a luxury vessel that measures 33.5m (109.9ft) in length. She was built by the famous Dynamique Yachts shipyard in 1995 and received a total refit in 2004 and smaller refits in 2012/14 and 2018 plus new interior fabrics in 2022. AMADEUS is an elegant cutter rigged sloop with a sleek hull design painted in an eye-catching ...
Amadeus Description. Built by the famous Dynamique Yachts shipyard, and having undergone a total refit in 2018, S/Y Amadeus was designed to please the most demanding of yachtsmen. Built for smooth sailing, this elegant cutter rigged sloop has a sleek hull design, comfortably reaching top speeds of 12 knots and ensuring excellent sailing ...
Length : 30.2 m / Passengers : 8. Special features : - One of the most elegant SW100- Excellent and experienced crew- Very elegant interiors- Available in West and East Med- Large outdoor spaceTender: 4.30... Price Per week from : 46 000€. View this yacht. AMADEUS is a fast cruising sailing yacht built by Dynamique Yachts and totally refit in ...
The 23.85m/78'3" sail yacht 'Amadeus' was built by Custom. Her interior is styled by design house Jean Marc Piaton and she was completed in 2018. Guest Accommodation. Amadeus has been designed to comfortably accommodate up to 8 guests in 4 suites. She is also capable of carrying up to 2 crew onboard to ensure a relaxed luxury yacht experience.
Built by the famous Dynamique Yachts shipyard, and having undergone a total refit in 2018. S/Y Amadeus was designed to please the most demanding of yachtsmen. Built for smooth sailing, this elegant cutter rigged sloop has a sleek hull design. Comfortably reaching top speeds of 12 knots and ensuring excellent sailing performance.
The yacht is maintained in excellent condition with a five-star crew year round. Sailing Yacht Amadeus was designed to please the most demanding of yachtsmen. Built for smooth sailing, this elegant cutter rigged sloop has a sleek hull design, comfortably reaching top speeds of 12 knots and ensuring excellent sailing performance.
AMADEUS I is a 44m/144' motor yacht for charter delivered by the Timmerman shipyard in 2014. Considered as a great luxury charter yacht for friends and family, AMADEUS I was fully upgraded in 2019. Her key features include a huge sundeck with a jacuzzi pool plus a brand-new beach club with a gym and sauna at sea level.
Built by the famous Dynamique Yachts shipyard, and having undergone a total refit in 2014, S/Y Amadeus was designed to please the most demanding of yachtsmen. Built for smooth sailing, this elegant cutter rigged sloop has a sleek hull design, comfortably reaching top speeds of 12 knots and ensuring excellent sailing performance.
AMADEUS was previously registered as project/yacht name Amadeus 1er. This 33 metre (109 ft) luxury yacht was built by Dynamique Yachts in 1991. Sailing Yacht AMADEUS is a well proportioned superyacht. The yacht is a modern sloop with a cutter rig. The naval architecture office whom authored the design work on this ship was Philippe Briand.
Amadeus is a 33.5 m sailing yacht. She was built by Dynamique Yachts in 1991. With a beam of 7.5 m and a draft of 3.9 m. The sailing yacht can accommodate 12 guests in 5 cabins. The yacht was designed by Philippe Briand.
Launched in 1996 by Dynamique Yachts, Amadeus is a 110 foot sailing sloop. To keep her up to date and comfortable for her guests, she has received refits in 2014 and 2018. She has been fitted with twin 320hp Perkins Rolls Royce engines for power, along with her sails.
33.5m / 109'11 Dragos Yachts 1996 / 2007. The 34.75m/114' 'Amadeus' motor yacht built by shipyard Dragos Yachts is available for charter for up to 12 guests in 5 cabins. This yacht features interior styling by Ugar Kose. Built in 1996, Amadeus's bespoke fittings and design ensure guests can explore the ocean's wonders in style and comfort.
Sailing Yacht AMADEUS can accommodate 10-12 guests in five large cabins, including a full-width master stateroom and two double cabins, each with an extra single bed. The two twin cabins can also be converted to doubles upon request, making her the only sailboat on the Greek market with five double beds.
Fully crewed Sailing Yacht AMADEUS available for private yacht charter in Greece, the best sailing holidays & vacation in the Greek Islands. +30 6948 295 207. [email protected] . Aten, Solonos 22-24, Agii Anargiri 135 61, Greece ... Sailing Yachts; Motor Sailer; Yacht Charter Terms; V.I.P. Services; Destinations; About us;
Charter theAMADEUS. AMADEUS is a 110-foot sailing yacht that can accommodate ten to twelve passengers in five staterooms as follows: a spacious Owner's stateroom with a double bed, a vanity and an entertainment unit including TV, DVD and music system; two cabins with a double bed and an additional single bed; two cabins with two twin beds each.
AMADEUS I is a 44m luxury motor super yacht available for charter built in 2014, refitted in 2019. Charter up to 10 guests in 5 cabins (1 Master, 2 VIP, 3 Double & 2 Twin) with a crew of 9. She is also available for events and corporate charter.
No:7 Kuşadası 09400 Aydın. + (90) 256 340 03 40. [email protected] . Mon - Fri: 9:00 - 18:00. Closed on Weekends. Istanbul Branch - Türkiye. Moscow - Russia. London - United Kingdom. New York - United States of America.
Küçükbakkalköy Mah. Fevzipaşa Cad. Bozkır Sok. No:1 ,K:3 D:15 Ataşehir 34750 Istanbul + (90) 216 900 28 62 +(90) 216 576 47 90. [email protected]
Get directions to Yuzhny prospekt, 6к1 and view details like the building's postal code, description, photos, and reviews on each business in the building
The 21.95m/72' 'Amadeus' motor yacht built by the British shipyard Sunseeker is available for charter for up to 6 guests in 3 cabins.. Primed for exploring secluded beaches and tucked-away lagoons or simply relaxing and soaking up the rays onboard, motor yacht Amadeus is tailor-made for family fun.
Known as the "Motor City of Russia." Elektrostal, a city located in the Moscow Oblast region of Russia, earned the nickname "Motor City" due to its significant involvement in the automotive industry.. Home to the Elektrostal Metallurgical Plant. Elektrostal is renowned for its metallurgical plant, which has been producing high-quality steel and alloys since its establishment in 1916.

2024 Lagoon 43 flybridge sailing catamaran revealed
All-new lagoon 43 features a semi-flybridge deck and easy dockside access.
French luxury catamaran group Lagoon has revealed the Lagoon 43, an all-new replacement for one of the best-selling models in the brand’s history.
The new Lagoon 43 will replace the Lagoon 42, a model responsible for more than 1000 sales worldwide.
Due for a European launch later this year, and an Australian market introduction in 2025, the Lagoon 43 features a semi-flybridge built into the trailing edge of the coachroof that introduces roof-level seating and a sun lounge.
The design allows the boom to sit lower than if the catamaran was designed with a traditional full flybridge as well as making the mainsail and jib/genoa easily visible from the raised, but still well-protected, helm position.
All the lines lead to winches located on the forward part of the semi-raised helm station, allowing for short-handed sail control.
Another feature to set this catamaran apart from the crowd is a special aft entryway built into the coaming of each hull.
The design provides a step-through space to enter or leave the Lagoon 43 via the aft cockpit space, as well as load or unload luggage or provisions. The void can be closed off using a pair of rail inserts.
The saloon features a forward galley, with the aft space taken up by a large table for up to 12 people that extends from inside to the open air of the cockpit, sheltered by the extended hardtop above. The saloon space offers all-around water views.
Forward, the Lagoon 43 features a large lounge space with three sunbeds and a central couch with a coffee table.
Key to the new Lagoon 43’s design are more generous interior volumes that have extended to the cabins. The owner’s cabin features a forward berth with an ensuite head and shower located aft similar, Lagoon says, to much larger yachts.
If the Lagoon 43 is to regularly have more guests onboard – think charter operations – two cabins in a mirror image of the starboard twin-cabin setup can replace the owner’s cabin.
Lagoon’s range of catamarans is sold in Australia via TMG Yachts .
Specifications Model: Lagoon 43 Length overall: 13.92m Beam: 7.69m Draft: 1.4m Mast clearance: 19.94m Weight: 13,319kg (light) Sail area: 68m 2 (square-topped main)/37m 2 (genoa) Engines: 2x57hp Fuel: 570L Water: 300L Berths: 6-13 Passengers: 12
Stay up to date
Become a boatsales member and get the latest news, reviews and advice straight to your inbox.
critical thinking basic questions & answers reflection
- Defining Critical Thinking
- A Brief History of the Idea of Critical Thinking
- Critical Thinking: Basic Questions & Answers
- Our Conception of Critical Thinking
- Sumner’s Definition of Critical Thinking
- Research in Critical Thinking
- Critical Societies: Thoughts from the Past
Translate this page from English...
*Machine translated pages not guaranteed for accuracy. Click Here for our professional translations.
For full copies of this and many other critical thinking articles, books, videos, and more, join us at the Center for Critical Thinking Community Online - the world's leading online community dedicated to critical thinking! Also featuring interactive learning activities, study groups, and even a social media component, this learning platform will change your conception of intellectual development.

1 Introduction to Critical Thinking
I. what is c ritical t hinking [1].
Critical thinking is the ability to think clearly and rationally about what to do or what to believe. It includes the ability to engage in reflective and independent thinking. Someone with critical thinking skills is able to do the following:
- Understand the logical connections between ideas.
- Identify, construct, and evaluate arguments.
- Detect inconsistencies and common mistakes in reasoning.
- Solve problems systematically.
- Identify the relevance and importance of ideas.
- Reflect on the justification of one’s own beliefs and values.
Critical thinking is not simply a matter of accumulating information. A person with a good memory and who knows a lot of facts is not necessarily good at critical thinking. Critical thinkers are able to deduce consequences from what they know, make use of information to solve problems, and to seek relevant sources of information to inform themselves.
Critical thinking should not be confused with being argumentative or being critical of other people. Although critical thinking skills can be used in exposing fallacies and bad reasoning, critical thinking can also play an important role in cooperative reasoning and constructive tasks. Critical thinking can help us acquire knowledge, improve our theories, and strengthen arguments. We can also use critical thinking to enhance work processes and improve social institutions.
Some people believe that critical thinking hinders creativity because critical thinking requires following the rules of logic and rationality, whereas creativity might require breaking those rules. This is a misconception. Critical thinking is quite compatible with thinking “out-of-the-box,” challenging consensus views, and pursuing less popular approaches. If anything, critical thinking is an essential part of creativity because we need critical thinking to evaluate and improve our creative ideas.
II. The I mportance of C ritical T hinking
Critical thinking is a domain-general thinking skill. The ability to think clearly and rationally is important whatever we choose to do. If you work in education, research, finance, management or the legal profession, then critical thinking is obviously important. But critical thinking skills are not restricted to a particular subject area. Being able to think well and solve problems systematically is an asset for any career.
Critical thinking is very important in the new knowledge economy. The global knowledge economy is driven by information and technology. One has to be able to deal with changes quickly and effectively. The new economy places increasing demands on flexible intellectual skills, and the ability to analyze information and integrate diverse sources of knowledge in solving problems. Good critical thinking promotes such thinking skills, and is very important in the fast-changing workplace.
Critical thinking enhances language and presentation skills. Thinking clearly and systematically can improve the way we express our ideas. In learning how to analyze the logical structure of texts, critical thinking also improves comprehension abilities.
Critical thinking promotes creativity. To come up with a creative solution to a problem involves not just having new ideas. It must also be the case that the new ideas being generated are useful and relevant to the task at hand. Critical thinking plays a crucial role in evaluating new ideas, selecting the best ones and modifying them if necessary.
Critical thinking is crucial for self-reflection. In order to live a meaningful life and to structure our lives accordingly, we need to justify and reflect on our values and decisions. Critical thinking provides the tools for this process of self-evaluation.
Good critical thinking is the foundation of science and democracy. Science requires the critical use of reason in experimentation and theory confirmation. The proper functioning of a liberal democracy requires citizens who can think critically about social issues to inform their judgments about proper governance and to overcome biases and prejudice.
Critical thinking is a metacognitive skill . What this means is that it is a higher-level cognitive skill that involves thinking about thinking. We have to be aware of the good principles of reasoning, and be reflective about our own reasoning. In addition, we often need to make a conscious effort to improve ourselves, avoid biases, and maintain objectivity. This is notoriously hard to do. We are all able to think but to think well often requires a long period of training. The mastery of critical thinking is similar to the mastery of many other skills. There are three important components: theory, practice, and attitude.
III. Improv ing O ur T hinking S kills
If we want to think correctly, we need to follow the correct rules of reasoning. Knowledge of theory includes knowledge of these rules. These are the basic principles of critical thinking, such as the laws of logic, and the methods of scientific reasoning, etc.
Also, it would be useful to know something about what not to do if we want to reason correctly. This means we should have some basic knowledge of the mistakes that people make. First, this requires some knowledge of typical fallacies. Second, psychologists have discovered persistent biases and limitations in human reasoning. An awareness of these empirical findings will alert us to potential problems.
However, merely knowing the principles that distinguish good and bad reasoning is not enough. We might study in the classroom about how to swim, and learn about the basic theory, such as the fact that one should not breathe underwater. But unless we can apply such theoretical knowledge through constant practice, we might not actually be able to swim.
Similarly, to be good at critical thinking skills it is necessary to internalize the theoretical principles so that we can actually apply them in daily life. There are at least two ways to do this. One is to perform lots of quality exercises. These exercises don’t just include practicing in the classroom or receiving tutorials; they also include engaging in discussions and debates with other people in our daily lives, where the principles of critical thinking can be applied. The second method is to think more deeply about the principles that we have acquired. In the human mind, memory and understanding are acquired through making connections between ideas.
Good critical thinking skills require more than just knowledge and practice. Persistent practice can bring about improvements only if one has the right kind of motivation and attitude. The following attitudes are not uncommon, but they are obstacles to critical thinking:
- I prefer being given the correct answers rather than figuring them out myself.
- I don’t like to think a lot about my decisions as I rely only on gut feelings.
- I don’t usually review the mistakes I have made.
- I don’t like to be criticized.
To improve our thinking we have to recognize the importance of reflecting on the reasons for belief and action. We should also be willing to engage in debate, break old habits, and deal with linguistic complexities and abstract concepts.
The California Critical Thinking Disposition Inventory is a psychological test that is used to measure whether people are disposed to think critically. It measures the seven different thinking habits listed below, and it is useful to ask ourselves to what extent they describe the way we think:
- Truth-Seeking—Do you try to understand how things really are? Are you interested in finding out the truth?
- Open-Mindedness—How receptive are you to new ideas, even when you do not intuitively agree with them? Do you give new concepts a fair hearing?
- Analyticity—Do you try to understand the reasons behind things? Do you act impulsively or do you evaluate the pros and cons of your decisions?
- Systematicity—Are you systematic in your thinking? Do you break down a complex problem into parts?
- Confidence in Reasoning—Do you always defer to other people? How confident are you in your own judgment? Do you have reasons for your confidence? Do you have a way to evaluate your own thinking?
- Inquisitiveness—Are you curious about unfamiliar topics and resolving complicated problems? Will you chase down an answer until you find it?
- Maturity of Judgment—Do you jump to conclusions? Do you try to see things from different perspectives? Do you take other people’s experiences into account?
Finally, as mentioned earlier, psychologists have discovered over the years that human reasoning can be easily affected by a variety of cognitive biases. For example, people tend to be over-confident of their abilities and focus too much on evidence that supports their pre-existing opinions. We should be alert to these biases in our attitudes towards our own thinking.
IV. Defining Critical Thinking
There are many different definitions of critical thinking. Here we list some of the well-known ones. You might notice that they all emphasize the importance of clarity and rationality. Here we will look at some well-known definitions in chronological order.
1) Many people trace the importance of critical thinking in education to the early twentieth-century American philosopher John Dewey. But Dewey did not make very extensive use of the term “critical thinking.” Instead, in his book How We Think (1910), he argued for the importance of what he called “reflective thinking”:
…[when] the ground or basis for a belief is deliberately sought and its adequacy to support the belief examined. This process is called reflective thought; it alone is truly educative in value…
Active, persistent and careful consideration of any belief or supposed form of knowledge in light of the grounds that support it, and the further conclusions to which it tends, constitutes reflective thought.
There is however one passage from How We Think where Dewey explicitly uses the term “critical thinking”:
The essence of critical thinking is suspended judgment; and the essence of this suspense is inquiry to determine the nature of the problem before proceeding to attempts at its solution. This, more than any other thing, transforms mere inference into tested inference, suggested conclusions into proof.
2) The Watson-Glaser Critical Thinking Appraisal (1980) is a well-known psychological test of critical thinking ability. The authors of this test define critical thinking as:
…a composite of attitudes, knowledge and skills. This composite includes: (1) attitudes of inquiry that involve an ability to recognize the existence of problems and an acceptance of the general need for evidence in support of what is asserted to be true; (2) knowledge of the nature of valid inferences, abstractions, and generalizations in which the weight or accuracy of different kinds of evidence are logically determined; and (3) skills in employing and applying the above attitudes and knowledge.
3) A very well-known and influential definition of critical thinking comes from philosopher and professor Robert Ennis in his work “A Taxonomy of Critical Thinking Dispositions and Abilities” (1987):
Critical thinking is reasonable reflective thinking that is focused on deciding what to believe or do.
4) The following definition comes from a statement written in 1987 by the philosophers Michael Scriven and Richard Paul for the National Council for Excellence in Critical Thinking (link), an organization promoting critical thinking in the US:
Critical thinking is the intellectually disciplined process of actively and skillfully conceptualizing, applying, analyzing, synthesizing, and/or evaluating information gathered from, or generated by, observation, experience, reflection, reasoning, or communication, as a guide to belief and action. In its exemplary form, it is based on universal intellectual values that transcend subject matter divisions: clarity, accuracy, precision, consistency, relevance, sound evidence, good reasons, depth, breadth, and fairness. It entails the examination of those structures or elements of thought implicit in all reasoning: purpose, problem, or question-at-issue, assumptions, concepts, empirical grounding; reasoning leading to conclusions, implications and consequences, objections from alternative viewpoints, and frame of reference.
The following excerpt from Peter A. Facione’s “Critical Thinking: A Statement of Expert Consensus for Purposes of Educational Assessment and Instruction” (1990) is quoted from a report written for the American Philosophical Association:
We understand critical thinking to be purposeful, self-regulatory judgment which results in interpretation, analysis, evaluation, and inference, as well as explanation of the evidential, conceptual, methodological, criteriological, or contextual considerations upon which that judgment is based. CT is essential as a tool of inquiry. As such, CT is a liberating force in education and a powerful resource in one’s personal and civic life. While not synonymous with good thinking, CT is a pervasive and self-rectifying human phenomenon. The ideal critical thinker is habitually inquisitive, well-informed, trustful of reason, open-minded, flexible, fairminded in evaluation, honest in facing personal biases, prudent in making judgments, willing to reconsider, clear about issues, orderly in complex matters, diligent in seeking relevant information, reasonable in the selection of criteria, focused in inquiry, and persistent in seeking results which are as precise as the subject and the circumstances of inquiry permit. Thus, educating good critical thinkers means working toward this ideal. It combines developing CT skills with nurturing those dispositions which consistently yield useful insights and which are the basis of a rational and democratic society.
V. Two F eatures of C ritical T hinking
A. how not what .
Critical thinking is concerned not with what you believe, but rather how or why you believe it. Most classes, such as those on biology or chemistry, teach you what to believe about a subject matter. In contrast, critical thinking is not particularly interested in what the world is, in fact, like. Rather, critical thinking will teach you how to form beliefs and how to think. It is interested in the type of reasoning you use when you form your beliefs, and concerns itself with whether you have good reasons to believe what you believe. Therefore, this class isn’t a class on the psychology of reasoning, which brings us to the second important feature of critical thinking.
B. Ought N ot Is ( or Normative N ot Descriptive )
There is a difference between normative and descriptive theories. Descriptive theories, such as those provided by physics, provide a picture of how the world factually behaves and operates. In contrast, normative theories, such as those provided by ethics or political philosophy, provide a picture of how the world should be. Rather than ask question such as why something is the way it is, normative theories ask how something should be. In this course, we will be interested in normative theories that govern our thinking and reasoning. Therefore, we will not be interested in how we actually reason, but rather focus on how we ought to reason.
In the introduction to this course we considered a selection task with cards that must be flipped in order to check the validity of a rule. We noted that many people fail to identify all the cards required to check the rule. This is how people do in fact reason (descriptive). We then noted that you must flip over two cards. This is how people ought to reason (normative).
- Section I-IV are taken from http://philosophy.hku.hk/think/ and are in use under the creative commons license. Some modifications have been made to the original content. ↵
Critical Thinking Copyright © 2019 by Brian Kim is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Module 1: success skills.
Critical thinking, introduction, learning objectives.
- define critical thinking
- identify the role that logic plays in critical thinking
- apply critical thinking skills to problem-solving scenarios
- apply critical thinking skills to evaluation of information

Consider these thoughts about the critical thinking process, and how it applies not just to our school lives but also our personal and professional lives.
“Thinking Critically and Creatively”
Critical thinking skills are perhaps the most fundamental skills involved in making judgments and solving problems. You use them every day, and you can continue improving them.
The ability to think critically about a matter—to analyze a question, situation, or problem down to its most basic parts—is what helps us evaluate the accuracy and truthfulness of statements, claims, and information we read and hear. It is the sharp knife that, when honed, separates fact from fiction, honesty from lies, and the accurate from the misleading. We all use this skill to one degree or another almost every day. For example, we use critical thinking every day as we consider the latest consumer products and why one particular product is the best among its peers. Is it a quality product because a celebrity endorses it? Because a lot of other people may have used it? Because it is made by one company versus another? Or perhaps because it is made in one country or another? These are questions representative of critical thinking.
The academic setting demands more of us in terms of critical thinking than everyday life. It demands that we evaluate information and analyze myriad issues. It is the environment where our critical thinking skills can be the difference between success and failure. In this environment we must consider information in an analytical, critical manner. We must ask questions—What is the source of this information? Is this source an expert one and what makes it so? Are there multiple perspectives to consider on an issue? Do multiple sources agree or disagree on an issue? Does quality research substantiate information or opinion? Do I have any personal biases that may affect my consideration of this information?
It is only through purposeful, frequent, intentional questioning such as this that we can sharpen our critical thinking skills and improve as students, learners and researchers.
—Dr. Andrew Robert Baker, Foundations of Academic Success: Words of Wisdom
Thinking comes naturally. You don’t have to make it happen—it just does. But you can make it happen in different ways. For example, you can think positively or negatively. You can think with “heart” and you can think with rational judgment. You can also think strategically and analytically, and mathematically and scientifically. These are a few of multiple ways in which the mind can process thought.
What are some forms of thinking you use? When do you use them, and why?
As a college student, you are tasked with engaging and expanding your thinking skills. One of the most important of these skills is critical thinking. Critical thinking is important because it relates to nearly all tasks, situations, topics, careers, environments, challenges, and opportunities. It’s not restricted to a particular subject area.

Critical thinking is clear, reasonable, reflective thinking focused on deciding what to believe or do. It means asking probing questions like, “How do we know?” or “Is this true in every case or just in this instance?” It involves being skeptical and challenging assumptions, rather than simply memorizing facts or blindly accepting what you hear or read.
Imagine, for example, that you’re reading a history textbook. You wonder who wrote it and why, because you detect certain assumptions in the writing. You find that the author has a limited scope of research focused only on a particular group within a population. In this case, your critical thinking reveals that there are “other sides to the story.”
Who are critical thinkers, and what characteristics do they have in common? Critical thinkers are usually curious and reflective people. They like to explore and probe new areas and seek knowledge, clarification, and new solutions. They ask pertinent questions, evaluate statements and arguments, and they distinguish between facts and opinion. They are also willing to examine their own beliefs, possessing a manner of humility that allows them to admit lack of knowledge or understanding when needed. They are open to changing their mind. Perhaps most of all, they actively enjoy learning, and seeking new knowledge is a lifelong pursuit.
This may well be you!
No matter where you are on the road to being a critical thinker, you can always more fully develop your skills. Doing so will help you develop more balanced arguments, express yourself clearly, read critically, and absorb important information efficiently. Critical thinking skills will help you in any profession or any circumstance of life, from science to art to business to teaching.
Critical Thinking in Action
The following video, from Lawrence Bland, presents the major concepts and benefits of critical thinking.
Critical Thinking and Logic
Critical thinking is fundamentally a process of questioning information and data. You may question the information you read in a textbook, or you may question what a politician or a professor or a classmate says. You can also question a commonly-held belief or a new idea. With critical thinking, anything and everything is subject to question and examination.
Logic’s Relationship to Critical Thinking
The word logic comes from the Ancient Greek logike , referring to the science or art of reasoning. Using logic, a person evaluates arguments and strives to distinguish between good and bad reasoning, or between truth and falsehood. Using logic, you can evaluate ideas or claims people make, make good decisions, and form sound beliefs about the world. [1]
Questions of Logic in Critical Thinking
Let’s use a simple example of applying logic to a critical-thinking situation. In this hypothetical scenario, a man has a PhD in political science, and he works as a professor at a local college. His wife works at the college, too. They have three young children in the local school system, and their family is well known in the community.
The man is now running for political office. Are his credentials and experience sufficient for entering public office? Will he be effective in the political office? Some voters might believe that his personal life and current job, on the surface, suggest he will do well in the position, and they will vote for him.
In truth, the characteristics described don’t guarantee that the man will do a good job. The information is somewhat irrelevant. What else might you want to know? How about whether the man had already held a political office and done a good job? In this case, we want to ask, How much information is adequate in order to make a decision based on logic instead of assumptions?
The following questions, presented in Figure 1, below, are ones you may apply to formulating a logical, reasoned perspective in the above scenario or any other situation:
- What’s happening? Gather the basic information and begin to think of questions.
- Why is it important? Ask yourself why it’s significant and whether or not you agree.
- What don’t I see? Is there anything important missing?
- How do I know? Ask yourself where the information came from and how it was constructed.
- Who is saying it? What’s the position of the speaker and what is influencing them?
- What else? What if? What other ideas exist and are there other possibilities?

Problem-Solving With Critical Thinking
For most people, a typical day is filled with critical thinking and problem-solving challenges. In fact, critical thinking and problem-solving go hand-in-hand. They both refer to using knowledge, facts, and data to solve problems effectively. But with problem-solving, you are specifically identifying, selecting, and defending your solution. Below are some examples of using critical thinking to problem-solve:
- Your roommate was upset and said some unkind words to you, which put a crimp in your relationship. You try to see through the angry behaviors to determine how you might best support your roommate and help bring your relationship back to a comfortable spot.

- Your final art class project challenges you to conceptualize form in new ways. On the last day of class when students present their projects, you describe the techniques you used to fulfill the assignment. You explain why and how you selected that approach.
- Your math teacher sees that the class is not quite grasping a concept. She uses clever questioning to dispel anxiety and guide you to new understanding of the concept.
- You have a job interview for a position that you feel you are only partially qualified for, although you really want the job and you are excited about the prospects. You analyze how you will explain your skills and experiences in a way to show that you are a good match for the prospective employer.
- You are doing well in college, and most of your college and living expenses are covered. But there are some gaps between what you want and what you feel you can afford. You analyze your income, savings, and budget to better calculate what you will need to stay in college and maintain your desired level of spending.
Problem-Solving Action Checklist
Problem-solving can be an efficient and rewarding process, especially if you are organized and mindful of critical steps and strategies. Remember, too, to assume the attributes of a good critical thinker. If you are curious, reflective, knowledge-seeking, open to change, probing, organized, and ethical, your challenge or problem will be less of a hurdle, and you’ll be in a good position to find intelligent solutions.
Evaluating Information With Critical Thinking
Evaluating information can be one of the most complex tasks you will be faced with in college. But if you utilize the following four strategies, you will be well on your way to success:
- Read for understanding by using text coding
- Examine arguments
- Clarify thinking

1. Read for Understanding Using Text Coding
When you read and take notes, use the text coding strategy . Text coding is a way of tracking your thinking while reading. It entails marking the text and recording what you are thinking either in the margins or perhaps on Post-it notes. As you make connections and ask questions in response to what you read, you monitor your comprehension and enhance your long-term understanding of the material.
With text coding, mark important arguments and key facts. Indicate where you agree and disagree or have further questions. You don’t necessarily need to read every word, but make sure you understand the concepts or the intentions behind what is written. Feel free to develop your own shorthand style when reading or taking notes. The following are a few options to consider using while coding text.
See more text coding from PBWorks and Collaborative for Teaching and Learning .
2. Examine Arguments
When you examine arguments or claims that an author, speaker, or other source is making, your goal is to identify and examine the hard facts. You can use the spectrum of authority strategy for this purpose. The spectrum of authority strategy assists you in identifying the “hot” end of an argument—feelings, beliefs, cultural influences, and societal influences—and the “cold” end of an argument—scientific influences. The following video explains this strategy.
3. Clarify Thinking
When you use critical thinking to evaluate information, you need to clarify your thinking to yourself and likely to others. Doing this well is mainly a process of asking and answering probing questions, such as the logic questions discussed earlier. Design your questions to fit your needs, but be sure to cover adequate ground. What is the purpose? What question are we trying to answer? What point of view is being expressed? What assumptions are we or others making? What are the facts and data we know, and how do we know them? What are the concepts we’re working with? What are the conclusions, and do they make sense? What are the implications?
4. Cultivate “Habits of Mind”
“Habits of mind” are the personal commitments, values, and standards you have about the principle of good thinking. Consider your intellectual commitments, values, and standards. Do you approach problems with an open mind, a respect for truth, and an inquiring attitude? Some good habits to have when thinking critically are being receptive to having your opinions changed, having respect for others, being independent and not accepting something is true until you’ve had the time to examine the available evidence, being fair-minded, having respect for a reason, having an inquiring mind, not making assumptions, and always, especially, questioning your own conclusions—in other words, developing an intellectual work ethic. Try to work these qualities into your daily life.
- "logic." Wordnik . n.d. Web. 16 Feb 2016 . ↵
- "Student Success-Thinking Critically In Class and Online." Critical Thinking Gateway . St Petersburg College, n.d. Web. 16 Feb 2016. ↵
- Outcome: Critical Thinking. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Self Check: Critical Thinking. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Foundations of Academic Success. Authored by : Thomas C. Priester, editor. Provided by : Open SUNY Textbooks. Located at : http://textbooks.opensuny.org/foundations-of-academic-success/ . License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
- Image of woman thinking. Authored by : Moyan Brenn. Located at : https://flic.kr/p/8YV4K5 . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Critical Thinking. Provided by : Critical and Creative Thinking Program. Located at : http://cct.wikispaces.umb.edu/Critical+Thinking . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Critical Thinking Skills. Authored by : Linda Bruce. Provided by : Lumen Learning. Project : https://courses.lumenlearning.com/lumencollegesuccess/chapter/critical-thinking-skills/. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Image of critical thinking poster. Authored by : Melissa Robison. Located at : https://flic.kr/p/bwAzyD . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Thinking Critically. Authored by : UBC Learning Commons. Provided by : The University of British Columbia, Vancouver Campus. Located at : http://www.oercommons.org/courses/learning-toolkit-critical-thinking/view . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Critical Thinking 101: Spectrum of Authority. Authored by : UBC Leap. Located at : https://youtu.be/9G5xooMN2_c . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Image of students putting post-its on wall. Authored by : Hector Alejandro. Located at : https://flic.kr/p/7b2Ax2 . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Image of man thinking. Authored by : Chad Santos. Located at : https://flic.kr/p/phLKY . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Critical Thinking.wmv. Authored by : Lawrence Bland. Located at : https://youtu.be/WiSklIGUblo . License : All Rights Reserved . License Terms : Standard YouTube License
All of our Thinker's Guides are now published by Rowman and Littlefield Publishers. In this section, you find samples sections from each guide. For the full guides, visit Rowman and Littlefield, (rowman.com)
- The Miniature Guide to Critical Thinking Concepts & Tools
- The Thinker's Guide to Analytic Thinking
- The Thinker's Guide to the Human Mind
- The Thinker's Guide for Students on How to Study & Learn a Discipline
- The Thinker's Guide to Ethical Reasoning
- Student Guide to Historical Thinking
- The Aspiring Thinker's Guide to Critical Thinking
- How to Read a Paragraph: The Art of Close Reading
- How to Write a Paragraph: The Art of Substantive Writing
- A Glossary of Critical Thinking Terms and Concepts
- The Art of Asking Essential Questions
- The Nature and Functions of Critical & Creative Thinking
- The Thinker's Guide to Scientific Thinking
- Fact over Fake: A Critical Thinker's Guide to Media Bias and Political Propaganda
- The Thinker's Guide to Fallacies: The Art of Mental Trickery
- The Thinker's Guide to Clinical Reasoning
- The Thinker's Guide to Engineering Reasoning
- The Thinker's Guide to Intellectual Standards
- Mass Media and Critical Thinking: Reasoning for a Second-Hand World
- Critical Thinking and Emotional Intelligence
- Critical Thinking and Command of Language
- A "Third Wave" Manifesto: Keynotes of the Sonoma Conference
- Thinking Critically About Identities
- Richard Paul's Contributions to the Field of Critical Thinking Studies and to the Establishment of First Principles in Critical Thinking
- Richard Paul and the Philosophical Foundations of Critical Thinking
- Truth-seeking Versus Confirmation Bias: How Richard Paul's Conception of Critical Thinking Cultivates Authentic Research and Fairminded Thinking
- Portaging Richard Paul's Model to Professional Practice: Ideas that Integrate
- Richard Paul's Approach to Critical Thinking: Comprehensiveness, Systematicity, and Practicality
- From Argument and Philosophy to Critical Thinking Across the Curriculum
- Reflections on the Nature of Critical Thinking, Its History, Politics, and Barriers, and on Its Status across the College & University Curriculum Part I
- Reflections on the Nature of Critical Thinking, Its History, Politics, and Barriers, and on Its Status across the College & University Curriculum Part II
- Sumner's Definition of Critical Thinking
- Our Concept and Definition of Critical Thinking
- International Critical Thinking Manifesto
- Distinguishing Between Inert Information, Activated Ignorance, Activated Knowledge
- Critical Thinking: Identifying the Targets
- Critical Thinking Development: A Stage Theory
- The Elements of Reasoning and the Intellectual Standards
- Becoming a Critic Of Your Thinking
- Bertrand Russell on Critical Thinking
- Valuable Intellectual Traits
- Universal Intellectual Standards
- Critical Thinking in the Engineering Enterprise: Novices Typically Don't Even Know What Questions to Ask
- Critical Thinking Movement: 3 Waves
- Critical Thinking and Nursing
- Radio Show and Podcast: Critical Thinking for Everyone!
- Strategy List: 35 Dimensions of Critical Thought
- Newton, Darwin, & Einstein
- The Critical Mind is A Questioning Mind: Learning How to Ask Powerful, Probing Questions
- Three Categories of Questions: Crucial Distinctions
- Complex Interdisciplinary Questions Exemplified: Ecological Sustainability
- Ethical Reasoning Essential to Education
- Engineering Reasoning
- Accelerating Change
- Natural Egocentric Dispositions
- Critical Thinking in Everyday Life: 9 Strategies
- Developing as Rational Persons: Viewing Our Development in Stages
- How to Study and Learn (Part One)
- How to Study and Learn (Part Two)
- How to Study and Learn (Part Three)
- How to Study and Learn (Part Four)
- The Art of Close Reading (Part One)
- The Art of Close Reading (Part Two)
- The Art of Close Reading (Part Three)
- Looking To The Future With a Critical Eye: A Message for High School Graduates
- Reading Backwards: Classic Books Online
- Liberating the Mind: Overcoming Sociocentric Thought and Egocentric Tendencies
- 30 Days to Better Thinking and Better Living through Critical Thinking - One-Week Sample
- 1 Table of Contents
- 2 Garbage and Powerful Ideas
- 3 Elements and Standards
- 4 Questions
- 5 Socratic Questioning
- 6 Designing Structures
- 7 Content as Thinking
- 8 Affective Dimension of Thinking....Ego and Non
- 9 Where Do We Stand
- Card 1 - Teach for Depth of Understanding
- Card 2 - The Elements of Thought
- Card 3 - Questions for Socratic Dialogue
- Card 4 - Intellectual Standards
- Card 5 - Dimensions of Critical Thought
- Card 6 - Intellectual Virtues
- Poster 1 - Analysis of Thought
- Poster 2 - Intellectual Standards
- Poster 3 - Elements of Thought
- Poster 4 - Elements, Standards, and Traits
- Poster 5 - Parts of Thinking
- Chapter 1 - The Critical Thinking Movement in Historical Perspective
- Chapter 2 - Critical thinking Basic Questions and Answers
- Chapter 3 - The Logic of Creative and Critical Thinking
- Chapter 4 - Critical Thinking in North America
- Chapter 5 - Background Logic, Critical Thinking, and Irrational Language Games
- Chapter 6 - A Model for the National Assessment of Higher Order Thinking
- Chapter 7 - Using Intellectual Standards to Assess Student Reasoning
- Chapter 8 - Why Students - and Teachers - Don't Reason Well
- Chapter 9 - Critical Thinking Fundamentals to Education for a Free Society
- Chapter 10 - Critical Thinking and the Critical Person
- Chapter 11 - Critical Thinking and the Nature of Prejudice
- Chapter 12 - Ethics Without Indoctrination
- Chapter 13 - Critical Thinking, Moral Integrity, and Citizenship Teaching for the Intellectual Virtues
- Chapter 14 - Dialogical Thinking Critical Thinking Thought Essential to the Acquisition of Rational Knowledge and Passions
- Chapter 15 - Power, Vested Interest, and Prejudice On the Need for Critical Thinking in the Ethics of Social and Economic Development
- Chapter 16 - The Critical Connection Higher Order Thinking that Unifies Curriculum, Instruction, and Learning
- Chapter 17 - Dialogical and Dialectical Thinking
- Chapter 18 - The Art of Redesigning Instruction
- Chapter 19 - Using Critical Thinking to Identify National Bias in the News
- Chapter 20 - Socratic Questioning
- Chapter 21 - Strategies Thirty-Five Dimensions of Critical Thinking
- Chapter 22 - Critical Thinking in the Elementary Classroom
- Chapter 23 - Critical Thinking in Elementary Social Studies
- Chapter 24 - Critical Thinking in Elementary Language Arts
- Chapter 25 - Critical Thinking in Elementary Science
- Chapter 26 - Teaching Critical Thinking in the Strong Sense A Focus on Self-Deception, World Views, and a Dialectical Mode of Analysis
- Chapter 27 - Critical Thinking Staff Development The Lesson Plan Remodeling Approach
- Chapter 28 - The Greensboro Plan A Sample Staff Development Plan
- Chapter 29 - Critical Thinking and Learning Centers
- Chapter 30 - McPeck's Mistakes Why Critical Thinking Applies Across Disciplines and Domains
- Chapter 31 - Bloom's Taxonomy and Critical Thinking Instruction Recall is Not Knowledge
- Chapter 32 - Critical and Cultural Literacy Where E.D. Hirsch Goes Wrong
- Chapter 33 - Critical Thinking and General Semantics On the Primacy of Natural Languages
- Chapter 34 - Philosophy and Cognitive Psychology Contrasting Assumptions
- Chapter 35 - The Contribution of Philosophy to Thinking
- Chapter 36 - Critical Thinking and Social Studies
- Chapter 37 - Critical Thinking and Language Arts
- Chapter 38 - Critical Thinking and Science
- Chapter 39 - Critical Thinking, Human Development, and Rational Productivity
- Chapter 40 - What Critical Thinking Means to Me The Views of Teachers
- Chapter 41 - Glossary An Educators Guide to Critical Thinking Terms and Concepts
- Arabic - The Miniature Guide to Critical Thinking Concepts & Tools
- Bulgarian - The Miniature Guide to Critical Thinking Concepts & Tools
- French - Asking Questions
- French - Elements of Thought
- French - How Skilled Is Your Thinking
- French - Miniature Guide to Critical Thinking Concepts & Tools
- French - Scientific Thinking
- French - Stages of Development
- French - Strategic Thinking
- French - Thinker's Guide to Engineering Reasoning
- French - Tools for Taking Charge
- French - Universal Intellectual Standards
- German - Miniature Guide to Critical Thinking Concepts & Tools
- Persian - Miniature Guide to Critical Thinking Concepts & Tools
- Spanish - Miniature Guide to Critical Thinking Concepts & Tools
- Spanish - Thinker's Guide to Analytic Thinking
- Spanish - Thinker's Guide to Asking Essential Questions
- Spanish - Thinker's Guide to How to Read a Paragraph
- Spanish - Thinker's Guide to How to Write a Paragraph
- Spanish - Miniature Guide to Critical Thinking for Children
- Spanish - Thinker's Guide to How to Study and Learn a Discipline
- Thai - Miniature Guide to Critical Thinking Concepts & Tools
- Thai - The Aspiring Thinker's Guide to Critical Thinking
- Turkish - Miniature Guide to Critical Thinking Concepts & Tools
- Turkish - Miniature Guide to Critical Thinking for Children
- Turkish - Thinker's Guide on How to Detect Media Bias and Propaganda
- Korean - How to Read a Paragraph
- Korean - How to Write a Paragraph
- Korean - Thinker's Guide to Analytic Thinking
- Persian - The Thinker's Guide to Clinical Reasoning

- Rasmussen University
- Transferable Skills
Critical Thinking
- Steps 1 & 2: Reflection and Analysis
Critical Thinking: Steps 1 & 2: Reflection and Analysis
- Step 3: Acquisition of Information
- Step 4: Creativity
- Step 5: Structuring Arguments
- Step 6: Decision Making
- Steps 7 & 8: Commitment and Debate
- In the Classroom
- In the Workplace
Identify, Reflect, and Analyze
- Step 1: Reflect
- Step 2: Analyze
Step 1: Reflecting on the Issue, Problem, or Task
Reflection is an important early step in critical thinking. There are various kinds of reflection that promote deeper levels of critical thinking (click on the table to view larger):

Brockbank, A., & McGill, I. (2007). Facilitating Reflective Learning in Higher Education . Maidenhead, England: McGraw-Hill Education.
Ask yourself questions to identify the nature and essence of the issue, problem, or task. Why are you examining this subject? Why is it important that you solve this problem?

Reflective Thinking

Game: There is 1 random word below. Use it as inspiration to think of something it would be interesting if we never had in this world.
Challenge: For extra challenge, reply to someone else’s suggestion and predict how life would be different if it never was. Try and think big. Think about profound and extreme ways in which the world may be different.
Strategy: We often think about how life would be better if only we had X (X being something we would quite like). It can be a fun way to pass the time but it tends to involve adding something new to our lives. Let's go the other way around and subtract something instead. But instead of something desirable it will be something that we take for granted, something simple. Then trying to predict how it would have a profound effect changing the world around us becomes an act in following a chain reaction of influences. Creativity often involves having keen insights into how everything influences and affects everything around it in often unobvious ways. This little game is a good way to practice that thinking.
- << Previous: Steps to Critical Thinking
- Next: Step 3: Acquisition of Information >>
- Last Updated: Apr 2, 2024 9:12 AM
- URL: https://guides.rasmussen.edu/criticalthinking

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

1: Basic Concepts of Critical Thinking
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 94992

- Jason Southworth & Chris Swoyer
- Fort Hays State & University University of Oklahoma
- 1.1: Basic Concepts
- 1.2: A Role for Reason
- 1.3: Improving Reasoning
- 1.4: Chapter Exercises

- Search Search Search …
- Search Search …
How to answer critical thinking questions

Whether you are studying and preparing to take the LSAT or looking to engage in more meaningful workplace discussions, you need to know how to properly answer critical thinking questions. Luckily, there are some key facets to critical thinking that can guide you along the way.
Thinking critically requires one to proceed beyond mere information recall. When asked to answer questions critically, one should engage their reasoning, evaluation, articulation, and questioning skills. You must closely examine the question in order to arrive at your justified answer.
In this guide, we’ll be sharing some tips to help you answer critical thinking questions adequately. Read along as we discuss the ways to answer by asking useful questions, relying on logic, anticipating specific problems and solutions, and clearly communicating your thoughts. Let’s get into it!
- Table of Contents
We’ll be discussing the following 6 methods of answering critical thinking questions in order to give you a framework to start with:
Ask the Important Questions
Consider all possible solutions, articulate yourself clearly, examine and reflect, research and inform yourself, organize your thoughts.
Sometimes, answering a question effectively requires you to ask some questions yourself. When it comes to thinking critically in your response, you may need to investigate by asking for context clues or clearing up any ambiguous aspects of the question.
When you follow-up a question with your own questions, you are engaging in truth-seeking behavior, which is a key element of critical thinking .
Examples of questions you can ask to arrive at a critical answer include:
- Why is this question or problem important?
- How would I solve this problem?
- What would be the consequences if I solved the problem X way?
- How would someone with a different opinion or set of values answer this question?
- Why do I agree or disagree?
- Can you provide me with an example?
- Who is this question geared towards?
- Who will be affected by the solution to this question/problem?
Another thing that sets critical thinkers apart from traditional thinkers is the ability to anticipate multiple different outcomes.
Don’t merely stop at your first answer to the problem you’re being asked about. Take things a step further by drafting several different solutions. Follow step-by-step routes in your mind to try and anticipate how these solutions would play out in reality.
Would there be negative consequences to these solutions? Would there be positive consequences to these solutions? What are they? This can help you to narrow down your ideas and provide the best possible solution.
Critical thinking requires you to communicate your thoughts effectively, in addition to arriving at those thoughts in the first place.
Whether you are answering a critical thinking question verbally in a debate, or writing your thoughts down on a paper exam, you should learn how to justify your answer.
For each point or claim that you make, you should have a valid justification or explanation. Let’s say, for example, that you are asked a question about how to distribute a low amount of resources to a large community.
If you claim that they should be distributed evenly among households, you should consider how that route would affect larger households vs. smaller ones.
Your answer can explore the advantages and disadvantages of your method, landing on an explanation of how it would best serve the community.
When presented with a critical thinking question, it’s not enough to just read the question once and arrive at the first answer that pops into your mind. You should examine the question closely by reading it several times, carefully.
Each time you read the question, check to see if there are meanings or intentions in the question that you didn’t notice before. You can also take this time of reflection to discover ways in which your own assumptions or biases may be negatively influencing your answer.
You can take notes on these things and reflect on them before providing your answer to the question.
Only after examining and reflecting can you get to the precise heart of the question at hand. Then, you can pair it with an equally precise answer.
Critical thinkers also rely on research and newfound knowledge to inform their answers to questions. This involves taking the time to learn about topics that you’re questioned about if you are unfamiliar with them.
For example, if you are asked a question about the economy of a country that you are unfamiliar with, you should research before answering.
Read up on recent economic reports for that country, using credible sources. Make sure that you fully understand every word in the question by pulling out a dictionary.
From there, you can make your answer more accurate and logical overall.
Lastly, a good critical thinker should be able to organize the opinions and thoughts in their answers. Write out a draft of your answer before arriving at your final solution.
Read the answer back to yourself and see if your message is coming across clearly based on the grammar and syntax you’ve used.
If you need to break the answer down into parts and rearrange them to improve it, do so. An organized answer will be easier to understand and may make the difference between a good idea getting lost in the weeds or being championed.
Final Thoughts – 6 Critical Thinking Answer Tips
If you’ve been wanting to learn how to better answer critical thinking questions, then hopefully our guide has given you some inspiration. Some of the key aspects of critical thinking involve one’s ability to ask pertinent questions, examine and reflect on one’s thoughts, set aside biases, make judgments, and clearly communicate.
Make sure to refer to our critical thinking answer tips the next time you are faced with a tough question. Remember, sometimes, a critical answer relies on you taking extra time to research, re-read, re-write, and clarify your own thoughts.
https://louisville.edu/ideastoaction/about/criticalthinking/what
https://www.criticalthinking.org/pages/defining-critical-thinking/766
https://www.utc.edu/academic-affairs/walker-center-for-teaching-and-learning/faculty-programs/faculty-fellow-programs/faculty-fellow-program-development/basic-elements-of-critical-thinking
You may also like
How to Use Artificial Intelligence in the Critical Thinking Process: Enhancing Human Decision-Making
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing the way critical thinking is approached in various sectors. By integrating AI into the critical thinking process, […]

Critical Thinking and Time-Management (How to get the most important things done)
Critical thinking and time management go together. Time management is really just a problem that needs to be solved, and that problem […]

How to Teach Critical Thinking in the Digital Age: Effective Strategies and Techniques
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, the ability to think critically has become increasingly important for individuals of all ages. As technology […]

Critical thinking and conflict resolution
Introduction Have you ever wondered how critical thinking can help in terms of conflict resolution? Critical thinking is a powerful tool, but […]
240 Philosophical Questions for Deep Critical Thinking & Debate

Philosophical questions are an effective tool to stimulate and develop critical thought. They examine profound matters like free will and human nature; the source and value of happiness; morality and ethics; love, logic, and knowledge; religion, death, and the meaning of life.
Although such questions can open a “rabbit hole” that leads to endless and seemingly unanswerable questions, a list of philosophical questions to ask about life—like the ones provided below—can be used as a springboard for critical thinking.
Such questions help us evaluate arguments, explore foreign ideas, identify potential biases, and think critically about our own beliefs and presuppositions.

We are preparing our our children to enter a society full of questions … and questionable ideas.
Consequently, it is our responsibility to train them to think critically and, above all, seek truth when asking the deep questions that arise in their own hearts.
First, let’s take a closer look at what a philosophy question is. Then I’ll provide some examples to help encourage deep thinking.
What is a Philosophical Question OR TOPIC?
A philosophical question is open-ended. Since philosophy itself means “love of wisdom,” it logically follows that a philosophical question is one that pursues a deep understanding of the subject examined.
The answer to this type of question isn’t necessarily an easy one—nor is it always black or white. It requires thoughtful reflection.
The deeper the reasoning behind the answer the better.
Bear in mind there’s no such thing as a dumb philosophical question . However, don’t be surprised if the way questions are answered borders on the brink of absurdity at times.
But the goal is to inspire thought .
So … even if your students gives nonsensical responses, if they’re willing to explain how they came to their answer, count it as a win.
(Even giving an incomplete answer is better than not pondering the question at all.)
A good example of a philosophical question is one of the three overarching “pillars” of philosophy.
The 3 Basic But Big Questions of Philosophy Deal with Existence
The fundamental questions of philosophy deal with existence and fall into three main categories::
- Where did we come from?
- Why are we here and how should we live?
- Is there hope for our future and life after death?
How we answer those questions determines what we will value and how we will behave.
With that in mind, it’s clear just how important it is to train our children to ask meaningful questions and seek truthful answers.
The study of philosophy can help us do that.
PDF Download of 240 Philosophical Questions

GET ALL 240 QUESTIONS IN AN INSTANT-DOWNLOAD EBOOK!
Includes strategies for using philosophical questions as debate topics.
It is natural to be inquisitive. Let’s steward our students’ curious natures well!
I’ve gathered 240 philosophy questions to help you (and your students) think through tough philosophical topics together.
It’s tempting to look at these questions as a mere academic exercise.
But philosophical ideas have shaped human history from ancient times until today — for better or for worse .
Look at them, instead, as a means of preparing your students to face (and combat) the deceptive ideas they will soon encounter.
Questions of Free Will and Human Nature

Are we really free?
The question of free will versus determinism has been debated by great thinkers for centuries.
Some contend that we have complete freedom of choice.
Others believe that humans have no free will and cannot be held morally responsible for their actions (determinism).They argue that the choices we make stem exclusively from the nature we are born with and all the influences that surround us.
The Bible teaches that we have free will, and we’re responsible for our actions. As Deuteronomy 30:19 explains:
“… I have set before you life and death, blessings and curses. Now choose life, so that you and your children may live …”
Here are some questions about will and humanity:
- Are humans innately good or evil?
- Can humans change their behavior if given enough time?
- Do humans need God to exist?
- What happens when we die?
- Does consciousness continue after physical death?
- Why does suffering happen?
- Should we try to prevent bad events from happening? If so, then how would we go about doing that?
- What makes human life so valuable?
- What makes us human?
- Why does it matter if we’re alive?
- Is there anything wrong with being selfish?
- Do humans need other people in order to live?
- Can animals feel pain? If so, why don’t they try to avoid hurting each other?
- Are children born good or evil?
- Is it okay to lie to protect yourself?
- What is beauty?
- Do all people deserve respect?
- Did you exist before you were born?
- Where do emotions come from?
- Can we choose our emotions or do they just happen?
- At what age are children held accountable for their actions? How do you determine that?
- Where does self-worth come from?
- How do you determine one’s self-worth?
- Is one human life worth more than another?
- Is ignorance really bliss?
- What is the goal of humanity?
- Can predestination and free will coexist?

Philosophical Questions About Happiness
The philosopher Aristotle held the view that, “Happiness is the meaning and the purpose of life, the whole aim and end of human existence.”
Yet the very definition of happiness is as diverse as the people who seek it. Some seek it in relationships, others in work, hobbies, or pleasure.
One school of thought says finding happiness requires a life in which every aspect contributes toward personal fulfillment.
Another believes that happiness is “happenstance”—an emotion based on positive circumstances.
What do you think?
Here are some questions to ponder about happiness:

- What does it mean to be happy?
- Can I be happy when faced with suffering?
- Is happiness universal or a matter of perspective?
- How much should we care about making ourselves happy?
- Is it possible to feel happy and sad at the same time?
- Is it really necessary to pursue happiness?
- Are we happier now as a society than in times past? Why or why not?
- Does anyone else’s happiness affect my own?
- If someone has less material wealth than me, does this automatically make him unhappy?
- What brings true happiness?
- Can happiness be measured or quantified, like money and power?
- Are certain types of experiences inherently “happier” than others?
- Is it always best to seek out pleasure over avoiding pain?
- Is happiness just the product of chemical reactions in the brain?
Questions Regarding Morals and Ethics

Questions of morals and ethics are important to explore if you wish to develop critical thinking skills.
Morality and ethics both relate to the distinction between good and bad or right and wrong. However, morality is usually thought of as personal and normative, while ethics is the standards of good and bad distinguished by a particular community or social setting.
Because the seriousness of the two topics can elicit emotional responses, if we’re not careful, debates on ethics and morality can get heated quickly.
A good moral or ethical argument takes the whole picture into account.
For instance, how would you answer the question, “ Is killing always wrong? ”
Our first instinct may be a resounding Yes!
But looking at the big picture, we might ask: What if it occurs in self-defense? What about soldiers? Are they held to the same ethical standard civilians are?
These are the types of philosophical questions we encounter in this category.
Here are some additional examples:

- Is morality relative or absolute?
- Where do morals come from?
- Is it possible to make moral judgments without religion?
- Is killing justified under certain conditions?
- What makes something immoral?
- How do you define “good” and “evil”?
- Why do most people think that lying is bad?
- Should all actions have equal consequences?
- Does every human life count equally?
- Is it ever justified to hurt others?
- Is it fair to punish criminals with death?
- Does morality come from within or outside ourselves?
- Is stealing ever permissible?
- Is it ever permissible to deceive others?
- Should we judge acts based on their outcomes alone?
- Should we always follow the rules even if doing so causes harm?
- Is slavery ever ethically defensible?
- Is dishonesty always wrong?
- Would you kill one person in order to save 1,000?
- Are lies permissible if they protect someone’s feelings?
- What defines a person?
- Are we obligated to help others?
- Is it wrong to kill animals?
- Are humans replaceable?
- What is virtue?
Love is an abstract concept defined in a number of different ways. It’s described as:
- a state of mind
- a relationship
- or a desire.
You’ll find a biblical definition of love in 1 Corinthians 13:4-8:
“Love is patient and kind; love does not envy or boast; it is not arrogant or rude. It does not insist on its own way; it is not irritable or resentful; it does not rejoice at wrongdoing, but rejoices with the truth. Love bears all things, believes all things, hopes all things, endures all things. Love never ends.…”

Here’s a collection of philosophical questions about love:
- Which is more important: love or money? Why?
- Is there such thing as true love? If yes, where does it come from?
- Do all human beings want to be loved?
- Can anyone ever really understand another’s feelings?
- Are children born with an innate love for their parents?
- Are some relationships better than others?
- Can life without love exist?
- What makes someone fall in love?
- Why do people get married?
- Is there a difference between love and lust?
- Is marriage necessary?
- Does love last forever?
- Is it okay to love yourself?
- Is love natural or a choice to be made?
- Where do we find love?
Hard Questions Concerning Death
Have you heard the cliché: “The only certainty in life is death and taxes”?
Death truly is a certainty of life.
While some people choose to face the reality of death head-on, others pretend like it doesn’t exist.
Perhaps it’s the finality of death that sparks fear.
Regardless of how we feel, our time on earth will end at some point in the future.
How should that impact how we live today?
Discussing death can be healthy when done in the right manner.

Here are some questions about death we can use to explore the topic, provoke thought, and potentially positively affect how we live:
- Why do people fear death?
- Can we know for certain if there is life after death?
- How would you like to be remembered after you die?
- What happens to the body after you die?
- Does “good death” exist?
- What would happen if we lived forever?
- Should we try to prolong our lives at any cost?
- Could immortality be possible?
- Is euthanasia wrong in all circumstances?
- Is death actually the beginning?
- Why is it acceptable to kill insects?
- Should terminally ill patients be able to choose death?
Questions with Respect to Universal Human Rights

Universal human rights are those rights which apply equally to everyone regardless of race, religion, gender, or creed.
They include freedom of speech , equality before law , right to justice , and more.
The philosophy behind human rights is based upon the idea that humans deserve respect and dignity, and—ultimately—the right to life.
They’re largely considered universal because they are natural, belonging to all members of humanity simply by virtue of being human.
Some philosophers argue that such rights can’t be taken away, while others claim they are conditional.
Here are a few questions to help us think critically about human rights:
- What makes something a human right?
- Do you believe human rights even exist?
- Are human rights actually universal?
- Are humans rights and entitlement the same thing?
- Can torture be justified?
- Is liberty a human right?
- Is personal autonomy a right?
- Do governments have the authority to regulate what people do?
- Does democracy guarantee individual liberty?
- How much control should individuals have over their own bodies?
- If someone commits murder, do they still have the right to life?
- Who has the ultimate responsibility for protecting human rights?
- Has modern technology made us more or less humane?
- Is education a human right for all people?
- Is war ever justifiable?
- Is due process a universal right no matter the crime?
- Is capital punishment ever appropriate?
- Are there any downsides to universal human rights?
- Is free speech a universal right?

Philosophical Questions About Politics, Government, and Society
This category contains some of the hardest philosophical questions out there. Most of us have strong beliefs about politics, government, and society that make it hard to form an unbiased opinion.
Besides political topics, questions in this category also address social issues , social construct , culture , power , and influence .
We can go so far as to question who gets what— when, where, and how.
If you wish to argue successfully—no matter what side of an issue you align with—it is paramount to understand the opposing viewpoint.
Let’s look at a few questions:
- What makes a country democratic?
- What responsibilities does a government have to its constituents?
- Do democracies always make better decisions than dictatorships?
- What constitutes good governance?
- Is rebellion against government ever justified?
- Is socialism fair? What is “fair”?
- If you rob from the rich and give to the poor, is it wrong?
- Are laws always good?
- Is taxation justified?
- What is the ideal government? Why?
- Should the will of the people always be followed?
- What role do political parties play?
- Who defines corruption?
- How do I know whether my views are correct?
- Is voting compulsory?
- Is there such a thing as too much freedom?
- Is bribery always bad?
- Are police officers obligated to protect criminals?
- Should citizens obey unjust laws?
- Who decides which laws apply to whom?
- Where do we draw the line between criminal behavior and civil disobedience?
- Does the state have the moral duty to provide healthcare for its citizens?
- Is wealth redistribution morally correct?
- Should college be free for all? What about grade school or high school?
- Are freedom and liberty the same thing?
- What makes someone free?
- What makes a crime a crime?
- Is it right to govern the number of children families can have to control the world’s population?

Deep Questions to Make You Think
Deep philosophical questions are designed to help you think critically and reflect on the subject at hand.
They are meant to challenge your beliefs so that you may stand more firmly in them , knowing why you believe what you do.
Here are some examples:

- What is reality?
- What are the limits of science?
- Where did all matter come from?
- Can I trust my senses?
- Is there an innnate moral code?
- Does time exist objectively?
- Who created God?
- Is there a soul?
- Are perceptions real?
- Is “fair” the same for everyone? Who determines whether or not something is “fair”?
- What is time?
- What makes you … you?
- What is truth?
- Is truth reality?
- What gives life meaning?
- What determines success vs. failure?
- Why do bad things happen to good people?
- How do I know what’s true?
- Should we judge others by their actions?
- What’s the purpose of life?
- Where do ideas come from?
- What is justice?
- What is evil?
- What makes someone “good” or “bad”?
- Can something be true without evidence?
- Is fate real?
- At what point does consciousness begin?
- Can time be altered?
- Is there a cause for every effect?
Easy and Funny Questions for Conversation Starters

Not all philosophy discussion topics have to be as serious as “What is the meaning of life?”
Learning should be fun and engaging, so don’t shy away from humor when asking deep questions or coming up with unorthodox answers.
Sometimes the most amusing questions lead to the most profound realizations.
Here’s a list of somewhat random philosophical questions to start fun conversations with kids, teens, and older students:

- Is time travel possible? Why or why not?
- Do memories still exist if you forget them?
- Are animals freer than man?
- Are twins unique?
- Are animals like people?
- Do trees feel pain?
- How do you know you’re not dreaming right now?
- Are insects conscious of life?
- What makes something humorous to some and not to others?
- If you save time on something, what happens to that time?
- Why do we talk to ourselves?
- If you try to fail and do, did you actually succeed?
- Can 2+2 ever be something other than 4?
For more ways to engage students in the study of philosophy, try these fun and creative philosophy activities .
Epistemology Questions
Epistemology is concerned with knowledge. It asks questions like::
- How does knowledge work?
- Why do we need it?
- What kind of things count as knowledge?
Epistemologists study these kinds of questions because they’re interested in understanding how humans acquire knowledge.
They also investigate how to differentiate between opinion and justified belief .
As such, epistemological questions analyze which types of evidence can be trusted as reliable sources of information and why.
Needless to say, this category can contain some pretty interesting philosophical questions:

- How do we determine if something is certain?
- How do you know if you know something?
- Does anyone ever truly learn anything?
- Who decides what counts as true knowledge?
- Who determines the difference between fact and fiction?
- What is the relationship between facts and opinions?
- What is the source of human knowledge?
- What is knowledge?
- What is the nature of certainty?
- What is the basis of our confidence in claims made by other people?
- What is the role of reason in determining what’s true?
- What is the relation between logic and reasoning?
- What is the connection between language and thought?
- What is the distinction between perception and imagination?
- What is intuition?
- What is the function of intuition?
- What are thoughts?
- What is the purpose of thinking?
- If two people understand things differently, who is right?
- If we had 1000 years to learn, could we know everything?
- Is there an end of knowledge?
- Is everything subjective?
Logic and the Universe

The historical discipline of logic largely began with Thales , known as the “Father of Western Philosophy.”
Before this point in history, questions of existence were largely “explained” with Greek mythology.
As it stands today, logic can be described as the discipline of distinguishing good vs bad reasoning.
But who defines “good” and “bad”?
It’s important to note that even the best logical conclusions can be false.
Logic doesn’t equal truth.
( Investigate the difference between logical thinking and critical thinking here if you’re interested).
You’ll notice many questions in this category address our origins and creation:
- Can order come from chaos?
- Can something be created from nothing?
- Where did matter come from?
- Is everything relative?
- Is there only one universe? How do we know?
- Is there such thing as absolute truth?
- Are there different levels of existence?
- Do we live forever?
- Was the Big Bang a real event?
- Is space finite?
- Is time eternal?
- Is logic a created concept?
- What time is it really?
- Is the mind the same as the brain?
- What are numbers?
- Does the universe end?
- Is there such a thing as perfection?
- Does sound exist without hearing?
- Are people in a different timezone in the past (or future)?
- Where does fear come from?
- Does pain exist in itself or just our perception of it?
- What is hope?
- Could there be a parallel universe?
Philosophical Questions About Religion
Maybe some of the toughest questions are those of religion. Religion for many is the driving force in their lives (and for good reason).
Religious views affect how we raise our children, interact with others, make decisions, and so much more.
As such, questioning religious principles can be tricky. Some parents go so far as to encourage their kids to not question at all.
Others choose a different route, knowing their children will soon enter a world that will challenge them to question what they believe.
Encouraging teens to question their beliefs—in a structured setting with the Word of God in hand—can prepare them to “make a defense” to those who ask about the hope that is within them (1 Peter 3:15).
Here are some questions about religion:

- Does God exist?
- Does God’s existence depend on our belief in him?
- Can love exist without God?
- What constitutes religion?
- Are miracles real?
- Is religion compatible with science?
- Why does faith matter?
- Who decides which religions are right?
- What makes a person a Christian?
- Should I follow my beliefs blindly?
- Is God a created being?
- Can morality exist without religion?
- Is there a higher power?
Unanswerable Philosophical Questions
Let’s talk about some of the challenges that arise when we delve into the world of ideas.
Since philosophical thought lives largely in grey territory, it deals with questions that can’t be answered with the usual “yes or no,” “this or that” definitive response.
And as our children search for answers to these philosophical questions, they will encounter deceptive lies disguised as logic.
Many college professors of philosophy today will tell you that life’s biggest questions remain unanswered.
Yet those who possess a biblical worldview have a much different perspective.
Even in a lost, confusing world, the Bible is a compass that always points true North. It declares truth in matters the world deems unanswerable.
That’s why it is so important to teach our children how to think and how to reason from a biblical perspective.
Philosophy and Critical Thinking Go Hand in Hand
Critical thinking involves asking questions, analyzing arguments, evaluating evidence, and making decisions based on those evaluations.
It requires us to use logic, reasoning skills, critical analysis, and judgment.
Sound familiar?
Critical thinking is an essential skill that allows us to make decisions and solve problems effectively.
And while it may not seem so at first glance, it is a skill that enables us to defend our beliefs effectively when challenged.
That’s why we focus so heavily on critical thinking from a biblical worldview in the resources we offer at Homeschool Adventure .
If you’re looking for a way to help your students develop critical thinking from a biblical worldview as they explore the history of ideas, check out Philosophy Adventure :

will your children recognize truth?
Philosophy Adventure teaches students 6th-12th grade how to write skillfully , think critically , and speak clearly as they explore the history of ideas .
It was written to bring history alive! Instead of memorizing facts, students “travel back in time” to walk alongside ancient philosophers.
All the while, they will be challenged to examine what they believe about the world around them, and why they believe it .
By the end of the year, students will have written their very own book of philosophy!
Tips for Using These Questions as Philosophical Debate Topics
Philosophical questions about life are naturally thought provoking.
When used properly, even controversial philosophy topics can be effective springboards for critical thinking—a skill that will benefit your teen for life!
Questions can spark wonderful, stimulating debate among older students, especially those in upper middle through high school.

And philosophical debates can be fun but also challenging, providing the perfect opportunity to practice critical thinking.
If you’ve never tried debating in your homeschool, you can use some of these philosophical questions to start.
A quick note:
Not all questions are practical for satisfying philosophical discussions.
The purpose of debate in the homeschool setting is to practice and improve critical thinking, active listening, argument formation, and even teamwork.
Its purpose is not to waste time on frivolous arguing.
Those of us who believe that the Bible is the Word of God know that absolute truth exists. Consequently, questions to which Scripture provides clear answers may not be the best choice for learning how to debate .
Likewise, you may want to avoid questions whose answers would have to be based solely on speculation—with no practical way to confirm facts or conclusions.
However, keeping all of that in mind, it can be immensely productive for older, more mature students to try to debate a stance they personally disagree with.
Doing so can help them better understand their opponent … and equip them to effectively counter opposing views they may face in “real life.”
Only you know whether your students are ready for such a task, so use discernment.
Since the list of questions we provided is pretty extensive, here’s an abbreviated list of questions that would make great philosophical debate topics :
- Does anyone else’s happiness affect my own?
- Is socialism fair? What is “fair’?
How to Debate Philosophy
When you debate a philosophical question, follow the same general outline as any other debate process.
An at-home, sibling-to-sibling or parent-child debate may proceed as follows:
- Assign the debate topic, first and second positions (for or against the question), and allow time for students to brainstorm ideas.
- Encourage students to organize their ideas into simple arguments or points.
- Practice structuring those ideas into a speech with an introduction, rebuttal (for those arguing in the second position), points to make, and a conclusion.
- Designate a neutral third party to declare a “winner.”
- Start the debate.
Depending on your schedule, this entire process can be done in a single day—or stretched over the course of a week (or even a month).
How to Handle Different Age Groups
Simply adjust how deeply you go into each step, depending on the ages of your students.
For younger middle school students, consider keeping the debate more like a simple discussion and less of an emphasis on structure and speeches.
However, you may want to encourage high school students to organize well-developed arguments and rebuttals.
Philosophical questions about life are naturally thought-provoking.
We actually have even more thought-provoking questions here .
When used properly, even controversial philosophy topics can be effective springboards for critical thinking — a skill that will benefit your teen for life!
About The Author
Jordan Mitchell
- Deakin University
- Learning and Teaching
Critical reflection for assessments and practice
- Reflective practice
Critical reflection for assessments and practice: Reflective practice
- Critical reflection
- How to reflect
- Critical reflection writing
- Recount and reflect
What is reflective practice?
"In general, reflective practice is understood as the process of learning through and from experience towards gaining new insights of self and/or practice. This often involves examining assumptions of everyday practice."
Linda Finlay - Reflecting on 'Reflective practice' (2008)
Reflection is critical to being a conscious, effective practitioner in any discipline. The important thing to keep in mind is that reflecting by itself is not reflective practice. Practice is tied into active, impactful change that emerges from deep reflective learning .
Thinking and doing
Reflective practice is the act of thinking about your experiences in order to learn from them to shape what you do in the future. It therefore includes all aspects of your practice (e.g. relationships, interactions, learning, assessments, behaviours, and environments). It also includes examining how your practice is influenced by your own world views and gaining insights and other perspectives to inform future decision making.
Why reflect?
Reflective practice benefits you on both professional and personal levels. Using critical reflection as a tool can give you insight and positively impact your study, your wellbeing and your worklife. Click the plus icons (+) to view some benefits of reflective practice.
When to critically reflect?
Critical reflection connects to past, current and future action. Click on each of the flip cards to learn the time-related actions you need to do as part of reflective practice.
Reflective practice and critical reflection
Reflective practice is part of your mindset and everyday doing for both uni and the workplace. The process also relies on using critical reflection as a tool to analyse your reflections and which allows you to evaluate, inform and continually change your practice.
Explore the infographic below for a visual depiction of the reflective practice and critical reflection relationship.
- Reflective practice infographic
Critical reflection and areas of your practice
Reflective practice relies on your ability to be open to change and to consider relevant evidence that can challenge or inform decision making. Critical reflection is what allows you to deeply understand your study or work practice and then to take actions to improve it.
You should critically reflect on all aspects of your practice including:

Reflective practice and you
How would you define reflective practice for yourself? There's no right or wrong answer to this question because it's so contextual. The way you enact reflective practice is tied to you and how you think, feel and do. We know that writing down or verbalising your thinking can help you better understand what something means to you. With that in mind...
Take a few moments to think about how you define reflective practice. You can then record yourself using the interactive audio activity below and download the soundbyte. Any recording you make is only available to you. Keep this definition in mind as you move through this critical reflection guide.
- << Previous: Homepage
- Next: Critical reflection >>
- Last Updated: Mar 15, 2024 4:53 PM
- URL: https://deakin.libguides.com/critical-reflection-guide
A Step-by-Step Guide to Critical Reflection

Introduction
Critical reflection is the process of analyzing and evaluating an experience in order to gain a deeper understanding of oneself and the situation. It involves taking a step back, examining the experience from different perspectives, and considering the different factors that influenced the outcome. Critical reflection helps us to learn from our experiences and make better choices in the future.
The importance of critical reflection cannot be overstated. It is a vital tool for personal and professional development, and it is essential for anyone who wants to grow and improve. This guide will provide a step-by-step process for practicing critical reflection, as well as tips and strategies for making the most of the process.
If you’re ready to start your journey of self-improvement and growth, this guide is for you. By following the steps outlined here and investing time and effort into the process of critical reflection, you can gain a deeper understanding of yourself, your experiences, and the world around you. So let’s get started!
What is Critical Reflection?
Critical reflection is a process of analyzing and evaluating a particular experience, situation, or problem in a thoughtful and structured way. It involves identifying your own assumptions and biases, as well as considering alternative perspectives and potential areas for improvement.
Definition of Critical Reflection
Simply put, critical reflection is a process of thinking deeply and critically about a particular experience or issue in order to gain insight and improve future outcomes. It is a self-directed and ongoing process that encourages individuals to evaluate their own actions, beliefs, and assumptions in a non-judgmental way.
Characteristics of Critical Reflection
Critical reflection is characterized by several important qualities, including:
- Critical thinking: It involves analyzing and evaluating information in a thoughtful and objective manner.
- Self-awareness: It requires individuals to be aware of their own assumptions and biases, as well as the impact of their actions on others.
- Open-mindedness: It encourages individuals to consider alternative perspectives and ideas, rather than relying solely on their own experiences and beliefs.
- Reflection: It involves taking the time to reflect on a particular experience or issue in order to gain insight and improve performance.
Process of Critical Reflection
Critical reflection is a process that involves several steps to analyze an experience or problem. Below is a step-by-step guide for critical reflection:
Identify the problem or experience to reflect on: The first step in critical reflection is to identify a particular experience or problem to reflect on. This could be a work-related issue, a personal experience, or a situation that occurred in your community.
Describe the experience in detail: Once you have identified the experience or problem to reflect on, the next step is to describe it in detail. This involves identifying the key players, events, and outcomes. Write down your thoughts, feelings, and reactions to the experience.
Analyze the experience: In this step, you need to analyze the experience by reflecting on the following questions: What happened? Why did it happen? What did you think and feel about it? What were the consequences of your actions? What were the consequences of others’ actions? Use critical thinking skills to examine the experience from multiple perspectives.
Evaluate your own role and actions: After analyzing the experience, evaluate your own role and actions. Ask yourself: What did I do well? What actions could I have done differently? What are the implications of my actions for myself and others? This step requires you to be honest and self-reflective.
Identify alternative actions: After evaluating your own role and actions, think about alternative actions that you could have taken. Ask yourself: What could I have done differently? How would that have changed the outcome? What did I learn from this experience?
Conclusion - What did you learn?: The final step in critical reflection is to draw conclusions from your reflection. Identify what you learned from the experience and how you can apply this learning in the future. This step is essential for personal growth and development.
Remember that critical reflection is not a one-time event. It is an ongoing process that requires regular practice. By engaging in critical reflection, you can develop improved communication, problem-solving, and decision-making skills.
Benefits of Critical Reflection
Critical reflection provides numerous benefits for personal and professional development. Here are some of the most common advantages of the process:
Personal growth and development : Critical reflection enables individuals to learn from their experiences and mistakes. This learning process fosters personal growth and development, as individuals are encouraged to examine their values, beliefs, and assumptions.
Improved decision-making skills : Critical reflection helps individuals make more informed and deliberate decisions. By analyzing their experiences and evaluating different courses of action, individuals are better equipped to make decisions that align with their goals and values.
Improved problem solving skills : Critical reflection also enhances problem-solving skills. By systematically examining a problem or experience, individuals can identify the underlying issues and develop more effective solutions.
Improved communication skills : Critical reflection requires individuals to articulate their thoughts and feelings clearly and concisely. This ability to communicate effectively can benefit individuals in a range of contexts, from personal relationships to professional settings.
Overall, critical reflection is a powerful tool for personal and professional development. The benefits of critical reflection extend beyond the individual, as they also enhance the quality of work and relationships with others.
Tips for Effective Critical Reflection
Here are some tips to help you engage in effective critical reflection:
Be Open-minded
Approach the reflection process with an open mind. Be receptive to new ideas and perspectives, and be willing to challenge your own assumptions or beliefs. This will help you gain a deeper understanding of the experience and identify alternative ways of thinking and behaving.
Use a Structured Process
Use a structured process or template to guide your reflection. This can help ensure that you cover all the necessary steps and stay focused on the key issues. It can also make the process more efficient and effective.
Be Honest with Yourself
Be honest and objective when reflecting on your experience. Don’t shy away from acknowledging your own mistakes or limitations, as this can help you grow and improve. However, be sure to also recognize your strengths and accomplishments, as this can help build confidence and motivation.
Practice Regularly
Make reflection a regular habit. Don’t wait for a major crisis or challenge to start reflecting on your experiences. Instead, try to incorporate reflection into your daily routine. This can help you identify patterns or trends over time and make continuous improvements.
By following these tips, you can enhance the effectiveness and impact of your critical reflection process.
In conclusion, critical reflection is an essential part of personal growth and development. Through the process of critical reflection, we can identify areas for improvement, evaluate our own actions and decisions, and come up with alternative solutions to challenging situations.
We hope that this step-by-step guide has provided you with a helpful roadmap for engaging in critical reflection. Remember to be open-minded, use a structured process, and be honest with yourself. By practicing critical reflection regularly, you can improve your decision-making and problem-solving skills, as well as your communication with others.
If you want to learn more about critical reflection, there are many additional resources available. We encourage you to continue to explore this topic and to incorporate critical reflection into your daily life.
Are You a Stoic Thinker?
Redefining your life's purpose through introspection, critical reflection for grad students seeking a career change, why is critical reflection so important ask yourself these questions, exclusive insights from experts on the power of critical reflection, creating anticipation in critical reflection: how to build momentum for change.
Top 20 Critical Thinking Interview Questions & Answers
Master your responses to Critical Thinking related interview questions with our example questions and answers. Boost your chances of landing the job by learning how to effectively communicate your Critical Thinking capabilities.

Critical thinking is a skill highly sought after in today’s complex and fast-paced world. It’s not merely about thinking clearly or rationally; it’s about analyzing and evaluating information to guide action, making it pivotal across all professions and industries. Whether you are applying for a role that explicitly lists critical thinking as a job requirement or you’re looking to enhance your problem-solving prowess in your current position, demonstrating strong critical thinking skills can set you apart from the competition.
This article aims to illuminate the significance of critical thinking in the professional realm by delving into interview questions designed to test this indispensable skill. We’ll provide insights into what employers are looking for when they assess critical thinking abilities and offer strategies for crafting responses that showcase your analytical acumen.
Common Critical Thinking Interview Questions
1. how would you differentiate between a problem that requires critical thinking and one that does not.
Navigating ambiguous situations and analyzing information objectively are key components of effective critical thinking. This skill is crucial for solving complex problems where standard protocols may not apply, and outcomes are unpredictable. Conversely, routine problems often have established methods and clear-cut solutions that don’t demand extensive analysis or creative thought. The question aims to assess a candidate’s ability to recognize when a nuanced approach is necessary versus when efficiency can be prioritized by following standard procedures. It also evaluates a candidate’s judgment in identifying the scale and impact of a problem, which is crucial for resource management and prioritization within a role.
When responding, a candidate should outline their thought process for assessing problems, highlighting their ability to identify key factors such as the complexity of the issue, potential risks, and the level of uncertainty involved. An effective response would include examples demonstrating how they have distinguished between routine and complex problems in past experiences, along with the strategies they employed to address each effectively. This showcases their problem-solving abilities and their understanding of when to leverage critical thinking skills.
Example: “ Differentiating between a problem that requires critical thinking and one that does not hinges on the analysis of several dimensions of the problem at hand. For instance, a problem that is routine, well-defined, and has a clear set of procedures or historical precedents for its resolution typically may not necessitate critical thinking. In contrast, a problem that is complex, ambiguous, involves multiple stakeholders with conflicting interests, or has significant consequences depending on the outcome, demands a critical thinking approach.
In practice, I assess the need for critical thinking by evaluating the problem’s novelty, the scope of impact, the level of uncertainty, and the interdependencies among variables. For example, when faced with a new market trend that could potentially disrupt our business model, I recognized this as a critical thinking scenario due to its complexity and high stakes. I systematically gathered and analyzed data, questioned assumptions, and explored alternative solutions. This involved not just an analytical breakdown of the problem but also creative synthesis to develop innovative strategies, demonstrating the application of critical thinking to navigate through the intricacies of the issue effectively.”
2. Describe an instance when your initial hypothesis about a complex issue was incorrect.
When it comes to critical thinking, the ability to form hypotheses and adjust them when presented with new information or evidence is fundamental. This question delves into a candidate’s flexibility of thought, their willingness to admit and learn from mistakes, and their capacity to approach problems from multiple angles. A well-rounded candidate will not only recognize when they are wrong but will also see it as an opportunity for growth rather than a setback. It’s a test of humility and intellectual integrity, key traits for roles demanding analytical prowess and decision-making.
In your response, recount a specific situation where you had to pivot from your original assumption. Briefly outline the context and the stakes involved. Then, focus on the process you underwent to re-evaluate the situation: the additional information you considered, the way you integrated new data, and how you ultimately arrived at a different conclusion. Emphasize your thought process and the lessons learned, ensuring you highlight your adaptability and continuous improvement mindset.
Example: “ In analyzing a complex issue within a project, my initial hypothesis was that the bottleneck was caused by an inefficiency in the operational workflow. Upon deeper analysis, however, I discovered that the issue was not the workflow itself but rather a mismatch in team skill sets and resource allocation. By incorporating data analytics and soliciting cross-departmental feedback, I realized that the workflow was designed optimally but was being executed by team members who were not best suited for their roles.
To address this, I facilitated a realignment of tasks to match individual strengths and brought in additional training for areas where the team was lacking expertise. This pivot not only resolved the bottleneck but also improved overall team performance and morale. The experience underscored the importance of a data-driven approach and the value of looking beyond surface-level symptoms to underlying causes. It also reinforced the necessity of maintaining a flexible mindset and being willing to challenge my own assumptions in the face of new evidence.”
3. What strategies do you employ to identify biases in your decision-making process?
Awareness of personal biases is a critical component of effective critical thinking. Recognizing and mitigating these biases ensures that decisions are based on objective analysis rather than subjective preference. This question aims to assess whether a candidate is self-aware and actively engaged in personal development, as well as their ability to maintain objectivity in professional scenarios. It also speaks to a candidate’s commitment to fairness and their potential for leadership, where unbiased decision-making is essential for team cohesion and trust.
When responding, candidates should articulate the specific techniques they use to keep their biases in check. This might include seeking diverse perspectives, consulting with colleagues, relying on data and evidence, or engaging in reflective practices such as journaling or meditation. Candidates should provide concrete examples of when they’ve identified a bias in their thinking and how they adjusted their approach to ensure a more balanced outcome. Demonstrating a proactive approach to personal growth and a dedication to fair decision-making will signal to interviewers a candidate’s suitability for roles requiring sound judgment.
Example: “ To identify biases in my decision-making process, I employ a combination of reflective practices and evidence-based evaluation. I actively engage in self-reflection to question my initial assumptions and consider the origins of my perspectives. This often involves journaling, which helps to externalize and critically assess my thought patterns. Additionally, I prioritize the collection and analysis of data to inform my decisions, ensuring that they are rooted in objective evidence rather than subjective intuition.
When I detect a potential bias, I seek out diverse viewpoints to challenge my preconceptions. This involves consulting with colleagues who may have different experiences or expertise, which provides a broader perspective and mitigates the risk of echo chambers. In a recent project, I recognized a confirmation bias in my analysis, where I was favoring information that supported my initial hypothesis. By acknowledging this, I revisited the data and actively searched for disconfirming evidence, which led to a more nuanced understanding and ultimately a more robust decision-making process. This approach not only enhances the quality of my decisions but also fosters a culture of critical thinking and continuous improvement.”
4. In what ways have you used critical thinking to improve a process at your previous job?
Dissecting a process, analyzing its components with a sharp eye, and envisioning a more efficient or effective method are all aspects of critical thinking that drive process improvement and innovation. This ability to objectively evaluate and enhance systems is not just about fixing what’s broken, but also about preempting potential issues and maximizing productivity. By asking this question, interviewers are looking for evidence of a candidate’s analytical skills and their initiative to bring about positive change within an organization.
When responding to this question, provide a concrete example of a time you identified a problem or area for improvement. Break down the steps you took to analyze the situation, emphasizing how you gathered data, considered various solutions, and weighed the pros and cons. Then, explain the action you took, the implementation of the new process, and most importantly, the outcome. Illustrate how your critical thinking led to tangible benefits for the company, such as time savings, cost reductions, increased revenue, or improved employee satisfaction.
Example: “ In a previous role, I identified a bottleneck in our project reporting process, which was causing delays in decision-making. I initiated a thorough analysis of the existing workflow and discovered that the report consolidation was the primary issue, as it relied on manual data entry from multiple departments. To tackle this, I conducted a root cause analysis to understand the underlying issues and engaged with stakeholders to gather insights and validate findings.
Armed with this information, I proposed and implemented an automated data aggregation tool that interfaced with our existing systems. This solution not only streamlined the data collection process but also reduced the potential for human error. By critically evaluating the process and considering the technological resources available, I was able to re-engineer the workflow, resulting in a 30% reduction in the time taken to generate reports. This improvement led to faster strategic decisions and a significant increase in overall team productivity.”
5. Can you provide an example of how you’ve dissected a multifaceted argument to assess its validity?
Breaking down complex issues into their component parts to understand the underlying logic and reasoning is a hallmark of effective critical thinking. This skill is particularly valuable as it allows for a nuanced approach to problem-solving, where the thinker can identify biases, logical fallacies, and the strength of the evidence presented. Employers seek individuals who can navigate through layers of information, differentiate between correlation and causation, and make informed decisions based on a sound analysis of available data. This question aims to reveal whether the candidate has a systematic approach to addressing intricate arguments and can remain objective while evaluating differing viewpoints.
When responding to this question, begin by outlining a specific scenario where you were faced with a challenging argument or problem. Walk the interviewer through your process step-by-step, explaining how you identified key issues, researched relevant information, and applied logical reasoning to each part. Highlight how you remained impartial, even if the argument related to a topic you felt strongly about, and conclude by sharing the outcome of your analysis. This approach not only demonstrates your critical thinking abilities but also shows that you can communicate complex ideas clearly and effectively.
Example: “ In one instance, I was presented with an argument that a particular business strategy would significantly increase market share. The argument was supported by a variety of data points and expert opinions. To assess its validity, I first deconstructed the argument into its core components: the underlying assumptions, the evidence provided, and the logical connections between the two.
I then conducted an independent evaluation of the evidence, scrutinizing the methodology behind the data collection and the credibility of the sources. Simultaneously, I challenged the assumptions by considering alternative scenarios and seeking out information that could either confirm or refute them. Throughout this process, I maintained an objective stance, ensuring that my personal biases did not color the analysis.
The outcome of this rigorous examination was a nuanced understanding of the strategy’s potential. I concluded that while the strategy had merit, it also carried risks that were not initially apparent. This comprehensive analysis allowed for a more informed decision-making process that considered both the strengths and weaknesses of the proposed strategy.”
6. Outline the steps you take when confronted with conflicting data points.
When presented with conflicting data, the ability to discern, analyze, and integrate information is paramount. This question not only assesses a candidate’s analytical skills but also evaluates their approach to uncertainty and complexity. It inspects the candidate’s methodology for handling information that doesn’t readily align, testing their intellectual rigor and commitment to evidence-based decision-making.
To respond, outline a systematic approach: begin by verifying the sources of the data for credibility. Next, cross-examine the information for errors or biases. If the data remains conflicting, consider alternative perspectives or additional research to provide context. Explain how you would weigh the evidence, perhaps employing specific analytical tools or consulting with knowledgeable colleagues. Conclude by describing how you would form a reasoned conclusion or make a recommendation, emphasizing your flexibility and openness to changing your stance as new information arises.
Example: “ When confronted with conflicting data points, my initial step is to authenticate the sources, ensuring their reliability and validity. I scrutinize the methodologies used to gather the data, looking for potential errors or methodological inconsistencies that could explain the discrepancies. If the sources and methods are sound, I proceed to examine the data for any inherent biases or contextual factors that might influence the results.
Following this critical evaluation, I explore additional research or data that could provide further insight, often utilizing statistical analysis or predictive modeling to discern patterns or anomalies. This process may also involve seeking expertise from colleagues who can offer alternative perspectives or specialized knowledge. Throughout this investigative phase, I maintain a balanced approach, considering all evidence on its merit.
Ultimately, I synthesize the findings, weighing the evidence carefully. My recommendation or conclusion is based on the most comprehensive and robust understanding of the data, with an acknowledgment of any remaining uncertainties. I remain adaptable, ready to adjust my position in light of new evidence or insights that may emerge.”
7. When evaluating evidence, how do you determine its relevance and reliability?
Analyzing information and making informed decisions hinge on determining the relevance and reliability of evidence. The question delves into the candidate’s thought process and methodology for discerning the quality and applicability of information. It also reveals their capacity for skepticism and due diligence, as well as their understanding of the sources and contexts that may affect the integrity of evidence. Employers ask this to ensure the potential employee can effectively sift through data, recognize biases, and draw conclusions that are not only logical but also empirically sound.
When responding to this question, a candidate should outline a systematic approach, starting with the assessment of the source’s credibility, including its origin, authorship, and purpose. They should then discuss the process of cross-referencing the information with other reliable sources and the importance of considering the context in which the evidence was produced. Demonstrating an awareness of one’s own cognitive biases and the potential for these to influence decision-making is also valuable. Lastly, articulating a clear, practical example of how they have applied these principles in a previous situation can help to solidify their response.
Example: “ In evaluating evidence, the first step is to scrutinize the source’s credibility. This includes examining the author’s qualifications, the publication’s reputation, and the methodology used to gather the information. I then assess the purpose of the evidence, looking for any signs of bias or intent to persuade rather than inform. To establish reliability, I cross-reference the evidence with other sources, ensuring they are independent and authoritative. This triangulation helps to confirm the consistency and validity of the information.
Context is paramount; understanding the circumstances under which the evidence was produced allows for a more nuanced interpretation. For instance, in a previous situation where I had to evaluate data from a study, I considered the sample size, the controls in place, and the study’s funding sources. Moreover, I remain vigilant about my cognitive biases, actively seeking disconfirming evidence to challenge my initial conclusions. This disciplined approach ensures that my decisions are based on robust and objective assessments of the evidence at hand.”
8. Share an experience where you had to make a decision without all the desired information.
Acting with confidence even when not all the facts are present is a common requirement in fast-paced environments where waiting for perfect information could lead to missed opportunities or compounded issues. The question aims to assess a candidate’s risk assessment capabilities, their comfort with ambiguity, and their problem-solving skills. It evaluates whether the candidate can pull from their knowledge, past experiences, and available resources to make an informed decision that could potentially affect the outcome of a project or the direction of a company.
When responding to this question, candidates should focus on a specific example that showcases their thought process during an uncertain situation. They should detail the steps they took to gather as much information as possible, weigh the potential risks and benefits, consider the impact of their decision, and explain how they arrived at their conclusion. It’s also beneficial to reflect on the outcome of the decision and what they learned from the experience, demonstrating an ability to learn and adapt from less-than-ideal situations.
Example: “ In a project where time-sensitive decisions were crucial, I encountered a situation where critical data was incomplete due to unforeseen circumstances. Understanding the urgency, I initiated a rapid but thorough risk assessment to evaluate potential impacts of various decision scenarios. I leveraged historical data, parallel case studies, and consulted with subject matter experts to fill in informational gaps to the greatest extent possible.
After synthesizing this information, I employed a decision matrix to prioritize options based on the project’s strategic objectives and stakeholder interests. I chose a course of action that balanced risk with potential reward, ensuring that the most critical project deliverables remained on track. The decision was successful, resulting in minimal disruption to the project timeline and budget. This experience reinforced the importance of a structured approach to decision-making under uncertainty and the value of drawing on diverse information sources to inform such decisions.”
9. Detail a situation in which your critical analysis led to a significant change in strategy or direction.
Strategic planning and problem-solving are areas where critical thinking is indispensable. When interviewers pose this question, they’re looking for evidence of your ability to dissect complex issues, consider diverse perspectives, and foresee potential outcomes. The ability to pivot and adapt strategies based on new information reflects an agile mindset, which is highly valued in dynamic business environments. It reveals your capacity to influence meaningful change and demonstrates foresight, adaptability, and the courage to challenge the status quo when necessary.
When responding, outline a specific scenario succinctly, emphasizing the complexity of the situation and the critical thinking processes you employed. Discuss the rationale behind your analysis, the different options you considered, and why you advocated for a particular change in strategy or direction. Highlight the impact of your decision—how it benefited the organization, improved efficiency, increased revenue, or mitigated risks. Your response should convey confidence in your judgment, an analytical approach to problem-solving, and a proactive stance in driving innovation or improvement.
Example: “ In a project where the initial strategy was to expand market share through aggressive pricing, I conducted a critical analysis of market trends, consumer behavior, and competitive responses. My analysis revealed that such a pricing strategy would trigger a price war with competitors that our company was not financially positioned to sustain. Instead, I proposed a value-added approach, focusing on differentiating our products through enhanced features and customer service rather than competing solely on price.
I presented a comprehensive business case to the leadership team, outlining the potential long-term consequences of the original strategy, including market erosion and reduced profitability. I contrasted this with the projected outcomes of the value-added strategy, which included increased customer loyalty, brand strength, and sustainable profit margins. The leadership adopted my recommendation, leading to a 15% increase in customer retention and a 10% rise in profit margins within the following fiscal year, validating the shift in strategy and demonstrating the importance of thorough critical analysis in strategic decision-making.”
10. How do you handle situations where team members resist your critical evaluations?
Providing feedback that may not be readily accepted, especially when it challenges established ideas or practices within a team, involves effective critical thinking. The ability to navigate resistance is a testament to one’s diplomatic skills and emotional intelligence. It reflects an understanding that critique is not a personal attack but a necessary part of growth and innovation. Employers value candidates who can diplomatically deliver critical evaluations and facilitate a constructive dialogue that leads to improved performance and collaboration, rather than discord and division.
When responding to this question, it’s important to emphasize your approach to communication and conflict resolution. Detail specific strategies you employ to ensure that your evaluations are objective, evidence-based, and presented in a way that underscores their intention to improve the team’s output. Highlight your ability to listen to and address concerns, foster an open environment for discussion, and ultimately guide the team towards a consensus or compromise that upholds the project’s best interests.
Example: “ In situations where team members resist critical evaluations, my approach is to first ensure that the feedback is grounded in objective data and aligns with predefined goals or standards. I present my evaluations with clarity, focusing on the issue at hand rather than personal attributes, to minimize defensiveness. When resistance occurs, I actively listen to the team members’ perspectives, acknowledging their viewpoints and concerns. This demonstrates respect for their expertise and fosters an environment of mutual trust.
I then facilitate a constructive dialogue, guiding the team towards understanding the evaluation’s rationale and the potential benefits of addressing the identified issues. By encouraging an open exchange of ideas, I often find that resistance gives way to collaborative problem-solving. If a consensus is not immediately reached, I propose incremental steps to test the recommended changes, allowing the team to see empirical results. This method not only validates the evaluation’s findings but also empowers the team to be part of the solution, ensuring that the critical evaluation serves as a catalyst for positive change rather than a point of contention.”
11. What is your approach to prioritizing issues requiring immediate critical thought over routine tasks?
Distinguishing between tasks that need immediate attention and those that follow a routine is often a critical component of professional critical thinking. Employers are looking for candidates who can swiftly analyze situations, recognize the urgency and potential impact of each task, and act accordingly to ensure efficiency and effectiveness. The ability to prioritize reflects a person’s judgment, time management skills, and ultimately their capability to contribute to the organization’s success without becoming overwhelmed or sacrificing quality.
When responding to this question, you should demonstrate your decision-making process by providing a clear and structured approach. Outline how you assess the importance of tasks, perhaps by considering factors such as deadlines, potential outcomes, and resources required. You could also mention any tools or techniques you use to stay organized, such as to-do lists or project management software. Giving concrete examples from past experiences where you successfully prioritized critical issues will illustrate your methodology in action and reassure the interviewer of your proficiency in this area.
Example: “ When faced with multiple tasks, my approach to prioritization begins with a swift evaluation of each issue’s potential impact and urgency. I consider the consequences of delayed action, weighing the risks against the benefits of immediate attention. Critical issues that could escalate into larger problems or have a significant negative impact on the project or organization take precedence. For instance, if a critical issue has the potential to disrupt service delivery or cause financial loss, it becomes the top priority.
I utilize a combination of Eisenhower’s Matrix for categorizing tasks by urgency and importance, and project management tools for tracking progress and deadlines. This method allows me to maintain a clear overview of the landscape of responsibilities and make informed decisions quickly. In practice, this approach has enabled me to effectively intervene in situations that required immediate critical thought, such as resolving a bottleneck in a project that threatened to derail the timeline, while ensuring that routine tasks are rescheduled appropriately and do not fall by the wayside.”
12. Could you give an example of a time when you had to challenge conventional wisdom using critical thinking?
The ability to step outside the norm, question the status quo, and innovate is a key aspect of critical thinking. This question aims to unearth a candidate’s ability to recognize when a widely accepted approach is flawed or inadequate and their courage and skill in devising and implementing a more effective alternative. It reveals their capability to not only recognize when a widely accepted approach is flawed or inadequate but also their courage and skill in devising and implementing a more effective alternative.
To respond effectively, choose a specific instance where you identified a problem that others had accepted as unsolvable or ignored due to traditional thinking. Explain your thought process in evaluating the situation, how you identified a novel approach, and the steps you took to challenge the prevailing wisdom. Highlight the outcome, what you learned, and how it demonstrates your critical thinking prowess. Be sure to convey confidence in your decision-making process while also acknowledging the risk and resistance that often accompanies going against the grain.
Example: “ In a project where the prevailing approach was to incrementally improve an existing product, I noticed that our incremental changes were no longer yielding significant benefits to the customer. Conventional wisdom suggested we continue with minor improvements, but my analysis of customer feedback and market trends indicated a plateau in satisfaction and a shift in consumer needs.
Using critical thinking, I dissected the core functions of our product, reevaluated our assumptions, and proposed a radical redesign that aligned more closely with emerging user preferences. I presented a data-driven case to stakeholders, illustrating the long-term benefits and potential market capture that a bold move could offer. Despite initial resistance, the evidence was compelling, and we pivoted to the new strategy.
The redesigned product not only reinvigorated the brand but also captured a new customer segment, leading to a substantial increase in market share. This experience underscored the importance of questioning the status quo and reinforced my belief in the power of critical thinking to drive innovation and strategic redirection.”
13. How do you maintain objectivity when critically assessing emotionally charged issues?
Detaching oneself from personal biases and emotional influences to arrive at logical, fair conclusions is a demand of critical thinking, especially in emotionally charged situations. Employers ask this question to discern whether a candidate possesses the self-awareness and strategies necessary to navigate emotionally-laden terrain without compromising their decision-making process. It’s a subtle test of a candidate’s professionalism and their capacity to handle workplace conflicts or sensitive projects with a level head.
When responding, illustrate with examples where you’ve successfully maintained impartiality during heated discussions or decisions. Emphasize techniques you use, such as stepping back to analyze the facts, seeking diverse perspectives, or employing established frameworks to guide your thought process. Your answer should reassure the interviewer that you can uphold the integrity of your role, even when emotions run high.
Example: “ Maintaining objectivity in emotionally charged situations hinges on a disciplined adherence to evidence and a structured analytical framework. For instance, during a contentious project debate, I anchor my assessment in data-driven criteria, ensuring that decisions are rooted in quantifiable metrics rather than subjective sentiments. This approach not only clarifies the decision-making process but also provides a common language for all stakeholders, facilitating a more rational discourse.
Additionally, I actively seek out diverse perspectives to challenge my own biases and broaden my understanding of the issue at hand. By engaging with viewpoints that differ from my own, I can construct a more comprehensive analysis that transcends personal emotions. This method was particularly effective when navigating a high-stakes negotiation, where synthesizing the various interests led to a consensus that balanced emotional concerns with strategic objectives. Employing these techniques consistently has proven to be instrumental in upholding impartiality and ensuring that critical thinking prevails in emotionally intense scenarios.”
14. What techniques do you use to foster critical thinking skills within a team environment?
Cultivating an environment where team members are encouraged to think deeply and challenge assumptions is a reflection of critical thinking in a team setting. When interviewers pose this question, they are looking for insight into how you foster intellectual growth and collaborative problem-solving. It reveals your leadership style and your ability to facilitate intellectual growth and collaborative problem-solving. The question also serves to understand if you can balance the need for diverse perspectives while steering the team towards cohesive, well-reasoned outcomes.
When responding, you should outline specific strategies you’ve employed to encourage critical thinking. This could include fostering open discussions, posing challenging problems for the team to solve, encouraging team members to question the status quo, and facilitating debates. Highlight examples from your experience where these techniques have led to innovative solutions or improved decision-making. Mention how you ensure all voices are heard and how you guide discussions to remain constructive and focused on the end goal.
Example: “ To cultivate critical thinking within a team, I implement a structured approach to problem-solving that encourages divergent thinking followed by convergent analysis. Initially, I facilitate brainstorming sessions that promote the free flow of ideas without immediate judgment, allowing team members to explore various perspectives and challenge preconceived notions. This openness fosters an environment where creativity is valued, and unconventional ideas can surface.
Once a broad range of ideas is on the table, I guide the team through a critical evaluation process. This involves systematically assessing the feasibility, potential impact, and risks associated with each idea. I encourage team members to ask probing questions and consider the implications of each approach. By employing techniques such as the Six Thinking Hats or SWOT analysis, I ensure that the team examines issues from multiple angles, leading to more robust and well-rounded solutions. Moreover, I make a conscious effort to create an inclusive atmosphere where every member feels empowered to contribute, ensuring a diversity of thought and preventing groupthink. Through these methods, we’ve consistently achieved innovative outcomes and enhanced our collective decision-making capabilities.”
15. Illustrate how you balance quick decision-making with thorough critical analysis under pressure.
Thinking on one’s feet while ensuring that decisions are well-considered and not rash is a crucial aspect of critical thinking, especially in roles where the stakes are high and the cost of a mistake is significant. Employers ask this question to assess a candidate’s ability to think on their feet while also ensuring that their decisions are well-considered and not rash. It’s crucial in roles where the stakes are high and the cost of a mistake is significant. The interviewer is looking for a glimpse into your decision-making process, particularly how you weigh the urgency of a situation against the need for comprehensive analysis.
To respond, describe a scenario where you were faced with a time-sensitive decision. Walk through your thought process, highlighting how you identified the key issues, evaluated the information at hand, and prioritized actions while maintaining a commitment to making a sound, well-reasoned choice. Focus on demonstrating your ability to discern which decisions require immediate action and which can benefit from more extensive analysis. It’s important to convey that you can strike a balance between speed and precision, leveraging your critical thinking skills to deliver optimal outcomes efficiently.
Example: “ In a situation where rapid decision-making was crucial, I employed a tiered approach to critical analysis. Initially, I identified the core issue that demanded immediate attention, separating it from less urgent factors. I then quickly gathered the most relevant data, applying heuristic techniques to assess the situation’s urgency and potential impact. This allowed me to prioritize actions that would mitigate immediate risks or capitalize on fleeting opportunities.
Simultaneously, I maintained an awareness of the broader context, ensuring that my swift decisions aligned with long-term objectives and values. By leveraging a combination of deductive reasoning to address the immediate issue and inductive reasoning to consider the potential implications, I was able to make a well-reasoned decision that was both timely and thoughtful. This method has consistently proven effective in balancing the need for expediency with the commitment to thorough analysis, ensuring that the decisions I make under pressure are both strategic and sound.”
16. Have you ever encountered a groupthink scenario and how did you apply critical thinking to address it?
Recognizing the signs of groupthink—such as a homogenization of ideas, pressure to conform, and an illusion of unanimity—and challenging the status quo to ensure diverse perspectives are considered is important for preventing suboptimal outcomes. Employers value candidates who can maintain objectivity, apply analytical skills to evaluate different opinions, and foster a culture of open dialogue, even when it’s uncomfortable or goes against the grain. This question assesses a candidate’s ability to maintain objectivity, apply analytical skills to evaluate different opinions, and foster a culture of open dialogue, even when it’s uncomfortable or goes against the grain.
When responding, it’s important to provide a specific example that illustrates your awareness of a groupthink situation. Detail how you identified the issue, the steps you took to encourage alternative viewpoints, and the outcome of your intervention. Emphasize your communication skills, your respect for diverse opinions, and your commitment to making decisions based on evidence and sound reasoning. It’s also beneficial to reflect on what you learned from the experience and how it has influenced your approach to teamwork and problem-solving in subsequent situations.
Example: “ Yes, I encountered a groupthink scenario during a project where the team was prematurely converging on a solution without thoroughly vetting alternatives. Recognizing the signs of groupthink, such as the lack of debate and the quick dismissal of outside opinions, I intervened by orchestrating a structured brainstorming session. I introduced a “devil’s advocate” approach, assigning team members to purposely challenge the prevailing assumptions and propose contrarian viewpoints.
This strategy fostered a more open dialogue and encouraged critical evaluation of the proposed solution. By systematically dissecting each argument and examining the evidence, the team was able to identify potential flaws and biases in our initial approach. The outcome was a more robust and innovative solution that had the benefit of diverse perspectives. The experience reinforced the importance of vigilance against groupthink and has since shaped my commitment to fostering an environment where critical thinking and dissenting opinions are valued in the decision-making process.”
17. Describe a complex project where your critical thinking uncovered an overlooked solution.
Evaluating sources, such as data, facts, observable phenomena, and research findings, is part of the critical thinking process. In the context of a job interview, this question serves to evaluate not only a candidate’s problem-solving capabilities but also their initiative and innovation. It reveals how a candidate approaches a problem, breaks it down into components, and systematically tackles it. It’s about assessing the candidate’s ability to not just think, but to think outside the box and recognize patterns that are not immediately obvious, which can lead to innovative solutions that others might miss.
When responding to this question, you should outline the context of the project briefly, highlighting its complexity. Proceed to explain the thought process you employed, detailing how you identified the problem, the various solutions you considered, and why they were dismissed or pursued. Emphasize the critical thinking techniques you used, such as questioning assumptions, analyzing potential outcomes, and synthesizing information from various sources. Conclude with the impact of your solution, such as cost savings, time efficiency, or improved outcomes. Demonstrating a structured approach to problem-solving will show employers that you possess the analytical skills necessary to tackle complex projects effectively.
Example: “ In a recent complex project, the primary challenge was optimizing the resource allocation process to reduce waste and increase efficiency. The existing system was sophisticated but had a persistent issue with over-provisioning, leading to significant financial drain. Upon a deep dive into the data and processes, I employed root cause analysis and discovered that the algorithm driving the allocation was based on outdated assumptions about usage patterns.
By questioning these assumptions and conducting a series of predictive analyses, I proposed a dynamic allocation model that adjusted resources in real-time based on current demand rather than historical trends. I also integrated a feedback loop that allowed the system to learn and adapt over time. This solution required a nuanced understanding of both the technical aspects and the behavioral patterns of system users. The implementation of this model led to a 20% reduction in resource waste within the first quarter, validating the effectiveness of the critical thinking process in uncovering this overlooked solution.”
18. What methods do you utilize to ensure your conclusions are sound when dealing with abstract concepts?
Dissecting and navigating theoretical or complex ideas ensures that a candidate’s thought process is logical, thorough, and evidence-based. The question seeks to explore a candidate’s ability to handle abstract concepts that are not easily quantifiable or observable. It is a test of not just intelligence but of a systematic and disciplined approach to problem-solving that can greatly affect the outcomes of projects and tasks. The interviewer is looking for a glimpse into the candidate’s intellectual rigor and how they handle ambiguity and uncertainty.
When responding, it is vital to discuss a structured approach to critical thinking. One could highlight the importance of questioning assumptions, seeking out a variety of sources for information, and applying logical reasoning. Emphasize the use of specific strategies such as breaking down complex problems into smaller, more manageable parts, employing analogies to better understand unfamiliar concepts, or using decision-making frameworks like the Cynefin framework to categorize problems and respond appropriately. Sharing examples from past experiences where these methods were applied to reach a well-reasoned conclusion can illustrate your proficiency in critical thinking.
Example: “ To ensure my conclusions are sound when dealing with abstract concepts, I systematically employ a combination of deductive and inductive reasoning, while rigorously questioning underlying assumptions. I begin by dissecting the abstract concept into its fundamental elements, which allows me to analyze the problem more effectively. This process of decomposition helps to identify any logical inconsistencies and to understand the relationships between the various components of the concept.
I also draw upon diverse informational sources to inform my understanding, ensuring that my perspective is not limited by a single viewpoint. By integrating these perspectives, I can construct a more comprehensive understanding of the abstract concept. Additionally, I use analogies to create parallels with more familiar concepts, which aids in grasping the essence of the abstract idea and in communicating my reasoning to others. When synthesizing my conclusion, I apply decision-making frameworks like the Cynefin framework, which assists in categorizing the problem and determining the most suitable approach for resolution. This structured methodology ensures that my conclusions are not only logical but also pragmatic, taking into account the complexity and context of the situation at hand.”
19. How do you integrate critical thinking into your everyday work routines?
Anticipating challenges and mitigating them before they impact the workflow is a key aspect of critical thinking. Employers want to know that a candidate can not only solve problems when they arise but also anticipate challenges and mitigate them before they impact the workflow. They are looking for evidence of a proactive mindset that employs logic, creativity, and strategic planning as part of the daily work routine rather than reactive thinking that only addresses issues as they come up.
When responding, candidates should describe specific strategies they use to apply critical thinking in their work. This might involve breaking down complex projects into manageable parts, asking probing questions to fully understand a situation, employing data-driven decision-making, or conducting regular reviews of processes to identify potential improvements. Sharing concrete examples of past situations where critical thinking led to successful outcomes can also demonstrate the candidate’s ability to effectively integrate this skill into their work habits.
Example: “ In my daily work, I routinely employ a methodical approach to problem-solving that hinges on breaking down complex issues into their fundamental components. This dissection allows for a clearer understanding of the underlying factors and variables at play. By doing so, I can systematically evaluate each element, considering both short-term and long-term implications, which is critical for informed decision-making.
I also maintain a disciplined practice of asking probing questions, not only to clarify the specifics of a challenge but also to uncover any hidden assumptions or biases that might skew my analysis. This practice is complemented by a commitment to data-driven decisions, ensuring that my conclusions are grounded in empirical evidence rather than conjecture. To ensure continuous improvement, I conduct regular process reviews, identifying areas for refinement or innovation, thereby fostering a dynamic and responsive work environment that leverages critical thinking to overcome obstacles and enhance productivity.”
20. Reflect on a time when your critical thinking abilities significantly impacted the outcome of a project.
Determining if a candidate can discern complex situations and act in a manner that leads to effective and innovative solutions is a crucial part of the interview process. Employers ask this question to determine if a candidate can not only discern complex situations but also act in a manner that leads to effective and innovative solutions. They are looking for evidence of a methodical approach to tackling challenges and the ability to anticipate potential pitfalls. This question also serves to highlight the candidate’s capacity for reflection and learning from past experiences, which is essential for continuous improvement and adaptability in a dynamic work environment.
When responding to this question, it’s crucial to outline a specific situation that showcases your critical thinking process. Begin by setting the scene and describing the challenge or project at hand. Then, explain the steps you took to analyze the situation, including any data gathering, research, or consultation with experts. Highlight how you weighed different options, considered the consequences, and came to a reasoned decision. Conclude with the outcome, focusing on the positive impact of your critical thinking skills on the project’s success, and if applicable, what you learned from the experience that has influenced your approach to future challenges.
Example: “ In a recent project, we faced a critical decision point when unexpected data discrepancies threatened to derail our progress. The initial analysis suggested a significant flaw in our methodology, which could have led to a complete overhaul of the project. Instead of hastily jumping to conclusions, I initiated a systematic review of our data collection and analysis processes. By breaking down each step, I identified a subtle but consistent error in the way certain data points were being recorded, which skewed our results.
After pinpointing the issue, I proposed a recalibration of our data input protocols and a reanalysis of our dataset. This approach required additional time and resources, but it was a more measured response than starting from scratch. The recalibration not only corrected the discrepancies but also improved the overall robustness of our data. As a result, we not only met our project milestones but also enhanced the credibility of our findings. This experience reinforced the value of methodical problem-solving and has honed my ability to navigate complex challenges by focusing on evidence and systematic evaluation.”
Top 20 Restaurant Management Interview Questions & Answers
Top 20 typography interview questions & answers, you may also be interested in..., top 20 self starter interview questions & answers, top 20 succession planning interview questions & answers, top 20 public finance interview questions & answers, top 20 data strategy interview questions & answers.

- New in this Archive
- Chronological
- Editorial Information
- About the SEP
- Editorial Board
- How to Cite the SEP
- Special Characters
- Support the SEP
- PDFs for SEP Friends
- Make a Donation
- SEPIA for Libraries
- Entry Contents
Bibliography
Academic tools.
- Friends PDF Preview
- Author and Citation Info
- Back to Top
Critical thinking is a widely accepted educational goal. Its definition is contested, but the competing definitions can be understood as differing conceptions of the same basic concept: careful thinking directed to a goal. Conceptions differ with respect to the scope of such thinking, the type of goal, the criteria and norms for thinking carefully, and the thinking components on which they focus. Its adoption as an educational goal has been recommended on the basis of respect for students’ autonomy and preparing students for success in life and for democratic citizenship. “Critical thinkers” have the dispositions and abilities that lead them to think critically when appropriate. The abilities can be identified directly; the dispositions indirectly, by considering what factors contribute to or impede exercise of the abilities. Standardized tests have been developed to assess the degree to which a person possesses such dispositions and abilities. Educational intervention has been shown experimentally to improve them, particularly when it includes dialogue, anchored instruction, and mentoring. Controversies have arisen over the generalizability of critical thinking across domains, over alleged bias in critical thinking theories and instruction, and over the relationship of critical thinking to other types of thinking.
2.1 Dewey’s Three Main Examples
2.2 dewey’s other examples, 2.3 further examples, 2.4 non-examples, 3. the definition of critical thinking, 4. its value, 5. the process of thinking critically, 6. components of the process, 7. contributory dispositions and abilities, 8.1 initiating dispositions, 8.2 internal dispositions, 9. critical thinking abilities, 10. required knowledge, 11. educational methods, 12.1 the generalizability of critical thinking, 12.2 bias in critical thinking theory and pedagogy, 12.3 relationship of critical thinking to other types of thinking, other internet resources, related entries.
Use of the term ‘critical thinking’ to describe an educational goal goes back to the American philosopher John Dewey (1910), who more commonly called it ‘reflective thinking’. He defined it as
active, persistent and careful consideration of any belief or supposed form of knowledge in the light of the grounds that support it, and the further conclusions to which it tends. (Dewey 1910: 6; 1933: 9)
and identified a habit of such consideration with a scientific attitude of mind. His lengthy quotations of Francis Bacon, John Locke, and John Stuart Mill indicate that he was not the first person to propose development of a scientific attitude of mind as an educational goal.
In the 1930s, many of the schools that participated in the Eight-Year Study of the Progressive Education Association (Aikin 1942) adopted critical thinking as an educational goal, for whose achievement the study’s Evaluation Staff developed tests (Smith, Tyler, & Evaluation Staff 1942). Glaser (1941) showed experimentally that it was possible to improve the critical thinking of high school students. Bloom’s influential taxonomy of cognitive educational objectives (Bloom et al. 1956) incorporated critical thinking abilities. Ennis (1962) proposed 12 aspects of critical thinking as a basis for research on the teaching and evaluation of critical thinking ability.
Since 1980, an annual international conference in California on critical thinking and educational reform has attracted tens of thousands of educators from all levels of education and from many parts of the world. Also since 1980, the state university system in California has required all undergraduate students to take a critical thinking course. Since 1983, the Association for Informal Logic and Critical Thinking has sponsored sessions in conjunction with the divisional meetings of the American Philosophical Association (APA). In 1987, the APA’s Committee on Pre-College Philosophy commissioned a consensus statement on critical thinking for purposes of educational assessment and instruction (Facione 1990a). Researchers have developed standardized tests of critical thinking abilities and dispositions; for details, see the Supplement on Assessment . Educational jurisdictions around the world now include critical thinking in guidelines for curriculum and assessment. Political and business leaders endorse its importance.
For details on this history, see the Supplement on History .
2. Examples and Non-Examples
Before considering the definition of critical thinking, it will be helpful to have in mind some examples of critical thinking, as well as some examples of kinds of thinking that would apparently not count as critical thinking.
Dewey (1910: 68–71; 1933: 91–94) takes as paradigms of reflective thinking three class papers of students in which they describe their thinking. The examples range from the everyday to the scientific.
Transit : “The other day, when I was down town on 16th Street, a clock caught my eye. I saw that the hands pointed to 12:20. This suggested that I had an engagement at 124th Street, at one o'clock. I reasoned that as it had taken me an hour to come down on a surface car, I should probably be twenty minutes late if I returned the same way. I might save twenty minutes by a subway express. But was there a station near? If not, I might lose more than twenty minutes in looking for one. Then I thought of the elevated, and I saw there was such a line within two blocks. But where was the station? If it were several blocks above or below the street I was on, I should lose time instead of gaining it. My mind went back to the subway express as quicker than the elevated; furthermore, I remembered that it went nearer than the elevated to the part of 124th Street I wished to reach, so that time would be saved at the end of the journey. I concluded in favor of the subway, and reached my destination by one o’clock.” (Dewey 1910: 68-69; 1933: 91-92)
Ferryboat : “Projecting nearly horizontally from the upper deck of the ferryboat on which I daily cross the river is a long white pole, having a gilded ball at its tip. It suggested a flagpole when I first saw it; its color, shape, and gilded ball agreed with this idea, and these reasons seemed to justify me in this belief. But soon difficulties presented themselves. The pole was nearly horizontal, an unusual position for a flagpole; in the next place, there was no pulley, ring, or cord by which to attach a flag; finally, there were elsewhere on the boat two vertical staffs from which flags were occasionally flown. It seemed probable that the pole was not there for flag-flying.
“I then tried to imagine all possible purposes of the pole, and to consider for which of these it was best suited: (a) Possibly it was an ornament. But as all the ferryboats and even the tugboats carried poles, this hypothesis was rejected. (b) Possibly it was the terminal of a wireless telegraph. But the same considerations made this improbable. Besides, the more natural place for such a terminal would be the highest part of the boat, on top of the pilot house. (c) Its purpose might be to point out the direction in which the boat is moving.
“In support of this conclusion, I discovered that the pole was lower than the pilot house, so that the steersman could easily see it. Moreover, the tip was enough higher than the base, so that, from the pilot's position, it must appear to project far out in front of the boat. Morevoer, the pilot being near the front of the boat, he would need some such guide as to its direction. Tugboats would also need poles for such a purpose. This hypothesis was so much more probable than the others that I accepted it. I formed the conclusion that the pole was set up for the purpose of showing the pilot the direction in which the boat pointed, to enable him to steer correctly.” (Dewey 1910: 69-70; 1933: 92-93)
Bubbles : “In washing tumblers in hot soapsuds and placing them mouth downward on a plate, bubbles appeared on the outside of the mouth of the tumblers and then went inside. Why? The presence of bubbles suggests air, which I note must come from inside the tumbler. I see that the soapy water on the plate prevents escape of the air save as it may be caught in bubbles. But why should air leave the tumbler? There was no substance entering to force it out. It must have expanded. It expands by increase of heat, or by decrease of pressure, or both. Could the air have become heated after the tumbler was taken from the hot suds? Clearly not the air that was already entangled in the water. If heated air was the cause, cold air must have entered in transferring the tumblers from the suds to the plate. I test to see if this supposition is true by taking several more tumblers out. Some I shake so as to make sure of entrapping cold air in them. Some I take out holding mouth downward in order to prevent cold air from entering. Bubbles appear on the outside of every one of the former and on none of the latter. I must be right in my inference. Air from the outside must have been expanded by the heat of the tumbler, which explains the appearance of the bubbles on the outside. But why do they then go inside? Cold contracts. The tumbler cooled and also the air inside it. Tension was removed, and hence bubbles appeared inside. To be sure of this, I test by placing a cup of ice on the tumbler while the bubbles are still forming outside. They soon reverse” (Dewey 1910: 70–71; 1933: 93–94).
Dewey (1910, 1933) sprinkles his book with other examples of critical thinking. We will refer to the following.
Weather : A man on a walk notices that it has suddenly become cool, thinks that it is probably going to rain, looks up and sees a dark cloud obscuring the sun, and quickens his steps (1910: 6–10; 1933: 9–13).
Disorder : A man finds his rooms on his return to them in disorder with his belongings thrown about, thinks at first of burglary as an explanation, then thinks of mischievous children as being an alternative explanation, then looks to see whether valuables are missing, and discovers that they are (1910: 82–83; 1933: 166–168).
Typhoid : A physician diagnosing a patient whose conspicuous symptoms suggest typhoid avoids drawing a conclusion until more data are gathered by questioning the patient and by making tests (1910: 85–86; 1933: 170).
Blur : A moving blur catches our eye in the distance, we ask ourselves whether it is a cloud of whirling dust or a tree moving its branches or a man signaling to us, we think of other traits that should be found on each of those possibilities, and we look and see if those traits are found (1910: 102, 108; 1933: 121, 133).
Suction pump : In thinking about the suction pump, the scientist first notes that it will draw water only to a maximum height of 33 feet at sea level and to a lesser maximum height at higher elevations, selects for attention the differing atmospheric pressure at these elevations, sets up experiments in which the air is removed from a vessel containing water (when suction no longer works) and in which the weight of air at various levels is calculated, compares the results of reasoning about the height to which a given weight of air will allow a suction pump to raise water with the observed maximum height at different elevations, and finally assimilates the suction pump to such apparently different phenomena as the siphon and the rising of a balloon (1910: 150–153; 1933: 195–198).
Diamond : A passenger in a car driving in a diamond lane reserved for vehicles with at least one passenger notices that the diamond marks on the pavement are far apart in some places and close together in others. Why? The driver suggests that the reason may be that the diamond marks are not needed where there is a solid double line separating the diamond line from the adjoining lane, but are needed when there is a dotted single line permitting crossing into the diamond lane. Further observation confirms that the diamonds are close together when a dotted line separates the diamond lane from its neighbour, but otherwise far apart.
Rash : A woman suddenly develops a very itchy red rash on her throat and upper chest. She recently noticed a mark on the back of her right hand, but was not sure whether the mark was a rash or a scrape. She lies down in bed and thinks about what might be causing the rash and what to do about it. About two weeks before, she began taking blood pressure medication that contained a sulfa drug, and the pharmacist had warned her, in view of a previous allergic reaction to a medication containing a sulfa drug, to be on the alert for an allergic reaction; however, she had been taking the medication for two weeks with no such effect. The day before, she began using a new cream on her neck and upper chest; against the new cream as the cause was mark on the back of her hand, which had not been exposed to the cream. She began taking probiotics about a month before. She also recently started new eye drops, but she supposed that manufacturers of eye drops would be careful not to include allergy-causing components in the medication. The rash might be a heat rash, since she recently was sweating profusely from her upper body. Since she is about to go away on a short vacation, where she would not have access to her usual physician, she decides to keep taking the probiotics and using the new eye drops but to discontinue the blood pressure medication and to switch back to the old cream for her neck and upper chest. She forms a plan to consult her regular physician on her return about the blood pressure medication.
Candidate : Although Dewey included no examples of thinking directed at appraising the arguments of others, such thinking has come to be considered a kind of critical thinking. We find an example of such thinking in the performance task on the Collegiate Learning Assessment (CLA+), which its sponsoring organization describes as
a performance-based assessment that provides a measure of an institution’s contribution to the development of critical-thinking and written communication skills of its students. (Council for Aid to Education 2017)
A sample task posted on its website requires the test-taker to write a report for public distribution evaluating a fictional candidate’s policy proposals and their supporting arguments, using supplied background documents, with a recommendation on whether to endorse the candidate.
Immediate acceptance of an idea that suggests itself as a solution to a problem (e.g., a possible explanation of an event or phenomenon, an action that seems likely to produce a desired result) is “uncritical thinking, the minimum of reflection” (Dewey 1910: 13). On-going suspension of judgment in the light of doubt about a possible solution is not critical thinking (Dewey 1910: 108). Critique driven by a dogmatically held political or religious ideology is not critical thinking; thus Paulo Freire (1968 [1970]) is using the term (e.g., at 1970: 71, 81, 100, 146) in a more politically freighted sense that includes not only reflection but also revolutionary action against oppression. Derivation of a conclusion from given data using an algorithm is not critical thinking.
What is critical thinking? There are many definitions. Ennis (2016) lists 14 philosophically oriented scholarly definitions and three dictionary definitions. Following Rawls (1971), who distinguished his conception of justice from a utilitarian conception but regarded them as rival conceptions of the same concept, Ennis maintains that the 17 definitions are different conceptions of the same concept. Rawls articulated the shared concept of justice as
a characteristic set of principles for assigning basic rights and duties and for determining… the proper distribution of the benefits and burdens of social cooperation. (Rawls 1971: 5)
Bailin et al. (1999b) claim that, if one considers what sorts of thinking an educator would take not to be critical thinking and what sorts to be critical thinking, one can conclude that educators typically understand critical thinking to have at least three features.
- It is done for the purpose of making up one’s mind about what to believe or do.
- The person engaging in the thinking is trying to fulfill standards of adequacy and accuracy appropriate to the thinking.
- The thinking fulfills the relevant standards to some threshold level.
One could sum up the core concept that involves these three features by saying that critical thinking is careful goal-directed thinking. This core concept seems to apply to all the examples of critical thinking described in the previous section. As for the non-examples, their exclusion depends on construing careful thinking as excluding jumping immediately to conclusions, suspending judgment no matter how strong the evidence, reasoning from an unquestioned ideological or religious perspective, and routinely using an algorithm to answer a question.
If the core of critical thinking is careful goal-directed thinking, conceptions of it can vary according to its presumed scope, its presumed goal, one’s criteria and threshold for being careful, and the thinking component on which one focuses As to its scope, some conceptions (e.g., Dewey 1910, 1933) restrict it to constructive thinking on the basis of one’s own observations and experiments, others (e.g., Ennis 1962; Fisher & Scriven 1997; Johnson 1992) to appraisal of the products of such thinking. Ennis (1991) and Bailin et al. (1999b) take it to cover both construction and appraisal. As to its goal, some conceptions restrict it to forming a judgment (Dewey 1910, 1933; Lipman 1987; Facione 1990a). Others allow for actions as well as beliefs as the end point of a process of critical thinking (Ennis 1991; Bailin et al. 1999b). As to the criteria and threshold for being careful, definitions vary in the term used to indicate that critical thinking satisfies certain norms: “intellectually disciplined” (Scriven & Paul 1987), “reasonable” (Ennis 1991), “skillful” (Lipman 1987), “skilled” (Fisher & Scriven 1997), “careful” (Bailin & Battersby 2009). Some definitions specify these norms, referring variously to “consideration of any belief or supposed form of knowledge in the light of the grounds that support it and the further conclusions to which it tends” (Dewey 1910, 1933); “the methods of logical inquiry and reasoning” (Glaser 1941); “conceptualizing, applying, analyzing, synthesizing, and/or evaluating information gathered from, or generated by, observation, experience, reflection, reasoning, or communication” (Scriven & Paul 1987); the requirement that “it is sensitive to context, relies on criteria, and is self-correcting” (Lipman 1987); “evidential, conceptual, methodological, criteriological, or contextual considerations” (Facione 1990a); and “plus-minus considerations of the product in terms of appropriate standards (or criteria)” (Johnson 1992). Stanovich and Stanovich (2010) propose to ground the concept of critical thinking in the concept of rationality, which they understand as combining epistemic rationality (fitting one’s beliefs to the world) and instrumental rationality (optimizing goal fulfillment); a critical thinker, in their view, is someone with “a propensity to override suboptimal responses from the autonomous mind” (2010: 227). These variant specifications of norms for critical thinking are not necessarily incompatible with one another, and in any case presuppose the core notion of thinking carefully. As to the thinking component singled out, some definitions focus on suspension of judgment during the thinking (Dewey 1910; McPeck 1981), others on inquiry while judgment is suspended (Bailin & Battersby 2009), others on the resulting judgment (Facione 1990a), and still others on the subsequent emotive response (Siegel 1988).
In educational contexts, a definition of critical thinking is a “programmatic definition” (Scheffler 1960: 19). It expresses a practical program for achieving an educational goal. For this purpose, a one-sentence formulaic definition is much less useful than articulation of a critical thinking process, with criteria and standards for the kinds of thinking that the process may involve. The real educational goal is recognition, adoption and implementation by students of those criteria and standards. That adoption and implementation in turn consists in acquiring the knowledge, abilities and dispositions of a critical thinker.
Conceptions of critical thinking generally do not include moral integrity as part of the concept. Dewey, for example, took critical thinking to be the ultimate intellectual goal of education, but distinguished it from the development of social cooperation among school children, which he took to be the central moral goal. Ennis (1996, 2011) added to his previous list of critical thinking dispositions a group of dispositions to care about the dignity and worth of every person, which he described as a “correlative” (1996) disposition without which critical thinking would be less valuable and perhaps harmful. An educational program that aimed at developing critical thinking but not the correlative disposition to care about the dignity and worth of every person, he asserted, “would be deficient and perhaps dangerous” (Ennis 1996: 172).
Dewey thought that education for reflective thinking would be of value to both the individual and society; recognition in educational practice of the kinship to the scientific attitude of children’s native curiosity, fertile imagination and love of experimental inquiry “would make for individual happiness and the reduction of social waste” (Dewey 1910: iii). Schools participating in the Eight-Year Study took development of the habit of reflective thinking and skill in solving problems as a means to leading young people to understand, appreciate and live the democratic way of life characteristic of the United States (Aikin 1942: 17–18, 81). Harvey Siegel (1988: 55–61) has offered four considerations in support of adopting critical thinking as an educational ideal. (1) Respect for persons requires that schools and teachers honour students’ demands for reasons and explanations, deal with students honestly, and recognize the need to confront students’ independent judgment; these requirements concern the manner in which teachers treat students. (2) Education has the task of preparing children to be successful adults, a task that requires development of their self-sufficiency. (3) Education should initiate children into the rational traditions in such fields as history, science and mathematics. (4) Education should prepare children to become democratic citizens, which requires reasoned procedures and critical talents and attitudes. To supplement these considerations, Siegel (1988: 62–90) responds to two objections: the ideology objection that adoption of any educational ideal requires a prior ideological commitment and the indoctrination objection that cultivation of critical thinking cannot escape being a form of indoctrination.
Despite the diversity of our 11 examples, one can recognize a common pattern. Dewey analyzed it as consisting of five phases:
- suggestions , in which the mind leaps forward to a possible solution;
- an intellectualization of the difficulty or perplexity into a problem to be solved, a question for which the answer must be sought;
- the use of one suggestion after another as a leading idea, or hypothesis , to initiate and guide observation and other operations in collection of factual material;
- the mental elaboration of the idea or supposition as an idea or supposition ( reasoning , in the sense on which reasoning is a part, not the whole, of inference); and
- testing the hypothesis by overt or imaginative action. (Dewey 1933: 106–107; italics in original)
The process of reflective thinking consisting of these phases would be preceded by a perplexed, troubled or confused situation and followed by a cleared-up, unified, resolved situation (Dewey 1933: 106). The term ‘phases’ replaced the term ‘steps’ (Dewey 1910: 72), thus removing the earlier suggestion of an invariant sequence. Variants of the above analysis appeared in (Dewey 1916: 177) and (Dewey 1938: 101–119).
The variant formulations indicate the difficulty of giving a single logical analysis of such a varied process. The process of critical thinking may have a spiral pattern, with the problem being redefined in the light of obstacles to solving it as originally formulated. For example, the person in Transit might have concluded that getting to the appointment at the scheduled time was impossible and have reformulated the problem as that of rescheduling the appointment for a mutually convenient time. Further, defining a problem does not always follow after or lead immediately to an idea of a suggested solution. Nor should it do so, as Dewey himself recognized in describing the physician in Typhoid as avoiding any strong preference for this or that conclusion before getting further information (Dewey 1910: 85; 1933: 170). People with a hypothesis in mind, even one to which they have a very weak commitment, have a so-called “confirmation bias” (Nickerson 1998): they are likely to pay attention to evidence that confirms the hypothesis and to ignore evidence that counts against it or for some competing hypothesis. Detectives, intelligence agencies, and investigators of airplane accidents are well advised to gather relevant evidence systematically and to postpone even tentative adoption of an explanatory hypothesis until the collected evidence rules out with the appropriate degree of certainty all but one explanation. Dewey’s analysis of the critical thinking process can be faulted as well for requiring acceptance or rejection of a possible solution to a defined problem, with no allowance for deciding in the light of the available evidence to suspend judgment. Further, given the great variety of kinds of problems for which reflection is appropriate, there is likely to be variation in its component events. Perhaps the best way to conceptualize the critical thinking process is as a checklist whose component events can occur in a variety of orders, selectively, and more than once. These component events might include (1) noticing a difficulty, (2) defining the problem, (3) dividing the problem into manageable sub-problems, (4) formulating a variety of possible solutions to the problem or sub-problem, (5) determining what evidence is relevant to deciding among possible solutions to the problem or sub-problem, (6) devising a plan of systematic observation or experiment that will uncover the relevant evidence, (7) carrying out the plan of systematic observation or experimentation, (8) noting the results of the systematic observation or experiment, (9) gathering relevant testimony and information from others, (10) judging the credibility of testimony and information gathered from others, (11) drawing conclusions from gathered evidence and accepted testimony, and (12) accepting a solution that the evidence adequately supports (cf. Hitchcock 2017: 485).
Checklist conceptions of the process of critical thinking are open to the objection that they are too mechanical and procedural to fit the multi-dimensional and emotionally charged issues for which critical thinking is urgently needed (Paul 1984). For such issues, a more dialectical process is advocated, in which competing relevant world views are identified, their implications explored, and some sort of creative synthesis attempted.
If one considers the critical thinking process illustrated by the 11 examples, one can identify distinct kinds of mental acts and mental states that form part of it. To distinguish, label and briefly characterize these components is a useful preliminary to identifying abilities, skills, dispositions, attitudes, habits and the like that contribute causally to thinking critically. Identifying such abilities and habits is in turn a useful preliminary to setting educational goals. Setting the goals is in its turn a useful preliminary to designing strategies for helping learners to achieve the goals and to designing ways of measuring the extent to which learners have done so. Such measures provide both feedback to learners on their achievement and a basis for experimental research on the effectiveness of various strategies for educating people to think critically. Let us begin, then, by distinguishing the kinds of mental acts and mental events that can occur in a critical thinking process.
- Observing : One notices something in one’s immediate environment (sudden cooling of temperature in Weather , bubbles forming outside a glass and then going inside in Bubbles , a moving blur in the distance in Blur , a rash in Rash ). Or one notes the results of an experiment or systematic observation (valuables missing in Disorder , no suction without air pressure in Suction pump )
- Feeling : One feels puzzled or uncertain about something (how to get to an appointment on time in Transit , why the diamonds vary in frequency in Diamond ). One wants to resolve this perplexity. One feels satisfaction once one has worked out an answer (to take the subway express in Transit , diamonds closer when needed as a warning in Diamond ).
- Wondering : One formulates a question to be addressed (why bubbles form outside a tumbler taken from hot water in Bubbles , how suction pumps work in Suction pump , what caused the rash in Rash ).
- Imagining : One thinks of possible answers (bus or subway or elevated in Transit , flagpole or ornament or wireless communication aid or direction indicator in Ferryboat , allergic reaction or heat rash in Rash ).
- Inferring : One works out what would be the case if a possible answer were assumed (valuables missing if there has been a burglary in Disorder , earlier start to the rash if it is an allergic reaction to a sulfa drug in Rash ). Or one draws a conclusion once sufficient relevant evidence is gathered (take the subway in Transit , burglary in Disorder , discontinue blood pressure medication and new cream in Rash ).
- Knowledge : One uses stored knowledge of the subject-matter to generate possible answers or to infer what would be expected on the assumption of a particular answer (knowledge of a city’s public transit system in Transit , of the requirements for a flagpole in Ferryboat , of Boyle’s law in Bubbles , of allergic reactions in Rash ).
- Experimenting : One designs and carries out an experiment or a systematic observation to find out whether the results deduced from a possible answer will occur (looking at the location of the flagpole in relation to the pilot’s position in Ferryboat , putting an ice cube on top of a tumbler taken from hot water in Bubbles , measuring the height to which a suction pump will draw water at different elevations in Suction pump , noticing the frequency of diamonds when movement to or from a diamond lane is allowed in Diamond ).
- Consulting : One finds a source of information, gets the information from the source, and makes a judgment on whether to accept it. None of our 11 examples include searching for sources of information. In this respect they are unrepresentative, since most people nowadays have almost instant access to information relevant to answering any question, including many of those illustrated by the examples. However, Candidate includes the activities of extracting information from sources and evaluating its credibility.
- Identifying and analyzing arguments : One notices an argument and works out its structure and content as a preliminary to evaluating its strength. This activity is central to Candidate . It is an important part of a critical thinking process in which one surveys arguments for various positions on an issue.
- Judging : One makes a judgment on the basis of accumulated evidence and reasoning, such as the judgment in Ferryboat that the purpose of the pole is to provide direction to the pilot.
- Deciding : One makes a decision on what to do or on what policy to adopt, as in the decision in Transit to take the subway.
By definition, a person who does something voluntarily is both willing and able to do that thing at that time. Both the willingness and the ability contribute causally to the person’s action, in the sense that the voluntary action would not occur if either (or both) of these were lacking. For example, suppose that one is standing with one’s arms at one’s sides and one voluntarily lifts one’s right arm to an extended horizontal position. One would not do so if one were unable to lift one’s arm, if for example one’s right side was paralyzed as the result of a stroke. Nor would one do so if one were unwilling to lift one’s arm, if for example one were participating in a street demonstration at which a white supremacist was urging the crowd to lift their right arm in a Nazi salute and one were unwilling to express support in this way for the racist Nazi ideology. The same analysis applies to a voluntary mental process of thinking critically. It requires both willingness and ability to think critically, including willingness and ability to perform each of the mental acts that compose the process and to coordinate those acts in a sequence that is directed at resolving the initiating perplexity.
Consider willingness first. We can identify causal contributors to willingness to think critically by considering factors that would cause a person who was able to think critically about an issue nevertheless not to do so (Hamby 2014). For each factor, the opposite condition thus contributes causally to willingness to think critically on a particular occasion. For example, people who habitually jump to conclusions without considering alternatives will not think critically about issues that arise, even if they have the required abilities. The contrary condition of willingness to suspend judgment is thus a causal contributor to thinking critically.
Now consider ability. In contrast to the ability to move one’s arm, which can be completely absent because a stroke has left the arm paralyzed, the ability to think critically is a developed ability, whose absence is not a complete absence of ability to think but absence of ability to think well. We can identify the ability to think well directly, in terms of the norms and standards for good thinking. In general, to be able do well the thinking activities that can be components of a critical thinking process, one needs to know the concepts and principles that characterize their good performance, to recognize in particular cases that the concepts and principles apply, and to apply them. The knowledge, recognition and application may be procedural rather than declarative. It may be domain-specific rather than widely applicable, and in either case may need subject-matter knowledge, sometimes of a deep kind.
Reflections of the sort illustrated by the previous two paragraphs have led scholars to identify the knowledge, abilities and dispositions of a “critical thinker”, i.e., someone who thinks critically whenever it is appropriate to do so. We turn now to these three types of causal contributors to thinking critically. We start with dispositions, since arguably these are the most powerful contributors to being a critical thinker, can be fostered at an early stage of a child’s development, and are susceptible to general improvement (Glaser 1941: 175)
8. Critical Thinking Dispositions
Educational researchers use the term ‘dispositions’ broadly for the habits of mind and attitudes that contribute causally to being a critical thinker. Some writers (e.g., Paul & Elder 2006; Hamby 2014; Bailin & Battersby 2016) propose to use the term ‘virtues’ for this dimension of a critical thinker. The virtues in question, although they are virtues of character, concern the person’s ways of thinking rather than the person’s ways of behaving towards others. They are not moral virtues but intellectual virtues, of the sort articulated by Zagzebski (1996) and discussed by Turri, Alfano, and Greco (2017).
On a realistic conception, thinking dispositions or intellectual virtues are real properties of thinkers. They are general tendencies, propensities, or inclinations to think in particular ways in particular circumstances, and can be genuinely explanatory (Siegel 1999). Sceptics argue that there is no evidence for a specific mental basis for the habits of mind that contribute to thinking critically, and that it is pedagogically misleading to posit such a basis (Bailin et al. 1999a). Whatever their status, critical thinking dispositions need motivation for their initial formation in a child—motivation that may be external or internal. As children develop, the force of habit will gradually become important in sustaining the disposition (Nieto & Valenzuela 2012). Mere force of habit, however, is unlikely to sustain critical thinking dispositions. Critical thinkers must value and enjoy using their knowledge and abilities to think things through for themselves. They must be committed to, and lovers of, inquiry.
A person may have a critical thinking disposition with respect to only some kinds of issues. For example, one could be open-minded about scientific issues but not about religious issues. Similarly, one could be confident in one’s ability to reason about the theological implications of the existence of evil in the world but not in one’s ability to reason about the best design for a guided ballistic missile.
Critical thinking dispositions can usefully be divided into initiating dispositions (those that contribute causally to starting to think critically about an issue) and internal dispositions (those that contribute causally to doing a good job of thinking critically once one has started) (Facione 1990a: 25). The two categories are not mutually exclusive. For example, open-mindedness, in the sense of willingness to consider alternative points of view to one’s own, is both an initiating and an internal disposition.
Using the strategy of considering factors that would block people with the ability to think critically from doing so, we can identify as initiating dispositions for thinking critically attentiveness, a habit of inquiry, self-confidence, courage, open-mindedness, willingness to suspend judgment, trust in reason, wanting evidence for one’s beliefs, and seeking the truth. We consider briefly what each of these dispositions amounts to, in each case citing sources that acknowledge them.
- Attentiveness : One will not think critically if one fails to recognize an issue that needs to be thought through. For example, the pedestrian in Weather would not have looked up if he had not noticed that the air was suddenly cooler. To be a critical thinker, then, one needs to be habitually attentive to one’s surroundings, noticing not only what one senses but also sources of perplexity in messages received and in one’s own beliefs and attitudes (Facione 1990a: 25; Facione, Facione, & Giancarlo 2001).
- Habit of inquiry : Inquiry is effortful, and one needs an internal push to engage in it. For example, the student in Bubbles could easily have stopped at idle wondering about the cause of the bubbles rather than reasoning to a hypothesis, then designing and executing an experiment to test it. Thus willingness to think critically needs mental energy and initiative. What can supply that energy? Love of inquiry, or perhaps just a habit of inquiry. Hamby (2015) has argued that willingness to inquire is the central critical thinking virtue, one that encompasses all the others. It is recognized as a critical thinking disposition by Dewey (1910: 29; 1933: 35), Glaser (1941: 5), Ennis (1987: 12; 1991: 8), Facione (1990a: 25), Bailin et al. (1999b: 294), Halpern (1998: 452), and Facione, Facione, & Giancarlo (2001).
- Self-confidence : Lack of confidence in one’s abilities can block critical thinking. For example, if the woman in Rash lacked confidence in her ability to figure things out for herself, she might just have assumed that the rash on her chest was the allergic reaction to her medication against which the pharmacist had warned her. Thus willingness to think critically requires confidence in one’s ability to inquire (Facione 1990a: 25; Facione, Facione, & Giancarlo 2001).
- Courage : Fear of thinking for oneself can stop one from doing it. Thus willingness to think critically requires intellectual courage (Paul & Elder 2006: 16).
- Open-mindedness : A dogmatic attitude will impede thinking critically. For example, a person who adheres rigidly to a “pro-choice” position on the issue of the legal status of induced abortion is likely to be unwilling to consider seriously the issue of when in its development an unborn child acquires a moral right to life. Thus willingness to think critically requires open-mindedness, in the sense of a willingness to examine questions to which one already accepts an answer but which further evidence or reasoning might cause one to answer differently (Dewey 1933; Facione 1990a; Ennis 1991; Bailin et al. 1999b; Halpern 1998, Facione, Facione, & Giancarlo 2001). Paul (1981) emphasizes open-mindedness about alternative world-views, and recommends a dialectical approach to integrating such views as central to what he calls “strong sense” critical thinking.
- Willingness to suspend judgment : Premature closure on an initial solution will block critical thinking. Thus willingness to think critically requires a willingness to suspend judgment while alternatives are explored (Facione 1990a; Ennis 1991; Halpern 1998).
- Trust in reason : Since distrust in the processes of reasoned inquiry will dissuade one from engaging in it, trust in them is an initiating critical thinking disposition (Facione 1990a, 25; Bailin et al. 1999b: 294; Facione, Facione, & Giancarlo 2001; Paul & Elder 2006). In reaction to an allegedly exclusive emphasis on reason in critical thinking theory and pedagogy, Thayer-Bacon (2000) argues that intuition, imagination, and emotion have important roles to play in an adequate conception of critical thinking that she calls “constructive thinking”. From her point of view, critical thinking requires trust not only in reason but also in intuition, imagination, and emotion.
- Seeking the truth : If one does not care about the truth but is content to stick with one’s initial bias on an issue, then one will not think critically about it. Seeking the truth is thus an initiating critical thinking disposition (Bailin et al. 1999b: 294; Facione, Facione, & Giancarlo 2001). A disposition to seek the truth is implicit in more specific critical thinking dispositions, such as trying to be well-informed, considering seriously points of view other than one’s own, looking for alternatives, suspending judgment when the evidence is insufficient, and adopting a position when the evidence supporting it is sufficient.
Some of the initiating dispositions, such as open-mindedness and willingness to suspend judgment, are also internal critical thinking dispositions, in the sense of mental habits or attitudes that contribute causally to doing a good job of critical thinking once one starts the process. But there are many other internal critical thinking dispositions. Some of them are parasitic on one’s conception of good thinking. For example, it is constitutive of good thinking about an issue to formulate the issue clearly and to maintain focus on it. For this purpose, one needs not only the corresponding ability but also the corresponding disposition. Ennis (1991: 8) describes it as the disposition “to determine and maintain focus on the conclusion or question”, Facione (1990a: 25) as “clarity in stating the question or concern”. Other internal dispositions are motivators to continue or adjust the critical thinking process, such as willingness to persist in a complex task and willingness to abandon nonproductive strategies in an attempt to self-correct (Halpern 1998: 452). For a list of identified internal critical thinking dispositions, see the Supplement on Internal Critical Thinking Dispositions .
Some theorists postulate skills, i.e., acquired abilities, as operative in critical thinking. It is not obvious, however, that a good mental act is the exercise of a generic acquired skill. Inferring an expected time of arrival, as in Transit , has some generic components but also uses non-generic subject-matter knowledge. Bailin et al. (1999a) argue against viewing critical thinking skills as generic and discrete, on the ground that skilled performance at a critical thinking task cannot be separated from knowledge of concepts and from domain-specific principles of good thinking. Talk of skills, they concede, is unproblematic if it means merely that a person with critical thinking skills is capable of intelligent performance.
Despite such scepticism, theorists of critical thinking have listed as general contributors to critical thinking what they variously call abilities (Glaser 1941; Ennis 1962, 1991), skills (Facione 1990a; Halpern 1998) or competencies (Fisher & Scriven 1997). Amalgamating these lists would produce a confusing and chaotic cornucopia of more than 50 possible educational objectives, with only partial overlap among them. It makes sense instead to try to understand the reasons for the multiplicity and diversity, and to make a selection according to one’s own reasons for singling out abilities to be developed in a critical thinking curriculum. Two reasons for diversity among lists of critical thinking abilities are the underlying conception of critical thinking and the envisaged educational level. Appraisal-only conceptions, for example, involve a different suite of abilities than constructive-only conceptions. Some lists, such as those in (Glaser 1941), are put forward as educational objectives for secondary school students, whereas others are proposed as objectives for college students (e.g., Facione 1990a).
The abilities described in the remaining paragraphs of this section emerge from reflection on the general abilities needed to do well the thinking activities identified in section 6 as components of the critical thinking process described in section 5 . The derivation of each collection of abilities is accompanied by citation of sources that list such abilities and of standardized tests that claim to test them.
Observational abilities : Careful and accurate observation sometimes requires specialist expertise and practice, as in the case of observing birds and observing accident scenes. However, there are general abilities of noticing what one’s senses are picking up from one’s environment and of being able to articulate clearly and accurately to oneself and others what one has observed. It helps in exercising them to be able to recognize and take into account factors that make one’s observation less trustworthy, such as prior framing of the situation, inadequate time, deficient senses, poor observation conditions, and the like. It helps as well to be skilled at taking steps to make one’s observation more trustworthy, such as moving closer to get a better look, measuring something three times and taking the average, and checking what one thinks one is observing with someone else who is in a good position to observe it. It also helps to be skilled at recognizing respects in which one’s report of one’s observation involves inference rather than direct observation, so that one can then consider whether the inference is justified. These abilities come into play as well when one thinks about whether and with what degree of confidence to accept an observation report, for example in the study of history or in a criminal investigation or in assessing news reports. Observational abilities show up in some lists of critical thinking abilities (Ennis 1962: 90; Facione 1990a: 16; Ennis 1991: 9). There are items testing a person’s ability to judge the credibility of observation reports in the Cornell Critical Thinking Tests, Levels X and Z (Ennis & Millman 1971; Ennis, Millman, & Tomko 1985, 2005). Norris and King (1983, 1985, 1990a, 1990b) is a test of ability to appraise observation reports.
Emotional abilities : The emotions that drive a critical thinking process are perplexity or puzzlement, a wish to resolve it, and satisfaction at achieving the desired resolution. Children experience these emotions at an early age, without being trained to do so. Education that takes critical thinking as a goal needs only to channel these emotions and to make sure not to stifle them. Collaborative critical thinking benefits from ability to recognize one’s own and others’ emotional commitments and reactions.
Questioning abilities : A critical thinking process needs transformation of an inchoate sense of perplexity into a clear question. Formulating a question well requires not building in questionable assumptions, not prejudging the issue, and using language that in context is unambiguous and precise enough (Ennis 1962: 97; 1991: 9).
Imaginative abilities : Thinking directed at finding the correct causal explanation of a general phenomenon or particular event requires an ability to imagine possible explanations. Thinking about what policy or plan of action to adopt requires generation of options and consideration of possible consequences of each option. Domain knowledge is required for such creative activity, but a general ability to imagine alternatives is helpful and can be nurtured so as to become easier, quicker, more extensive, and deeper (Dewey 1910: 34–39; 1933: 40–47). Facione (1990a) and Halpern (1998) include the ability to imagine alternatives as a critical thinking ability.
Inferential abilities : The ability to draw conclusions from given information, and to recognize with what degree of certainty one’s own or others’ conclusions follow, is universally recognized as a general critical thinking ability. All 11 examples in section 2 of this article include inferences, some from hypotheses or options (as in Transit , Ferryboat and Disorder ), others from something observed (as in Weather and Rash ). None of these inferences is formally valid. Rather, they are licensed by general, sometimes qualified substantive rules of inference (Toulmin 1958) that rest on domain knowledge—that a bus trip takes about the same time in each direction, that the terminal of a wireless telegraph would be located on the highest possible place, that sudden cooling is often followed by rain, that an allergic reaction to a sulfa drug generally shows up soon after one starts taking it. It is a matter of controversy to what extent the specialized ability to deduce conclusions from premisses using formal rules of inference is needed for critical thinking. Dewey (1933) locates logical forms in setting out the products of reflection rather than in the process of reflection. Ennis (1981a), on the other hand, maintains that a liberally-educated person should have the following abilities: to translate natural-language statements into statements using the standard logical operators, to use appropriately the language of necessary and sufficient conditions, to deal with argument forms and arguments containing symbols, to determine whether in virtue of an argument’s form its conclusion follows necessarily from its premisses, to reason with logically complex propositions, and to apply the rules and procedures of deductive logic. Inferential abilities are recognized as critical thinking abilities by Glaser (1941: 6), Facione (1990a: 9), Ennis (1991: 9), Fisher & Scriven (1997: 99, 111), and Halpern (1998: 452). Items testing inferential abilities constitute two of the five subtests of the Watson Glaser Critical Thinking Appraisal (Watson & Glaser 1980a, 1980b, 1994), two of the four sections in the Cornell Critical Thinking Test Level X (Ennis & Millman 1971; Ennis, Millman, & Tomko 1985, 2005), three of the seven sections in the Cornell Critical Thinking Test Level Z (Ennis & Millman 1971; Ennis, Millman, & Tomko 1985, 2005), 11 of the 34 items on Forms A and B of the California Critical Thinking Skills Test (Facione 1990b, 1992), and a high but variable proportion of the 25 selected-response questions in the Collegiate Learning Assessment (Council for Aid to Education 2017).
Experimenting abilities : Knowing how to design and execute an experiment is important not just in scientific research but also in everyday life, as in Rash . Dewey devoted a whole chapter of his How We Think (1910: 145–156; 1933: 190–202) to the superiority of experimentation over observation in advancing knowledge. Experimenting abilities come into play at one remove in appraising reports of scientific studies. Skill in designing and executing experiments includes the acknowledged abilities to appraise evidence (Glaser 1941: 6), to carry out experiments and to apply appropriate statistical inference techniques (Facione 1990a: 9), to judge inductions to an explanatory hypothesis (Ennis 1991: 9), and to recognize the need for an adequately large sample size (Halpern 1998). The Cornell Critical Thinking Test Level Z (Ennis & Millman 1971; Ennis, Millman, & Tomko 1985, 2005) includes four items (out of 52) on experimental design. The Collegiate Learning Assessment (Council for Aid to Education 2017) makes room for appraisal of study design in both its performance task and its selected-response questions.
Consulting abilities : Skill at consulting sources of information comes into play when one seeks information to help resolve a problem, as in Candidate . Ability to find and appraise information includes ability to gather and marshal pertinent information (Glaser 1941: 6), to judge whether a statement made by an alleged authority is acceptable (Ennis 1962: 84), to plan a search for desired information (Facione 1990a: 9), and to judge the credibility of a source (Ennis 1991: 9). Ability to judge the credibility of statements is tested by 24 items (out of 76) in the Cornell Critical Thinking Test Level X (Ennis & Millman 1971; Ennis, Millman, & Tomko 1985, 2005) and by four items (out of 52) in the Cornell Critical Thinking Test Level Z (Ennis & Millman 1971; Ennis, Millman, & Tomko 1985, 2005). The College Learning Assessment’s performance task requires evaluation of whether information in documents is credible or unreliable (Council for Aid to Education 2017).
Argument analysis abilities : The ability to identify and analyze arguments contributes to the process of surveying arguments on an issue in order to form one’s own reasoned judgment, as in Candidate . The ability to detect and analyze arguments is recognized as a critical thinking skill by Facione (1990a: 7–8), Ennis (1991: 9) and Halpern (1998). Five items (out of 34) on the California Critical Thinking Skills Test (Facione 1990b, 1992) test skill at argument analysis. The College Learning Assessment (Council for Aid to Education 2017) incorporates argument analysis in its selected-response tests of critical reading and evaluation and of critiquing an argument.
Judging skills and deciding skills : Skill at judging and deciding is skill at recognizing what judgment or decision the available evidence and argument supports, and with what degree of confidence. It is thus a component of the inferential skills already discussed.
Lists and tests of critical thinking abilities often include two more abilities: identifying assumptions and constructing and evaluating definitions.
In addition to dispositions and abilities, critical thinking needs knowledge: of critical thinking concepts, of critical thinking principles, and of the subject-matter of the thinking.
We can derive a short list of concepts whose understanding contributes to critical thinking from the critical thinking abilities described in the preceding section. Observational abilities require an understanding of the difference between observation and inference. Questioning abilities require an understanding of the concepts of ambiguity and vagueness. Inferential abilities require an understanding of the difference between conclusive and defeasible inference (traditionally, between deduction and induction), as well as of the difference between necessary and sufficient conditions. Experimenting abilities require an understanding of the concepts of hypothesis, null hypothesis, assumption and prediction, as well as of the concept of statistical significance and of its difference from importance. They also require an understanding of the difference between an experiment and an observational study, and in particular of the difference between a randomized controlled trial, a prospective correlational study and a retrospective (case-control) study. Argument analysis abilities require an understanding of the concepts of argument, premiss, assumption, conclusion and counter-consideration. Additional critical thinking concepts are proposed by Bailin et al. (1999b: 293), Fisher & Scriven (1997: 105–106), and Black (2012).
According to Glaser (1941: 25), ability to think critically requires knowledge of the methods of logical inquiry and reasoning. If we review the list of abilities in the preceding section, however, we can see that some of them can be acquired and exercised merely through practice, possibly guided in an educational setting, followed by feedback. Searching intelligently for a causal explanation of some phenomenon or event requires that one consider a full range of possible causal contributors, but it seems more important that one implements this principle in one’s practice than that one is able to articulate it. What is important is “operational knowledge” of the standards and principles of good thinking (Bailin et al. 1999b: 291–293). But the development of such critical thinking abilities as designing an experiment or constructing an operational definition can benefit from learning their underlying theory. Further, explicit knowledge of quirks of human thinking seems useful as a cautionary guide. Human memory is not just fallible about details, as people learn from their own experiences of misremembering, but is so malleable that a detailed, clear and vivid recollection of an event can be a total fabrication (Loftus 2017). People seek or interpret evidence in ways that are partial to their existing beliefs and expectations, often unconscious of their “confirmation bias” (Nickerson 1998). Not only are people subject to this and other cognitive biases (Kahneman 2011), of which they are typically unaware, but it may be counter-productive for one to make oneself aware of them and try consciously to counteract them or to counteract social biases such as racial or sexual stereotypes (Kenyon & Beaulac 2014). It is helpful to be aware of these facts and of the superior effectiveness of blocking the operation of biases—for example, by making an immediate record of one’s observations, refraining from forming a preliminary explanatory hypothesis, blind refereeing, double-blind randomized trials, and blind grading of students’ work.
Critical thinking about an issue requires substantive knowledge of the domain to which the issue belongs. Critical thinking abilities are not a magic elixir that can be applied to any issue whatever by somebody who has no knowledge of the facts relevant to exploring that issue. For example, the student in Bubbles needed to know that gases do not penetrate solid objects like a glass, that air expands when heated, that the volume of an enclosed gas varies directly with its temperature and inversely with its pressure, and that hot objects will spontaneously cool down to the ambient temperature of their surroundings unless kept hot by insulation or a source of heat. Critical thinkers thus need a rich fund of subject-matter knowledge relevant to the variety of situations they encounter. This fact is recognized in the inclusion among critical thinking dispositions of a concern to become and remain generally well informed.
Experimental educational interventions, with control groups, have shown that education can improve critical thinking skills and dispositions, as measured by standardized tests. For information about these tests, see the Supplement on Assessment .
What educational methods are most effective at developing the dispositions, abilities and knowledge of a critical thinker? Abrami et al. (2015) found that in the experimental and quasi-experimental studies that they analyzed dialogue, anchored instruction, and mentoring each increased the effectiveness of the educational intervention, and that they were most effective when combined. They also found that in these studies a combination of separate instruction in critical thinking with subject-matter instruction in which students are encouraged to think critically was more effective than either by itself. However, the difference was not statistically significant; that is, it might have arisen by chance.
Most of these studies lack the longitudinal follow-up required to determine whether the observed differential improvements in critical thinking abilities or dispositions continue over time, for example until high school or college graduation. For details on studies of methods of developing critical thinking skills and dispositions, see the Supplement on Educational Methods .
12. Controversies
Scholars have denied the generalizability of critical thinking abilities across subject domains, have alleged bias in critical thinking theory and pedagogy, and have investigated the relationship of critical thinking to other kinds of thinking.
McPeck (1981) attacked the thinking skills movement of the 1970s, including the critical thinking movement. He argued that there are no general thinking skills, since thinking is always thinking about some subject-matter. It is futile, he claimed, for schools and colleges to teach thinking as if it were a separate subject. Rather, teachers should lead their pupils to become autonomous thinkers by teaching school subjects in a way that brings out their cognitive structure and that encourages and rewards discussion and argument. As some of his critics (e.g., Paul 1985; Siegel 1985) pointed out, McPeck’s central argument needs elaboration, since it has obvious counter-examples in writing and speaking, for which (up to a certain level of complexity) there are teachable general abilities even though they are always about some subject-matter. To make his argument convincing, McPeck needs to explain how thinking differs from writing and speaking in a way that does not permit useful abstraction of its components from the subject-matters with which it deals. He has not done so. Nevertheless, his position that the dispositions and abilities of a critical thinker are best developed in the context of subject-matter instruction is shared by many theorists of critical thinking, including Dewey (1910, 1933), Glaser (1941), Passmore (1980), Weinstein (1990), and Bailin et al. (1999b).
McPeck’s challenge prompted reflection on the extent to which critical thinking is subject-specific. McPeck argued for a strong subject-specificity thesis, according to which it is a conceptual truth that all critical thinking abilities are specific to a subject. (He did not however extend his subject-specificity thesis to critical thinking dispositions. In particular, he took the disposition to suspend judgment in situations of cognitive dissonance to be a general disposition.) Conceptual subject-specificity is subject to obvious counter-examples, such as the general ability to recognize confusion of necessary and sufficient conditions. A more modest thesis, also endorsed by McPeck, is epistemological subject-specificity, according to which the norms of good thinking vary from one field to another. Epistemological subject-specificity clearly holds to a certain extent; for example, the principles in accordance with which one solves a differential equation are quite different from the principles in accordance with which one determines whether a painting is a genuine Picasso. But the thesis suffers, as Ennis (1989) points out, from vagueness of the concept of a field or subject and from the obvious existence of inter-field principles, however broadly the concept of a field is construed. For example, the principles of hypothetico-deductive reasoning hold for all the varied fields in which such reasoning occurs. A third kind of subject-specificity is empirical subject-specificity, according to which as a matter of empirically observable fact a person with the abilities and dispositions of a critical thinker in one area of investigation will not necessarily have them in another area of investigation.
The thesis of empirical subject-specificity raises the general problem of transfer. If critical thinking abilities and dispositions have to be developed independently in each school subject, how are they of any use in dealing with the problems of everyday life and the political and social issues of contemporary society, most of which do not fit into the framework of a traditional school subject? Proponents of empirical subject-specificity tend to argue that transfer is more likely to occur if there is critical thinking instruction in a variety of domains, with explicit attention to dispositions and abilities that cut across domains. But evidence for this claim is scanty. There is a need for well-designed empirical studies that investigate the conditions that make transfer more likely.
It is common ground in debates about the generality or subject-specificity of critical thinking dispositions and abilities that critical thinking about any topic requires background knowledge about the topic. For example, the most sophisticated understanding of the principles of hypothetico-deductive reasoning is of no help unless accompanied by some knowledge of what might be plausible explanations of some phenomenon under investigation.
Critics have objected to bias in the theory, pedagogy and practice of critical thinking. Commentators (e.g., Alston 1995; Ennis 1998) have noted that anyone who takes a position has a bias in the neutral sense of being inclined in one direction rather than others. The critics, however, are objecting to bias in the pejorative sense of an unjustified favoring of certain ways of knowing over others, frequently alleging that the unjustly favoured ways are those of a dominant sex or culture (Bailin 1995). These ways favour:
- reinforcement of egocentric and sociocentric biases over dialectical engagement with opposing world-views (Paul 1981, 1984; Warren 1998)
- distancing from the object of inquiry over closeness to it (Martin 1992; Thayer-Bacon 1992)
- indifference to the situation of others over care for them (Martin 1992)
- orientation to thought over orientation to action (Martin 1992)
- being reasonable over caring to understand people’s ideas (Thayer-Bacon 1993)
- being neutral and objective over being embodied and situated (Thayer-Bacon 1995a)
- doubting over believing (Thayer-Bacon 1995b)
- reason over emotion, imagination and intuition (Thayer-Bacon 2000)
- solitary thinking over collaborative thinking (Thayer-Bacon 2000)
- written and spoken assignments over other forms of expression (Alston 2001)
- attention to written and spoken communications over attention to human problems (Alston 2001)
- winning debates in the public sphere over making and understanding meaning (Alston 2001)
A common thread in this smorgasbord of accusations is dissatisfaction with focusing on the logical analysis and evaluation of reasoning and arguments. While these authors acknowledge that such analysis and evaluation is part of critical thinking and should be part of its conceptualization and pedagogy, they insist that it is only a part. Paul (1981), for example, bemoans the tendency of atomistic teaching of methods of analyzing and evaluating arguments to turn students into more able sophists, adept at finding fault with positions and arguments with which they disagree but even more entrenched in the egocentric and sociocentric biases with which they began. Martin (1992) and Thayer-Bacon (1992) cite with approval the self-reported intimacy with their subject-matter of leading researchers in biology and medicine, an intimacy that conflicts with the distancing allegedly recommended in standard conceptions and pedagogy of critical thinking. Thayer-Bacon (2000) contrasts the embodied and socially embedded learning of her elementary school students in a Montessori school, who used their imagination, intuition and emotions as well as their reason, with conceptions of critical thinking as
thinking that is used to critique arguments, offer justifications, and make judgments about what are the good reasons, or the right answers. (Thayer-Bacon 2000: 127–128)
Alston (2001) reports that her students in a women’s studies class were able to see the flaws in the Cinderella myth that pervades much romantic fiction but in their own romantic relationships still acted as if all failures were the woman’s fault and still accepted the notions of love at first sight and living happily ever after. Students, she writes, should
be able to connect their intellectual critique to a more affective, somatic, and ethical account of making risky choices that have sexist, racist, classist, familial, sexual, or other consequences for themselves and those both near and far… critical thinking that reads arguments, texts, or practices merely on the surface without connections to feeling/desiring/doing or action lacks an ethical depth that should infuse the difference between mere cognitive activity and something we want to call critical thinking. (Alston 2001: 34)
Some critics portray such biases as unfair to women. Thayer-Bacon (1992), for example, has charged modern critical thinking theory with being sexist, on the ground that it separates the self from the object and causes one to lose touch with one’s inner voice, and thus stigmatizes women, who (she asserts) link self to object and listen to their inner voice. Her charge does not imply that women as a group are on average less able than men to analyze and evaluate arguments. Facione (1990c) found no difference by sex in performance on his California Critical Thinking Skills Test. Kuhn (1991: 280–281) found no difference by sex in either the disposition or the competence to engage in argumentative thinking.
The critics propose a variety of remedies for the biases that they allege. In general, they do not propose to eliminate or downplay critical thinking as an educational goal. Rather, they propose to conceptualize critical thinking differently and to change its pedagogy accordingly. Their pedagogical proposals arise logically from their objections. They can be summarized as follows:
- Focus on argument networks with dialectical exchanges reflecting contesting points of view rather than on atomic arguments, so as to develop “strong sense” critical thinking that transcends egocentric and sociocentric biases (Paul 1981, 1984).
- Foster closeness to the subject-matter and feeling connected to others in order to inform a humane democracy (Martin 1992).
- Develop “constructive thinking” as a social activity in a community of physically embodied and socially embedded inquirers with personal voices who value not only reason but also imagination, intuition and emotion (Thayer-Bacon 2000).
- In developing critical thinking in school subjects, treat as important neither skills nor dispositions but opening worlds of meaning (Alston 2001).
- Attend to the development of critical thinking dispositions as well as skills, and adopt the “critical pedagogy” practised and advocated by Freire (1968 [1970]) and hooks (1994) (Dalgleish, Girard, & Davies 2017).
A common thread in these proposals is treatment of critical thinking as a social, interactive, personally engaged activity like that of a quilting bee or a barn-raising (Thayer-Bacon 2000) rather than as an individual, solitary, distanced activity symbolized by Rodin’s The Thinker . One can get a vivid description of education with the former type of goal from the writings of bell hooks (1994, 2010). Critical thinking for her is open-minded dialectical exchange across opposing standpoints and from multiple perspectives, a conception similar to Paul’s “strong sense” critical thinking (Paul 1981). She abandons the structure of domination in the traditional classroom. In an introductory course on black women writers, for example, she assigns students to write an autobiographical paragraph about an early racial memory, then to read it aloud as the others listen, thus affirming the uniqueness and value of each voice and creating a communal awareness of the diversity of the group’s experiences (hooks 1994: 84). Her “engaged pedagogy” is thus similar to the “freedom under guidance” implemented in John Dewey’s Laboratory School of Chicago in the late 1890s and early 1900s. It incorporates the dialogue, anchored instruction, and mentoring that Abrami (2015) found to be most effective in improving critical thinking skills and dispositions.
What is the relationship of critical thinking to problem solving, decision-making, higher-order thinking, creative thinking, and other recognized types of thinking? One’s answer to this question obviously depends on how one defines the terms used in the question. If critical thinking is conceived broadly to cover any careful thinking about any topic for any purpose, then problem solving and decision making will be kinds of critical thinking, if they are done carefully. Historically, ‘critical thinking’ and ‘problem solving’ were two names for the same thing. If critical thinking is conceived more narrowly as consisting solely of appraisal of intellectual products, then it will be disjoint with problem solving and decision making, which are constructive.
Bloom’s taxonomy of educational objectives used the phrase “intellectual abilities and skills” for what had been labeled “critical thinking” by some, “reflective thinking” by Dewey and others, and “problem solving” by still others (Bloom et al. 1956: 38). Thus, the so-called “higher-order thinking skills” at the taxonomy’s top levels of analysis, synthesis and evaluation are just critical thinking skills, although they do not come with general criteria for their assessment (Ennis 1981b). The revised version of Bloom’s taxonomy (Anderson et al. 2001) likewise treats critical thinking as cutting across those types of cognitive process that involve more than remembering (Anderson et al. 2001: 269–270). For details, see the Supplement on History .
As to creative thinking, it overlaps with critical thinking (Bailin 1987, 1988). Thinking about the explanation of some phenomenon or event, as in Ferryboat , requires creative imagination in constructing plausible explanatory hypotheses. Likewise, thinking about a policy question, as in Candidate , requires creativity in coming up with options. Conversely, creativity in any field needs to be balanced by critical appraisal of the draft painting or novel or mathematical theory.
- Abrami, Philip C., Robert M. Bernard, Eugene Borokhovski, David I. Waddington, C. Anne Wade, and Tonje Person, 2015, “Strategies for Teaching Students to Think Critically: A Meta-analysis”, Review of Educational Research , 85(2): 275–314. doi:10.3102/0034654314551063
- Aikin, Wilford M., 1942, The Story of the Eight-year Study, with Conclusions and Recommendations , Volume I of Adventure in American Education , New York and London: Harper & Brothers. [ Aikin 1942 available online ]
- Alston, Kal, 1995, “Begging the Question: Is Critical Thinking Biased?”, Educational Theory , 45(2): 225–233. doi:10.1111/j.1741-5446.1995.00225.x
- –––, 2001, “Re/Thinking Critical Thinking: The Seductions of Everyday Life”, Studies in Philosophy and Education , 20(1): 27–40. doi:10.1023/A:1005247128053
- American Educational Research Association, 2014, Standards for Educational and Psychological Testing / American Educational Research Association, American Psychological Association, National Council on Measurement in Education , Washington, DC: American Educational Research Association.
- Anderson, Lorin W., David R. Krathwohl, Peter W. Airiasian, Kathleen A. Cruikshank, Richard E. Mayer, Paul R. Pintrich, James Raths, and Merlin C. Wittrock, 2001, A Taxonomy for Learning, Teaching and Assessing: A Revision of Bloom’s Taxonomy of Educational Objectives , New York: Longman, complete edition.
- Bailin, Sharon, 1987, “Critical and Creative Thinking”, Informal Logic , 9(1): 23–30. [ Bailin 1987 available online ]
- –––, 1988, Achieving Extraordinary Ends: An Essay on Creativity , Dordrecht: Kluwer. doi:10.1007/978-94-009-2780-3
- –––, 1995, “Is Critical Thinking Biased? Clarifications and Implications”, Educational Theory , 45(2): 191–197. doi:10.1111/j.1741-5446.1995.00191.x
- Bailin, Sharon and Mark Battersby, 2009, “Inquiry: A Dialectical Approach to Teaching Critical Thinking”, in Juho Ritola (ed.), Argument Cultures: Proceedings of OSSA 09 , CD-ROM (pp. 1–10), Windsor, ON: OSSA. [ Bailin & Battersby 2009 available online ]
- –––, 2016, “Fostering the Virtues of Inquiry”, Topoi , 35(2): 367–374. doi:10.1007/s11245-015-9307-6
- Bailin, Sharon, Roland Case, Jerrold R. Coombs, and Leroi B. Daniels, 1999a, “Common Misconceptions of Critical Thinking”, Journal of Curriculum Studies , 31(3): 269–283. doi:10.1080/002202799183124
- –––, 1999b, “Conceptualizing Critical Thinking”, Journal of Curriculum Studies , 31(3): 285–302. doi:10.1080/002202799183133
- Berman, Alan M., Seth J. Schwartz, William M. Kurtines, and Steven L. Berman, 2001, “The Process of Exploration in Identity Formation: The Role of Style and Competence”, Journal of Adolescence , 24(4): 513–528. doi:10.1006/jado.2001.0386
- Black, Beth (ed.), 2012, An A to Z of Critical Thinking , London: Continuum International Publishing Group.
- Bloom, Benjamin Samuel, Max D. Engelhart, Edward J. Furst, Walter H. Hill, and David R. Krathwohl, 1956, Taxonomy of Educational Objectives. Handbook I: Cognitive Domain , New York: David McKay.
- Casserly, Megan, 2012, “The 10 Skills That Will Get You Hired in 2013”, Forbes , Dec. 10, 2012. Available at https://www.forbes.com/sites/meghancasserly/2012/12/10/the-10-skills-that-will-get-you-a-job-in-2013/#79e7ff4e633d ; accessed 2017 11 06.
- Center for Assessment & Improvement of Learning, 2017, Critical Thinking Assessment Test , Cookeville, TN: Tennessee Technological University.
- Cohen, Jacob, 1988, Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences , Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, 2nd edition.
- College Board, 1983, Academic Preparation for College. What Students Need to Know and Be Able to Do , New York: College Entrance Examination Board, ERIC document ED232517.
- Commission on the Relation of School and College of the Progressive Education Association, 1943, Thirty Schools Tell Their Story , Volume V of Adventure in American Education , New York and London: Harper & Brothers.
- Council for Aid to Education, 2017, CLA+ Student Guide . Available at http://cae.org/images/uploads/pdf/CLA_Student_Guide_Institution.pdf ; accessed 2017 09 26.
- Dalgleish, Adam, Patrick Girard, and Maree Davies, 2017, “Critical Thinking, Bias and Feminist Philosophy: Building a Better Framework through Collaboration”, Informal Logic , 37(4): 351–369. [ Dalgleish et al. available online ]
- Dewey, John, 1910, How We Think , Boston: D.C. Heath. [ Dewey 1910 available online ]
- –––, 1916, Democracy and Education: An Introduction to the Philosophy of Education , New York: Macmillan.
- –––, 1933, How We Think: A Restatement of the Relation of Reflective Thinking to the Educative Process , Lexington, MA: D.C. Heath.
- –––, 1936, “The Theory of the Chicago Experiment”, Appendix II of Mayhew & Edwards 1936: 463–477.
- –––, 1938, Logic: The Theory of Inquiry , New York: Henry Holt and Company.
- Dominguez, Caroline (coord.), 2018a, A European Collection of the Critical Thinking Skills and Dispositions Needed in Different Professional Fields for the 21st Century , Vila Real, Portugal: UTAD. Available at http://bit.ly/CRITHINKEDUO1 ; accessed 2018 04 09.
- ––– (coord.), 2018b, A European Review on Critical Thinking Educational Practices in Higher Education Institutions , Vila Real: UTAD. Available at http://bit.ly/CRITHINKEDUO2 ; accessed 2018 04 14.
- Dumke, Glenn S., 1980, Chancellor’s Executive Order 338 , Long Beach, CA: California State University, Chancellor’s Office. Available at https://www.calstate.edu/eo/EO-338.pdf ; accessed 2017 11 16.
- Ennis, Robert H., 1958, “An Appraisal of the Watson-Glaser Critical Thinking Appraisal”, The Journal of Educational Research , 52(4): 155–158. doi:10.1080/00220671.1958.10882558
- –––, 1962, “A Concept of Critical Thinking: A Proposed Basis for Research on the Teaching and Evaluation of Critical Thinking Ability”, Harvard Educational Review , 32(1): 81–111.
- –––, 1981a, “A Conception of Deductive Logical Competence”, Teaching Philosophy , 4(3/4): 337–385. doi:10.5840/teachphil198143/429
- –––, 1981b, “Eight Fallacies in Bloom’s Taxonomy”, in C. J. B. Macmillan (ed.), Philosophy of Education 1980: Proceedings of the Thirty-seventh Annual Meeting of the Philosophy of Education Society , Bloomington, IL: Philosophy of Education Society, pp. 269–273.
- –––, 1984, “Problems in Testing Informal Logic, Critical Thinking, Reasoning Ability”. Informal Logic , 6(1): 3–9. [ Ennis 1984 available online ]
- –––, 1987, “A Taxonomy of Critical Thinking Dispositions and Abilities”, in Joan Boykoff Baron and Robert J. Sternberg (eds.), Teaching Thinking Skills: Theory and Practice , New York: W. H. Freeman, pp. 9–26.
- –––, 1989, “Critical Thinking and Subject Specificity: Clarification and Needed Research”, Educational Researcher , 18(3): 4–10. doi:10.3102/0013189X018003004
- –––, 1991, “Critical Thinking: A Streamlined Conception”, Teaching Philosophy , 14(1): 5–24. doi:10.5840/teachphil19911412
- –––, 1996, “Critical Thinking Dispositions: Their Nature and Assessability”, Informal Logic , 18(2–3): 165–182. [ Ennis 1996 available online ]
- –––, 1998, “Is Critical Thinking Culturally Biased?”, Teaching Philosophy , 21(1): 15–33. doi:10.5840/teachphil19982113
- –––, 2011, “Critical Thinking: Reflection and Perspective Part I”, Inquiry: Critical Thinking across the Disciplines , 26(1): 4–18. doi:10.5840/inquiryctnews20112613
- –––, 2013, “Critical Thinking across the Curriculum: The Wisdom CTAC Program”, Inquiry: Critical Thinking across the Disciplines , 28(2): 25–45. doi:10.5840/inquiryct20132828
- –––, 2016, “Definition: A Three-Dimensional Analysis with Bearing on Key Concepts”, in Patrick Bondy and Laura Benacquista (eds.), Argumentation, Objectivity, and Bias: Proceedings of the 11th International Conference of the Ontario Society for the Study of Argumentation (OSSA), 18–21 May 2016 , Windsor, ON: OSSA, pp. 1–19. Available at http://scholar.uwindsor.ca/ossaarchive/OSSA11/papersandcommentaries/105 ; accessed 2017 12 02.
- –––, 2018, “Critical Thinking Across the Curriculum: A Vision”, Topoi , 37(1): 165–184. doi:10.1007/s11245-016-9401-4
- Ennis, Robert H., and Jason Millman, 1971, Manual for Cornell Critical Thinking Test, Level X, and Cornell Critical Thinking Test, Level Z , Urbana, IL: Critical Thinking Project, University of Illinois.
- Ennis, Robert H., Jason Millman, and Thomas Norbert Tomko, 1985, Cornell Critical Thinking Tests Level X & Level Z: Manual , Pacific Grove, CA: Midwest Publication, 3rd edition.
- –––, 2005, Cornell Critical Thinking Tests Level X & Level Z: Manual , Seaside, CA: Critical Thinking Company, 5th edition.
- Ennis, Robert H. and Eric Weir, 1985, The Ennis-Weir Critical Thinking Essay Test: Test, Manual, Criteria, Scoring Sheet: An Instrument for Teaching and Testing , Pacific Grove, CA: Midwest Publications.
- Facione, Peter A., 1990a, Critical Thinking: A Statement of Expert Consensus for Purposes of Educational Assessment and Instruction , Research Findings and Recommendations Prepared for the Committee on Pre-College Philosophy of the American Philosophical Association, ERIC Document ED315423.
- –––, 1990b, California Critical Thinking Skills Test, CCTST – Form A , Millbrae, CA: The California Academic Press.
- –––, 1990c, The California Critical Thinking Skills Test--College Level. Technical Report #3. Gender, Ethnicity, Major, CT Self-Esteem, and the CCTST , ERIC Document ED326584.
- –––, 1992, California Critical Thinking Skills Test: CCTST – Form B, Millbrae, CA: The California Academic Press.
- –––, 2000, “The Disposition Toward Critical Thinking: Its Character, Measurement, and Relationship to Critical Thinking Skill”, Informal Logic , 20(1): 61–84. [ Facione 2000 available online ]
- Facione, Peter A. and Noreen C. Facione, 1992, CCTDI: A Disposition Inventory , Millbrae, CA: The California Academic Press.
- Facione, Peter A., Noreen C. Facione, and Carol Ann F. Giancarlo, 2001, California Critical Thinking Disposition Inventory: CCTDI: Inventory Manual , Millbrae, CA: The California Academic Press.
- Facione, Peter A., Carol A. Sánchez, and Noreen C. Facione, 1994, Are College Students Disposed to Think? , Millbrae, CA: The California Academic Press. ERIC Document ED368311.
- Fisher, Alec, and Michael Scriven, 1997, Critical Thinking: Its Definition and Assessment , Norwich: Centre for Research in Critical Thinking, University of East Anglia.
- Freire, Paulo, 1968 [1970], Pedagogia do Oprimido . Translated as Pedagogy of the Oppressed , Myra Bergman Ramos (trans.), New York: Continuum, 1970.
- Glaser, Edward Maynard, 1941, An Experiment in the Development of Critical Thinking , New York: Bureau of Publications, Teachers College, Columbia University.
- Halpern, Diane F., 1998, “Teaching Critical Thinking for Transfer Across Domains: Disposition, Skills, Structure Training, and Metacognitive Monitoring”, American Psychologist , 53(4): 449–455. doi:10.1037/0003-066X.53.4.449
- –––, 2016, Manual: Halpern Critical Thinking Assessment , Mödling, Austria: Schuhfried. Available at https://drive.google.com/file/d/0BzUoP_pmwy1gdEpCR05PeW9qUzA/view ; accessed 2017 12 01.
- Hamby, Benjamin, 2014, The Virtues of Critical Thinkers , Doctoral dissertation, Philosophy, McMaster University. [ Hamby 2014 available online ]
- –––, 2015, “Willingness to Inquire: The Cardinal Critical Thinking Virtue”, in Martin Davies and Ronald Barnett (eds.), The Palgrave Handbook of Critical Thinking in Higher Education , New York: Palgrave Macmillan, pp. 77–87.
- Haynes, Ada, Elizabeth Lisic, Kevin Harris, Katie Leming, Kyle Shanks, and Barry Stein, 2015, “Using the Critical Thinking Assessment Test (CAT) as a Model for Designing Within-Course Assessments: Changing How Faculty Assess Student Learning”, Inquiry: Critical Thinking Across the Disciplines , 30(3): 38–48. doi:10.5840/inquiryct201530316
- Hitchcock, David, 2017, “Critical Thinking as an Educational Ideal”, in his On Reasoning and Argument: Essays in Informal Logic and on Critical Thinking , Dordrecht: Springer, pp. 477–497. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-53562-3_30
- hooks, bell, 1994, Teaching to Transgress: Education as the Practice of Freedom , New York and London: Routledge.
- –––, 2010, Teaching Critical Thinking: Practical Wisdom , New York and London: Routledge.
- Johnson, Ralph H., 1992, “The Problem of Defining Critical Thinking”, in Stephen P, Norris (ed.), The Generalizability of Critical Thinking , New York: Teachers College Press, pp. 38–53.
- Kahane, Howard, 1971, Logic and Contemporary Rhetoric: The Use of Reason in Everyday Life , Belmont, CA: Wadsworth.
- Kahneman, Daniel, 2011, Thinking, Fast and Slow , New York: Farrar, Straus and Giroux.
- Kenyon, Tim, and Guillaume Beaulac, 2014, “Critical Thinking Education and Debasing”, Informal Logic , 34(4): 341–363. [ Kenyon & Beaulac 2014 available online ]
- Krathwohl, David R., Benjamin S. Bloom, and Bertram B. Masia, 1964, Taxonomy of Educational Objectives, Handbook II: Affective Domain , New York: David McKay.
- Kuhn, Deanna, 1991, The Skills of Argument , New York: Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511571350
- Lipman, Matthew, 1987, “Critical Thinking–What Can It Be?”, Analytic Teaching , 8(1): 5–12. [ Lipman 1987 available online ]
- Loftus, Elizabeth F., 2017, “Eavesdropping on Memory”, Annual Review of Psychology , 68: 1–18. doi:10.1146/annurev-psych-010416-044138
- Martin, Jane Roland, 1992, “Critical Thinking for a Humane World”, in Stephen P. Norris (ed.), The Generalizability of Critical Thinking , New York: Teachers College Press, pp. 163–180.
- Mayhew, Katherine Camp, and Anna Camp Edwards, 1936, The Dewey School: The Laboratory School of the University of Chicago, 1896–1903 , New York: Appleton-Century. [ Mayhew & Edwards 1936 available online ]
- McPeck, John E., 1981, Critical Thinking and Education , New York: St. Martin’s Press.
- Nickerson, Raymond S., 1998, “Confirmation Bias: A Ubiquitous Phenomenon in Many Guises”, Review of General Psychology , 2(2): 175–220. doi:10.1037/1089-2680.2.2.175
- Nieto, Ana Maria, and Jorge Valenzuela, 2012, “A Study of the Internal Structure of Critical Thinking Dispositions”, Inquiry: Critical Thinking across the Disciplines , 27(1): 31–38. doi:10.5840/inquiryct20122713
- Norris, Stephen P., 1985, “Controlling for Background Beliefs When Developing Multiple-choice Critical Thinking Tests”, Educational Measurement: Issues and Practice , 7(3): 5–11. doi:10.1111/j.1745-3992.1988.tb00437.x
- Norris, Stephen P. and Robert H. Ennis, 1989, Evaluating Critical Thinking (The Practitioners’ Guide to Teaching Thinking Series), Pacific Grove, CA: Midwest Publications.
- Norris, Stephen P. and Ruth Elizabeth King, 1983, Test on Appraising Observations , St. John’s, NL: Institute for Educational Research and Development, Memorial University of Newfoundland.
- –––, 1984, The Design of a Critical Thinking Test on Appraising Observations , St. John’s, NL: Institute for Educational Research and Development, Memorial University of Newfoundland. ERIC Document ED260083.
- –––, 1985, Test on Appraising Observations: Manual , St. John’s, NL: Institute for Educational Research and Development, Memorial University of Newfoundland.
- –––, 1990a, Test on Appraising Observations , St. John’s, NL: Institute for Educational Research and Development, Memorial University of Newfoundland, 2nd edition.
- –––, 1990b, Test on Appraising Observations: Manual , St. John’s, NL: Institute for Educational Research and Development, Memorial University of Newfoundland, 2nd edition.
- Obama, Barack, 2014, State of the Union Address , January 28, 2014. [ Obama 2014 available online ]
- OCR [Oxford, Cambridge and RSA Examinations], 2011, AS/A Level GCE: Critical Thinking – H052, H452 , Cambridge: OCR. Information available at http://www.ocr.org.uk/qualifications/as-a-level-gce-critical-thinking-h052-h452/ ; accessed 2017 10 12.
- OECD [Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development] Centre for Educational Research and Innovation, 2018, Fostering and Assessing Students’ Creative and Critical Thinking Skills in Higher Education , Paris: OECD. Available at http://www.oecd.org/education/ceri/Fostering-and-assessing-students-creative-and-critical-thinking-skills-in-higher-education.pdf ; accessed 2018 04 22.
- Ontario Ministry of Education, 2013, The Ontario Curriculum Grades 9 to 12: Social Sciences and Humanities . Available at http://www.edu.gov.on.ca/eng/curriculum/secondary/ssciences9to122013.pdf ; accessed 2017 11 16.
- Passmore, John Arthur, 1980, The Philosophy of Teaching , London: Duckworth.
- Paul, Richard W., 1981, “Teaching Critical Thinking in the ‘Strong’ Sense: A Focus on Self-Deception, World Views, and a Dialectical Mode of Analysis”, Informal Logic , 4(2): 2–7. [ Paul 1981 available online ]
- –––, 1984, “Critical Thinking: Fundamental to Education for a Free Society”, Educational Leadership , 42(1): 4–14.
- –––, 1985, “McPeck’s Mistakes”, Informal Logic , 7(1): 35–43. [ Paul 1985 available online ]
- Paul, Richard W. and Linda Elder, 2006, The Miniature Guide to Critical Thinking: Concepts and Tools , Dillon Beach, CA: Foundation for Critical Thinking, 4th edition.
- Payette, Patricia, and Edna Ross, 2016, “Making a Campus-Wide Commitment to Critical Thinking: Insights and Promising Practices Utilizing the Paul-Elder Approach at the University of Louisville”, Inquiry: Critical Thinking Across the Disciplines , 31(1): 98–110. doi:10.5840/inquiryct20163118
- Possin, Kevin, 2008, “A Field Guide to Critical-Thinking Assessment”, Teaching Philosophy , 31(3): 201–228. doi:10.5840/teachphil200831324
- –––, 2013a, “Some Problems with the Halpern Critical Thinking Assessment (HCTA) Test”, Inquiry: Critical Thinking across the Disciplines , 28(3): 4–12. doi:10.5840/inquiryct201328313
- –––, 2013b, “A Serious Flaw in the Collegiate Learning Assessment (CLA) Test”, Informal Logic , 33(3): 390–405. [ Possin 2013b available online ]
- –––, 2014, “Critique of the Watson-Glaser Critical Thinking Appraisal Test: The More You Know, the Lower Your Score”, Informal Logic , 34(4): 393–416. [ Possin 2014 available online ]
- Rawls, John, 1971, A Theory of Justice , Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- Rousseau, Jean-Jacques, 1762, Émile , Amsterdam: Jean Néaulme.
- Scheffler, Israel, 1960, The Language of Education , Springfield, IL: Charles C. Thomas.
- Scriven, Michael, and Richard W. Paul, 1987, Defining Critical Thinking , Draft statement written for the National Council for Excellence in Critical Thinking Instruction. Available at http://www.criticalthinking.org/pages/defining-critical-thinking/766 ; accessed 2017 11 29.
- Sheffield, Clarence Burton Jr., 2018, “Promoting Critical Thinking in Higher Education: My Experiences as the Inaugural Eugene H. Fram Chair in Applied Critical Thinking at Rochester Institute of Technology”, Topoi , 37(1): 155–163. doi:10.1007/s11245-016-9392-1
- Siegel, Harvey, 1985, “McPeck, Informal Logic and the Nature of Critical Thinking”, in David Nyberg (ed.), Philosophy of Education 1985: Proceedings of the Forty-First Annual Meeting of the Philosophy of Education Society , Normal, IL: Philosophy of Education Society, pp. 61–72.
- –––, 1988, Educating Reason: Rationality, Critical Thinking, and Education , New York: Routledge.
- –––, 1999, “What (Good) Are Thinking Dispositions?”, Educational Theory , 49(2): 207–221. doi:10.1111/j.1741-5446.1999.00207.x
- Simpson, Elizabeth, 1966–67, “The Classification of Educational Objectives: Psychomotor Domain”, Illinois Teacher of Home Economics , 10(4): 110–144, ERIC document ED0103613. [ Simpson 1966–67 available online ]
- Skolverket, 2011, Curriculum for the Compulsory School, Preschool Class and the Recreation Centre , Stockholm: Ordförrådet AB. Available at http://malmo.se/download/18.29c3b78a132728ecb52800034181/pdf2687.pdf ; accessed 2017 11 16.
- Smith, B. Othanel, 1953, “The Improvement of Critical Thinking”, Progressive Education , 30(5): 129–134.
- Smith, Eugene Randolph, Ralph Winfred Tyler, and the Evaluation Staff, 1942, Appraising and Recording Student Progress , Volume III of Adventure in American Education , New York and London: Harper & Brothers.
- Splitter, Laurance J., 1987, “Educational Reform through Philosophy for Children”, Thinking: The Journal of Philosophy for Children , 7(2): 32–39. doi:10.5840/thinking1987729
- Stanovich Keith E., and Paula J. Stanovich, 2010, “A Framework for Critical Thinking, Rational Thinking, and Intelligence”, in David D. Preiss and Robert J. Sternberg (eds), Innovations in Educational Psychology: Perspectives on Learning, Teaching and Human Development , New York: Springer Publishing, pp 195–237.
- Stanovich Keith E., Richard F. West, and Maggie E. Toplak, 2011, “Intelligence and Rationality”, in Robert J. Sternberg and Scott Barry Kaufman (eds.), Cambridge Handbook of Intelligence , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 3rd edition, pp. 784–826. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511977244.040
- Tankersley, Karen, 2005, Literacy Strategies for Grades 4–12: Reinforcing the Threads of Reading , Alexandria, VA: Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development.
- Thayer-Bacon, Barbara J., 1992, “Is Modern Critical Thinking Theory Sexist?”, Inquiry: Critical Thinking Across the Disciplines , 10(1): 3–7. doi:10.5840/inquiryctnews199210123
- –––, 1993, “Caring and Its Relationship to Critical Thinking”, Educational Theory , 43(3): 323–340. doi:10.1111/j.1741-5446.1993.00323.x
- –––, 1995a, “Constructive Thinking: Personal Voice”, Journal of Thought , 30(1): 55–70.
- –––, 1995b, “Doubting and Believing: Both are Important for Critical Thinking”, Inquiry: Critical Thinking across the Disciplines , 15(2): 59–66. doi:10.5840/inquiryctnews199515226
- –––, 2000, Transforming Critical Thinking: Thinking Constructively , New York: Teachers College Press.
- Toulmin, Stephen Edelston, 1958, The Uses of Argument , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Turri, John, Mark Alfano, and John Greco, 2017, “Virtue Epistemology”, in Edward N. Zalta (ed.), The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy (Winter 2017 Edition). URL = < https://plato.stanford.edu/archives/win2017/entries/epistemology-virtue/ >
- Warren, Karen J. 1988. “Critical Thinking and Feminism”, Informal Logic , 10(1): 31–44. [ Warren 1988 available online ]
- Watson, Goodwin, and Edward M. Glaser, 1980a, Watson-Glaser Critical Thinking Appraisal, Form A , San Antonio, TX: Psychological Corporation.
- –––, 1980b, Watson-Glaser Critical Thinking Appraisal: Forms A and B; Manual , San Antonio, TX: Psychological Corporation,
- –––, 1994, Watson-Glaser Critical Thinking Appraisal, Form B , San Antonio, TX: Psychological Corporation.
- Weinstein, Mark, 1990, “Towards a Research Agenda for Informal Logic and Critical Thinking”, Informal Logic , 12(3): 121–143. [ Weinstein 1990 available online ]
- –––, 2013, Logic, Truth and Inquiry , London: College Publications.
- Zagzebski, Linda Trinkaus, 1996, Virtues of the Mind: An Inquiry into the Nature of Virtue and the Ethical Foundations of Knowledge , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1017/CBO9781139174763
How to cite this entry . Preview the PDF version of this entry at the Friends of the SEP Society . Look up this entry topic at the Internet Philosophy Ontology Project (InPhO). Enhanced bibliography for this entry at PhilPapers , with links to its database.
- Association for Informal Logic and Critical Thinking (AILACT)
- Center for Teaching Thinking (CTT)
- Critical Thinking Across the European Higher Education Curricula (CRITHINKEDU)
- Critical Thinking Definition, Instruction, and Assessment: A Rigorous Approach (criticalTHINKING.net)
- Critical Thinking Research (RAIL)
- Foundation for Critical Thinking
- Insight Assessment
- Partnership for 21st Century Learning (P21)
- The Critical Thinking Consortium
- The Nature of Critical Thinking: An Outline of Critical Thinking Dispositions and Abilities , by Robert H. Ennis
abilities | bias, implicit | children, philosophy for | civic education | decision-making capacity | Dewey, John | dispositions | education, philosophy of | epistemology: virtue | logic: informal
Copyright © 2018 by David Hitchcock < hitchckd @ mcmaster . ca >
Support SEP
Mirror sites.
View this site from another server:
- Info about mirror sites

The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy is copyright © 2016 by The Metaphysics Research Lab , Center for the Study of Language and Information (CSLI), Stanford University
Library of Congress Catalog Data: ISSN 1095-5054

Two things are crucial: 1) critical thinking is not just thinking, but thinking which entails self-improvement. 2) this improvement comes from skill in using standards by which one appropriately assesses thinking. To put it briefly, it is self-improvement (in thinking) through standards (that assess thinking).
A Brief Definition: Critical thinking is the art of analyzing and evaluating thinking with a view to improving it. A well-cultivated critical thinker: communicates effectively with others in figuring out solutions to complex problems. Critical thinking is, in short, self-directed, self-disciplined, self-monitored, and self-corrective thinking.
Critical thinking is, in short, self-directed, self-disciplined, self-monitored, and self-corrective thinking. It presupposes assent to rigorous standards of excellence and mindful command of their use. It entails effective communication and problem solving abilities and a commitment to overcome our native egocentrism and sociocentrism.
Critical thinking is the ability to think clearly and rationally about what to do or what to believe. It includes the ability to engage in reflective and independent thinking. Someone with critical thinking skills is able to do the following: Understand the logical connections between ideas. Identify, construct, and evaluate arguments.
This page titled 1.4: Critical Thinking Questions, Reflection, and Group Activities is shared under a CC BY 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Sravani Banerjee, Elizabeth Eckford, Nicholas Goodwin, Robin Hahn, and Binh Vo (Open Educational Resource Initiative at Evergreen Valley College) .
Critical Thinking. Critical thinking is a widely accepted educational goal. Its definition is contested, but the competing definitions can be understood as differing conceptions of the same basic concept: careful thinking directed to a goal. Conceptions differ with respect to the scope of such thinking, the type of goal, the criteria and norms ...
Critical Thinking 101: Spectrum of Authority. 3. Clarify Thinking. When you use critical thinking to evaluate information, you need to clarify your thinking to yourself and likely to others. Doing this well is mainly a process of asking and answering probing questions, such as the logic questions discussed earlier.
Chapter 2 - Critical thinking Basic Questions and Answers; Chapter 3 - The Logic of Creative and Critical Thinking; Chapter 4 - Critical Thinking in North America; Chapter 5 - Background Logic, Critical Thinking, and Irrational Language Games; Chapter 6 - A Model for the National Assessment of Higher Order Thinking;
Identify, Reflect, and Analyze. Step 1: Reflect. Step 2: Analyze. Step 1: Reflecting on the Issue, Problem, or Task. Reflection is an important early step in critical thinking. There are various kinds of reflection that promote deeper levels of critical thinking (click on the table to view larger): Brockbank, A., & McGill, I. (2007).
These are some of the questions posed by one of our favorite resources — What, So What, Now What — which leans on our core values of critical reflection and cycles of inquiry. Developed by Gene Thompson-Grove in 2004 and revised 2012, this protocol allows you to do several things at once: gather information, analyze and interpret a problem ...
Importance of the Study. Learning is enhanced by critical reflection, which involves the "creation of meaning and conceptualization from experience" (Brockbank & McGill, 1998, p. 56). As educators we need to facilitate critical reflection to enable students to move beyond a superficial understanding of their world.
This page titled 1: Basic Concepts of Critical Thinking is shared under a CC BY-NC 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Jason Southworth & Chris Swoyer via source content that was edited to the style and standards of the LibreTexts platform; a detailed edit history is available upon request.
Questions to Provoke Critical Thinking. Varying question stems can sustain engagement and promote critical thinking. The timing, sequence and clarity of questions you ask students can be as important as the type of question you ask. The table below is organized to help formulate questions provoking gradually higher levels of thinking.
Critical thinking is the ability to effectively analyze information and form a judgment. To think critically, you must be aware of your own biases and assumptions when encountering information, and apply consistent standards when evaluating sources. Critical thinking skills help you to: Identify credible sources. Evaluate and respond to arguments.
Table of Contents. We'll be discussing the following 6 methods of answering critical thinking questions in order to give you a framework to start with: Ask the Important Questions. Consider All Possible Solutions. Articulate Yourself Clearly. Examine and Reflect. Research and Inform Yourself. Organize Your Thoughts.
240 Philosophical Questions for Deep Critical Thinking & Debate. Philosophical questions are an effective tool to stimulate and develop critical thought. They examine profound matters like free will and human nature; the source and value of happiness; morality and ethics; love, logic, and knowledge; religion, death, and the meaning of life.
Critical reflection and areas of your practice. Reflective practice relies on your ability to be open to change and to consider relevant evidence that can challenge or inform decision making. Critical reflection is what allows you to deeply understand your study or work practice and then to take actions to improve it.
TOPIC: " Critical Thinking: Basic Questions & Answers" Reflection The interview of Richard Paul that was conducted for think magazine gave insight and as well some knowledge in how critical thinking is not defined as only one but in numerous ways and differ in ways, we use it. A lot of strong points in the question and answers you will see and agree and some you may disagree but show some ...
Reflection - how critical thinking helps; CRWT - Essay; CRWT Persuasive - About reading comprehension; ... job skills for the future, national standards, and assessment strategies. The first question, "Critical thinking is essential to effective learning and productive living. Would you share your definition of critical thinking?"
20. Reflect on a time when your critical thinking abilities significantly impacted the outcome of a project. Determining if a candidate can discern complex situations and act in a manner that leads to effective and innovative solutions is a crucial part of the interview process.
Critical Thinking. First published Sat Jul 21, 2018. Critical thinking is a widely accepted educational goal. Its definition is contested, but the competing definitions can be understood as differing conceptions of the same basic concept: careful thinking directed to a goal. Conceptions differ with respect to the scope of such thinking, the ...
- business plan
- course work
- research paper
qatar airways travel alerts


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Catamaran sailing vessels for sale on YachtWorld are listed for a range of prices from $51,329 on the relatively moderate end all the way up to $6,716,159 for the most unique, one-of-a-kind yachts. Catamaran By Condition. Used Catamaran 1,294 listings . New Catamaran 464 listings .
2015 Fountaine Pajot Helia 44. US$599,000. ↓ Price Drop. US $4,687/mo. GL Yachting USA Inc. / GUNBOAT | Cardinal, Virginia. Request Info. Find Sail Catamaran boats for sale in United States. Offering the best selection of boats to choose from.
Ideal for overnight cruising and day sailing these Catamaran boats vary in length from 27ft to 80ft and can carry 5 to 43 passengers. There are a wide range of Catamaran boats for sale from popular brands like Fountaine Pajot, Lagoon and Leopard with 481 new and 1,411 used and an average price of $558,626 with boats ranging from as little as ...
Find catamaran sailboats for sale near you, including boat prices, photos, and more. Locate boat dealers and find your boat at Boat Trader! ... Catamaran sailing vessels for sale on Boat Trader are offered at an assortment of prices, from $16,623 on the more modest side all the way up to $9,077,859 for the most unique, one-of-a-kind yachts. ...
catamarans for sale preowned sailboats for sale by owner. Home. Register & Post. View All Sailboats. Search. ... Performance Cruising 105Mc: Length: 34' Type: cruiser: Hull: fiberglass catamaran: Engine: gas inboard. Sailboat Added 26-Mar-2024 More Details: Max Cruise Marine 44 SC: Length:
Introducing the Tao 452: On Display At The Annapolis Boat Show October 12 - 15, 2023. The Multihull Company is thrilled to unveil the new Tao 452, an exciting addition to the world of blue-water performance cruising catamarans. Meticulously engineered and crafted to perfection, the Tao 452 is set to redefine the catamaran experience for ...
Welcome to the Moorings Yacht Brokerage. Our brokerage offices specialize in pre-owned cruising boats, including sailing catamarans and monohulls as well as power yachts. These used yachts come not only from our worldwide Moorings sailboat charter fleet, but also the worldwide fleets of Moorings Power, Sunsail and Footloose.
Introducing the Tao 452: On Display At The Annapolis Boat Show October 12 - 15, 2023. The Multihull Company is thrilled to unveil the new Tao 452, an exciting addition to the world of blue-water performance cruising catamarans. Meticulously engineered and crafted to perfection, the Tao 452 is set to redefine the catamaran experience for ...
The median cost of preowned cruising catamaran sailboats model year range 2000 to 2009 and 40-42ft length, currently available in the USA, is $219,900. Worldwide median cost is about $35K higher. For preowned model year range 2010 to 2019, 40-42ft length currently available in USA, median cost is $487,500. Worldwide median is about $10K lower ...
Lagoon 410 S2 (Caribbean) Asking: $240,000 (USD) S/V Breezy is a Red Deer, St. Lucia based 2004 Lagoon 410 S2 Catamaran For Sale by Owner. Photos & Details Contact Catamaran Owner. S/V Breezy is a 2004 Lagoon 410 S2 catamaran, for sale by owner. We are selling our 2004 Lagoon 410 S2. A current survey from August 2023, with a job list completed.
2012. $135,000. CATAMARAN GEMINI 105MC, 2012, SPECIAL EDITION PRICE : $ 135,000 US. Freshwater boating on Lake Champlain in New York State since 2014. Location : Rouses Point, NY. Waterway from Lake Champlain to the sea via the Hudson River to New York City. This Gemini 105MC is the best equipped on the market today.
The Multihull Company Announces the Sale of the First Pre-Owned Balance 482. ... Multihull Company is thrilled to unveil the new Tao 452, an exciting addition to the world of blue-water performance cruising catamarans. Meticulously engineered and crafted to perfection, the Tao 452 is set to redefine the catamaran experience for sailors ...
These sailboats have a minimum total sail area of 296 square feet, a maximum total sail area of 2,176 square feet and an average of 814 square feet. Boat Trader currently has 844 cruiser sailboats for sale, including 251 new vessels and 593 used and custom yachts listed by both private sellers and professional yacht brokers and boat dealerships ...
Preowned racing, cruising, dailsailer, and multihull sailboats for sale, including Beneteau, Burger , Cal, Catalina, C & C, Cheoy Lee, Columbia, Coronado, Corsair ...
Sail Catamarans 40ft > 50ft Used Yachts For Sale in Australia. Boat Shares and Yacht Charter. Yacht brokers. Catamarans, trimarans, power boats, sailing boats, monohulls, mulithulls, trailer sailers, cruisers in New South Wales, Queensland, Victoria, South Australia, West Australia, Northern Territory, Tasmania, Australian Capital Territory.
Find Sail Cruiser boats for sale in your area & across the world on YachtWorld. Offering the best selection of boats to choose from. ... Cruiser sailing vessels for sale on YachtWorld are offered at a swath of prices from $9,917 on the relatively more affordable end all the way up to $2,429,517 for the biggest, most advanced vessels.
There are a wide range of Power Catamaran boats for sale from popular brands like World Cat, Aquila and Twin Vee with 533 new and 701 used and an average price of $457,008 with boats ranging from as little as $18,176 and $7,244,759. High performance boats for sale.
Built by the famous Dynamique Yachts shipyard and having undergone a refit in 2018, sailing Yacht Amadeus was designed to please the most demanding of yachtsmen. Built for smooth sailing, this elegant cutter rigged sloop has a sleek hull design, comfortably reaching top speeds of 12 knots and ensuring excellent sailing performance. ..... The 33.5m/109'11" 'Amadeus' sail yacht built by the ...
The new Lagoon 43 will replace the Lagoon 42, a model responsible for more than 1000 sales worldwide. Due for a European launch later this year, and an Australian market introduction in 2025, the Lagoon 43 features a semi-flybridge built into the trailing edge of the coachroof that introduces roof-level seating and a sun lounge.
Sailboats are available in a variety of models and rigs, including racing boats, sloops, schooners, catamarans, trimarans, sailing cruisers, and others. Some of the first sailboats on record date back as far as Ancient Greece and Ancient Rome, although it is likely this type of boat construction has been used for centuries even before that point.
Apr 24, 2018. Hanse's E-motion electric rudder drive represents a true breakthrough in auxiliary propulsion for saiboats. When news that Hanse Yachts had launched a new form of electric-powered yacht first broke in the winter of 2016, it was widely reported. After all, Hanse is one of the world's biggest builders of sailing boats, so this .....
There are a wide range of Power Catamaran boats for sale from popular brands like World Cat, Twin Vee and Aquila with 553 new and 692 used and an average price of $465,889 with boats ranging from as little as $18,161 and $7,222,544. ... Power catamarans enjoy several other advantages as compared to monohull boats, too.